Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (33): 5375-5382.doi: 10.12307/2024.669
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of different fusion devices on cervical sagittal parameters after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for cervical spondylotic myelopathy
Ren Hangling1, Song Na2, Xu Daxia1, Li Zonghuan1, Zhang Zhi1, Zhang Jingtao1
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, 2Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Laboratory, Liaocheng People’s Hospital, Liaocheng 252000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-21Accepted:2023-10-12Online:2024-11-28Published:2024-01-30 -
Contact:Zhang Jingtao, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, Liaocheng People’s Hospital, Liaocheng 252000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Ren Hangling, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, Liaocheng People’s Hospital, Liaocheng 252000, Shandong Province, China Song Na, Master, Assistant researcher, Technician-in-charge, Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Laboratory, Liaocheng People’s Hospital, Liaocheng 252000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ren Hangling, Song Na, Xu Daxia, Li Zonghuan, Zhang Zhi, Zhang Jingtao. Effect of different fusion devices on cervical sagittal parameters after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for cervical spondylotic myelopathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5375-5382.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
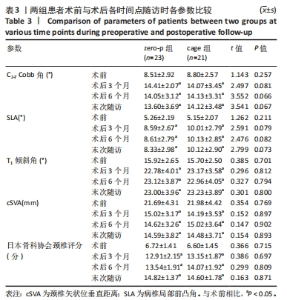
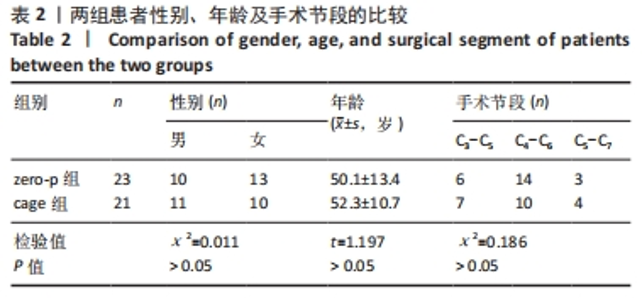
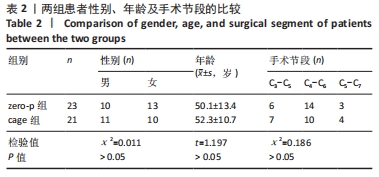
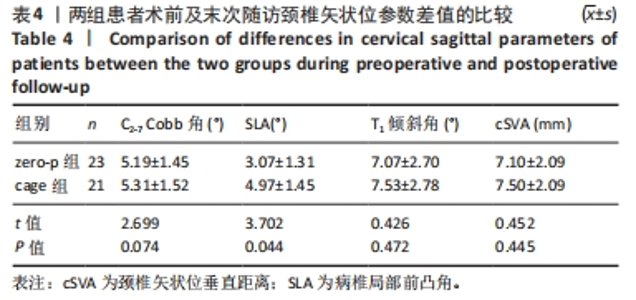
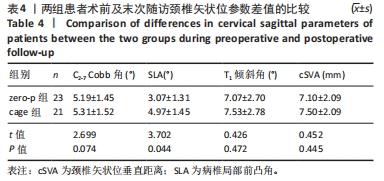
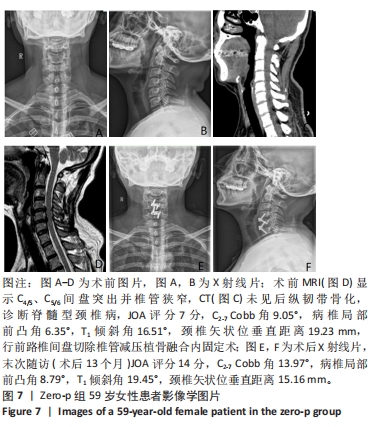
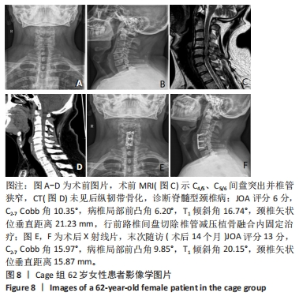
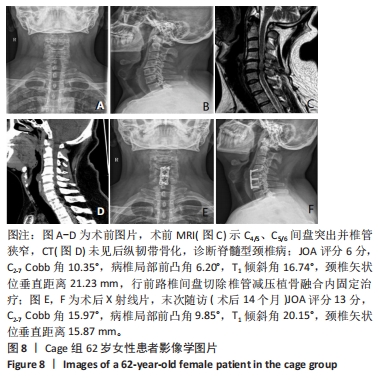
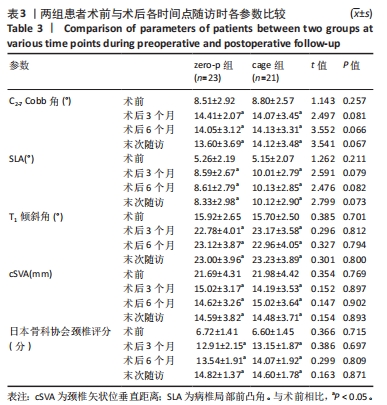
2.4 临床疗效结果 44例患者均获得随访,zero-p组随访(15.0±2.1)个月,cage组随访(14.8±1.9)个月,两组患者均骨性融合,融合率100%,无假关节形成、无内固定断裂移位(融合情况:颈椎侧位X射线片示植骨块或融合器与上下终板间密度均匀,无透亮带形成,可见骨小梁形成则提示融合)。zero-p组手术时间(89.22±7.47) min,cage组手术时间(93.34±9.79) min,zero-p 组较cage 组手术时间短,但差异无显著性意义(t=3.638,P=0.053)。zero-p组术中出血量(50.58±4.27) mL,cage组术中出血量(54.25±3.74) mL,两组比较差异无显著性意义(t=3.617,P=0.056)。末次随访时对所有患者进行Bazaz吞咽困难评分,结果cage组轻度者6例、中度者1例(7/21,33%),zero-p组轻度者3例(3/23,13%),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。两组患者术前、术后3,6个月及末次随访时颈椎矢状位参数及JOA评分变化结果见表3。"
| [1] SCHROEDER GD, KURD MF, MILLHOUSE PW, et al. Performing an anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Clin Spine Surg. 2016;29(5): 186-190. [2] 朱彦奇,王红霞,曹锐,等.零切迹椎间融合器与钛板椎间融合器治疗多节段颈椎病的Meta 分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019, 29(9):805-814. [3] MOSTAFA AG, ELISABETH T, AMOL PY, et al. Improved Dysphagia Outcomes in Anchored Spacers Versus Plate-Screw Systems in Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Systematic Review. Global Spine J. 2020;10(8):1057-1065. [4] SCHOLZ M, ONAL B, SCHLEICHER P, et al. Two-level ACDF with a Zero-profile stand-alone spacer compared to conventional plating: a prospective randomized single-center study. Eur Spine J. 2020;29:2814-2822. [5] 余彬,彭银虓,薛力,等.