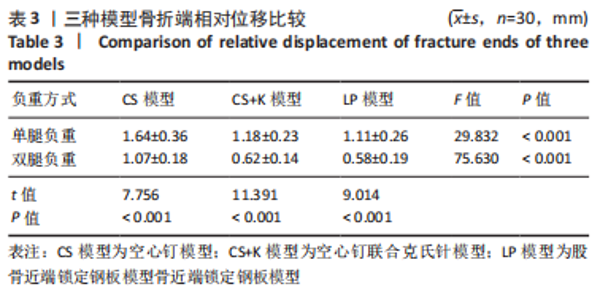
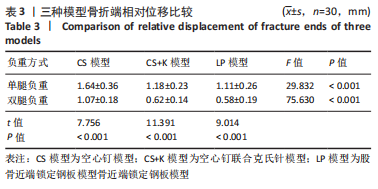
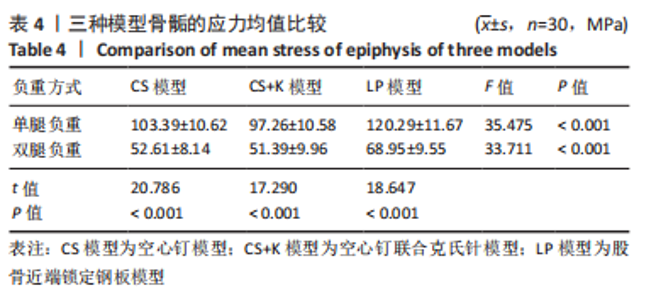
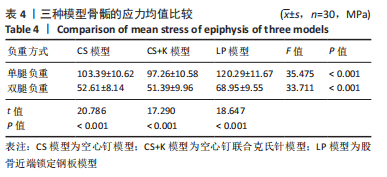
[1] MOON ES, MEHLMAN CT. Risk factors for avascular necrosis after femoral neck fractures in children: 25 Cincinnati cases and meta-analysis of 360 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(5):323-329.
[2] 田守进,朱贤,缪健荣,等.切开与闭合复位内固定治疗移位型儿童股骨颈骨折的Meta分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(7): 560-565.
[3] 杨蓉蓉,谭俊峰,刘洋,等.空心拉力钉锁定板与空心钉固定股骨颈骨折的生物力学研究[J].生物医学工程与临床,2016,20(3):225-228.
[4] 徐刚,郭源.空心钉治疗儿童股骨颈骨折早期手术结果分析[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2012,33(12):932-935.
[5] 陈顺有,梅海波,郭跃明,等.儿童髋部锁定加压接骨板和空心钉治疗儿童股骨颈骨折(DelbetⅡ、Ⅲ型)的比较研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2016,37(12):898-902.
[6] 丁强,刘玉峰,苏艺,等.克氏针与空心螺钉内固定治疗儿童DelbetⅡ、Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折[J].中医正骨,2020,32(11):69-71.
[7] 张炼,王洋,邓银栓,等.儿童股骨颈骨折治疗方法的研究进展[J].中国医药,2019,14(5):795-798.
[8] 陈宇峰,任栋,耿林丹,等.菱形构型空心钉固定PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020, 22(12):1080-1085.
[9] 郭江博,梁婷,车艳军,等.髋关节软骨高,低负重区微纳结构的力学性质对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3157-3161.
[10] 相庚,冯亚非,程建刚,等.单头与双头螺纹空心钉固定治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的生物力学性能比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(12):1064-1065.
[11] 任栋,程培焱,宋朝晖,等.不同数量和空间构型的空心拉力螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(9): 815-822.
[12] BOARDMAN MJ, HERMAN MJ, BUCK B, et al. Hip fractures in children. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(3):162-173.
[13] PALOCAREN T. Femoral Neck Fractures in Children: A Review. Indian J Orthop. 2018;52(5):501-506.
[14] YERANOSIAN M, HORNEFF JG, BALDWIN K, et al. Factors affecting the outcome of fractures of the femoral neck in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(1):135-142.
[15] BUKVA B, ABRAMOVIĆ D, VRGOČ G, et al. Femoral neck fractures in children and the role of early hip decompression in final outcome. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 6:S44-47.
