Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (14): 2234-2241.doi: 10.12307/2024.210
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which terpenoid herbal monomers prevent osteoporosis by regulating nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway
Pan Chengzhen, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Mo Jian, Zhang Chi, Wei Yuanxun, Wei Zongbo
- Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-01-28Accepted:2023-03-04Online:2024-05-18Published:2023-07-28 -
Contact:Lin Zonghan, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Affiliated Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Pan Chengzhen, Master candidate, Ruikang Affiliated Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, No. 2021GXNSFAA220089 (to CF); Guangxi Postgraduate Education Innovation Program, No. YCBZ2021075 (to ZC); Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Class A Guipai Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Innovation Team, No. 2022A004 (to MJ [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Chengzhen, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Mo Jian, Zhang Chi, Wei Yuanxun, Wei Zongbo. Mechanism by which terpenoid herbal monomers prevent osteoporosis by regulating nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2234-2241.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
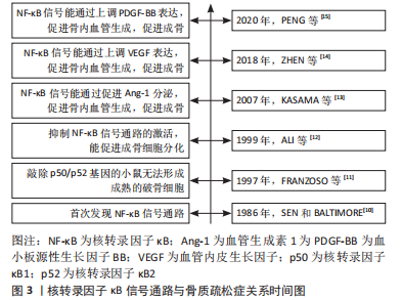
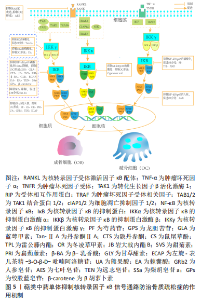
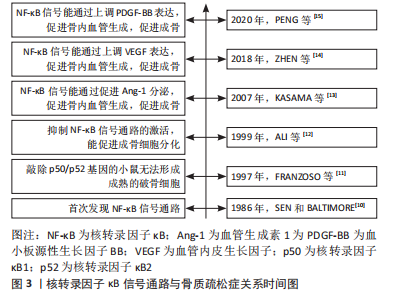
2.1 核转录因子κB信号通路与骨质疏松症的关系 核转录因子κB信号通路最早是由SEN和 BALTIMORE教授[10]在1986年发现的,他们研究B淋巴细胞核内的蛋白质结构时,发现了一种能够与DNA结合的蛋白质,被命名为核转录因子κB,这为后续核转录因子κB信号通路的研究奠定了基础。成骨细胞的分化、破骨细胞的形成以及骨内血管生成都与骨质疏松症密切相关,研究者们发现早在1997年,FRANZOSO等[11]通过研究表明敲除小鼠p50(核转录因子κB1)和p52(核转录因子κB2)基因,能阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,进而减少成熟破骨细胞的形成。同样的,ALI等[12]在此基础上研究发现阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,能促进成骨细胞的分化。关于核转录因子κB信号通路调控骨内血管生成的研究,早在2007年就陆续有研究者报道核转录因子κB信号通路与血管生成素1、血管内皮生长因子和血小板源性生长因子BB等血管生成相关因子的关系[13-15]。研究时间线见图3。"
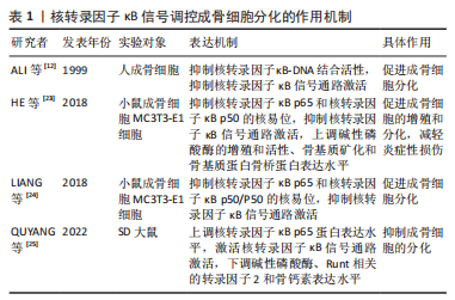
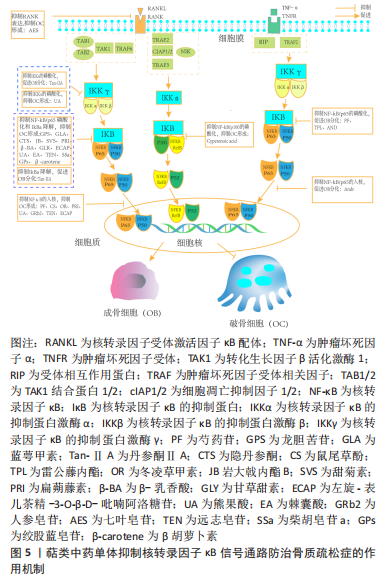
因此,核转录因子κB信号通路在骨代谢和血管生成方面扮演着重要的角色,研究表明阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的激活能够直接减少成熟破骨细胞的形成、促进成骨细胞的分化,同时通过上调血管生成素1、血管内皮生长因子及血小板源性生长因子BB等细胞因子的表达,能促进血管生成,间接促进成骨细胞的分化。这些发现为深入研究骨代谢和血管生成机制提供了重要的理论基础,也为骨质疏松症的治疗提供了新的思路。但是,研究者们仍然需要深入了解核转录因子κB信号通路的调控机制、作用靶点以及与其他信号通路的交叉作用等方面的问题,以期更好地利用和发挥其在临床治疗中的作用。 2.2 核转录因子κB信号通路的组成及激活过程 核转录因子κB家族成员与逆转录病毒癌蛋白v-Rel具有相同的结构特征,共包含RelA(p65),p50,p52,RelB及c-Rel 5个成员,每个成员N端都具有高度保守的Rel同源区(Rel homology region,RHR),在与DNA结合、寡聚化、抑制核转录因子κB抑制蛋白(inhibitor of NF-κB,IκB)和核易位中具有关键作用。成员之间通过相互作用合成一个同源或异源二聚体参与机体相关靶基因的调控[16]。在无刺激的状态下,核转录因子κB二聚体通过与核转录因子κB抑制蛋白相互作用保留在细胞质中,核转录因子κB抑制蛋白具有7个锚蛋白重复序列特征的蛋白,分别是IKBα,IKBβ,IKBγ,IKBζ,IKBε,IKBNS及B细胞淋巴瘤-(3 Bcl-3),都可以通过其C末端特定锚蛋白重复序列蛋白与核转录因子κB结合,阻止核转录因子κB从细胞质进入细胞核[17]。相关研究显示,经典/非经典核转录因子κB信号通路都需要核转录因子κB二聚体参与激活[18]。 经典核转录因子κB通路是指机体损伤、缺氧、细菌病原体、毒性及细胞因子等特定刺激作用于核转录因子κB信号通路,由IKKα,IKKβ和IKKγ构成的IκB激酶(Inhibitor of kappa B kinase,IKK)被激活,导致IKK复合物促进核转录因子κB抑制蛋白磷酸化,进而促使核转录因子κB二聚体(主要由p65、p50和c-Rel亚基组成)从细胞质中移位进细胞核内,在细胞核内通过调控相关基因的表达介导细胞氧化、凋亡、增殖和炎症等生物学过程[8]。非经典核转录因子κB信号通路,当机体受到肿瘤坏死因子受体(tumor necrosis factor receptor,TNFR)家族配体(如肿瘤坏死因子α,β,OX40L及CD40L等)及其他激活因子刺激后,导致相应的受体被激活,进而激活核转录因子κB诱导激酶(NF-κB-inducing kinase,NIK),导致NIK磷酸化和激活IKKα,在此过程中被激活的IKK1促进p52的前体p100磷酸化降解合成p52,在细胞质中的p52与RelB结合成二聚体后进入细胞核,通过对相应靶基因的调节,进而参与多种生物学反应[19]。 目前,关于核转录因子κB信号通路的组成与激活过程的研究已取得一定的成果,但在激活途径方面仍存在一些不足,在某些特定的细胞类型和环境条件下,核转录因子κB信号通路的激活机制可能还没有被完全理解或清楚。此外,核转录因子κB信号通路还可能与其他信号通路存在复杂的交叉调节作用,如JAK/STAT及MAPK等信号通路,这些交叉调节作用可能会增加核转录因子κB信号通路激活的复杂性和不确定性,需要进一步的研究来揭示这些作用。在未来,利用单细胞技术、生物信息学和系统生物学等手段,可以更加全面地分析核转录因子κB信号通路在不同细胞和组织中的功能和调控机制,从而为疾病治疗提供更加精准的策略。 