Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (14): 2242-2247.doi: 10.12307/2024.287
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis and its traditional Chinese medicine interventions
Gao Zhengang, Zhang Xiaoyun, Jiang Wen
- Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-03-07Accepted:2023-04-14Online:2024-05-18Published:2023-07-28 -
Contact:Jiang Wen, Master, Associate chief physician, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Gao Zhengang, Master candidate, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960803; Guangxi Natural Science Foundation for the Youth, No. 2020GXNSFBA159053 (to ZXY); Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine Appropriate Technology Development and Promotion Project, No. GZSY22-36 (to ZXY); Huang Yourong Gui School Project for Traditional Chinese Medicine Master Training, No. [202]6; Gui School Chinese Medicine Inheritance Innovation Team of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022A004 (to ZXY [project participant]); Youth Innovation Research Team Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2021TD001 (to ZXY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Zhengang, Zhang Xiaoyun, Jiang Wen. Mechanism of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis and its traditional Chinese medicine interventions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2242-2247.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
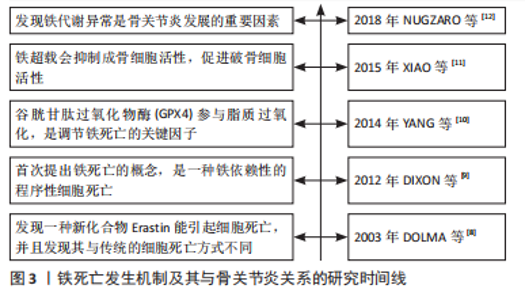
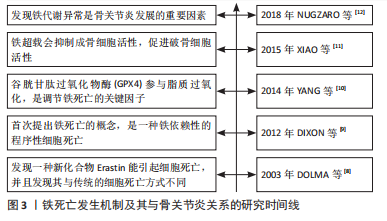
2.2 铁死亡的概述 传统的细胞的死亡方式主要包括有凋亡、自噬、坏死、焦亡、胀亡、坏死性凋亡等,而铁死亡与传统的细胞死亡方式不同,其主要是由于铁含量的增高引起细胞内脂质活性氧生成与降解的平衡失调而引起的细胞死亡[13-14]。当铁死亡发生时,细胞在形态上表现为细胞整体变小、细胞膜挛缩,但膜密度增加;细胞核正常,染色质未见凝集;线粒体膜密度增高并且出现裂痕,线粒体嵴减少,最终出现线粒体萎缩[15]。此外,铁死亡具有典型的生物化学特征,如谷胱甘肽耗竭以及谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 4(glutathione peroxidase 4,GPX4)被抑制,使得细胞内活性氧浓度上升、细胞内二价铁离子水平升高,同时还会出现线粒体膜电位的下降、发生炎症反应等现象[16-17]。在遗传学方面,目前发现铁死亡的整个过程是由多种基因共同调控的,主要涉及铁稳态、氨基酸代谢、脂质过氧化过程等方面基因的改变[18-19]。具体见图4所示。"
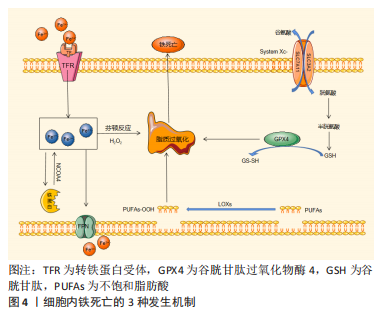
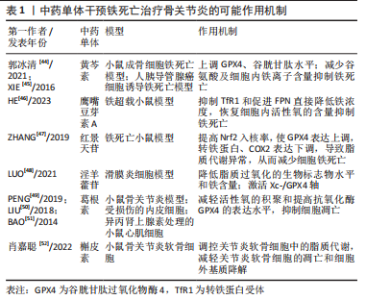
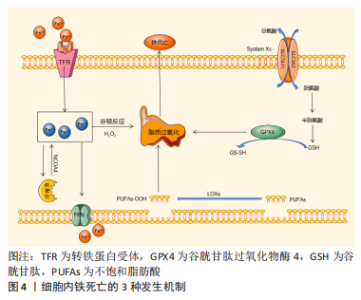
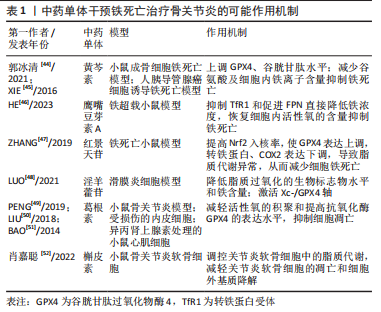
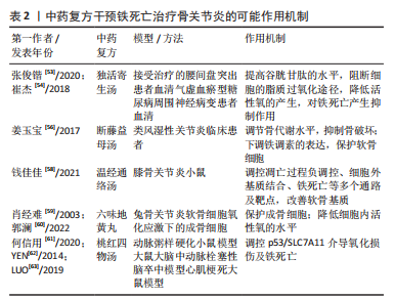
2.3 铁死亡诱发骨关节炎的机制 2.3.1 铁超载 铁元素是人体所必需的微量元素之一,在人体的生理活动中发挥着重要作用,其主要以Fe2+存在于机体中。细胞内铁的平衡性通过铁转运系统维持,这种平衡表现在铁的吸收、利用、输出和储存之间的动态平衡,即细胞外铁的吸收通过转铁蛋白(TF)及其载体转铁蛋白受体(TFR)完成,吸收的铁主要以铁蛋白复合物的形式在细胞内储存和运输,细胞内的铁主要是由膜铁转运蛋白(FNP)输出。当铁死亡发生时,这种输出与输入的动态平衡就会破坏,细胞大量的游离Fe2+无法输出,大量累积于细胞内。铁代谢紊乱是铁死亡的关键因素之一,过量的铁通过芬顿反应与H2O2相互作用产生羟基自由基,引发脂质过氧化反应,造成活性氧积累,最终导致铁死亡的发生[20-21]。 骨关节炎的主要发病机制是软骨发生退行性变化,这种退变首先发生在软骨,使软骨成分发生改变,最终导致关节疼痛和功能丧失,研究表明软骨细胞凋亡是引起软骨成分改变的重要因素之一。软骨细胞的软骨代谢失衡导致基质降解酶的分泌,从而损害软骨基质的完整性[22-23]。