[1] NG JWG, MYINT Y, ALI FM. Management of multiligament knee injuries. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(3):145-155.
[2] FANELLI GC. Multiple Ligament Injured Knee: Initial Assessment and Treatment. Clin Sports Med. 2019;38(2):193-198.
[3] MOSQUERA MF, JARAMILLO A, GIL R, et al. Controversies in acute multiligamentary knee injuries (MLKI). J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):56.
[4] STRAUSS MJ, VARATOJO R, BOUTEFNOUCHET T, et al. The use of allograft tissue in posterior cruciate, collateral and multi-ligament knee reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(6): 1791-1809.
[5] ROSTEIUS T, JETTKANT B, RAUSCH V, et al. Anatomical repair and ligament bracing of Schenck III and IV knee joint dislocations leads to acceptable subjective and kinematic outcomes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06501-2.
[6] IMBERGAMO C, BRZEZINSKI A, SMITH T, et al. Bilateral Knee Dislocations Treated with Acute, Single-Stage Multiligament Reconstructions. Case Rep Orthop. 2021;2021:9985788.
[7] BERNHOFF K, MICHAËLSSON K, BJÖRCK M. Incidence and Outcome of Popliteal Artery Injury Associated with Knee Dislocations, Ligamentous Injuries, and Close to Knee Fractures: A Nationwide Population Based Cohort Study. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021;61(2):297-304.
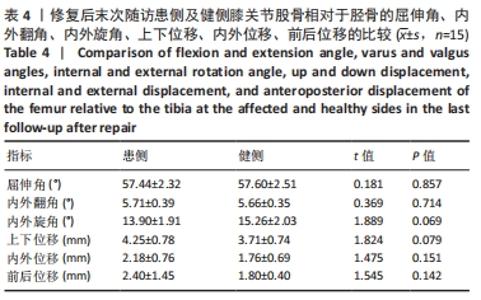
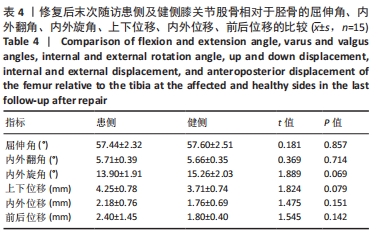
[8] 孙正宇,张承昊,唐新,等.一期修复重建膝关节脱位多发韧带损伤的疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(6):690-694.
[9] 黄华强,云翥,蒋海,等.急性膝关节后外侧旋转脱位修复治疗后的步态分析及其指导意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(31): 5007-5013.
[10] ITO N, CAPIN JJ, ARHOS EK, et al. Sex and mechanism of injury influence knee joint loading symmetry during gait 6 months after ACLR. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(5):1123-1132.
[11] YAN W, XU X, XU Q, et al. In vivo gait kinematics of the knee after anatomical and non-anatomical single-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction-a prospective study. Ann Transl Med. 2019; 7(24):799.
[12] LEVY BA, DAJANI KA, WHELAN DB, et al. Decision making in the multiligament-injured knee: an evidence-based systematic review. Arthroscopy. 2009;25(4):430-438.
[13] TRASOLINI NA, LINDSAY A, GIPSMAN A, et al. The Biomechanics of Multiligament Knee Injuries: From Trauma to Treatment. Clin Sports Med. 2019;38(2):215-234.
[14] CHAHLA J, MOATSHE G, DEAN CS, et al. Posterolateral Corner of the Knee: Current Concepts. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2016;4(2):97-103.
[15] HUGHES JD, LYNCH AD, SMITH CN, et al. External fixation increases complications following surgical treatment of multiple ligament knee injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06508-9.
[16] JAMES EW, WOLFE I, MARX RG. Results of Treatment of the Multiple Ligament Injured (Dislocated) Knee. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2020; 28(3):116-119.
[17] SCHECK J, CHAKRABORTY A, ZIMMERMANN G. Arthroscopic suture bracing of posterior cruciate ligament in a multiple ligament knee injury - A technical report. Trauma Case Rep. 2020;25:100279.
[18] TARUN G, PAUL S, BANERJEE S, et al. Outcomes of one-stage reconstruction for chronic multiligament injuries of knee. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2021;33(1):3.
[19] HEITMANN M, AKOTO R, KRAUSE M, et al. Management of acute knee dislocations: anatomic repair and ligament bracing as a new treatment option-results of a multicentre study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(8):2710-2718.
[20] ROBBINS SM, COSSETTE-LEVASSEUR M, KIKUCHI K, et al. Neuromuscular Activation Differences During Gait in Patients With Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and Healthy Adults. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(11):1653-1662.
[21] 王文锦,田斐,李柠薇,等.新型膝关节运动分析系统的研制及临床应用[J].中华关节外科杂志,2020,14(1):78-84.
[22] HUTCHISON RE, LUCAS EM, MARRO J, et al. The effects of simulated knee arthrodesis on gait kinematics and kinetics. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019;233(7):723-734.
[23] KAUR M, RIBEIRO DC, THEIS JC, et al. Movement Patterns of the Knee During Gait Following ACL Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2016;46(12):1869-1895.
[24] BĄCZKOWICZ D, SKIBA G, CZERNER M, et al. Gait and functional status analysis before and after total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(5): 888-896.
[25] SUN M, ZHANG Y, PENG Y, et al. Gait Analysis after Total Knee Arthroplasty Assisted by 3D-Printed Personalized Guide. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6485178.
[26] SUN M, YANG L, HE R, et al. Gait analysis after total knee arthroplasty assisted by three-dimensional printing navigation template. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(8):953-959.
[27] PELLEGRINO P, CONTI A, PAUTASSO A, et al. Gait analysis: Comparative evaluation of conventional total knee replacement and modular distal femoral megaprosthesis. Knee. 2020;27(5):1567-1576.
[28] MINE T, KAJINO M, SATO J, et al. Gait oscillation analysis during gait and stair-stepping in elder patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):21.
[29] BONNEFOY-MAZURE A, FAVRE T, PRAPLAN G, et al. Associations between gait analysis parameters and patient satisfaction one year following primary total knee arthroplasty. Gait Posture. 2020;80:44-48.
[30] HADDAS R, JU KL, BELANGER T, et al. The use of gait analysis in the assessment of patients afflicted with spinal disorders. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(8):1712-1723.
[31] SIEBERS HL, ESCHWEILER J, PINZ J, et al. The effect of a knee brace in dynamic motion-An instrumented gait analysis. PLoS One. 2020; 15(9):e0238722.
[32] MAIER MW, ASCHAUER S, WOLF SI, et al. Three dimensional gait analysis in patients with symptomatic component mal-rotation after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2019;43(6):1371-1378.
[33] MCCLELLAND JA, WEBSTER KE, FELLER JA. Gait analysis of patients following total knee replacement: a systematic review. Knee. 2007; 14(4):253-263.
[34] BÉREŠ M, SVOBODA Z, GALLO J, et al. Vliv rekonstrukce předního zkříženého vazu na kinematiku chůze [Influence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction on Gait Kinematics]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2020;87(1):17-23.
|