2.3 核转录因子κB信号通路与骨质疏松症的关系 2.3.1 核转录因子κB信号通路对成骨细胞的影响 骨质疏松症是以骨质的吸收为主要特征的疾病,表现为骨质吸收和骨质形成的失衡。成骨细胞是骨形成过程中最重要的一种功能细胞,它的增殖与分化能力对成骨过程起着至关重要的作用[20-21]。有研究表明核转录因子κB信号通路能增强破骨细胞的活性,抑制成骨细胞的生长,能通过抑制代偿骨的生成保持骨稳态[22]。对于核转录因子κB信号通路与成骨细胞的关系可以追塑到1999年,ALI等[12]对人类成骨细胞进行实验,发现肿瘤坏死因子α能以剂量和时间依赖的方式增加核转录因子κB与人类成骨细胞的DNA结合,核转录因子κB信号通路的激活可能是成骨细胞介导的吸收信号传导的重要途径,但他们未提供任何临床试验的证据,这可能会导致对结果的片面报道。 近年来,随着细胞实验和动物实验技术的不断成熟,诸多研究者对核转录因子κB信号通路调控成骨细胞的分化,进而防治骨质疏松症的机制进行了研究。如HE等[23]的研究表明单核素能抑制p65和核转录因子κB/P50蛋白的核易位,阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,进而增加脂多糖损伤的小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞(MC3T3-E1细胞)中碱性磷酸酶的增殖和活性、骨基质矿化和骨基质蛋白骨桥蛋白的表达,起到预防和治疗炎症性骨质流失的作用。可知促进IkBa的磷酸化、核转录因子κB的核易位,是激活核转录因子κB信号通路的关键步骤。同样的,LIANG等[24]的研究发现在地塞米松处理的小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞中,地塞米松能通过刺激IkBa的降解和核转录因子κB的核易位,激活核转录因子κB信号通路,使裂解半胱天冬酶3(caspase-3)、半胱天冬酶3显著下调,导致成骨细胞凋亡,而Klotho能逆转这一过程,阻断核转录因子κB信号的激活,起到有效治疗糖皮质激素诱导的骨质疏松症的作用。此外,核转录因子κB/p65蛋白作为核转录因子κB信号通路中的标志性蛋白之一,其表达量的高低常被用来衡量核转录因子κB信号通路的活性,有研究证实了上调核转录因子κB/p65蛋白的表达水平,能激活核转录因子κB信号通路,导致异染色检测碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关的转录因子2(recombinant runt related transcription factor 2,Runx2)和骨钙素等表达水平下调,进而抑制成骨细胞的分化,增加患骨质疏松症的风险[25]。 综上所述,核转录因子κB信号通路对于成骨细胞的增殖和分化具有负调控的作用,通过降低核转录因子κB/p65的表达水平、阻断核转录因子κB/p65核易位、抑制DNA结合活性等途径,可以抑制核转录因子κB信号通过的激活,促进成骨细胞的分化,最终达到防治骨质疏松症的作用。目前关于核转录因子κB信号通路调控成骨细胞分化的机制大多是关于经典核转录因子κB信号通路的研究,对于非经典核转录因子κB信号途径的机制研究较少,未来需要更多的研究证明非经典信号途径与成骨细胞的关系。核转录因子κB信号调控成骨细胞分化的作用机制见表1。"
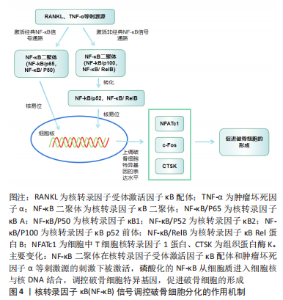
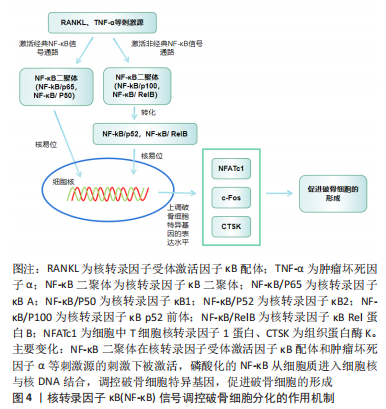
2.3.2 核转录因子κB信号通路对破骨细胞的影响 破骨细胞的源头是骨髓中的单核细胞和巨噬细胞的骨吸收细胞。在经典核转录因子κB信号通路的激活过程中,机体在没有受到刺激的情况下,核转录因子κB二聚体与IκB相互作用存在于细胞质中,当肿瘤坏死因子α、核转录因子受体激活因子κB配体 (receptor activator for nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)等刺激细胞后,激活IKBα激酶,从而致使IKBα的磷酸化或者泛素化,导致核转录因子κB与IKBα分离,随后从细胞质中移位到细胞核内,导致细胞中T细胞核转录因子1蛋白(Nuclear factor of activated t-cells,Cytoplasmic 1,NFATc1)和c-Fos、组织蛋白酶K(CaThepSin K,CTSK)等破骨细胞特异基因表达量增加,最终通过一系列的生物学反应调控破骨细胞的分化和增殖[26-27],其中核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体介导核转录因子κB信号通路的激活研究数量最多。 相关研究显示,RANK募集肿瘤坏死因子受体激活因子(tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors,TRAFs)是激活相关信号通路的关键[28]。TRAFs由多个亚型组成,众多亚型中以TRAF2,TRAF3和TRAF6的研究最为普遍。TRAF6的激活是由TRAF6环指区域与数种泛素结合酶形成一条特殊的泛素链,该泛素链可以透过泛素的赖氨酸63链接到相关的激酶,从而介导下游信号通路的活化,例如招募和活化转化生长因子β活化激酶1(TGF-beta-activated kinase 1,TAK1),进而引起IKK/核转录因子κB降解导致经典核转录因子κB信号通路的激活[29]。除此之外,核转录因子κB/p65作为经典核转录因子κB信号通路中的关键蛋白,当具有活性的核转录因子κB/p65与NFATc1启动子在细胞核内结合后,可加速细胞内基因的转录[30]。 同样地,有研究在此基础上发现抑制IKBα降解和核转录因子κB/P65磷酸化,可以阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的传导,进而抑制破骨细胞形成[31-32]。非经典核转录因子κB信号通路主要由肿瘤坏死因子受体TNFR家族配体(如肿瘤坏死因子α、肿瘤坏死因子β、OX40L及CD40L等)、核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体等激活[29],调控核转录因子激活的NFATc1,介导破骨细胞的分化和增殖。有研究显示配体TRAF2,TRAF3和细胞凋亡抑制因子1/2(cellular inhibitors of apoptosis 1 and 2,cIAP1/2)可以激活非经典核转录因子κB信号通路,3者可形成一个复合物,以TRAF3为中心,致使cIAP1/2介导核转录因子κB诱导激酶的K48链接泛素化,进而激活核转录因子κB诱导激酶,最终促进破骨细胞的形成[33-35]。 总之,核转录因子κB信号通路对于破骨细胞的形成具有正向调控作用,当肿瘤坏死因子α、核转录因子κB受体活化因子配体等刺激细胞后,激活核转录因子κB信号通路,上调破骨细胞特异基因(NFATc1,c-Fos,CTSK),促进破骨细胞的分化,最终达到防治骨质疏松症的效果。但现有研究主要是基于体外细胞实验和动物模型,对于人体内复杂的生理、病理过程尚未有明确证据,而且对于核转录因子κB信号通路与其上下游分子的机制研究也还不够深入。总之,核转录因子κB信号通路调控破骨细胞干预骨质疏松的作用机制研究还有许多需要探究的问题,但随着技术和研究手段的不断提高,相信未来将会有更多的突破和发展,为骨质疏松的预防和治疗提供更加有效的手段。核转录因子κB信号调控破骨细胞分化的作用机制,见图4。"
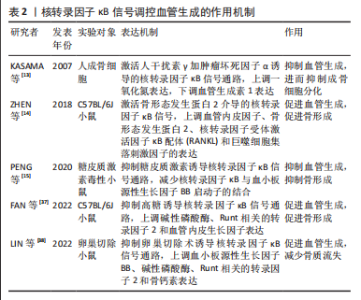
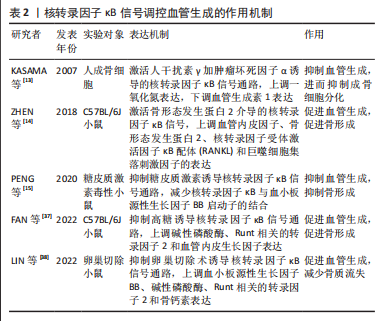