临床研究表明,关节软骨损伤的骨关节炎患者的软骨细胞大量表达基质金属蛋白酶13(matrix metalloproteinase 13,MMP-13)[24],MMP-13是基质金属蛋白酶靶向软骨降解过程中最重要的酶之一,可以降解软骨中的多种蛋白分子[25],因此,当MMP-13表达升高时,软骨基质及细胞会被显著破坏。JING等[26]使用柠檬酸铁铵(ferric ammonium citrate,FAC)制备铁超载环境,研究发现铁过量会导致MMP-3和MMP-13的表达,加速软骨细胞凋亡,影响软骨细胞的稳态,进而诱导骨关节炎的发生。SIM?O等[27]通过将小鼠中分离得到的关节软骨细胞放入高浓度铁的环境中发现,软骨细胞会表现出MMP-13表达增加、细胞外基质破坏等,进而诱导骨关节炎的发生与发展,表明细胞内铁超载是骨关节炎发生的一个重要诱导因素。因此,作者认为根据铁超载可通过干预与软骨细胞凋亡相关的基质酶或直接破坏软骨细胞基质,加快骨关节炎发生的作用,未来可通过直接调节细胞内铁浓度,或者干预相关转铁蛋白间接调节细胞内铁含量,来抑制软骨细胞的凋亡及软骨基质的破坏,从而达到治疗或者延缓骨关节炎病情的发展。 2.3.2 氨基酸代谢异常 谷氨酸和谷氨酰胺是细胞铁死亡的重要调节因子[28]。谷氨酸在谷氨酸/胱氨酸转运体(cystine/glutamate transporter,xc-)系统中以1∶1的比例与胱氨酸交换,参与谷胱甘肽的合成。Xc-系统是存在于细胞表面的一种逆向转运蛋白,是由重链胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆向转运蛋白溶质载体家族3成员2(solute carrier family 3 member 2,SLC3A2)和轻链胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆向转运蛋白溶质载体家族7成员11(solute carrier protein 7 family member 11,SLC7A11)组成的异二聚体,它可以将胞外的胱氨酸运入胞内并将胞内多余的谷氨酸排出去。胱氨酸可以在细胞内被还原成半胱氨酸,成为合成谷胱甘肽(GSH)的重要底物,因此谷氨酸水平影响xc-系统的功能。谷胱甘肽是GPX4的主要成分[29],而GPX4也是抑制铁死亡的另一类小分子物质,其能够抗脂质过氧化。氨基酸代谢异常时,谷氨酸与胱氨酸交换失衡,导致谷氨酸在细胞外积聚,细胞外高浓度的谷氨酸会抑制System Xc-的功能,导致谷胱甘肽被耗尽,间接抑制了GPX4的功能,对铁死亡也起到促进作用[30]。 PIEPOLI等[31]通过观察大鼠软骨细胞中的谷氨酸信号发现谷氨酸代谢主要包括谷氨酰胺释放、钠和钙依赖性谷氨酸摄取以及谷氨酸转运体n-甲基-d-天冬氨酸(N-methyl-D-aspartic acid,NMDA)及谷氨酸受体(N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor,NMDAR)的表达,而软骨细胞表达了一种自给自足的谷氨酸信号传导机制,包括具有独特性质的外周NMDA受体。该受体可能在与软骨退化相关的炎症过程中发挥作用,因此成为骨关节炎的潜在药理学靶点。KALEV-ZYLINSKA等[32]研究发现通过白细胞介素1β刺激软骨细胞,谷氨酸的释放显著增加,同时谷氨酰胺的吸收明显减少,在骨关节炎中表达的NMDAR亚基类型也会随着氨基酸代谢的异常而发生改变,进而导致X型胶原蛋白水平降低,而X型胶原蛋白在软骨细胞的分化过程中也发挥着重要作用,表明氨基酸代谢的异常参与了骨关节炎的病理,进而诱导骨关节炎的发生与发展。同时PIEPOLI等[31]在大鼠软骨细胞中检测到了NMDA谷氨酸受体和非NMDA谷氨酸受体,同时还发现NMDA受体拮抗剂(MK-801)可以抑制滑膜增殖及软骨退变。因此,作者认为谷氨酸可能通过激活NMDA受体从而诱发骨关节炎患者关节内炎症反应及异常疼痛,对骨关节炎的发展具有重要影响。干预细胞内氨基酸代谢抑制软骨型细胞发生铁死亡可以作为临床治疗骨关节炎的一个新手段,同时继续深入研究NMDA受体导致疼痛及炎性反应的具体机制,是未来研究骨关节炎的一个重要方向。 2.3.3 脂质代谢异常 脂质代谢主要指脂质在自由基或脂质过氧化酶的作用下发生脂质过氧化,最终造成细胞损伤的脂质氧化降解反应[33],在细胞发生铁死亡时,细胞膜的重要组成部分不饱和脂肪酸(polyunsaturated fatty acid,PUFAs)失去双烯丙基氢原子,发生脂质过氧化[34]。因此,PUFAs的浓度和定位决定了细胞中发生脂质过氧化的程度,从而决定了铁死亡的有效程度。游离PUFAs是合成脂质信号介质的底物,但它们必须被酯化成膜磷脂,并经过氧化才能成为铁死亡的信号[29]。脂质组学研究表明,含有花生四烯酸或其延伸产物肾上腺酸的磷脂酰乙醇胺(phosphatidyl ethanolamine,PEs)是发生氧化并推动细胞走向铁死亡的关键磷脂。因此,形成这些PUFAs的辅酶衍生物并将其插入磷脂是产生铁死亡信号的必要条件,这是调控铁死亡的另一个潜在点,可继续深入研究,进一步证明铁死亡是通过调节含PUFAs的膜磷脂生物合成的酶来诱导发生的。 在对骨关节炎研究中,BAKER等[35]发现omega-3多不饱和脂肪酸总量(n-3 PUFAs)与髌股软骨损失呈负相关,而omega-6多不饱和脂肪酸(n-6 PUFA)与滑膜炎呈正相关。另有研究显示,男性餐后血浆饱和脂肪酸(saturated fatty acid,SFA)和PUFA水平与临床手关节炎和结构性膝关节炎呈正相关,但与女性无相关性[36]。一项病例对照研究也表明,高脂血症可能是新发骨关节炎的独立危险因素[37]。此外,一项研究表明,三酰甘油每增加一个单位(1 mmol/L),临床膝骨关节炎患病率和临床膝骨关节炎发病风险分别增加9%和5%[38]。综上所述,从多种角度来看,脂质(脂肪酸和胆固醇)和脂质代谢调节剂可以参与骨关节炎的发病机制,脂质代谢的异常可以诱导软骨细胞发生铁死亡,软骨细胞发生病变,进而诱发骨关节炎[39-42]。因此作者认为抑制脂质过氧化进而抑制软骨细胞发生铁死亡,可以作为治疗骨关节炎的一个新手段。