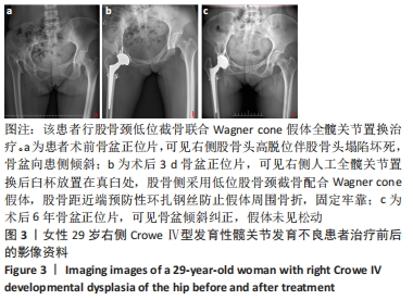
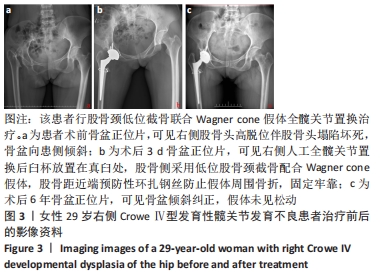
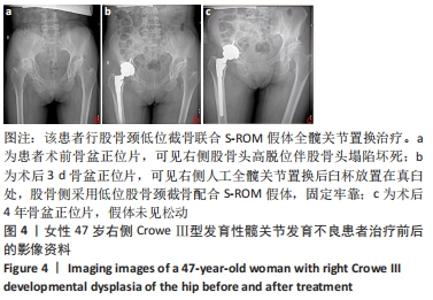
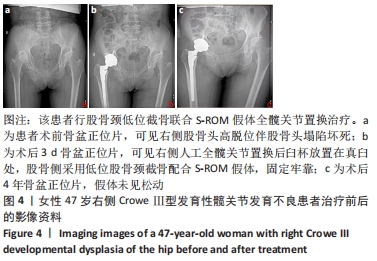
[1] CROWE J, MANI V, RANAWAT C. Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61(1):15-23.
[2] GREBER E, PELT C, GILILLAND J, et al. Challenges in Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Setting of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32:S38-S44.
[3] CAYLAK R, ORS C, TOGRUL E. Minimum 10-Year Results of Cementless Ceramic-On-Ceramic Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed With Transverse Subtrochanteric Osteotomy in Crowe Type IV Hips. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(10):3519-3526.
[4] ZENG W, LIU J, WANG F, et al. Total hip arthroplasty for patients with Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia of the hip: Ten years results. Int J Surg. 2017;42:17-21.
[5] WANG D, LI L, WANG H, et al. Long-Term Results of Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty With Subtrochanteric Shortening Osteotomy in Crowe Type IV Developmental Dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(4):1211-1219.
[6] SUN C, ZHANG Y, LI L, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Transverse Subtrochanteric Shortening Osteotomy and Modular Stem in Crowe IV Developmental Dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(2):630-635.
[7] KARAISMAILOGLU B, KARAISMAILOGLU T. Comparison of Trochanteric Slide and Subtrochanteric Shortening Osteotomy in the Treatment of Severe Hip Dysplasia: Mid-Term Clinical Outcomes of Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(9): 2529-2536.
[8] NAGOYA S, KAYA M, SASAKI M, et al. Cementless total hip replacement with subtrochanteric femoral shortening for severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(9):1142-1147.
[9] WU X, LI S, LOU L, et al. The techniques of soft tissue release and true socket reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop, 2012;36(9):1795-801.
[10] LI H, YUAN Y, XU J, et al. Direct Leverage for Reducing the Femoral Head in Total Hip Arthroplasty Without Femoral Shortening Osteotomy for Crowe Type 3 to 4 Dysplasia of the Hip. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(3):794-799.
[11] 郭江,张忠杰,夏波,等.紧贴小转子截骨结合Wagner coneg股骨假体治疗成人Crowe Ⅳ型先天性髋关节发育不良[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(4):435-448.
[12] 李慧武,朱振安,毛远青,等.非截骨全髋关节置换术治疗单侧CroweⅣ型髋关节发育不良[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(12):1205-1211.
[13] HARRIS W. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.
[14] BROOKER AF, BOWERMAN JW, ROBINSON RA, et al. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(8):1629-1632.
[15] GRUEN TA, MCNEICE GM, AMSTUTZ HC. “Modes of failure” of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; (141):17-27.
[16] KUSANO T, SEKI T, HIGUCHI Y, et al. Preoperative Canal Bone Ratio is Related to High-Degree Stress Shielding: A Minimum 5-Year Follow-Up Study of a Proximally Hydroxyapatite-Coated Straight Tapered Titanium Femoral Component. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(6):1764-1769.
[17] BAO N, MENG J, ZHOU L, et al. Lesser trochanteric osteotomy in total hip arthroplasty for treating CROWE type IV developmental dysplasia of hip. Int Orthop. 2013;37(3):385-390.
[18] MU W, YANG D, XU B, et al. Midterm Outcome of Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty in Crowe IV-Hartofilakidis Type III Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(3):668-675.
[19] OLLIVIER M, ABDEL M, KRYCH A, et al. Long-Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Shortening Subtrochanteric Osteotomy in Crowe IV Developmental Dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(8):1756-1760.
[20] SOFU H, KOCKARA N, GURSU S, et al. Transverse Subtrochanteric Shortening Osteotomy During Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty in Crowe Type-III or IV Developmental Dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(6):1019-1023.
[21] YAN F, CHEN G, YANG L, et al. A reduction technique of arthroplasty without subtrochanteric femoral shortening osteotomy for the treatment of developmental high dislocation of hip: a case series of 28 hips. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(12):2289-2293.
[22] LAI K, SHEN W, HUANG L, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty and limb-length equalization in patients with unilateral Crowe type-IV hip dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(2):339-345.
[23] LI H, XU J, QU X, et al. Comparison of Total Hip Arthroplasty With and Without Femoral Shortening Osteotomy for Unilateral Mild to Moderate High Hip Dislocation. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(3):849-856.
|