2.3.3 核转录因子κB信号通路对血管生成的影响 血管生成是组织发育、维护和修复过程中的一个重要步骤,与多种疾病的发生和发展密切相关。研究表明血管生成与骨质疏松症之间存在复杂的关系,骨骼组织需要足够的血液供应以获得足够的氧气和营养物质,这对于骨骼的健康至关重要[36]。血管生成素1是一种重要的促血管生成因子,在成骨细胞中的表达对于调节正常和病理生理条件下的骨重塑非常重要,KASAMA等[13]的研究表明人前骨细胞在没有任何刺激的情况下都会自发分泌大量的血管生成素1,而人干扰素γ加肿瘤坏死因子α共同刺激会减少人前骨细胞中血管生成素1的分泌,其机制与激活核转录因子κB信号通路上调一氧化氮表达有关。血管内皮生长因子在骨形成中发挥着重要的作用,其可以刺激骨母细胞、成骨细胞和内皮细胞增殖,促进血管生成和骨组织形成,ZHEN等[14]研究表明表明肝细胞生长因子能增加实验小鼠成骨细胞中p65、IkB β和IkB α的表达,上调血管内皮生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白2 受体、核转录因子κB配体受体激活剂和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(Macrophage colony stimulating factor,M-CSF)的表达水平,进而促进血管再生、骨的形成和血运重建。 同样地,FAN等[37]利用姜黄素抑制高血糖诱导的核转录因子κB信号通路,发现姜黄素能上调碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关的转录因子2和血管内皮生长因子表达水平,恢复“血管生成-成骨”偶联,达到预防糖尿病性骨质疏松症的效果。血小板源性生长因子BB是一种由血小板、内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞和其他类型的细胞产生的生长因子,有研究表明糖皮质激素能通过减少前骨细胞中血小板源性生长因子BB的产生而破坏骨骼血管的形成,其机制与减少核转录因子κB与血小板源性生长因子BB启动子的结合,导致血小板源性生长因子BB转录减少有关[15]。同样地,LIN等[38]在此基础上通过体内和体外实验,证明了乙酸乙酯能抑制核转录因子受体激活因子κB配体诱导的IκBα和核转录因子κB/p65的磷酸化,减弱核转录因子κB信号通路传导,上调血小板源性生长因子BB表达水平,促进H型血管形成,防止卵巢切除诱导的小鼠骨质流失。 综上,核转录因子κB信号可以通过上调血管生成素1、血小板源性生长因子BB、血管内皮生长因子等细胞因子的表达水平,参与骨再生,血管生成和骨质细胞之间的平衡,起到干预骨质疏松症的作用。目前关于核转录因子κB信号调控相关因子促进“血管生成-成骨”偶联的研究尚不够全面,如碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、轴突导向分子3、低氧诱导转录因子1α等细胞因子也能促进“血管生成-成骨”生成偶联[39],但与核转录因子κB信号的关系研究尚缺乏,未来需要更多的基础实验和临床实验验证核转录因子κB信号通过调控“血管生成-成骨”偶联,进而防治骨质疏松症的机制。核转录因子κB信号调控血管生成的作用机制如表2。"

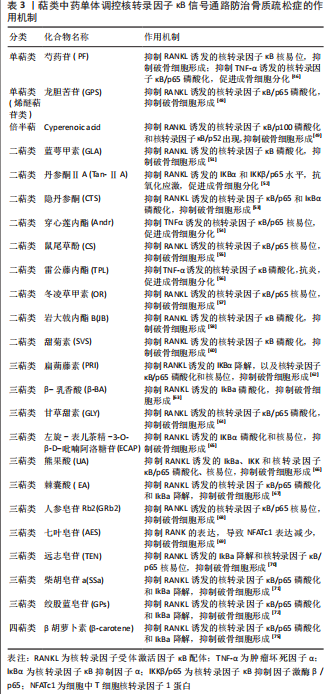
目前,核转录因子κB信号通路在成骨细胞、破骨细胞和血管生成等方面的研究已经取得一定的进展,但仍有一些不足之处:首先,核转录因子κB信号通路在不同类型的骨细胞中具有复杂的作用机制,尚需进一步深入研究;其次,虽然核转录因子κB信号通路在血管生成中发挥着重要作用,但其具体作用机制仍不完全清楚。未来需要建立更为完整的骨细胞信号网络,深入研究核转录因子κB信号通路在骨质疏松方面的作用机制,进一步阐明其在骨代谢调控中的作用和意义。此外,可以借助现代生物技术手段,从多个角度深入探究核转录因子κB信号通路在骨细胞中的作用,为未来骨质疏松症的治疗和预防提供更加有效的策略和手段。 2.4 萜类中药单体调控核转录因子κB信号通路对骨质疏松症的干预 萜类化合物是一种生物源挥发性的有机化合物,可以构成多种不同结构的次生植物代谢产物[40],其结构基于异戊二烯基的连接,能产生各种萜烯类化合物。根据连接的异戊二烯基的数量大小不同,生成的萜烯被分为半萜、单萜、倍半萜、二萜、三萜、四萜和多萜类(C5,C10,C15,C20,C30,C40和C5的长链)[41]。骨组织工程是治疗骨缺损和骨骼疾病的前沿领域之一,萜类化合物由于其天然来源、广泛分布、生物活性多样性和低毒性等特点,越来越受到研究者的关注。 在骨组织工程领域,萜类化合物已被证明具有多种骨生物学特性,如促进成骨细胞和软骨细胞的增殖,上调成骨细胞和软骨细胞的碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的表达,促进骨基质沉积和钙化等[42]。萜类化合物与传统的合成材料相比,具有特性材料多样、更容易被生物体接受、来源更加广泛等优势。此外,萜类化合物还具有可调节的生物活性,可以通过调整化合物的化学结构来调节其生物活性。虽然萜类化合物在骨组织工程领域具有广阔的应用前景,但也存在着限制和挑战。首先,有些萜类化合物可能存在毒性或不良反应。例如,有研究表明高剂量的人参皂苷化合物K可能导致肝脏和肾脏毒性[43]。部分萜类化合物的生物利用度较低,需要额外的材料来提高生物利用度和稳定性[44],这可能增加药物的成本和潜在的毒性风险。此外,萜类化合物的稳定性也是一个问题,化合物可能在体内被代谢或分解,从而降低它们的生物活性和持续时间[45]。所以,未来的研究应重点关注萜类化合物的毒性和稳定性,以及生物利用度,开发更安全、更有效的治疗药物,为骨组织工程领域的临床实践做出更大的贡献。 核转录因子κB信号通路是一条重要的细胞信号传导通路。在骨组织中,核转录因子κB信号通路也扮演着重要的角色,可以通过调节骨细胞的分化和功能影响骨代谢的平衡。近年来的研究表明多种来源于中药的萜类化合物可以通过调控核转录因子κB信号通路起到防治骨质疏松的作用,虽然目前的研究还处于初级阶段,但已经有许多有前景的发现和进展。因此,文章归纳近年来关于萜类中药单体化合物调控核转录因子κB信号通路防治骨质疏松的研究,为进一步研究和开发具有临床应用前景的防治骨骨质疏松症的药物奠定基础。 2.4.1 单萜类 单萜类化合物一般存在于单子叶和双子叶被子植物、真菌、细菌和裸子植物[41]。芍药苷是由芍药中分离出来的水溶性单萜类化合物。WANG等[46]的研究发现,芍药苷可降低核转录因子κB的活性,阻断核转录因子κB信号的激活,上调碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、骨保护蛋白和Runx2基因的表达水平,下调NFATc1基因表达水平,抑制破骨细胞形成,促进成骨细胞分化,从而起到预防和治疗骨质疏松症的作用。龙胆苦苷(Gentiopicroside,GPS)是一种来源于北川龙胆的烯醚萜苷类化合物,具有广泛的药理活性,包括护胆、抑制炎症反应和抗氧化应激反应等[47]。CHEN等[48]使用龙胆苦苷干预RANKL诱导的小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞,发现龙胆苦苷可以通过降低核转录因子κB/p65和IKBα的表达,阻断核转录因子κB信号的激活,抑制破骨细胞形成相关标记基因(碱性磷酸酶和Runx2等)的表达,起到抑制RANKL诱导的小鼠巨噬细胞向破骨细胞分化的作用。 2.4.2 倍半萜类 环丙烯酸是从植物萜菜根部提取出来的具有多种生物活性的倍半萜化合物,能起到抗菌、抗肿瘤和抗炎等作用。有研究表明环丙烯酸在RANKL刺激下不影响MAPK通路和典型核转录因子κB通路,但会损害非典型核转录因子κB通路中p100/p52的活化,进而降低破骨细胞相关基因NFATc1、CTSK、酰基载体蛋白(Acyl carrier protein,ACP5)和c-Fos的表达,在老年性骨质疏松症小鼠模型中,能延迟饲喂环丙烯酸饮食的小鼠的骨质流失,具有防治骨质疏松症的巨大潜力[49]。 2.4.3 二萜类 二萜是拥有4个异戊二烯单元的非挥发性C20碳氢化合物,具有抑制炎症反应、抗肿瘤、抑制氧化应激反应、抗菌及抑制免疫等多种生物活性[50]。蓝萼甲素(Glaucocalyxin A,GLA)是唇形科植物冬凌草地上部分最丰富的活性成分,ZHU等[51]的研究发现蓝萼甲素能降低破骨细胞特异性基因(NFATc1,CTSK,c-Fos)及树突状细胞特异性跨膜蛋白等的表达,抑制RANKL诱发的核转录因子κB磷酸化,进而抑制破骨细胞的形成、减少骨质流失、增加骨小梁密度,具有显著的治疗骨质疏松症潜力。