并且已有研究发现脂质过氧化酶抑制剂如脂溶性抗氧化剂维生素 E,具有抑制铁死亡的作用[43],但其对骨关节炎的作用效果尚不清晰,因此未来可加强脂质过氧化酶抑制类药物作用机制的研究,为开发治疗骨关节炎新药物提供支持。 综上所述,软骨细胞铁死亡在骨关节炎的发生发展中起到重要作用,当细胞内铁代谢、氨基酸代谢、脂质代谢过程发生异常时,会诱导软骨细胞发生铁死亡,进而促进骨关节炎的发生。所以,通过调节细胞内的代谢过程,避免软骨细胞铁死亡的发生,有望成为临床防治骨关节炎的重要手段。并且已有研究发现多种中药复方、单味药、活性成分及其它中医疗法可干预软骨细胞内的多种代谢过程,抑制细胞铁死亡,对骨关节炎的治疗具有明显优势。 2.4 中医药通过干预铁死亡治疗骨关节炎 2.4.1 中药单体干预铁死亡治疗骨关节炎 研究表明黄芩素可能通过Wnt/β-catenin信号传导通路上调GPX4和减少谷氨酸释放促进成骨细胞增殖[44]。此外,黄芩素还可限制erastin诱导的亚铁生成、谷胱甘肽耗竭、GPX4降解和脂质过氧化[45],抑制膜脂质过氧化来抑制细胞铁死亡,进而可以推测黄芩素可通过促进成骨细胞的增殖或减轻软骨细胞的退行性改变的作用,发挥治疗骨关节炎的效果。鹰嘴豆芽素A(BCA)是从黄芪中分离得到的一种新型多功能生物活性天然化合物,具有保护骨质流失的作用。研究表明鹰嘴豆芽素A可以通过抑制TFR1和促进FPN直接降低铁浓度,挽救被铁杀死的软骨细胞。并且不同浓度的鹰嘴豆芽素A处理使细胞内铁、活性氧和脂质活性氧含量恢复,起到抑制细胞铁死亡的作用[46]。 中医认为骨关节炎患者多因外感风寒蕴久化热,或素体阴虚阳盛,内有蕴热或阴虚阳亢之体而发病。感受外邪,外邪每易从阳化热;或直接感受寒热风邪,痹阻于经络肌肉关节筋骨诱导骨关节炎的发生,称为寒热风痹。《名医别录》中记载“景天主治寒热风痹”,表明了红景天治疗骨关节炎的优势作用。研究表明红景天主要成分之一红景天苷(SLA)可通过介导相关通路发挥调控软骨细胞的凋亡,达到治疗骨关节炎的作用。ZHANG等[47]通过建立铁死亡小鼠模型,注入不同浓度的红景天注射液发现,红景天注射液能提高Nrf2入核率,使GPX4表达上调,转铁蛋白及COX2表达下调,从而减少细胞铁死亡,由此可以推测红景天可以抑制细胞发生铁死亡,进而抑制骨关节炎的发生与发展。研究发现淫羊藿苷通过降低脂质过氧化的生物标志物水平和铁含量以及增加细胞中的GPX水平来发挥抗氧化作用,并且还可通过激活Xc-/GPX4轴抑制铁死亡来减轻细胞死亡[48]。此外,PENG等[49]研究表明葛根素具有促进软骨细胞增殖、减轻关节软骨的退变,从而达到治疗骨关节炎的目的。LIU等[50]通过建立异丙肾上腺素损伤的大鼠心肌细胞并将其放在葛根素溶液中,发现葛根素还可抑制脂质过氧化和铁过载,进而抑制细胞铁死亡。BAO等[51]发现葛根素还可以减轻活性氧积聚和提高抗氧化酶GPX4的表达水平,抑制损伤的内皮细胞细胞凋亡。肖嘉聪等[52]研究结果表明槲皮素可以通过CH25H/CYP7B1/RORα信号通路调控软骨细胞中的脂质代谢,抑制软骨细胞的凋亡。上述研究表明,某些中药单体能够对软骨细胞起到保护作用,虽然其机制比较复杂,但主要是通过调节软骨细胞内活性氧含量、GPX4水平、铁代谢和脂质代谢等,对铁死亡起到抑制作用。详见表1。"
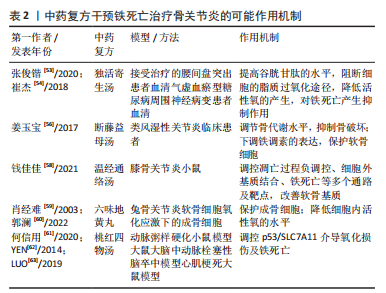
2.4.2 中药复方干预铁死亡治疗骨关节炎 临床上已有大量中药复方用于骨关节炎的治疗中,取得了很好的临床疗效,但其治疗的作用机制复杂,尚未得到诠释。研究表明独活寄生汤能显著提高腰间盘突出症患者血清谷胱甘肽的水平,减少活性氧的产生。而独活寄生汤药物组成中的川芎中含有较多的川芎内脂,其可降低患者血脂质过氧化物,具有抗自由基的作用,能够减轻和阻断脂质过氧化[53-54]。此外,已经有研究证明,独活寄生汤会促进细胞核内Nrf2水平,而Nrf2在细胞铁死亡中发挥着重要作用[55]。虽然尚未有研究证明独活寄生汤对细胞铁死亡产生影响,但其可能会通过抗脂质过氧化的作用抑制铁死亡,发挥治疗骨关节炎的作用,这一推测仍需进一步研究证实。断藤益母汤具有“补益肝肾、祛风除湿、化瘀通络”的功效,在临床上取得了很好的治疗效果,得到了患者的认可,常用于临床骨关节炎的治疗。有学者通过动物实验发现,断藤益母汤能有效改善类风湿性关节炎骨代谢水平,抑制骨破坏,并且下调铁调素的表达,进而起到骨保护作用[56],而铁调素是一种在铁代谢中起着重要作用的小分子多肽,在机体铁代谢平衡的调节中起关键作用[57]。因此,可以推测断藤益母汤可通过调节细胞内铁的含量抑制细胞铁死亡,达到治疗骨关节炎的效果。此外,钱佳佳[58]通过蛋白组学及网络药理学研究证实温经通络汤含药血清可从凋亡过程负调控、细胞外基质结合、铁死亡等多通路多靶点抑制血管生成,改善膝骨关节炎小鼠的软骨基质降解及炎症反应。 六味地黄丸是治疗肾阴亏虚型骨关节炎的代表方剂,其具有补肾益精的作用,通过保护和修复关节软骨达到治疗骨关节炎的作用[59],研究发现其含药血清可减轻H2O2对成骨细胞造成的氧化损伤,降低成骨细胞内活性氧水平,从而对关节软骨起到保护作用[60],由此推测其治疗骨关节炎的机制与抑制软骨细胞发生铁死亡有一定的关系。有学者借助网络药理学方法发现二陈汤合桃红四物汤抗动脉粥样硬化的机制可能是通过调控p53/SLC7A11介导的氧化损伤及铁死亡有关[61-63],而桃红四物汤已成为中医临床使用最广泛的活血化瘀方剂之一,以其养血和活血化瘀功效为核心应用于血瘀型骨关节炎的治疗,由此可以推测桃红四物汤可能通过调节氧化损伤及软骨细胞铁死亡从而达到治疗骨关节炎的目的。 综上所述,中药复方治疗骨关节炎的机制可能与激活Nrf2通路、提高活性氧和谷胱甘肽水平等过程干预铁代谢、氨基酸代谢和脂质代谢来调控铁死亡,从而达到治疗骨关节炎的作用。详见表2。"
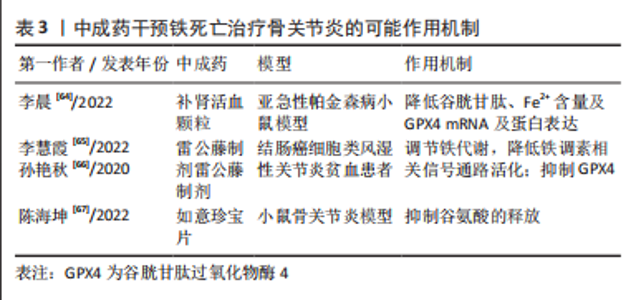
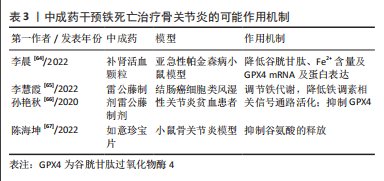