[16] ALKHATIB N, YOUNIS MH, HEGAZY A, et al. Early versus late treatment of paediatric femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2019;43(3):677-685.
[17] WANG W, LI Y, XIONG Z, et al. Effect of the Number, Size, and Location of Cannulated Screws on the Incidence of Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head in Pediatric Femoral Neck Fractures: A Review of 153 Cases. J Pediatr Orthop. 2022;42(3):149-157.
[18] 陈晋宸,陈顺有,潘源城.螺钉置入深度对Delbet Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型儿童股骨颈骨折治疗效果的影响研究[J].临床小儿外科杂志,2020,19(7): 573-578.
[19] GURNEA TP, NIELSEN RC, ALTHAUSEN PL. Use of Proximal Humerus Locking Plates for Fixation of Pediatric Femoral Neck Fractures: Technical Trick. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(9):e312-e315.
[20] SAMSAMI S, AUGAT P, ROUHI G. Stability of femoral neck fracture fixation: A finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019;233(9): 892-900.
[21] MACLEOD A, SIMPSON AHRW, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation into the influence of loading conditions in biomechanical testing of locking plate fracture fixation devices. Bone Joint Res. 2018; 7(1):111-120.
[22] 李建涛,张里程,徐高翔,等.股骨近端三角形结构重建失效对骨折手术失败的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(14):928-935.
[23] 李佳,陈华,李建涛,等.三角稳定固定系统治疗股骨颈骨折术后骨不连临床疗效[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(7):795-800.
[24] 黄煊怀,廖瑛,范伟杰,等.新型儿童股骨颈螺钉设计中的生物力学因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(39):6954-6961.
[25] YU YX, MA JZ, ZHU LB, et al. Failure of internal fixation on displaced femoral neck fractures in adults under fifty-five years old. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7):542-545.
[26] 陈振光,余国荣.儿童股骨头骺板的解剖定位及其临床意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,1997,14(2):92-93.
[27] KHAN SK, KHANNA A, PARKER MJ. Posterior multifragmentation of the femoral neck: does it portend a poor outcome in internally fixed intracapsular hip fractures? Injury. 2009;40(3):280-282.
[28] NETO PF, DOS REIS FB, FILHO JL, et al. Nonunion of fractures of the femoral neck in children. J Child Orthop. 2008;2(2):97-103.
[29] 曹进,胡珊珊,郑华江,等.带螺纹内固定贯穿股骨头骺板实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(3):240-244.
[30] 张菁,陈珽,范清,等.大龄髋脱位儿童股骨颈前倾角变化与骨骺应力的有限元分析研究[J].生物医学工程与临床,2011,15(2):152-155.
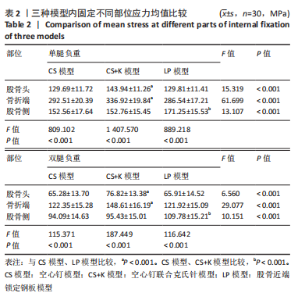
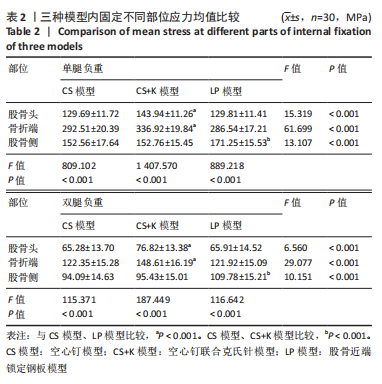
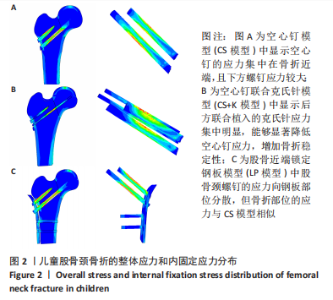
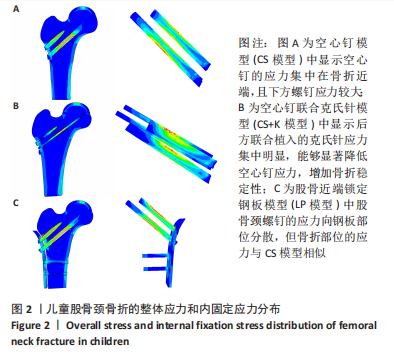
|