丹参酮ⅡA(TanshinoneⅡA,Tan-ⅡA)、隐丹参酮(Cryptotanshinone,CTS)是来源于中草药丹参的二萜类化合物,ZHU等[52]的研究表明,丹参酮ⅡA可以抑制核转录因子κB及其靶基因肿瘤坏死因子α、诱导性一氧化氮合酶(inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase,iNOS)和环加氧酶2(cyclooxygenase-2,COX-2)的活化,提高骨细胞中TRAF1和CIAP-1/2的水平,进而改善骨强度,抗氧化应激。WANG等[53]的实验发现,隐丹参酮能抑制RANKL诱导的骨髓巨噬细胞中抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶的表达水平,减弱细胞外调节蛋白激酶磷酸化和核转录因子κB泛素化,从而抑制破骨细胞形成,达到防治骨质疏松症的功效。 此外,二萜化合物穿心莲内酯可以提高肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的骨髓巨噬细胞中的Runx2、骨保护素和Col1基因表达水平,阻断p65从细胞质移位到细胞核,抑制核转录因子κB信号通路传导,促进骨髓巨噬细胞向成骨细胞分化,从而防治由炎症因子所致的骨质疏松症[54]。鼠尾草酚能降低RANKL诱导的RAW264.7细胞中的TRAP,CTSK,MMP-9,c-Fos以及NFATc1的mRNA表达量,阻断p65入核,减弱经典核转录因子κB通路的激活,抑制破骨细胞的分化[55]。雷公藤内酯能显著抑制肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的成骨细胞分化中核转录因子κB的磷酸化,阻断核转录因子κB通路的激活,促进成骨细胞的分化,对骨重塑和骨折修复具有积极作用[56]。冬凌草甲素能增强成骨细胞功能和抑制破骨细胞分化,进而调节骨代谢,其机制与抑制核转录因子κB核易位和干扰素相关发育调控因子1降解有关[57]。岩大戟内酯B因具有高活性和多种药理活性而备受关注,可以通过降低IkBa的活性,抑制核转录因子κB/p65的磷酸化,减弱核转录因子κB信号的激活,抑制骨髓巨噬细胞向破骨细胞分化,防治骨质疏松症[58]。有研究表明重组人醛糖还原酶(recombinant human aldose reductase,AKR1B1)是一类能催化各种醛和酮还原为相应的醇的还原型辅酶Ⅱ依赖性酶,能促进核转录因子κB/p65的磷酸化,激活核转录因子κB信号通路[59],甜菊素(Steviosin,SVS)能干预巨噬细胞向破骨细胞分化,其机制可能就与抑制AKR1B1/核转录因子κB轴相关,下调细胞中NFATc1和c-Fos基因的表达水平,抑制破骨细胞增殖和分化[60]。 2.4.4 三萜类 三萜类化合物具有40多个不同的碳骨架,大部分通过游离酯或苷的形态分布于蕨类、菌类、单子叶和双子叶植物,只有少部分分布在动物体内[61]。扁蒴藤素是一种重要的醌甲基三萜类化合物,广泛分布于于卫矛科和希藤科植物,有研究表明扁蒴藤素能阻断核转录因子κB和ERK、MAPK信号级联的早期激活,从而抑制c-Fos和NFATc1基因表达,最终阻止成熟破骨细胞的形成[62]。β-乳香酸(β-boswellic acid,β-BA)是从中药乳香中分离出的的三萜类化合物,PARK等[63]通过免疫印迹法评估β-乳香酸对RANKL刺激的早期信号转导的影响,结果发现β-乳香酸不能调控氨酸苏氨酸蛋白激酶和p38的磷酸化,但是却能抑制IKB、BTk和PLCγ2的磷酸化,这表明β-乳香酸可通过阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,调控钙信号传导,进而抑制破骨细胞分化。 甘草甜素是一种来源于甘草根茎中的三萜类化合物,有研究表明甘草甜素能抑制RANKL诱导的骨髓巨噬细胞IκBα和核转录因子κB/p65磷酸化,阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,进而下调c-Fos和NFATc1基因的表达,抑制破骨细胞的分化,对抗骨丢失[64]。(?)-表儿茶素3-O-β-d-别吡喃糖苷(L-epigallocatechin-3-O-β-D-allopyranoside,ECAP)来源于大叶骨碎补的根茎,是一种常见的三萜类化合物,HSIAO等[65]使用ECAP干预卵巢切除小鼠模型,发现ECAP可以降低核转录因子κB/p65的表达水平以及阻断其核易位,下调NFATc1基因表达水平,抑制破骨细胞形成,降低骨吸收的程度。熊果酸(Ursolic acid,UA)是从杜鹃花科常绿蔓生灌木熊果中提取的一种五环三萜类化合物,具有多种生物活性,如抗菌、抗氧化及抗炎等。JIANG等[66]通过体外和体内实验研究熊果酸对破骨细胞生成和骨溶解的影响,发现熊果酸能抑制RANKL诱使的细胞IkBa降解和IKK、IkBa和p65的磷酸化,阻断核转录因子κB信号通路的传导,减少破骨细胞的形成。棘囊酸是来自中药皂荚的一种五环三萜类化合物,在不同疾病中表现出抑制炎症反应,抗氧化和镇痛的作用,YANG等[67]利用棘囊酸干预RANKL诱导的骨髓巨噬细胞,探讨其对巨噬细胞分化成破骨细胞的影响,结果发现棘囊酸能抑制核转录因子κB/p65磷酸化和IkBa降解,减弱核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,进而降低NFATc1,c-Fos和CTSK基因表达,抑制破骨细胞的生成。 人参皂苷Rb2(Ginsenoside Rb2,GRb2)、七叶皂苷(Aesculin,AES)、远志皂苷(Tenuigenin,TEN)、柴胡皂苷a(Saikosaponin a,SSa)、绞股蓝皂苷(Gynostemma saponin,GPs)是一类具有三萜皂苷元糖基的三萜类化合物。柳嘉伟等[68]的研究表明人参皂苷Rb2能使去势大鼠细胞核中核转录因子κB/p65蛋白减少,抑制核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,进而降低血清破骨细胞分化标志物TRAP、Ⅰ型胶原C端肽(Cross linked C-telopeptide of type I collagen,CTX-1)水平,达到抑制破骨细胞、抗骨质疏松的目的。有研究证实七叶皂苷能减弱RANKL诱导下的骨髓巨噬细胞MAPK和核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,从而下调NFATc1 mRNA、Rank的表达,抑制破骨细胞分化,维持骨稳态[69]。 YANG等[70]通过体外和体内实验探讨远志皂苷对破骨细胞生成的影响及其机制,发现远志皂苷可以减弱RANKL诱发的骨髓巨噬细胞转录核转录因子κB活性,抑制核转录因子κB/p65核易位和活化,进而抑制破骨细胞形成,是一种能有效治疗和缓解骨质疏松症的萜类化合物。ZHOU等[71]利用柴胡皂苷a干预RANKL诱导的小鼠骨髓单核细胞,探讨其对单核细胞分化成破骨细胞的影响,结果发现柴胡皂苷a能抑制RANKL加巨噬细胞集落刺激因子诱导的破骨细胞形成,其机制与抑制核转录因子κB/p65磷酸化和IkBa降解,降低破骨细胞生成相关标志蛋白的表达(包括NFATc1、c-Fos和CTSK)有关。有研究证明绞股蓝皂苷可以抑制RANKL诱导的巨噬细胞核转录因子κB/p65和IκBα的表达,阻断核转录因子κB信号的激活,下调MMP-9、NFATc1和CTSK蛋白表达,进而抑制破骨细胞的形成[72]。 2.4.5 四萜类 四萜是一种含有8个异戊二烯单位的化合物,类胡萝卜素是研究最多的一类四萜类化合物[73],目前,常见的类胡萝卜素有β胡萝卜素、番茄红素、玉米黄质素及叶黄素等,并且已有研究证实β胡萝卜素能改善骨密度、降低骨质疏松和骨折的风险[74]。WANG等[75]的研究发现β胡萝卜素可以抑制RANKL诱发的骨髓巨噬细胞中核转录因子κB/p65磷酸化和IkBa降解,从而减弱核转录因子κB信号传导,下调NFATc1和c-Fos蛋白表达,抑制破骨细胞的形成,能有效预防和治疗骨质疏松症。 综上,萜类化合物可以通过不同的机制调节核转录因子κB信号通路,包括直接或者间接影响核转录因子κB的激活和转录活性以及影响其他相关信号通路和细胞因子。目前的研究表明,萜类化合物可以通过上述机制预防和治疗骨质疏松。然而,仍存在一些不足之处:首先,尽管实验室研究表明萜类化合物可能对骨质疏松有益,但是缺乏足够的临床研究支持其临床应用;其次,虽然核转录因子κB信号通路在骨质疏松中发挥着关键作用,但它也是细胞生长、免疫反应及炎症反应等许多生理和病理过程的重要调节因子。因此,在开发新的治疗方法时,需要平衡安全性和治疗效果。未来的研究应该更加注重在人类体内验证其疗效和安全性,并探索不同萜类化合物之间的相互作用和协同效应。此外,发展基于萜类化合物的新型治疗方法也是一种值得探索的方向,如开发更安全、有效的萜类化合物,以及将萜类化合物与其他治疗方法相结合,以提高其治疗效果和安全性。 萜类中药单体调控核转录因子κB信号通路防治骨质疏松症汇总表见表3,机制图见图5。"
