Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (35): 5700-5706.doi: 10.12307/2022.939
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Chrono-moxibustion on core clock genes Clock, Bmal1 and pyroptosis in rats with rheumatoid arthritis
Yu Mingfang1, 2, Chen Bailu1, He Xinling1, Wang Aiyang1, Wu Xiao1
- 1College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 640000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Acupuncture, Luzhou T.C.M. Hospital, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-05Accepted:2022-02-11Online:2022-12-18Published:2022-05-18 -
Contact:Wu Xiao, MD, Associate chief physician, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 640000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Yu Mingfang, Master candidate, Attending physician, College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated to Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 640000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Acupuncture, Luzhou T.C.M. Hospital, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81804208 (to WX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Mingfang, Chen Bailu, He Xinling, Wang Aiyang, Wu Xiao. Effects of Chrono-moxibustion on core clock genes Clock, Bmal1 and pyroptosis in rats with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5700-5706.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
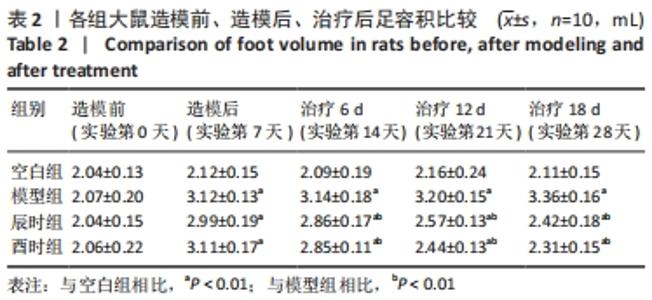
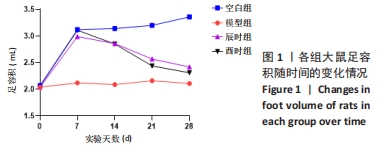
2.1 实验动物数量分析 40只SD成年大鼠随机分为4组,每组10只,实验全程未出现实验动物死亡及其他原因所致的脱落情况,故40只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 不同时辰艾灸对各组大鼠足容积的影响 各组大鼠在模型制备前其足容积大小大致相同,组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),说明模型制备前基线较为一致,有可比性。模型制备后模型组、辰时组和酉时组足容积均显著高于空白组(P < 0.01),表明成功制备类风湿关节炎模型;模型制备后艾灸组大鼠与模型组相比差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),说明模型制备后基线较为一致,有可比性。艾灸干预结束后,模型组大鼠与空白组比较足容积明显增加(P < 0.01);艾灸组大鼠足容积较模型组显著降低(P < 0.01),说明艾灸对类风湿关节炎具有治疗明显作用;酉时组相比于辰时组足容积降低程度稍降低,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2及图 1。"
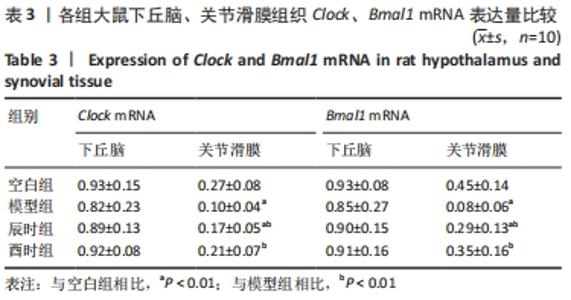
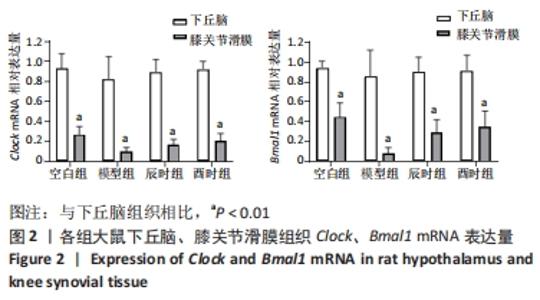
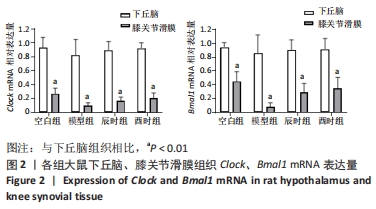
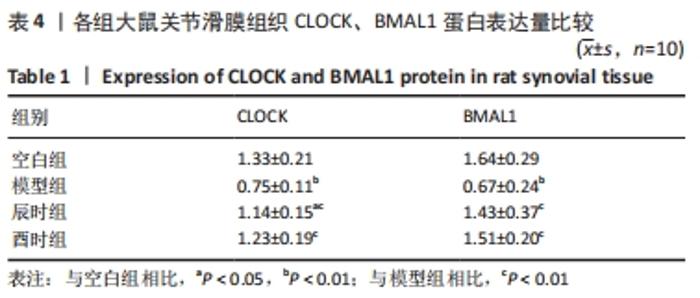
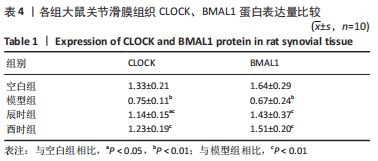
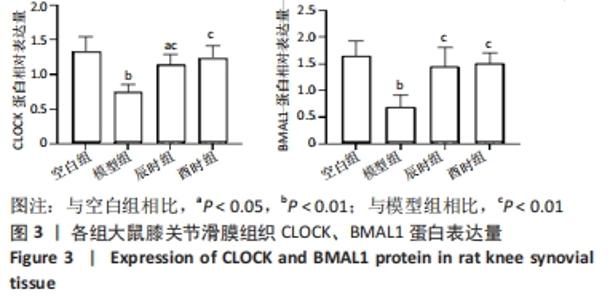
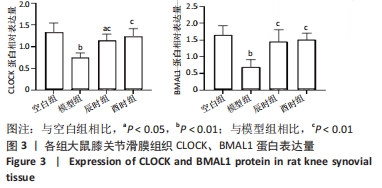
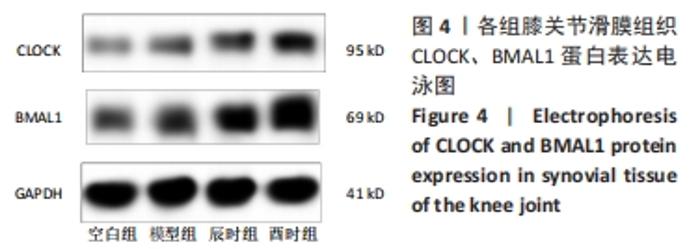
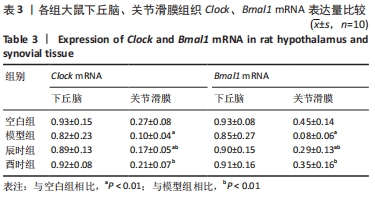
2.3 时辰艾灸对实验性类风湿关节炎大鼠下丘脑、膝关节滑膜组织Clock、Bmal1基因表达的影响 在下丘脑中,各组大鼠Clock、Bmal1 mRNA表达量均为空白组最高,2个艾灸组次之,模型组最低,但组间比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。在大鼠关节滑膜组织中,与空白组相比,模型组大鼠Clock、Bmal1 mRNA表达量均明显降低(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,辰时组和酉时组大鼠的Clock、Bmal1 mRNA表达量均显著升高(P < 0.01);与辰时组相比,酉时组Clock、Bmal1 mRNA表达量稍升高,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。下丘脑各组大鼠Clock、Bmal1 mRNA表达丰度均比膝关节滑膜明显升高(P < 0.01),见表3及图2。"

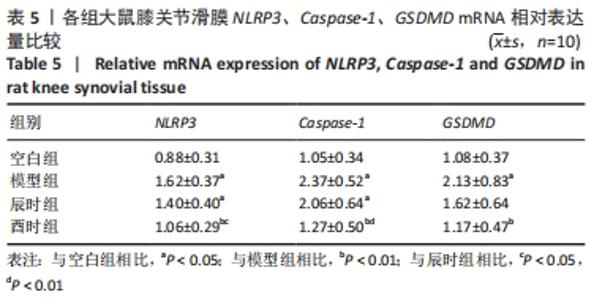
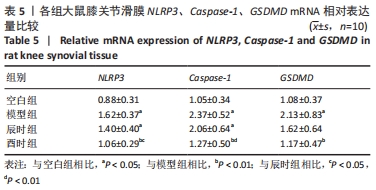
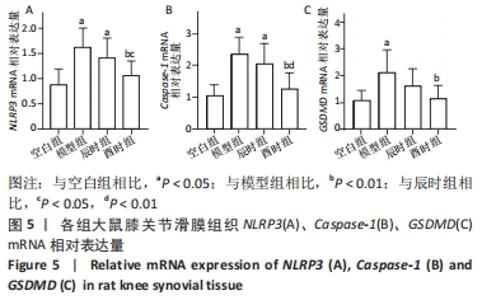