2.4.3 中成药干预铁死亡治疗骨关节炎 越来越多的临床研究发现中成药可通过干预软骨细胞铁死亡治疗骨关节炎。补肾活血颗粒原方来源于《伤科大成》,处方是以补肾活血法为治则的基本前提下进行研制的。该方剂经过十几年的临床应用研究,在临床治疗骨关节炎中取得了良好的疗效。李晨等[64]通过小鼠实验建立补肾活血颗粒组、铁死亡抑制剂组和模型组发现,与模型组及铁死亡抑制剂组比较,补肾活血颗粒组小鼠谷胱甘肽含量、GPX4 mRNA及蛋白表达升高,Fe2+含量降低,由此表明补肾活血颗粒可以通过调节细胞内铁浓度及氨基酸代谢干预骨关节炎发生与发展。 雷公藤是常用治疗骨关节炎的中药,具有祛风除湿、活血通络、消肿止痛的功效,雷公藤制剂也被广泛用于类风湿关节炎等免疫系统疾病,且取得较好疗效。有学者通过细胞实验证实雷公藤内酯通过抑制GPX4激活结肠癌细胞铁死亡,从而抑制癌细胞增殖[65]。并且研究通过观察不同雷公藤制剂对类风湿关节炎贫血患者的临床疗效,检测铁代谢相关信号传导通路的变化发现,雷公藤多苷片、新风胶囊两种不同雷公藤制剂均能够改善患者的贫血状态,与降低类风湿性关节炎患者机体炎症反应、调节铁代谢,降低铁调素相关信号通路活化[66]。因此作者认为雷公藤制剂在治疗骨关节炎的过程中,可通过调节铁代谢及抑制GPX4的活性抑制软骨细胞发生铁死亡,但具体机制需进一步研究证实。 临床上也常用如意珍宝片治疗骨关节炎,由珍珠母、沉香、石灰华等具有舒筋通络、通利关节作用的药物组成。陈海坤等[67]研究发现如意珍宝片发挥其治疗效果可能主要是作用于突触前膜,抑制谷氨酸的释放,从而减弱痛觉信息的传递,起到止痛的作用,从而达到缓解骨关节炎疼痛症状。因此,作者认为如意珍宝片可能通过干预谷氨酸代谢参与调节软骨细胞铁死亡,对骨关节炎发挥治疗作用。 以上研究表明,中成药在治疗骨关节炎中机制复杂,但根据目前已有研究可推测其主要通过调节细胞内Fe2+、GPX4、谷胱甘肽及谷氨酸的水平干预软骨细胞铁死亡,恢复细胞活性或减缓软骨细胞的凋亡,从而达到治疗骨关节炎的目的。详见表3。"
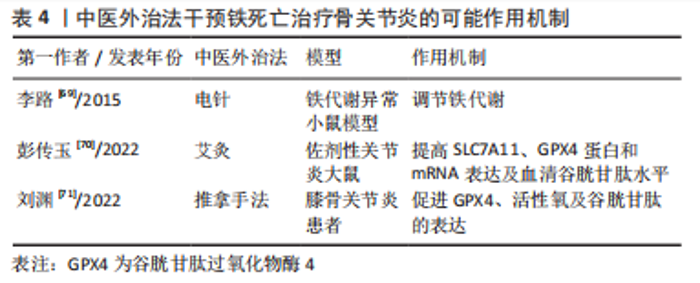
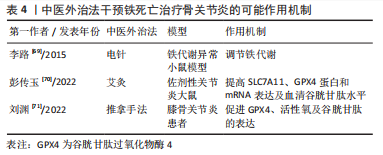
2.4.4 中医外治干预铁死亡治疗骨关节炎 针灸、艾灸、推拿手法等也是中医药的重要组成部分,都可起到缓解骨关节炎的作用。 针灸治疗中的电针疗法是一种起效快、不良反应少的方法,对于骨关节炎的治疗具有明显优势,电针通过微量电流加强针刺作用,缓解肌肉痉挛,具有消除炎症、改善血液循环、缓解疼痛的作用[68]。李路等[69]研究表明电针可以调节铁代谢,调节机体内铁的含量,从而改善小鼠铁代谢情况,避免细胞内铁超载,抑制细胞铁死亡。 此外,彭传玉等[70]观察到艾灸后佐剂性关节炎大鼠滑膜组织损伤明显改善,滑膜组织及血清活性氧表达强度显著降低,滑膜组织SLC7A11、GPX4表达水平及血清谷胱甘肽水平明显升高,因此,作者认为艾灸改善膝关节滑膜组织炎性反应的作用可能与其调控铁死亡相关因子的表达密切相关。 推拿手法在骨关节炎的治疗过程中也具有明显的优势,尤其是合并软组织损伤的患者。刘渊等[71]运用足阳明经筋手法治疗膝骨关节炎,发现治疗后抽取的膝关节液中铁死亡相关因子GPX4、活性氧及谷胱甘肽的表达明显升高,表明推拿手法可以调节软骨细胞铁死亡,改善骨关节炎的临床症状。 综上,针灸治疗主要干预铁代谢,参与调节铁死亡中铁超载现象,艾灸和推拿手法则主要干预GPX4、谷胱甘肽、活性氧水平调节细胞铁死亡。详见表4。"
| [1] RUBIO JE, SCANZELLO C, FELSON DT, et al. Correlation between senescence-associated secretory phenotypes factors in synovial fluid and serum and structural changes in osteoarthritis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2020;7(1):44-45. [2] PIVA SR, SUSKO AM, KHOJA SS, et al. Links between osteoarthritis and diabetes:implications for management from a physical activity perspective. Clin Geriatr Med. 2015;31(1):67-87. [3] 廖德发.我国骨性关节炎流行病学调查现状[J].微创医学,2017,12(4):521-524. [4] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020,104(2):293-311. [5] 邢丹,林剑浩.《骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)》更新解读及方法学评价[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(4):391-395. [6] 张俊锴.针刀松解术治疗膝骨关节炎的临床疗效观察[J].深圳中西医结合杂志, 2019,29(22):57-58. [7] 庾明,张廷玖,张东.中药离子导入联合膝关节镜清理术治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床疗效及机制[J].西部医学,2018,30(8):1138-1142. [8] DOLMA S, LESSNICK SL, HAHN WC, et al. Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell. 2003;3(3):285-296. [9] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072. [10] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331. [11] XIAO W, BEIBEI F, GUANGSI S, et al.Iron overload increases osteoclastogenesis and aggravates the effects of ovariectomy on bone mass. J Endocrinol. 