零切迹椎间融合固定器与传统颈前路钢板Cage融合内固定治疗双节段颈椎病的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1342-1347. [6] 刘光谱,韩猛,汤浩,等.颈前路零切迹与钢板椎间融合系统治疗单节段脊髓型颈椎病疗效比较[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2016, 21(6):541-546. [7] 黎一兵,高文杰,杨小卫,等.颈前路减压植骨融合Zero-p钢板与传统钢板内固定治疗单节段颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(3):225-228. [8] 罗俊普,何永志,林斌,等.颈前路减压cage与zero-p椎间植骨融合内固定治疗单节段颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(9):897-900. [9] LIN T, WANG Z, CHEN G, et al. Is Cervical Sagittal Balance Related to the Progression of Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy? World Neurosurg. 2020;137:e52-e67. [10] 李祖昌,蒋继乐,何达,等.颈椎矢状面平衡参数与颈椎手术关系的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(8):532-540. [11] 杨鹏,温冰涛,格日勒,等.C3-7单开门椎管扩大成形术后颈椎矢状位序列的变化及其与颈椎功能的相关性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2020,30(2):123-129. [12] REDDY R, TEDLA J, DIXIT S, et al. Cervical proprioception and its relationship with neck pain intensity in subjects with cervical spondylosis. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2019;20(1): 293-296. [13] 王志钢,田纪伟,汪海滨,等.颈前路减压融合手术对颈椎矢状位形态的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(3):270-272. [14] XU Z, RAO H, ZHANG L, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion versus hybrid decompression and fusion for the treatment of 3⁃level cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a comparative analysis of cervical sagittal balance and outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:e752-e758. [15] 王超,石志才,栗景峰,等.零切迹融合器与钛板椎间融合器内固定治疗伴后凸畸形的脊髓型颈椎病[J].中华骨科杂志,2020, 40(22):1513-1521. [16] LEE HC, CHEN CH, WU CY, et al. Comparison of radiological outcomes and complications between single-level and multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) by using a polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage-plate fusion system. Medicine(Baltimore). 2019;98(5):e14277. [17] OPSENAK R, HANKO M, SNOPKO P, et al. Subsidence of anchored cage after anterior cervical discectomy. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2019;120(5):356-361. [18] 于杰,田伟.C2-C7角度变化与颈椎术后吞咽困难的相关性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(19):1180-1185. [19] 曾祥鸿,梁博伟,谢克恭,等.脊髓型颈椎病ACDF术后近期颈椎矢状位参数的变化及意义[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2021,27(3):193-198. [20] 张国栋,种衍学,李勇,等.两种不同颈前路固定系统治疗双节段脊髓型颈椎病早期临床效果观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2021,36(3):229-231. [21] 潘宇波,冯皓宇,陈晨,等.颈椎后路单开门椎管扩大椎板成形术对颈椎矢状面平衡的影响[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(7):577-582. [22] 王广超,李永军,吕志刚.颈椎间盘退变程度与颈椎矢状力线参数的相关性分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2020,41(1):32-35. [23] 陈江,李晋玉,郑晨颖,等.双节段颈人工椎间盘置换与颈椎间盘切除融合后颈椎矢状位参数的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(15):2341-2346. [24] 刘涛,邱水强,黄宇峰,等.颈前路椎间融合术后矢状位参数变化与临床疗效的相关性研究 [J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(2):79-85. [25] 何阿祥,谢栋,杨立利,等.Zero-P用于三节段颈椎前路融合术的中期疗效[J].脊柱外科杂志,2017,17(3):129-133. [26] GUO Z, WU X, YANG S, et al. