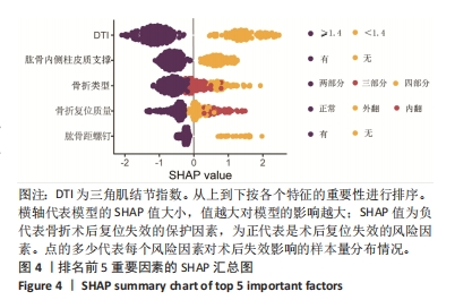
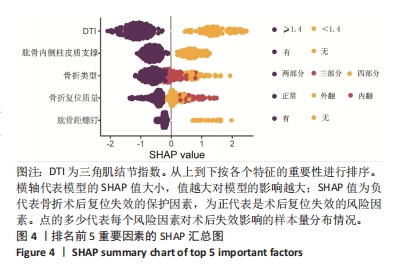
[1] ZHANG Y, WAN L, ZHANG L, et al. Reduction and fixation of proximal humeral fracture with severe medial instability using a small locking plate. BMC Surg. 2021;21(1):387.
[2] 唐迪,钟鸿志,梁凯路.锁定钢板结合异体腓骨支撑与单独锁定钢板固定治疗肱骨近端骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中国骨伤,2022,35(2):186-193.
[3] HAWS BE, SAMBORSKI SA, KARNYSKI S, et al. Risk factors for loss of reduction following locked plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures in older adults. Injury. 2023;54(2):567-572.
[4] LORENZ G, SCHONTHALER W, HUF W, et al. Complication rate after operative treatment of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus: locking plate osteosynthesis versus proximal humeral nail. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021;47(6):2055-2064.
[5] PADEGIMAS EM, CHANG G, NAMJOUYAN K, et al. Failure to restore the calcar and locking screw cross-threading predicts varus collapse in proximal humerus fracture fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(2):291-295.
[6] KRAPPINGER D, BIZZOTTO N, RIEDMANN S, et al. Predicting failure after surgical fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Injury. 2011;42(11):1283-1288.
[7] NOWAK LL, HALL J, DAVIS AM, et al. Development and Internal Validation of Novel Risk Tools to Predict Subsequent Shoulder Surgery After Proximal Humerus Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2022;36(6):e236-e242.
[8] MIN KS, SHERIDAN B, WARYASZ GR, et al. Predicting reoperation after operative treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021; 31(6):1105-1112.
[9] 何继业,张家红,蔡贵泉,等.锁定钢板治疗不稳定肱骨近端骨折术后内翻的危险因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2020,36(5):448-454.
[10] 常祖豪,张伟,唐佩福,等.内侧支撑重建增强固定技术在肱骨近端骨折治疗中的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(3):375-380.
[11] BEERES F, HALLENSLEBEN N, RHEMREV SJ, et al. Plate fixation of the proximal humerus: an international multicentre comparative study of postoperative complications. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(12):1685-1692.
[12] PANCHAL K, JEONG JJ, PARK SE, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of unstable proximal humeral fractures treated with a locking plate and fibular strut allograft. Int Orthop. 2016;40(3):569-577.
[13] KENDALE S, KULKARNI P, ROSENBERG AD, et al. Supervised Machine-learning Predictive Analytics for Prediction of Postinduction Hypotension. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(4):675-688.
[14] 白皙,罗云云,周智博,等.基于机器学习算法的大于胎龄儿风险预测模型[J].中华流行病学杂志,2021,42(12):2143-2148.
[15] NEVIASER AS, HETTRICH CM, DINES JS, et al. Rate of avascular necrosis following proximal humerus fractures treated with a lateral locking plate and endosteal implant. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(12):1617-1622.
[16] WANG F, WANG Y, DONG J, et al. A novel surgical approach and technique and short-term clinical efficacy for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures with the combined use of medial anatomical locking plate fixation and minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):29.
[17] SPROSS C, KAESTLE N, BENNINGER E, et al. Deltoid Tuberosity Index: A Simple Radiographic Tool to Assess Local Bone Quality in Proximal Humerus Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(9):3038-3045.
[18] 汪秋柯,陈云丰.浅谈肱骨近端骨折的分型[J].国际外科学杂志,2017,44(11): 727-730.
[19] HILL BW, JOYCE CD, SINGH A, et al. Patients With Mild Osteoarthritis Are Less Likely to Achieve a Clinically Important Improvement in Pain or Function After Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023;481(8):1464-1470.
[20] WANG JQ, JIANG BJ, GUO WJ, et al. Serial changes in the head-shaft angle of proximal humeral fractures treated by placing locking plates: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):420.
[21] WANG Q, SHENG N, RUI B, et al. The neck-shaft angle is the key factor for the positioning of calcar screw when treating proximal humeral fractures with a locking plate. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(12):1629-1635.
[22] XU J, ZHAN S, LING M, et al. How can medial support for proximal humeral fractures be achieved when positioning of regular calcar screws is challenging? Slotting and off-axis fixation strategies. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31(4):782-791.
[23] FLETCHER J, WINDOLF M, GRUNWALD L, et al. The influence of screw length on predicted cut-out failures for proximal humeral fracture fixations predicted by finite element simulations. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(8):1069-1074.
[24] 李丽秋,许成燕,王晓丽,等.基于社区大数据的骨关节炎患病风险XGboost预测模型研究[J].中华全科医学,2022,20(12):2080-2083.
[25] NATHAN N. Future Tense: Machine Learning and the Future of Medicine. Anesth Analg. 2020;130(5):1114.