| [1] IOLASCON G, DE SIRE A, CURCI C, et al. Osteoporosis guidelines from a rehabilitation perspective: systematic analysis and quality appraisal using AGREE II. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021;57(2):273-279. [2] ZOU Z, LIU W, CAO L, et al. Advances in the occurrence and biotherapy of osteoporosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020;48(4):1623-1636. [3] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623. [4] SHEN Y, HUANG X, WU J, et al. The global burden of osteoporosis, low bone mass, and its related fracture in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:882241. [5] 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂,2019,12(4):317-318. [6] 朱洁云,高敏,宋秋韵,等.中国老年人骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(3):346-353. [7] 文学,孙红,王洪,等.PTHrP类似物阿巴洛肽在骨质疏松症中的研究进展[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2021,7(2):117-121. [8] ZHUO Y, LI M, JIANG Q, et al. Evolving roles of natural terpenoids from traditional chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:901545. [9] CAPECE D, VERZELLA D, FLATI I, et al. NF-κB: blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2022;43(9):757-775. [10] SEN R, BALTIMORE D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46(5):705-716. [11] FRANZOSO G, CARLSON L, XING L, et al. Requirement for NF-kappaB in osteoclast and B-cell development. Genes Dev. 1997;11(24):3482-3496. [12] ALI NN, GILSTON V, WINYARD PG. Activation of NF-kappaB in human osteoblasts by stimulators of bone resorption. FEBS Lett. 1999;460(2):315-320. [13] KASAMA T, ISOZAKI T, ODAI T, et al. Expression of angiopoietin-1 in osteoblasts and its inhibition by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma. Transl Res. 2007;149(5):265-273. [14] ZHEN R, YANG J, WANG Y, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor improves bone regeneration via the bone morphogenetic protein2mediated NFκB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4):6045-6053. [15] PENG Y, LV S, LI Y, et al. Glucocorticoids disrupt skeletal angiogenesis through transrepression of NF-κB-mediated preosteoclast Pdgfb transcription in young mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(6):1188-1202. [16] POMA P. NF-κB and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(23):9181. [17] YU H, LIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases:mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):209. [18] THOMS HC, STARK LA. The NF-κB nucleolar stress response pathway. Biomedicines. 2021;9(9):1082. [19] MULERO MC, HUXFORD T, GHOSH G. NF-κB, IκB, and IKK: integral components of immune system signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1172:207-226. [20] LU RJ, XING HL, LIU CJ, et al. Antibacterial peptides inhibit MC3T3-E1 cells apoptosis induced by TNF-αthrough p38 MAPK pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(15):943. [21] REMMERS SJA, YAN DER HEIJDEN FC, DE WILDT BWM, et al. Tuning the resorption-formation balance in an in vitro 3D osteoblast-osteoclast co-culture model of bone. Bone Rep. 2022;18:101646. [22] MISHRA R, SEHRING I, CEDERLUND M, et al. NF-κB signaling negatively regulates osteoblast dedifferentiation during zebrafish bone regeneration. Dev Cell. 2020;52(2):167-182. [23] HE YQ, YANG H, SHEN Y, et al. Monotropein attenuates ovariectomy and LPS-induced bone loss in mice and decreases inflammatory impairment on osteoblast through blocking activation of NF-κB pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;291:128-136. [24] LIANG X, LI B, HUANG Q, et al. Klotho prevents DEX-induced apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;507(1-4):355-361. [25] QUYANG X, LI S, DING Y. et al. Foxf1 gene increases the risk of osteoporosis in rats by inhibiting osteoblast formation and promoting osteoclast differentiation through the upregulation of NF-κB pathway. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2022;22(2):242-250. [26] TIAN H, CHEN F, WANG Y, et al. Nur77 prevents osteoporosis by inhibiting the nf-κb signalling pathway and osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(8):2163-2176. [27] ZHUANG Q, CHEN S, ZHANG W, et al. Avicularin alleviates osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis through NF-κB pathway inhibition. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. doi: 1021.2/acs.jafc.05954. [28] KIM B, LEE KW, PARK B. Icariin abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264. 7 cells. Phytomedicine. 2018;51:181-190. [29] SWARNKAR G, CHEN TH, ARRA M, et al. NUMBL interacts with TAK1, TRAF6 and NEMO to negatively regulate NF-κB signaling during osteoclastogenesis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12600. [30] XU J, WU HF, ANG ES, et al. NF-kappaB modulators in osteolytic bone diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(1):7-17. [31] DONG M, ZENG J, YANG C, et al. Asiatic acid attenuates osteoporotic bone loss in ovariectomized mice through inhibiting NF-kappaB/MAPK/Protein Kinase B signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:829741. [32] ZHANG F, HUANG X, QI Y, et al. Juglanin inhibits osteoclastogenesis in ovariectomized mice via the suppression of NF-κB signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2021;11:596230. [33] SHEN G, LIUI X, LEI W, et al. Plumbagin is a NF-κB-inducing kinase inhibitor with dual anabolic and antiresorptive effects that prevents menopausal-related osteoporosis in mice. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(4):101767. [34] AVNET S, CHANO T, MASSA A, et al. Acid microenvironment promotes cell survival of human bone sarcoma through the activation of cIAP proteins and NF-κB pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9(6):1127-1144. [35] YAO Z, LEI W, DUAN R, et al. RANKL cytokine enhances TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis independently of TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) 6 by degrading TRAF3 in osteoclast precursors. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(24):10169-10179. [36] WANG W, WANG B. Expression of angiogenesis-related proteins in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by osteoprotegerin during osteogenic differentiation in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;98:107821. [37] FAN D, LU J, YU N, et al. Curcumin prevents diabetic osteoporosis through promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis coupling via NF-κB signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:4974343. [38] LIN X, XU F, ZHANG KW, et al. Acacetin prevents bone loss by disrupting osteoclast formation and promoting type H vessel formation in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:796227. [39] 张杰,董万涛,赵宝宝,等.中医药干预骨质疏松成血管-成骨耦联因子研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂,2023,29(1):151-156. [40] KANWAL A, BILAL M, RASOOL N, et al. Total synthesis of terpenes and their biological significance: a critical review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15(11):1392. [41] NINKUU V, ZHANG L, YANG J, et al. Biochemistry of terpenes and recent advances in plant protection. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5710. [42] BELLAVIA D, CARADONNA F, DIMARCO E, et al. Terpenoid treatment in osteoporosis: this is where we have come in research. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021;32(11):846-861. [43] GAO Y, WANG T, WANNG G, et al. Preclinical safety of ginsenoside compound K: acute, and 26-week oral toxicity studies in mice and rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019;131: 110578. [44] NURCAHYANTI ADR, SATRIAWAN N, SHAROPOV F. Free radical scavenging synergism of fucoxanthin with lipophilic plant products. Nat Prod Res. 2023;37(5):782-787. [45] ZOU L, DING W, HUANG Q, et al. Andrographolide/phospholipid/cyclodextrin complex-loaded nanoemulsion: preparation, optimization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2022;45(8):1106-1115. [46] WANG Y,DAI J, ZHU Y, et al. Paeoniflorin regulates osteoclastogenesis and osteoblastogenesis via manipulating NF-κB signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2017;9(7):7372-7388. [47] JIN M, FENG H, WANG Y, et al. Gentiopicroside ameliorates oxidative stress and lipid accumulation through nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:2940746. [48] CHEN F, XIE L, KANG R, et al. Gentiopicroside inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by regulating NF-κB and JNK signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;100: 142-146. [49] CHAWALITPONG S, CHOKCHAISIRI R, SUKSAMRAM A, et al. Cyperenoic acid suppresses osteoclast differentiation and delays bone loss in a senile osteoporosis mouse model by inhibiting non-canonical NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5625. [50] 徐硕,姜文清,吴学军,等.中药中二萜类化学成分分析方法的研究进展[J].西北药学杂志,2020,35(5):788-791. [51] ZHU M, SHAN J, XU H, et al. Glaucocalyxin A suppresses osteoclastogenesis induced by RANKL and osteoporosis induced by ovariectomy by inhibiting the NF-κB and Akt pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;276:114176. [52] ZHU S, WEI W, LIU Z, et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates the deleterious effects of oxidative stress in osteoporosis through the NFκB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(5):6969-6976. [53] WANG W, HUANG M, HUI Y, et al. Cryptotanshinone inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by regulating ERK and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(5):7333-7340. [54] 丁丁,车千红,徐樱溪,等.穿心莲内酯通过抑制TNF-α活化的核转录因子κB信号途径保护和促进成骨分化[J].解剖科学进展,2019,25(3):316-319,334. [55] 李婧,程梁,郭吕华,等.银杏叶中异鼠李素对RAW264.7细胞向破骨细胞分化的影响及其分子机制[J].口腔疾病防治,2018,26(3):158-165. [56] LIU SP, WANG GD, DU XJ, et al. Triptolide inhibits the function of TNF-αin osteoblast differentiation by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(3): 2235-2240. [57] XIE Z, YU H, SUN X, et al. A novel diterpenoid suppresses osteoclastogenesis and promotes osteogenesis by inhibiting ifrd1-mediated and IκBα-mediated p65 nuclear translocation. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(4):667-678. [58] MA X, LIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Jolkinolide B inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing the activation NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;445(2):282-288. [59] BAI Q, WANG X, MAO X, et al. Aldo-keto reductase 1 member B1(AKR1B1)inhibits retinal ganglion cell activity via activating NF-κB pathway and inducing mouse BV-2 microglia activation. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;36(12):1063-1068. [60] 陈莎,周佳瑛,储非凡,等.甜菊素对RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化和功能的影响[J].