Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (21): 3357-3362.doi: 10.12307/2022.644
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different material attributes are assigned to the vertebral body for statics analysis
Guan Tianmin, Chen Xiangyu, Zhu Ye, Ren Dong
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian 116028, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-05-26Accepted:2021-07-24Online:2022-07-28Published:2022-01-28 -
Contact:Zhu Ye, PhD, Lecturer, School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian 116028, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Guan Tianmin, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian 116028, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guan Tianmin, Chen Xiangyu, Zhu Ye, Ren Dong. Different material attributes are assigned to the vertebral body for statics analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3357-3362.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
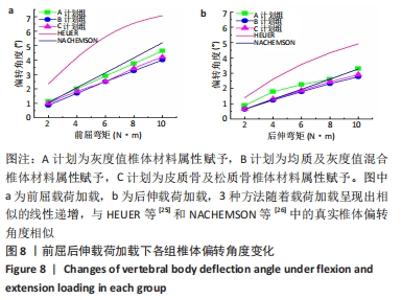
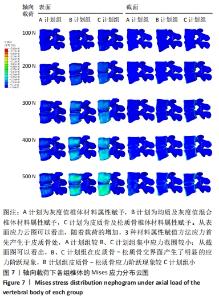
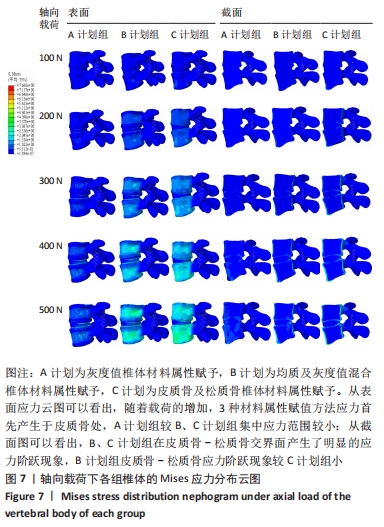
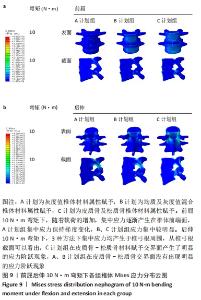
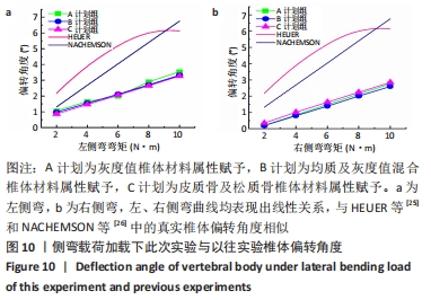
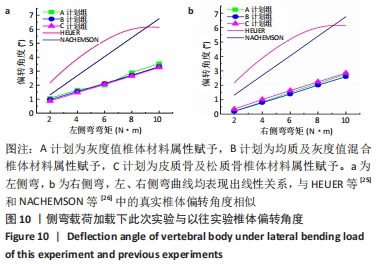
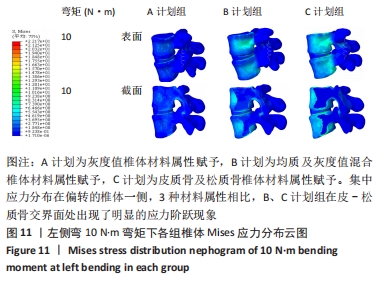
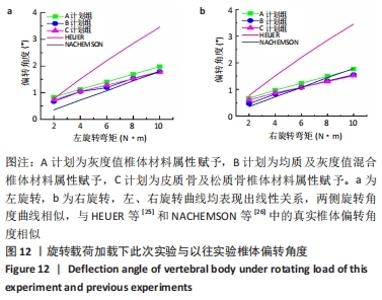
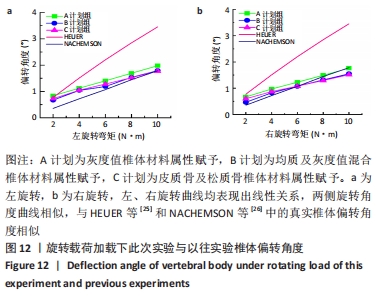
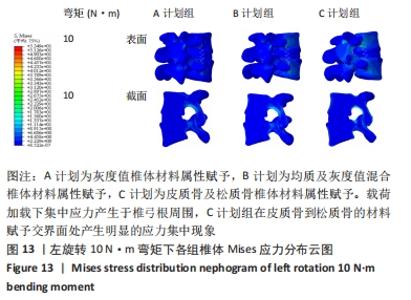
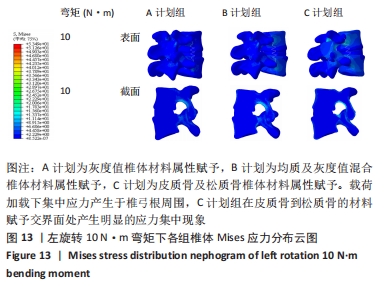
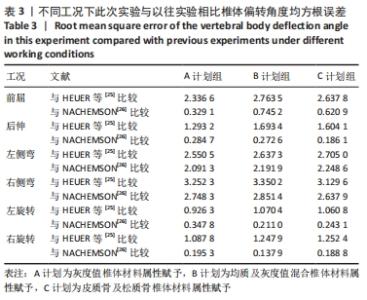
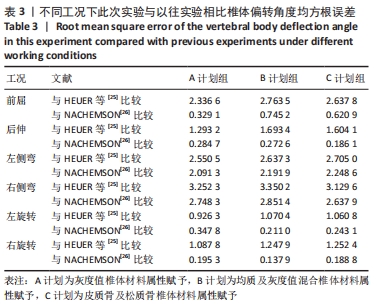
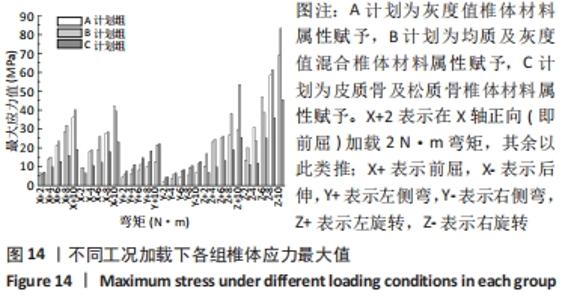
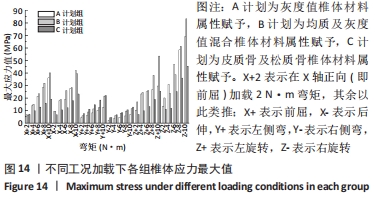
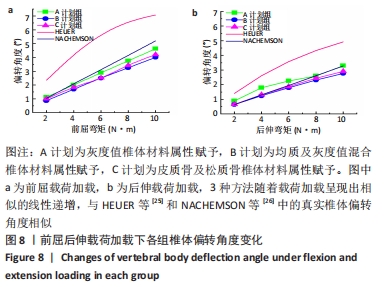
2.2 不同工况下各组椎体应力应变情况 2.2.1 前屈、后伸工况应力应变情况 前屈弯矩加载偏转角度变化如图8a所示,椎体Mises应力分布云图如图9a所示。从偏转角度曲线中可以看出,随着弯矩的增加,3种方法偏转角度呈线性增加,A计划组的偏转角度较 C、B计划组明显大一些,HEUER等[25]、NACHEMSON等[26]为相同工况下人体实验数据。Mises应力云图显示随着载荷的增加,集中应力逐渐产生在椎体前端面,A计划组集中应力保持梯度变化,B、C计划组应力集中较明显。 后伸弯矩加载偏转角度如图8b所示,Mises应力分布云图如图9b所示。3种方法下集中应力均产生于椎弓根周围,C计划组集中应力最明显,B、A计划组其次,符合椎体力学特性;从椎弓根截面可以看出,C计划组在皮质骨-松质骨材料赋予交界面产生了明显的应力阶跃现象,A、B计划组由于椎弓根周围采用梯度赋予材料属性,在皮质骨-松质骨交界面没有出现明显的应力阶跃现象。"
