Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (14): 2227-2233.doi: 10.12307/2024.223
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of treadmill exercise on the structure and diversity of intestinal microflora in rats with Parkinson’s disease
Ma Xinran1, Liu Xinhao1, Li Yujia1, Luo Kailiang2, Ma Shujie3, Hu Jun1, 3
- 1School of Rehabilitation Science, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350005, Fujian Province, China; 3The Second Rehabilitation Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 200441, China
-
Received:2023-01-19Accepted:2023-03-13Online:2024-05-18Published:2023-07-28 -
Contact:Hu Jun, MD, Chief physician, Associate professor, School of Rehabilitation Science, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; The Second Rehabilitation Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 200441, China -
About author:Ma Xinran, Master candidate, School of Rehabilitation Science, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Project), No. 81603713 (to MSJ); Scientific Research Fund Project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission, No. 202040485 (to HJ); Shanghai Baoshan District Science and Technology Fund Project, No. 20-E-43 (to MSJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Xinran, Liu Xinhao, Li Yujia, Luo Kailiang, Ma Shujie, Hu Jun. Effect of treadmill exercise on the structure and diversity of intestinal microflora in rats with Parkinson’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2227-2233.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
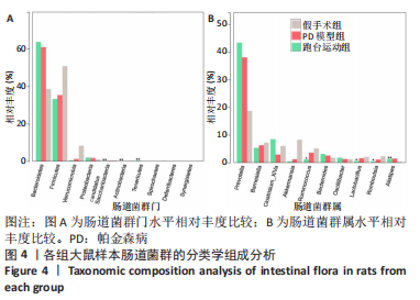
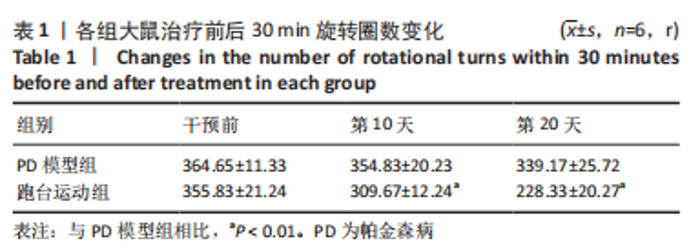
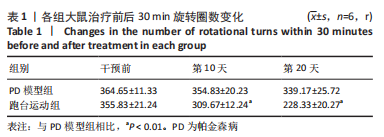
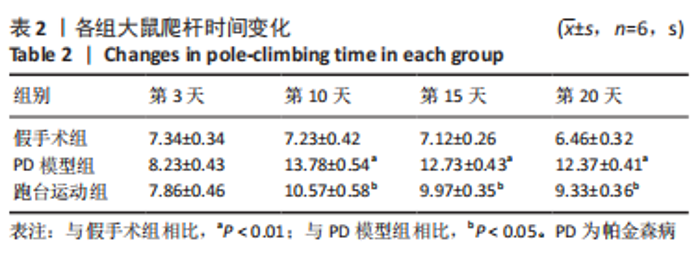
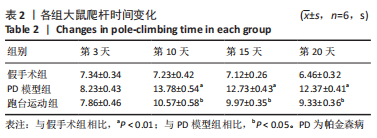
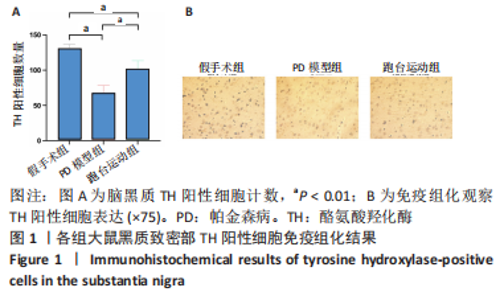
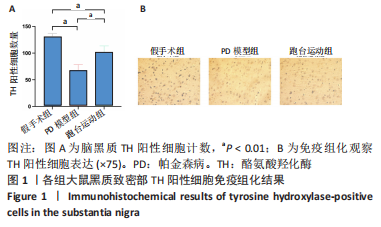
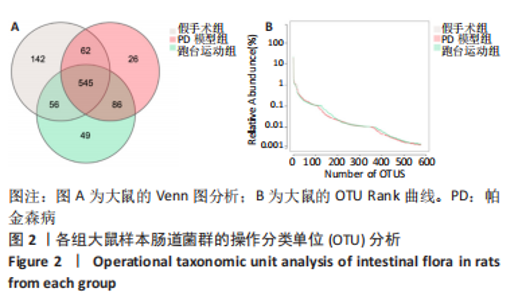
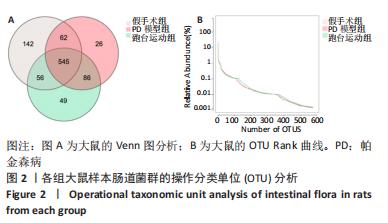
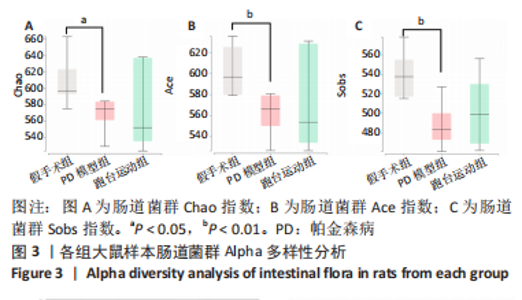
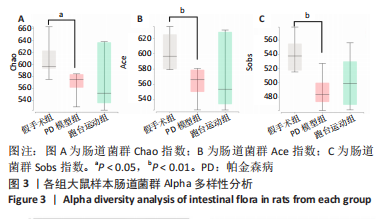
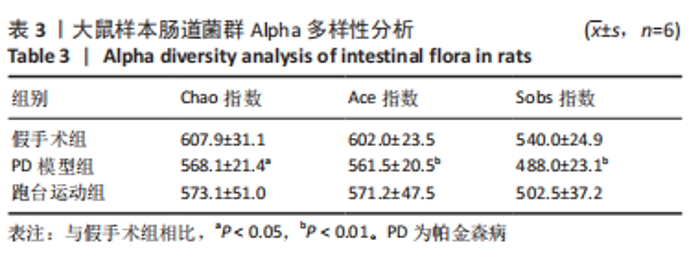
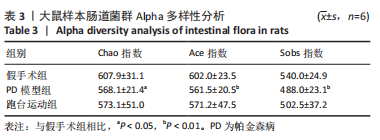
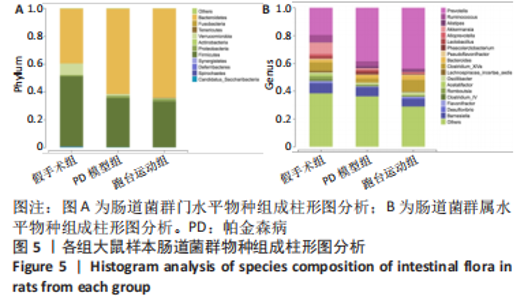
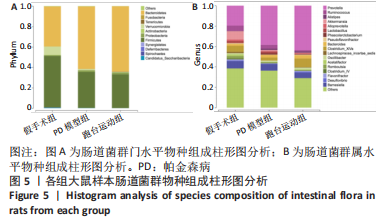
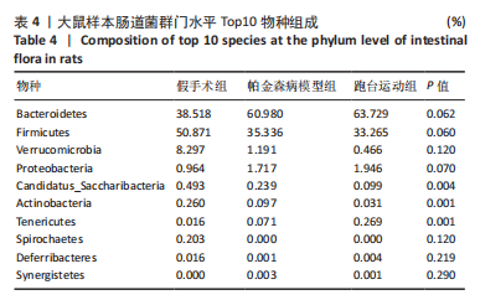
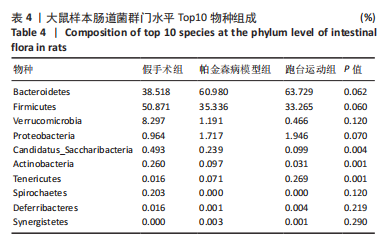
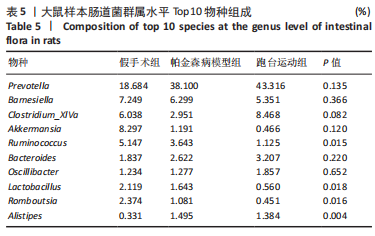
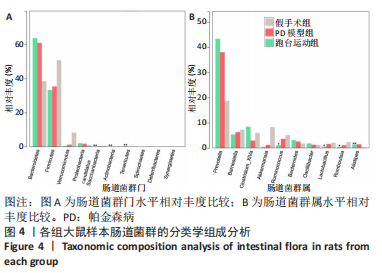
2.7 大鼠样本肠道菌群的分类学组成分析 在门水平,样本菌群中相对丰度最高的前4种菌群分别为Bacteroidetes (拟杆菌门) 、Firmicutes (厚壁菌门) 、Verrucomicrobia (疣微菌门)和Proteobacteria (变形菌门),四者比例之和在各组中均达97%以上。值得关注的是,与假手术照相比,PD模型组中Tenericutes(无壁菌门)的丰度水平由0.016 2%升高为0.071 3%,Actinobacteria(放线菌门)的丰度水平由0.259 6%显著降低至 0.097 1%; Candidatus_Saccharibacteria的丰度水平由0.492 6%显著降低至0.239 3%;经跑台运动干预后,Tenericutes的丰度水平升高至0.268 7%,Actinobacteria和Candidatus_Saccharibacteria的丰度分别降低至0.030 6%和0.099 3%。进一步对肠道菌群进行属水平分析,发现与PD模型组的优势菌群相比,跑台运动组的Barnesiella、Ruminococcus、Lactobacillus、Romboutsia均有所降低,而有益菌Prevotella、Bacteroides、Clostridium_XlVa等呈上升趋势,见图4,5和表4,5。"