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Using Zero-P System for Treatment of Cervical Spondylosis: a Meta-Analysis. Pain Res Management. 2021;16(12):1-15. [27] WEI Z, ZHANG Y, YANG S, et al. Retrospective Analysis of Sagittal Balance Parameters and Clinical Efficacy After Short-Segment Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery with Different Fusion Devices. Inter J Gen Med. 2022;15(3):3237-3246. [28] 章戈,张亚中,郑培炎,等.Mobi-C人工颈椎间盘置换术与ROI-C辅助的颈椎前路减压融合术治疗单节段颈椎病的临床研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(6):481-487. [29] ZHANG T, GUO N, GAO G, et al. Comparison of outcomes between Zero-p implant and anterior cervical plate interbody fusion systems for anterior cervical decompression and fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):47. [30] 刘正蓬,王雅辉,张义龙,等. 3D打印椎间融合器置入治疗脊髓型颈椎病:颈椎曲度及椎间高度恢复的半年随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(6):849-853. [31] GERILMEZ A, NADERI S. A Novel Perspective for Analyzing Craniocervical Sagittal Balance and Horizontal Gaze. World Neurosurg. 2021;149:e924-e930. [32] INOUE T, ANDO K, KOBAYASHI K, et al. Age-related changes in T1 and C7 slope and the correlation between them in more than 300 asymptomatic subjects. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(8):E474-E481. [33] XING R, LIU W, LI X, et al. Characteristics of cervical sagittal parameters in healthy cervical spine adults and patients with cervical disc degeneration. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):37. [34] LI J, ZHANG D, SHEN Y. Impact of cervical sagittal parameters on axial neck pain in patients with cervical kyphosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020; 15(1):434. [35] ZHAO J, JIANG R, YANG Y, et al. Preoperative T1 Slope as a Predictor of Change in Cervical Alignment and Range of Motion After Cervical Disc Arthroplasty. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:5844-5850. [36] YANG P, LI Y, LI J, et al. Impact of T1 slope on surgical and adjacent segment degeneration after Bryan cervical disc arthroplasty. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:1119-1125. [37] 曹胜,孔令伟,徐昆,等.颈椎矢状位序列参数在评估颈前路椎间盘切除融合术疗效中的价值[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(6):761-764. [38] 张浩,周文超,陈元元,等.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症单开门椎管扩大成形术后颈椎矢状位参数变化与疗效的关系[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(3):206-210. [39] PATWARDHAN AG, KHAYATZADEH S, HAVEY RM, et al. Cervical sagittal balance: a biomechanical perspective can help clinical practice. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(Suppl 1):25-38. [40] 赵文奎,于淼,韦峰,等.无症状成人颈推矢状位曲度分析及其与全脊柱矢状位参数的关系[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(3):231-238. |
| [1] | Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin, Wang Yang, Wang Xiaojuan, Lyu Peng, Chen Long, Shi Zhen, Xie Wei, Zhu Yiliang, Li Xugui. Risk factors for cage retropulsion following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1394-1398. |
| [2] | Wang Qiang, Li Shiyun, Xiong Ying, Li Tiantian. Biomechanical changes of the cervical spine in internal fixation with different anterior cervical interbody fusion systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 821-826. |
