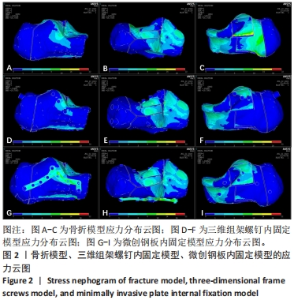
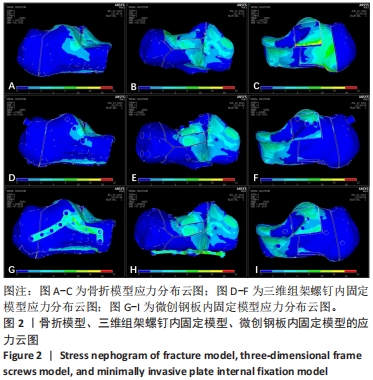
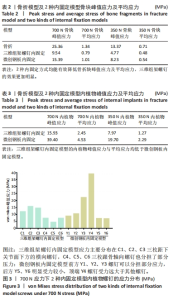
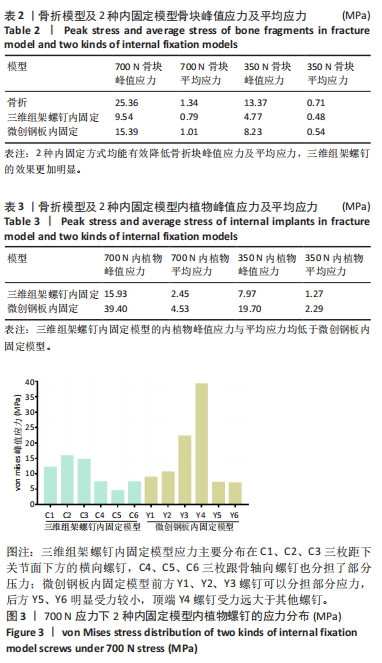
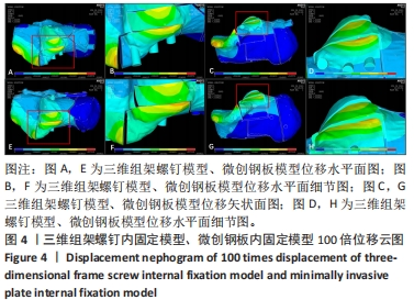
[1] ZHANG G, DING S, RUAN Z. Minimally invasive treatment of calcaneal fracture. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(8):3946-3954.
[2] STEPHENSON JR. Treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus using medial and lateral approaches, internal fixation, and early motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(1):115-130.
[3] ALAJMIl T, SHARIF AF, MAJOUN MA, et al. Minimally Invasive Sinus Tarsi Approach for Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Calcaneal Fractures: Complications, Risk Factors, and Outcome Predictors. J Cureus. 2022;14(1):e21791.
[4] BLASIUS FM, STOCKEM LE, KNOBE M, et al. Predictors for wound healing complications and prolonged hospital stay in patients with isolated calcaneal fractures. J Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(4): 3157-3163.
[5] XIE W, CUI X, ZHANG C, et al. Modified sinus tarsi approach with a variable-angle locking anterolateral plate for Sanders type II and III calcaneal fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;28(7):872-878.
[6] LIN J, XIE C, CHEN K, et al. Comparison of sinus tarsi approach versus extensile lateral approach for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Sanders type IV. J Int Orthop. 2019;43(9):2141-2149.
[7] 王建锋, 钱建军. 跗骨窦微创切口与外侧L形切口治疗跟骨关节内骨折的疗效研究[J]. 浙江创伤外科,2022,27(1):50-51.
[8] 范鑫斌, 张波, 吴亮, 等. 微创跗骨窦切口联合经皮空心螺钉内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ和Ⅲ型跟骨骨折的临床疗效[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2021,42(4):252-257.
[9] GULYEKIN A, ACAR E, UGUR L, et al. The importance of Bohler’s angle in calcaneus geometry: A finite element model study. J Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2021;32(2):420-427.