[26] RAMKUMAR PN, KARNUTA JM, NAVARRO SM, et al. Deep Learning Preoperatively Predicts Value Metrics for Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Development and Validation of an Artificial Neural Network Model. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(10): 2220-2227.
[27] 聂卉,吴晓燕.结合梯度提升树算法与可解释机器学习模型SHAP的抑郁症影响因素研究[J].数据分析与知识发现,2023.[2023-05-05]
[28] 梁乐乐,王凯,邢浩,等.老年肱骨近端骨折内固定强化措施的研究进展[J].医学综述,2020,26(21):4283-4287.
[29] HENKELMANN R, THEOPOLD J, KITSCHE J, et al. Comorbidities, substance abuse, weight and age are independent risk factors for postoperative complications following operation for proximal humerus fractures: a retrospective analysis of 1109 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(10):2701-2709.
[30] BOULIANE M, SILVEIRA A, ALEIDAN A, et al. Factors associated with maintaining reduction following locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures: a population-based retrospective cohort study. JSES Int. 2020;4(4):724-729.
[31] ZHENXING W, XIAOYI M, SHENGLI Z, et al. Study on Risk Factors of Primary Non-traumatic OVCF in Chinese Elderly and a Novel Prediction Model. Orthopaedic surgery. 2022;14(11):2925-2938.
[32] WANG JQ, ZHAO YM, JIANG BJ, et al. A nomogram for predicting reduction loss risk after locking plate fixation for proximal humeral fractures. Injury. 2021; 52(10):2947-2951.
[33] 高永祥,张晋昕.Logistic回归分析的样本量确定[J].循证医学,2018,18(2): 122-124.
[34] 丁坤.基于SHAP和机器学习构建可解释性前列腺穿刺预测模型的初步研究[D].济南:山东大学, 2022.
[35] 黄小琴,吕东来,周丽梅.基于微信平台的延续护理在使用PICC的消化道肿瘤患者中的应用[J].中华全科医学,2021,19(8):1419-1422.
[36] MA H, XU CF, SHEN Z, et al. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Clinical Predictive Modeling: A Cross-Sectional Study on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in China. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:4304376.
[37] LABATE D, KAYASANDIK C. Advances in quantitative analysis of astrocytes using machine learning. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(2):313-314.
[38] 李佳思.基于机器学习的糖尿病预测及SHAP特征分析[J].智能计算机与应用,2023,13(1):153-157.
[39] JUNG SW, SHIM SB, KIM HM, et al. Factors that Influence Reduction Loss in Proximal Humerus Fracture Surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(6):276-282.
[40] 梁志军,沈圣兵.老年人肱骨近端骨折治疗的进展[J].贵州医药,2021,45(7): 1041-1043.
[41] SPROSS C, ZELEDON R, ZDRAVKOVIC V, et al. How bone quality may influence intraoperative and early postoperative problems after angular stable open reduction-internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(9):1566-1572.
[42] MAJED A, MACLEOD I, BULL AM, et al. Proximal humeral fracture classification systems revisited. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(7):1125-1132.
[43] SHIN WC, KANG SW, SON SM, et al. High bone union rate using a locking plate for proximal humeral fractures in patients older than 70 years: importance of the medial column. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(4):2937-2942.
[44] LAFLAMME GY, MOISAN P, CHAPLEAU J, et al. Novel Technical Factors Affecting Proximal Humerus Fixation Stability. J Orthop Trauma. 2021;35(5):259-264.
[45] 张玉富,蒋协远.肱骨近端骨折手术治疗的进展与思考[J].中国骨伤,2023, 36(2):99-102.
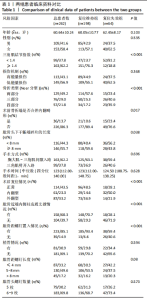
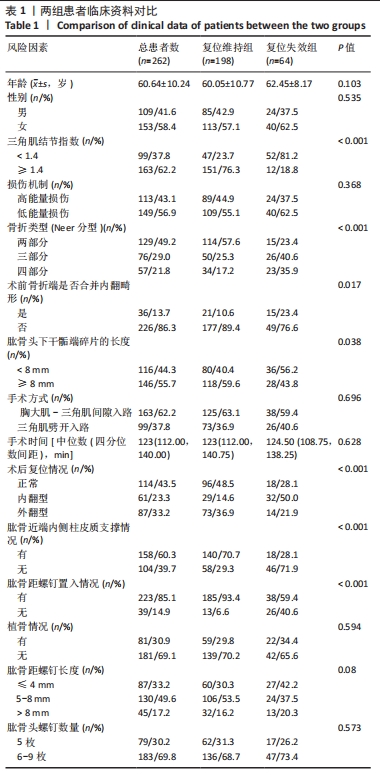
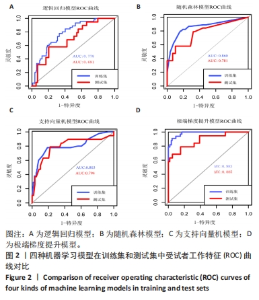
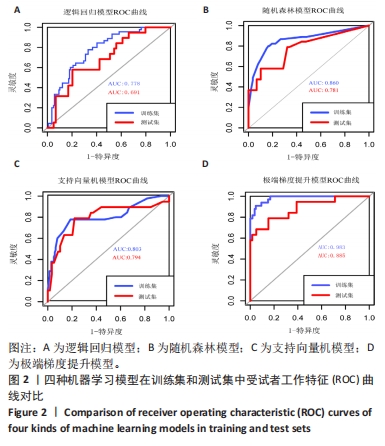
|