中成药,2022,44(6):1804-1809. [61] LIU S, LIU H, ZHANG L, et al. Edible pentacyclic triterpenes: a review of their sources, bioactivities, bioavailability, self-assembly behavior, and emerging applications as functional delivery vehicles. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. doi: 1080.10408398/2022.2153238.36476115. [62] LI X, LIN X, WU Z, et al. Pristimerin protects against OVX-mediated bone loss by attenuating osteoclast formation and activity via inhibition of RANKL-mediated activation of NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:61-74. [63] PARK GD, CHEON YH, EUN SY, et al. β-boswellic acid inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and function by attenuating NF-κB and Btk-PLCγ2 signaling pathways. Molecules. 2021;26(9):2665. [64] TANG Y, LV XL, BAO YZ, et al. Glycyrrhizin improves bone metabolism inovariectomized mice via inactivating NF-κB signaling. Climacteric. 2021;24(3):253-260. [65] HSIAO HB, WU JB, LIN WC. (-)-Epicatechin 3-O-β-D-allopyranoside prevent ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice by suppressing RANKL-induced NF-κB and NFATc1 signaling pathways. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):245. [66] JIANG C, XIAO F, GU X, et al. Inhibitory effects of ursolic acid on osteoclastogenesis and titanium particle-induced osteolysis are mediated primarily via suppression of NF-κB signaling. Biochimie. 2015;111:107-18. [67] YANG JH, LI B, WU Q, et al. Echinocystic acid inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by regulating NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 477(4):673-677. [68] 柳嘉伟,苏柯,黄鑫,等.人参皂苷Rb2体内抑制破骨细胞的作用及其机制研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(4):293-298. [69] ZHAO XL, CHEN LF, WANG Z. Aesculin modulates bone metabolism by suppressing receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastogenesis and transduction signals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;488(1):15-21. [70] YANG S, LI X, CHENG L, et al. Tenuigenin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by down-regulating NF-κB activation and suppresses bone loss in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;466(4):615-621. [71] ZHOU C, LIU W, HE W, et al. Saikosaponin a inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015;25(1):49-54. [72] HAN J, GAO W, SU D, et al. Gypenoside inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by regulating NF-κB, AKT, and MAPK signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(9):7310-7318. [73] MAOKA T. Carotenoids as natural functional pigments. J Nat Med. 2020;74:1-16. [74] GAO SS, ZHAO Y. The effects ofβ-carotene on osteoporosis:a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos Int. 2022. doi: 1007.00198/s022-06593-7-36380163. [75] WANG F, WANG N, GAO Y, et al. β-Carotene suppresses osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2017;174:15-20. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [3] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [4] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [5] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [6] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [7] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [8] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [9] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [10] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [11] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [13] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [14] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [15] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||