2015;226(3):121-134. [12] NUGZAR O, ZANDMAN-GODDARD G, OZ H, et al. The role of ferritin and adiponectin as predictors of cartilage damage assessed by arthroscopy in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(5):662-668. [13] ZHAO LR, XING RL, WANG PM, et al. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LPS/ATP induced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4): 5463-5469. [14] XY A, KAI SA, SY B, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;27:33-43. [15] KAZAN K, KALAIPANDIAN S. Ferroptosis: Yet Another Way to Die. Trends Plant Sci. 2019; 24(6):479-481. [16] XIE Y, HOU W, SONG X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016; 23(3):369-379. [17] WOO JH, SHIMONI Y, YANG WS, et al. Elucidating Compound Mechanism of Action by Network Perturbation Analysis. Cell. 2015;162(2):441-451. [18] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN AJ, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology,and Disease. Cell. 2017;171(2):273-285. [19] TANG D, KANG R, BERGHE TV, et al.The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. 2019;29(5):347-364. [20] MUCKENTHALER MU, RIVELLA S, HENTZE MW, et al. A red carpet for iron metabolism. Cell. 2017;168(3):344-361. [21] HAO S, LIANG B, HUANG Q, et al. Metabolic networks in ferroptosis. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15(4):5405-5411. [22] VERMA P, DALAL K. ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5: Key enzymes in osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(12):3507-3514. [23] EL-SAYED ME, ASMAA KF, SAMAR E, et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019;234:116786. [24] SALERNO A, BRADY K, RIKKERS M, et al. MMP13 and TIMP1 are functional markers for two different potential modes of action by mesenchymal stem/stromal cells when treating osteoarthritis. Stem Cells. 2020;38(11):1438-1453. [25] SHIOMI T, LEMAÎTRE V, D’ARMIENTO J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases, a disintegrin and metalloproteinases,and a disintegrin and metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs in non‐neoplastic diseases. Pathol Int. 2010;60(7):477-496. [26] JING X, LIN J, DU T, et al. Iron overload is associated with accelerated progression of osteoarthritis: the role of DMT1 mediated iron homeostasis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021; 8:594509. [27] SIMÃO M, GAVAIA PJ, CAMACHO A, et al. Intracellular iron uptake is favored in Hfe‐KO mouse primary chondrocytes mimicking an osteoarthritis‐related phenotype. Biofactors.2019;45(4):583-597. [28] GAO M, MONIAN P, QUADRI N, et al. Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2015;59(2):298-308. [29] KAGAN VE, MAO G, QU F, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;13(1):81-90. [30] FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, SCHNEIDER M, PRONETH B, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(12):1180-1191. [31] PIEPOLI T, MENNUNI L, ZERBI S, et al. Glutamate signaling in chondrocytes and the potential involvement of NMDA receptors in cell proliferation and inflammatory gene expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(8):1076-1083. [32] KALEV-ZYLINSKA ML, HEARN JI, RONG J, et al. Altered N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subunit expression causes changes to the circadian clock and cell phenotype in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(11):1518-1530. [33] STOYANOVSKY DA, TYURINA YY, SHRIVASTAVA I, et al. Iron catalysis of lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis:regulated enzymatic or random free radical reaction?. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:153-161. [34] YANG WS, KIM KJ, GASCHLER MM, et al. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(34):E4966-E4975. [35] BAKER KR, MATTHAN NR, LICHTENSTEIN AH, et al. Association of plasma n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with synovitis in the knee:the MOST study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(5):382-387. [36] LOEF M, SCHOONES JW, KLOPPENBURG M, et al. Fatty acids and osteoarthritis:different types, different effects. Joint Bone Spine. 2019;86(4):451-458. [37] FREY N, HÜGLE T, JICK SS, et al. Hyperlipidaemia and incident osteoarthritis of the hand: a population-based case-control study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(7):1040-1045. [38] ZHOU M, GUO Y, WANG D, et al. The cross-sectional and longitudinal effect of hyperlipidemia on knee osteoarthritis: Results from the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort in China. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9739. [39] BAUDART P, LOUATI K, MARCELLI C, et al. Association between osteoarthritis and dyslipidaemia:a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. RMD Open. 2017;3(2): e000442. [40] FARNAGHI S, CRAWFORD R, XIAO Y, et al. Cholesterol metabolism in pathogenesis of osteoarthritis disease. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(2):131-140. [41] GKRETSI V, SIMOPOULOU T, TSEZOU A, et al. Lipid metabolism and osteoarthritis:lessons from atherosclerosis. Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50(2):133-140. [42] IOAN-FACSINAY A, KLOPPENBURG M. Bioactive lipids in osteoarthritis: risk or benefit? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(1):108-113. [43] MA TL, CHEN JX, ZHU P, et al. Focus on ferroptosis regulation: exploring novel mechanisms and applications of ferroptosis regulator. Life Sci. 2022;307:120868. [44] 郭冰清.