Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (13): 2033-2037.doi: 10.12307/2023.312
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mid- and long-term follow-up of valgus knees with total knee arthroplasty via subvastus approach
Liu Hongwen1, 2, Yin Li3, Xu Wenhao3, Li Jiao3, Luo Fenqi2, Liu Shaojiang1, Xu Jie2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, 3Department of Discipline Construction Office, Panzhihua Central Hospital, Panzhihua 617000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-10Accepted:2022-06-06Online:2023-05-08Published:2022-08-12 -
Contact:Xu Jie, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Liu Hongwen, Doctoral candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Panzhihua Central Hospital, Panzhihua 617000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China Yin Li, MD, Associate professor, Master’s professor, Department of Discipline Construction Office, Panzhihua Central Hospital, Panzhihua 617000, Sichuan Province, China Xu Wenhao, Chief physician, Master’s professor, Department of Discipline Construction Office, Panzhihua Central Hospital, Panzhihua 617000, Sichuan Province, China Liu Hongwen, Yin Li and Xu Wenhao contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Special Project, No. 2020JC0087 (to YL); a Special Project for Scientific Research on Subject Talents of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. YYZX20211097 (to LHW); Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, No. 2019J01173 (to XJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Hongwen, Yin Li, Xu Wenhao, Li Jiao, Luo Fenqi, Liu Shaojiang, Xu Jie. Mid- and long-term follow-up of valgus knees with total knee arthroplasty via subvastus approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2033-2037.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
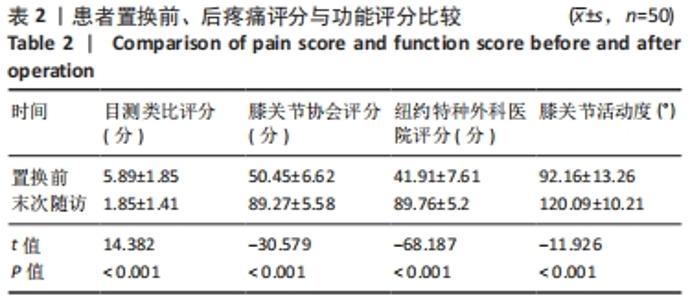
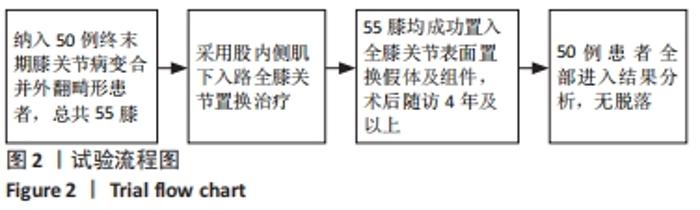
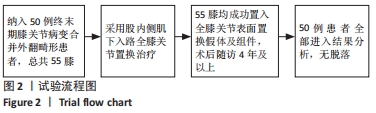
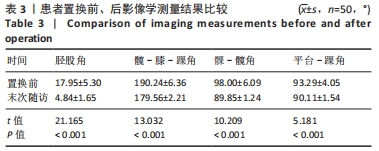
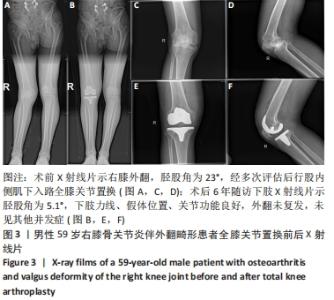
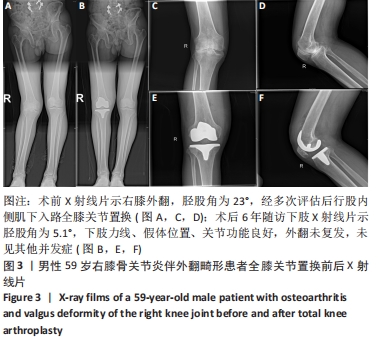
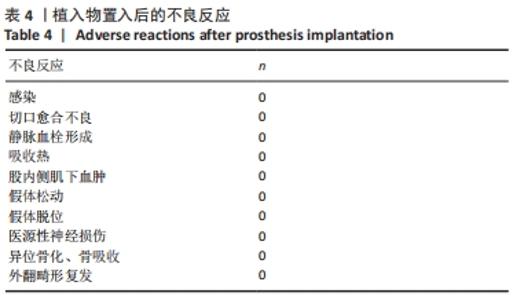
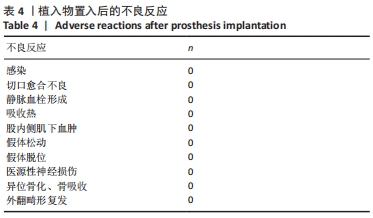
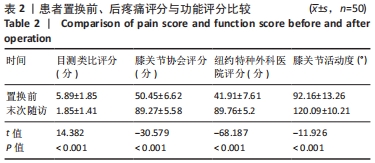
2.3 一般资料 此组患者随访时间为4.7-11.1年。手术时间(67.2±6.2) min,显性出血量(317.3±109.6) mL,切口长度(11.5±1.2) cm,起始下地时间(1.1±0.5) d,起始上下楼梯时间(2.3±0.9) d,住院天数(4.9±1.2) d。所有患者切口均Ⅰ期愈合,术后未发生腓总神经麻痹、感染、深静脉栓塞等并发症;随访期间假体位置良好,未发现假体松动、下沉、假体周围骨折等情况,无翻修病例。 2.4 术后疗效及假体位置 末次随访时,此组患者目测类比评分显著降低,KSS和HSS评分显著升高,膝关节活动度显著增大,差异均有显著性意义(均P < 0.001);下肢力线基本矫正,胫股角、髋-膝-踝角、髁-髋角、平台-踝角均显著降低,差异均有显著性意义(均P < 0.001),见表2,3。"
| [1] WELSH RL, WILD DL, KARMARKAR AM, et al. Predictors of Discharge Settings After Total Knee Arthroplasty in Medicare Patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(9):1509-1514. [2] SAPPEY-MARINIER E, MEYNARD P, SHATROV J, et al. Kinematic alignment matches functional alignment for the extension gap: a consecutive analysis of 749 primary varus osteoarthritic knees with stress radiographs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06832-0. [3] DALAL SS, CHANDRATREYA A, SINGHAL K, et al. Incidence of Soft-Tissue Releases, Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Lateral Parapatellar Approach for Valgus Arthritic Knees: A 4-year Follow-up Study with A Review of Literature. Indian J Orthop. 2021;55(Suppl 1):38-45. [4] LI H, PONZIO D Y, ONG A, et al. Total Knee Arthroplasty for Fixed Valgus Deformity Correction Using a Modified Lateral Parapatellar Approach. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(4):372-377. [5] REN J, ZHANG X, WULAMU W, et al. Total knee arthroplasty with the least-constrained implant possible for type II valgus knee > 20°: a 3-14 years’ follow-up. Arthroplasty (London, England). 2020;2(1):17. [6] XU J, LIU H, LUO F, et al. Common peroneal nerve ‘pre-release’ in total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformities. Knee. 2020;27(3):980-986. [7] 刘洪文, 陈锦成, 朱国涛, 等. 