| [1] 梁建庆.帕金森病的发病机制、诊断标准及治疗策略[J].解放军医学杂志, 2018,43(8):631-635. [2] 张贺,姜立刚.帕金森病非运动症状研究现状[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2021,24(1):72-76. [3] 陈芝君,马建,唐娜,等.中国帕金森病疾病负担变化趋势分析及预测[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2022,30(9):649-654. [4] PD MED Collaborative Group. Long-term effectiveness of dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors compared with levodopa as initial treatment for Parkinson’s disease (PD MED): a large, open-label, pragmatic randomised trial. Lancet. 2014;384(9949):1196-205. [5] 王宽,詹彦,蒋理,等.丘脑底核脑深部电刺激术治疗伴有异动的帕金森病的疗效分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2020,42(24):2426-2432. [6] Schmidt TSB, Raes J, Bork P. The human gut microbiome: from association to modulation. Cell. 2018;172:1198-1215. [7] 马艺鑫,隋国媛,韩阳.基于阴阳失衡探讨肠道菌群失调与亚健康状态的关系[J].辽宁中医杂志,2020,47(3):104-105. [8] 邹嫄媛, 郑钦日, 徐君铭. 肠道菌群与神经性疾病的研究进展[J]. 临床医学进展,2022,12(1):6. [9] SkjAErbAEk C, Knudsen K, Horsager J, et al. Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. J Clin Med. 2021;10(3):493. [10] ZHU Y, YUAN M, LIU Y, et al. Association between inflammatory bowel diseases and Parkinson’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(2):344-353. [11] 余锋,贾芳芳,徐帅,等.运动介导肠道微生物-肠-脑轴调控神经功能的机制[J].上海体育学院学报,2021,45(1):66-77. [12] Motiani KK, Collado MC, Eskelinen JJ, et al. Exercise Training Modulates Gut Microbiota Profile and Improves Endotoxemia. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020; 52(1):94-104. [13] Crowley EK, Nolan YM, Sullivan AM. Exercise as a therapeutic intervention for motor and non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: Evidence from rodent models. Prog Neurobiol. 2019;172:2-22. [14] UNGERSTEDT U. 6-Hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of central monoamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol.1968;5(1):107-110. [15] 王利,何建成.复方地黄颗粒对帕金森病大鼠细胞凋亡的干预作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(8):4122-4125. [16] CARMAN LS, GAGE FH, SHULTS CW. Partial lesion of the substantia nigra: relation between extent of lesion and rotational behavior. Brain Res. 1991;553(2):275-283. [17] Wang W, Lv Z, Gao J, et al. Treadmill exercise alleviates neuronal damage by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome and microglial activation in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res Bull. 2021,174:349-358. [18] Islam MS, Azim F, Saju H, et al. Pesticides and Parkinson’s disease: Current and future perspective. J Chem Neuroanat. 