如表5、图5 A所示,在大鼠膝关节滑膜NLRP3 mRNA表达量中,模型组、辰时组较空白组显著上调(P < 0.01);酉时组与模型组相比表达明显下调(P < 0.01);辰时组与模型组相比也有所下降,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);与辰时组相比,酉时组显著下调(P < 0.05)。 如表5、图5B所示,大鼠滑膜Caspase-1 mRNA表达量中,与空白组相比,模型组、辰时组均显著上调(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,酉时组显著降低(P < 0.01);辰时组与模型组相比也有所下降,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);与辰时组相比,酉时组明显下调(P < 0.01)。 如表5、图5C所示,大鼠滑膜GSDMD mRNA表达量中,与对照组相比,模型组明显升高(P < 0.01);酉时组与模型组相比表达显著下调(P < 0.01);辰时组相较于模型组同样也有所下调,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);酉时组与辰时组相比有下调趋势,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 "

| [1] CUTOLO M. Circadian rhythms and rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2019; 86(3):327-333. [2] JAHANBAN-ESFAHLAN R, MEHRZADI S, REITER RJ, et al. Melatonin in regulation of inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: involvement of circadian clock genes. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175(16):3230-3238. [3] OHDO S, KOYANAGI S, MATSUNAGA N. Chronopharmacological strategies: Intra- and inter-individual variability of molecular clock. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(9-10):885-897. [4] WU X, REN G, ZHOU R, et al. The role of Ca(2+) in acid-sensing ion channel 1a-mediated chondrocyte pyroptosis in rat adjuvant arthritis. Lab Invest. 2019;99(4):499-513. [5] WU XY, LI KT, YANG HX, et al. Complement C1q synergizes with PTX3 in promoting NLRP3 inflammasome over-activation and pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;106:102336. [6] LI Z, GUO J, BI L. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in autoimmune diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110542. [7] RANA AK, LI Y, DANG Q, et al. Monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Circulating precursors of macrophages and osteoclasts and, their heterogeneity and plasticity role in RA pathogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;65:348-359. [8] KHALID S, YOUSAF MJ, RASHID A, et al. Gene expression of Interleukin-18 in rheumatoid arthritis patients on disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug therapy. Pak J Med Sci. 2019;35(3):802-806. [9] WU X, LIU X, JING Z, et al. Moxibustion benignantly regulates circadian rhythm of REV-ERBalpha in RA rats. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(5):1459-1468. [10] 葛冉, 孙志岭, 纪伟. 择时艾灸治疗类风湿关节炎26例临床研究[J]. 江苏中医药,2014,46(4):66-67. [11] PERRY MG, KIRWAN JR, JESSOP DS, et al. Overnight variations in cortisol, interleukin 6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and other cytokines in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(1):63-68. [12] GALBO H, KALL L. Circadian variations in clinical symptoms and concentrations of inflammatory cytokines, melatonin, and cortisol in polymyalgia rheumatica before and during prednisolone treatment: a controlled, observational, clinical experimental study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):174. [13] 张敏, 赵晨, 蒋玲, 等. 艾灸联合西药治疗肝肾亏虚型类风湿关节炎临床疗效及机制探讨[J]. 