两种入路对人工全膝关节置换术后快速康复的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(16):1441-1445. [8] 徐杰, 刘春华, 周仕国, 等. 全膝关节置换:股内侧肌下与内侧髌旁入路的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(35):6240-6246. [9] ZHANG Z, CHAI W, ZHAO G, et al. Association of HSS score and mechanical alignment after primary TKA of patients suffering from constitutional varus knee that caused by combined deformities: a retrospective study. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):3130. [10] OH SM, BIN SI, KIM JY, et al. Impact of preoperative varus deformity on postoperative mechanical alignment and long-term results of “mechanical” aligned total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(6):1061-1066. [11] WANG JW, CHEN GF, SHIH HN, et al. Total Knee Arthroplasty with Intra-Articular Resection of Bone for Knee Arthritis Secondary to Malunion of a Tibial Shaft Fracture: A Radiological Evaluation of Correction of the Tibial Deformity. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021:6970591. [12] GREENBERG A, KANDEL L, LIEBERGALL M, et al. Total Knee Arthroplasty for Valgus Deformity via a Lateral Approach: Clinical Results, Comparison to Medial Approach, and Review of Recent Literature. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(8):2076-2083. [13] KAWAGUCHI K, INUI H, TAKETOMI S, et al. Rotational kinematics differ between mild and severe valgus knees in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2021;28:81-88. [14] SHAH NA, JAIN NP. Total knee arthroplasty in valgus knees using minimally invasive medial-subvastus approach. Indian J Orthop. 2016; 50(1):25-33. [15] PARK A, STAMBOUGH JB, NUNLEY RM, et al. The Inadequacy of Short Knee Radiographs in Evaluating Coronal Alignment After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(4):878-882. [16] ALESI D, MEENA A, FRATINI S, et al. Total knee arthroplasty in valgus knee deformity: is it still a challenge in 2021? Musculoskelet Surg. 2022;106(1): 1-8. [17] CHEUNG A, YAN CH, CHAN PK, et al. The Medial Collateral Ligament in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Injury. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(12):e510-e516. [18] MANCINO F, FALEZ F, MOCINI F, et al. Is varus-valgus constraint a reliable option in complex primary total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review. J Orthop. 2021;24:201-211. [19] RODRIGUEZ-MERCHAN EC. Patient Satisfaction Following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Contributing Factors. Arch Bone Joint Surg. 2021; 9(4):379-386. [20] KARACHALIOS T, SARANGI PP, NEWMAN JH. Severe varus and valgus deformities treated by total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 1994; 76(6):938-942. [21] ERARD J, BATAILLER C, SWAN J, et al. Lateral approach total knee arthroplasty achieves equivalent patellar tracking in severe valgus deformity compared to mild valgus deformity. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(2):740-752. [22] WANG B, XING D, LI JJ, et al. Lateral or medial approach for valgus knee in total knee arthroplasty - which one is better? A systematic review. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(11):5400-5413. [23] BOUCH PA, CORSIA S, NIZARD R, et al. Comparative Efficacy of the Different Surgical Approaches in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic-Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(3):1187-1194.e1. [24] LIN W, NIU J, DAI Y, et al. Mini-midvastus versus medial parapatellar approach in total knee arthroplasty: difference in patient-reported outcomes measured with the Forgotten Joint Score. J orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):336. [25] GULER O, GÜMÜŞSUYU G, SOFU H, et al. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Total Knee Arthroplasty Performed with Midvastus and Medial Parapatellar Approaches in Obese Patients. Adv Orthop. 