2021;115:101966. [19] Armstrong MJ, Okun MS. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA. 2020,323(6):548-560. [20] 李胜德,王琳,关鸿志,等.脑积水脑室-腹腔分流术后帕金森综合征三例临床分析[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2017,17(2):127-132. [21] Turcano P, Mielke MM, Bower JH, et al. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson disease: A population-based cohort study. Neurology. 2018;91(24): e2238-e2243. [22] Prange S, Danaila T, Laurencin C, et al. Age and time course of long-term motor and nonmotor complications in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2019,92(2): e148-e160. [23] 王孟迪,张秋梅,范蓓,等.基于文献数据库的6-OHDA帕金森病大鼠模型特点分析及在中药研究中的应用[J].中国比较医学杂志,2023,33(1):93-102. [24] Minaei A, Sarookhani MR,Haghdoost YH, et al. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates induction and prevents progress of the 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinsonism in rat through activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels and suppression of ER stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021;15(423):115558. [25] 华嵘暄,高晗,王博雅,等.菌-肠-脑轴与血脑屏障通透性的相关性研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志,2022,30(2):100-108. [26] YEMULA N, NJOKU P, TAKYI J. The second brain in Parkinson’s disease: fact or fantasy? Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(8):1737-1738. [27] Houser MC, Tansey MG. The gut-brain axis: is intestinal inflammation a silent driver of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis? NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2017;3(1):3. [28] Scheperjans F, Aho V, Pereira PA, et al. Gut microbiota are related to Parkinson’s disease and clinical phenotype. Mov Disord. 2015;30(3):350-358. [29] Hill-Burns EM, Debelius JW, Morton JT, et al.Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease medications have distinct signatures of the gut microbiome. Mov Disord. 2017;32(5):739-749. [30] 宋刚,廖帅雄.运动与肠道菌群研究综述[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(10):56-61. [31] 廖沁,曾来生,陈杨,等.基于16S rRNA测序分析游泳运动对小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].江西医药,2022,57(5):437-443. [32] 张博枰,申延琴.肠道菌群与帕金森病的研究进展[J].延安大学学报(医学科学版),2021,19(1):80-86. [33] Sun MF, Zhu YL, Zhou ZL, et al. Neuroprotective effects of fecal microbiota transplantation on MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mice: Gut microbiota, glial reaction and TLR4/TNF-α signaling pathway. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;70:48-60. [34] PEREZ-Pardo P, Dodiya HB, Engen PA, et.al. Role of TLR4 in the gut-brain axis in Parkinson’s disease: a translational study from men to mice. Gut. 2019; 68(5):829-843. [35] 刘蓉,栾春光,王德良,等.基于高通量测序分析黄酒对D-半乳糖致衰老小鼠模型肠道微生物菌群的影响[J].