黄芩素对erastin诱导成骨细胞铁死亡的影响及潜在机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2021. [45] XIE Y, SONG X, SUN X, et al. Identification of baicalein as a ferroptosis inhibitor by natural product library screening. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;473(4):775-780. [46] HE Q, YANG J, PAN Z, et al. Biochanin A protects against iron overload associated knee osteoarthritis via regulating iron levels and NRF2/System xc-/GPX4 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;157:113915. [47] ZHANG W, HUAI Y, MIAO Z, et al. Systems pharmacology approach to investigate the molecular mechanisms of herb Rhodiola rosea L. radix. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45(3):456-464. [48] LUO H, ZHANG R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc /GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(1):1-1. [49] PENG L, XIE Z, PEI J, et al. Puerarin alters the function of monocytes/macrophages and exhibits chondroprotection in mice. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(4):2876-2882. [50] LIU B, ZHAO C, LI H, et al. Puerarin protects against heart failure induced by pressure overload through mitigation of ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1): 233-240.. [51] BAO M, ZHANG Y, LOU X, et al. Puerarin protects endothelial cells from oxidized low density lipoprotein induced injuries via the suppression of LOX-1 and induction of eNOS. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;92(4):299-306 [52] 肖嘉聪,麦嘉乐,张罡瑜,等.槲皮素调控关节炎软骨细胞胆固醇代谢的机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(9):1336-1341. [53] 张俊锴,肖斌,许啸.独活寄生汤联合针刺治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床效果[J].世界中医药,2020,15(7):1067-1070. [54] 崔杰,谈力欣,牛素贞,等.独活寄生汤口服或熏蒸对气虚血瘀型糖尿病周围神经病变患者MDA和GSH-Px水平的影响[J].江苏中医药,2018,50(12):27-30. [55] LO SC, HANNINK M. PGAM5, a Bcl-XL-interacting protein, is a novel substrate for the redox-regulated Keap1-dependent ubiquitin ligase complex. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(49): 37893-37903. [56] 姜玉宝.基于铁调素探讨断藤益母汤对类风湿关节炎骨代谢的影响及作用机制[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2017. [57] WANG CY, BABITT JL. Liver iron sensing and body iron homeostasis. Blood. 2019;133(1): 18-29. [58] 钱佳佳.基于蛋白组学研究温经通络汤调控血管新生治疗膝骨关节炎的作用机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2021. [59] 肖经难,谢丹,祁开泽.六味地黄丸对兔骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].长沙:湖南中医学院学报,2003(5):11-13. [60] 郭澜.基于ERK/mTOR通路调控自噬探讨六味地黄丸减轻成骨细胞氧化应激损伤的分子机制[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2022. [61] 何信用,王俊岩,宋囡,等.