| [3] | Li Chengwei, Zhang Yisheng, Li Zhifei, Zhong Yuanming, Meng Jiwen, Liang Qinqiu, Chen Hualong. Finite element analysis of characteristics of spinal cord compression in patients with early cervical spondylotic myelopathy under dynamic position [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5257-5264. |
| [4] | Jin Yikai, Ma Zhanhua, Fu Su, Yan Xu, Zhang Chunlin. Effect of neutral position magnetic resonance imaging on cervical discs herniation volume and cervical curvature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4860-4865. |
| [5] | Liu Jiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Ding Yiwei, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Huang Jie, Yang Guangnan, Ding Yu. Finite element analysis of interspinous fixation-assisted endoscopic interbody fusion in treatment of severe lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3789-3795. |
| [6] | Tang Long, Zheng Jiazhuang, Wang Fandong, Liu Yuanbin, Song Zhaojun, Zhang Zhi, Wang Miao, Zhou Yong, Liu Huiyi, Chen Yu. Uniaxial endoscopic intervertebral fusion combined with pedicle screw fixation in treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3873-3878. |
| [7] | Tang Fubo, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei. Finite element mechanical analysis of different screw-rod internal fixation methods in lateral lumbar fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3293-3298. |
| [8] | Chen Liuxu, Yang Han, Yang Jian, Yang Linyu, Kang Jianping. Finite element analysis of lumbar vertebra biomechanics after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion combined with bilateral transpedicular transdiscal lumbar screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1815-1822. |
| [9] | Li Ting, Liao Wenao, Zhong Wenjie, Liu Xilin, Wang Fei, Hu Jiang. Robot-assisted minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1855-1862. |
| [10] | Wan Jian, Wang Ning, Bei Chaoyong, Chen Yuanming, Wang Honggang. Two lumbar fusion regimens in treatment of single-level lumbar degenerative diseases based on propensity score matching [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1914-1919. |
| [11] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Li Zhifei, Yang Hanli, Wang Weiwei, Zhou Jinyan, Zhong Yuanming. Serum differential proteomics between developmental cervical spinal stenosis and cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1704-1711. |
| [12] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [13] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [14] | Liu Jinyu, Zhang Hanshuo, Cui Hongpeng, Pan Lingzhi, Zhao Boran, Li Fei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical analysis of minimally invasive treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and accurate exercise rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [15] | Li Jiarui, Yan Yang, Wu Xiaogang, Feng Haoyu, He Liming. Biomechanical analysis of unilateral biportal endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5523-5529. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||