食品与发酵工业,2020,46(2):32-39. [36] Strandwitz P, Kim KH, Terekhova D, et al. GABA-modulating bacteria of the human gut microbiota. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4(3):396-403. [37] Otaru N, Ye K, Mujezinovic D, et al. GABA Production by Human Intestinal Bacteroides spp.: Prevalence, Regulation, and Role in Acid Stress Tolerance. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:656895. [38] 李雪,孟庆雄.肠道微生物对寿命的影响及其机制[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2022,42(4):49-57. [39] 卢芳,闫静思,张冶,等.基于16S rRNA基因测序技术研究刺五加对帕金森病模型大鼠肠道菌群结构及多样性的影响[J].药物生物技术,2021,28(6): 551-560. [40] Hayashi A, Nagao-Kitamoto H, Kitamoto S, et al. The Butyrate-Producing Bacterium Clostridium butyricum Suppresses Clostridioides difficile Infection via Neutrophil- and Antimicrobial Cytokine-Dependent but GPR43/109a-Independent Mechanisms. J Immunol. 2021;206(7):1576-1585. [41] GASALY N, Hermoso MA, Gotteland M. Butyrate and the Fine-Tuning of Colonic Homeostasis: Implication for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):3061. |
| [1] | Cai Yaohao, Lang Lyu, Li Hong. Assessing the bone mass of the residual alveolar ridge in the first molar for implant placement by cone-beam computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1572-1577. |
| [2] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [3] | Su Xiaoyang, Chen Wenting, Fu Yidan, Zhao Yan, Lan Danfeng, Yang Qiuping. Correlation between Mer receptor tyrosine kinase and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [4] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [5] | Jing Ruyi, Chen Yingxin, Cao Lei . Prognosis of deep lamellar keratoplasty versus penetrating keratoplasty in the treatment of stromal corneal dystrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [6] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| [7] | Zheng Huakun, Yin Mingyue, Liu Qian. Effects of interval and continuous training on the quality of life in physically inactive adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1727-1740. |
| [8] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [9] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [10] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [11] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [12] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [13] | He Longcai, Song Wenxue, Ming Jiang, Chen Guangtang, Wang Junhao, Liao Yidong, Cui Junshuan, Xu Kaya. An experimental method for simultaneous extraction and culture of primary cortical neurons and microglial cells from SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1395-1400. |
| [14] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [15] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||