2021; 2021:5512930. [26] UGBEYE ME, ITAKPE SE, AYODABO OJ. Subvastus versus Medial Parapatellar Approach in Primary Total Knee Replacement: An Assessment of Early Function. West Afr J Med. 2018;35(1):15-19. [27] MORRELL AT, LAYON DR, SCOTT MJ, et al. Enhanced Recovery After Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021;103(20):1938-1947. [28] RIPOLL S-MELCHOR J, ABAD-MOTOS A, D EZ-REMESAL Y, et al. Association Between Use of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Protocol and Postoperative Complications in Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the Postoperative Outcomes Within Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Protocol in Elective Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Study (POWER2). JAMA Surg. 2020;155(4):e196024. [29] TOMEK IM, KANTOR SR, CORI LA, et al. Early Patient Outcomes After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty with Quadriceps-Sparing Subvastus and Medial Parapatellar Techniques: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(11):907-915. [30] JHURANI A, AGARWAL P, ASWAL M, et al. Subvastus Exposure Compared to Parapatellar Approach in Navigated Sequential Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty (SBTKA): A Prospective Randomized Study. The journal of knee surgery. 2021;34(6):635-643. [31] MIGLIORINI F, ARETINI P, DRIESSEN A, et al. Better outcomes after mini-subvastus approach for primary total knee arthroplasty: a Bayesian network meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(6):979-992. |
| [1] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [3] | Xu Xiangjun, Wang Chao, Song Qunshan, Li Bingyan, Zhang Jichao, Wang Guodong, Dong Yuefu. Optimal angle for prosthesis implantation in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 612-618. |
| [4] | Xu Yangyang, He Peiliang, Meng Qingqi, Li Siming. A meta-analysis of the effects of continuous adductor canal block and continuous femoral nerve block on early activity after knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 640-645. |
| [5] | Chai Hao, Yang Deyong, Zhang Lei, Shu Li. 3D printing personalized osteotomy guide technology versus conventional total knee arthroplasty on the accuracy of lower limb force alignment: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 646-654. |
| [6] | Wei Bo, Yao Qingqiang, Tang Cheng, Li Xuxiang, Xu Yan, Wang Liming. Advantage of medial pivot prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty via medial subvastus approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 552-557. |
| [7] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [8] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [9] | Zhang Jinbiao, Li Xiaoming, Xing Wanlin, Ma Fei, Yu Qiaoya, Dai Rongqin. Early warning efficacy of thrombus molecular markers after total knee arthroplasty in patients complicated with venous thromboembolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 572-577. |
| [10] | You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492. |
| [11] | Huang Huida, Huang Yongming, Zhou Junde, Liu Wenbo, Lin Yuewei, Su Haitao. Comparison of two techniques in locating tibial prosthesis during total knee arthroplasty of varus knee [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2038-2043. |
| [12] | Wu Qian, Liu Lingfeng, Li Lisong, Lu Yingjie, Zhou Liyu, Xu Wu, Huang Lixin, Jiang Dinghua. Deep vein thrombosis distribution and risk factors after total knee arthroplasty during enhanced recovery after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2044-2050. |
| [13] | Wu Di, Si Lina, Wu Lizhu, Wang Jianhua, Luo Jinwei, Chang Qiankun, Lyu Yongming, Du Yuanliang. Feasibility of three-dimensional printing technology combined with computer-aided design in total knee arthroplasty for severe knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2051-2057. |
| [14] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [15] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||