二陈汤合桃红四物汤调控p53/SLC7A11介导的氧化损伤及铁死亡抗动脉粥样硬化的作用及机制研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(5): 2344-2348. [62] YEN TL, ONG ET, LIN KH, et al. Potential advantages of Chinese medicine Taohong Siwu Decoction (桃红四物汤) combined with tissue-plasminogen activator for alleviating middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced embolic stroke in rats. Chin J Integr Med. 2014 Sep 24. doi: 10.1007/s11655-014-1847-x. [63] LUO ZR, LI H, XIAO X, et al. Taohong Siwu Decoction Exerts a Beneficial Effect on Cardiac Function by Possibly Improving the Microenvironment and Decreasing Mitochondrial Fission after Myocardial Infarction. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019;2019:5198278. [64] 李晨,王鹏,王亮,等.补肾活血颗粒对亚急性帕金森病模型小鼠脑黑质多巴胺神经元铁死亡的影响[J].中医杂志,2022,63(15):1463-1469. [65] 李慧霞,尤伟波,陈丽,等.谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4在雷公藤内酯酮激活结肠癌细胞铁死亡中的作用[J].浙江医学,2022,44(10):1038-1041. [66] 孙艳秋,刘健,黄旦,等.不同雷公藤制剂对类风湿关节炎贫血患者的疗效及其机制[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020,36(3):360-364. [67] 陈海坤,柏虎虎,李宇哲,等.如意珍宝片对骨关节炎性痛的抑制作用[J].中国药理学通报,2022,28(10):1579-1585. [68] 白晓东,李顺月,宋晓晶,等.针灸治疗仪作用原理及其临床应用[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(2):488-491. [69] 李路,张立德.电针双侧足三里、三阴交穴治疗脾气虚证大鼠和对机体铁代谢影响实验研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2015,17(7):81-85. [70] 彭传玉,胡玲,吴子建,等.艾灸对佐剂性关节炎大鼠脊髓中N-甲基-D天冬氨酸受体-一氧化氮-环鸟苷酸通路的影响[J].针刺研究,2022,47(3):250-255. [71] 刘渊,邓健,孙雪莲,等.足阳明经筋手法治疗对膝关节骨性关节炎患者股四头肌力学性能及软骨细胞铁死亡的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(9):5504-5507. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [3] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [4] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [5] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [6] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [7] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [8] | Zhao Nannan, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Zhu Bochao, Ding Huimin, Xu Zhenhua. Changes in ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons of vascular dementia model rats treated with Tongmai Kaiqiao Pill [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1401-1407. |
| [9] | Zhang Mingyang, Yang Xinling. Verbascoside inhibits Erastin-induced ferroptosis of dopaminergic nerve cell line MN9D cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1408-1413. |
| [10] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [11] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [12] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [13] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [14] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [15] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||