中国针灸,2021,41(5):489-492. [14] 朱艳, 张敏, 赵晨. 艾灸“足三里”“肾俞”对佐剂性关节炎大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2021,41(10):1119-1125. [15] 栗占国, 张奉春, 鲍春德. 类风湿关节炎 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010. [16] 李忠仁. 实验针灸学[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社,2003. [17] POOLE EI, MCGAVIN JJ, COCHKANOFF NL, et al. Stereotaxic surgery for implantation of guide cannulas for microinjection into the dorsomedial hypothalamus in young rats. Methods X. 2019;6:1652-1659. [18] SAG S, SAG MS, TEKEOGLU I, et al. Relationship of hematologic markers with IL-17 and IL-1 beta in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2018;31(4):703-707. [19] 吴晓, 景中坤, 陈洋, 等. 卯时、酉时艾灸对实验性RA大鼠IL-1β、IL-6血清含量的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药,2018,29(11):2783-2786. [20] 吴晓, 刘旭光, 景中坤, 等. 择时艾灸对实验性RA大鼠足肿胀度、血清TNF-α含量及其昼夜节律的影响[J]. 中国针灸,2018,38(11):1189-1194. [21] BERING T, HERTZ H, RATH MF. The Circadian Oscillator of the Cerebellum: Triiodothyronine Regulates Clock Gene Expression in Granule Cells in vitro and in the Cerebellum of Neonatal Rats in vivo. Front Physiol. 2021;12:706433. [22] HONMA S. The mammalian circadian system: a hierarchical multi-oscillator structure for generating circadian rhythm. J Physiol Sci. 2018;68(3):207-219. [23] HAND LE, DICKSON SH, FREEMONT AJ, et al. The circadian regulator Bmal1 in joint mesenchymal cells regulates both joint development and inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):5. [24] HASHIRAMOTO A, YAMANE T, TSUMIYAMA K, et al. Mammalian clock gene Cryptochrome regulates arthritis via proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 2010;184(3):1560-1565. [25] KOURI VP, OLKKONEN J, KAIVOSOJA E, et al. Circadian timekeeping is disturbed in rheumatoid arthritis at molecular level. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54049. [26] 王少贤, 李振彬. 雷公藤多苷对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠下丘脑视交叉上核Bmal1、Clock表达的调节作用[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2020,9(7):1-6. [27] WU X, LIU X, JING Z, et al. Moxibustion benignantly regulates circadian rhythm of REV-ERBalpha in RA rats. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(5):1459-1468. [28] KIM M, YOO SJ, KANG SW, et al. TNFα and IL-1β in the synovial fluid facilitate mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cell migration. Cytokine. 2017;99:91-98. [29] MATHEWS RJ, ROBINSON JI, BATTELLINO M, et al. Evidence of NLRP3-inflammasome activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA); genetic variants within the NLRP3-inflammasome complex in relation to susceptibility to RA and response to anti-TNF treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1202-1210. [30] 王帅. 时钟蛋白REV-ERBα调控NLRP3炎症小体及溃疡性结肠炎的分子机制研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学,2019. [31] POURCET B, ZECCHIN M, FERRI L, et al. Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group D Member 1 Regulates Circadian Activity of NLRP3 Inflammasome to Reduce the Severity of Fulminant Hepatitis in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(5):1449-1464. [32] OKA S, LI X, SATO F, et al. A deficiency of Dec2 triggers periodontal inflammation and pyroptosis. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(3):492-500. [33] GILLETT G, WATSON G, SAUNDERS KE, et al. Sleep and circadian rhythm actigraphy measures, mood instability and impulsivity: A systematic review. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;144:66-79. [34] 张赛. 右美托咪定对术后睡眠剥夺大鼠心肌细胞焦亡的作用及其机制研究[D]. 张家口: 河北北方学院,2021. [35] URSINI F, NATY S, BRUNO C, et al. Old But Good: Modified-Release Prednisone in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2017;12(2):124-128. [36] TO H, YOSHIMATSU H, TOMONARI M, et al. Methotrexate chronotherapy is effective against rheumatoid arthritis. Chronobiol Int. 2011;28(3):267-274. [37] 王志强, 宫彩霞, 张晓刚, 等. 重组人Ⅱ型肿瘤坏死因子受体-抗体融合蛋白优化治疗活动期类风湿关节炎的研究[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2020,40(3): 301-304. [38] 洪昆达, 万甜, 张丽瑛. 子午流注灸法治疗不同证型类风湿性关节炎的临床研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2017,32(11):5233-5236. [39] 李雨彦, 刘良. 首届国医大师治疗痹证学术思想与临床经验撷要[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2015,10(10):1451-1455. [40] 张阔, 徐媛, 丁沙沙, 等. 基于文献研究针刺治疗类风湿关节炎选穴规律[J]. 中国针灸,2017,37(2):221-224. [41] 周丹萍, 江星, 纪伟, 等. 灸法治疗类风湿关节炎的文献计量学分析[J]. 北京中医药,2015,34(6):434-437. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | FAN Yaru, LI Ruixin , LI Fengji, LUO Rui, LIU Hao, YAN Yingbin. Characterization and photothermal effect of indocyanine green encapsulated poly lactic acid-co-glycolic acid microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [3] | Bao Xianguo, Gao Zengxin, Wu Zhanpo, Chen Youmin, Cheng Qinghua, Lu Haitao, Guo Changzheng, Xu Shuai. Correlation between lumbar posterior muscle and local kyphosis in patients with degenerative thoracolumbar kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1418-1423. |
| [4] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [5] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [6] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [7] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [8] | Gu Zhengqiu, Xu Fei, Wei Jia, Zou Yongdi, Wang Xiaolu, Li Yongming. Exploratory study on talk test as a measure of intensity in blood flow restriction training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1154-1159. |
| [9] | Kong Yamin, Yan Juntao, Ma Bingxiang, Li Huawei. Massage vibration intervenes with MyoD expression and proliferation and differentiation of muscle satellite cells in rats with sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1160-1166. |
| [10] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [11] | Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209. |
| [12] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [13] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [14] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [15] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||