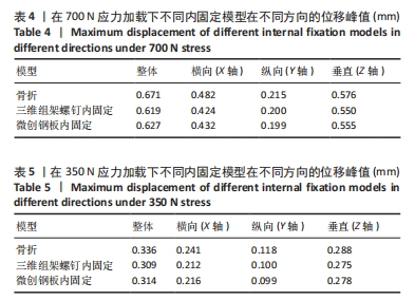
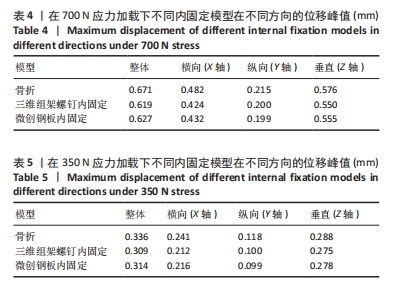
[10] 水洋洋, 张敏, 郑诚功. 基于有限元仿真的骨板结构生物力学分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2021,36(S1):221.
[11] 范鑫斌, 宋超, 丁志宏, 等. 内侧副韧带修补与冠状突骨折固定对恐怖三联征肘关节稳定性的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2020,35(5): 540-545.
[12] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF T. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. J Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
[13] 温明韬, 梁学振, 李嘉程, 等. 两种方式固定Sanders Ⅱ型跟骨骨折后的力学稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6):838-842.
[14] HE K, FU S, LIU S, et al. Comparisons in finite element analysis of minimally invasive, locking, and non-locking plates systems used in treating calcaneal fractures of Sanders type II and type III. J Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(22):3894-3901.
[15] 刘文东, 夏洪乐, 刘林, 等. 三维数字模型辅助微创穿针与钢板内固定治疗SandersⅡ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023, 28(18):2819-2824.
[16] 于健, 施玲玲, 申屠刚, 等. 跗骨窦切口海马钢板微创内固定治疗后关节面塌陷跟骨骨折疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022, 37(2):213-215.
[17] PANG QJ, YU X, GUO ZH. The sustentaculum tali screw fixation for the treatment of Sanders type II calcaneal fracture: A finite element analysis. J Pak J Med Sci. 2014;30(5):1099-1103.
[18] 陈城, 杨云峰, 李兵, 等. 内翻型踝关节炎有限元模型的建立及不同胫骨远端关节面正位角矫正模型的生物力学分析[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(7):796-801.
[19] 毛宾尧, 贾学文, 郑菲蓉, 等. 行走和站立时足底应力分布研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2002,10(12):68-70.
[20] YU B, CHEN WC, LEE PY, et al. Biomechanical comparison of conventional and anatomical calcaneal plates for the treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures - a finite element study. J Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016;19(13):1363-1370.
[21] 杨佳惠, 张一凡, 武俊霞, 等. 生物医用钛合金研究进展[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金,2021,49(5):29,34+40.
[22] WILMSEN L, NEUBERT A, WINDOLF J, et al. Screw fixation in the treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneus fractures: a systematic review protocol. J Syst Rev. 2022;11(1):199.
[23] FENG Y, SHUI X, WANG J, et al. Comparison of percutaneous cannulated screw fixation and calcium sulfate cement grafting versus minimally invasive sinus tarsi approach and plate fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:288.
[24] 彭亮, 刘双, 魏国华, 等. 距下关节镜辅助下经皮撬拨复位内固定治疗合并糖尿病的跟骨骨折[J]. 中医正骨,2021,33(3):64-67.
[25] 李景光, 陈先进, 吕维宝, 等. 经皮撬拨复位空心螺钉与切开复位钢板内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(16):1449-1455.
[26] 廖文利, 何久盛, 曹立峰. 经皮撬拨复位空心螺钉与切开复位钢板内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折的比较[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2019,22(4):492-495.
[27] SAJADIFAR TW, YAPICI GG, NIENDORF T. Effect of grain size on the very high cycle fatigue behavior and notch sensitivity of titanium. J Theoret Appl Fracture Mech. 2019:102362.
[28] QIANG MF, SINGH RK, CHEN YX, et al. Computational Biomechanical Analysis of Postoperative Calcaneal Fractures with Different Placement of the Sustentaculum Screw. J Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):661-667.
[29] HUANG M, YU B, LI Y, et al. Biomechanics of calcaneus impacted by talus: a dynamic finite element analysis. J Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2023:1-8. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2023.2213369.
[30] OUYANG H, DENG Y, XIE P, et al. Biomechanical comparison of conventional and optimised locking plates for the fixation of intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a finite element analysis. J Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017;20(12):1339-1349. |