| [1] 孙枫原,李宗远,何希,等.有限元分析在脊柱侧凸生物力学研究中的应用及进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5221-5226. [2] LIANG L, LIU ML, MARTIN C, et al. A deep learning approach to estimate stress distribution: a fast and accurate surrogate of finite-element analysis. J R Soc Interface. 2018;15(138):20170844. [3] 赵鹏飞,陈玲,门玉涛.有限元分析肌肉力对腰椎内固定系统的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3654-3658. [4] 刘慧,沈国权,张喜林,等.肌肉加载下腰椎间盘突出的有限元研究[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(5):493-499. [5] CHOI HW, KIM YE. Effect of lumbar fasciae on the stability of the lower lumbar spine. Comput Method Biomec. 2017;20(13):1431-1437. [6] ANDERSSON G, SCHULTZ AB. Effects of fluid injection on mechanical properties of intervertebral discs. J Biomech. 1979;12(6):453-458. [7] TENCER AF. Some static mechanical properties of the lumbar intervertebral joint, intact and injured. J Biomech Eng. 1982;104(3):193-201. [8] 文毅,苏峰,刘肃,等.L4-5椎体有限元模型建立及退变椎间盘力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(8):1222-1227. [9] 薛志鹏,李泰贤,李龚,等.基于CT灰度值赋值的股骨头坏死有限元模型对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(3):395-400. [10] 罗林聪,马立敏,林泽,等.基于AnyBody骨骼肌肉多体动力学分析的有限元仿真[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(3):237-242+250. [11] 张聪,赵岩,杜小宇,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸腰主弯患者腰椎-骨盆的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1155-1161. [12] 成博,赵文,罗伟,等.基于CT三维重建模型在数字化骨科的应用研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2017,39(2):89-94. [13] RASMUSSEN J, TRHOLM S, ZEE MD. Computational analysis of the influence of seat pan inclination and friction on muscle activity and spinal joint forces. Nt J Ind Ergonom. 2009;39(1):52-57. [14] 李丹.基于腰椎多层螺旋CT扫描三维形态学分析的腰椎材料、形态及结构属性变化与骨折相关性的FEA研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2011. [15] MORGAN EF, BAYRAKTAR HH, KEAVENY TM. Trabecular bone modulus-density relationships depend on anatomic site. J Biomech. 2003;36(7):897-904. [16] RHO JY, KUHN-SPEARING L, ZIOUPOS P. Mechanical properties and the hierarchical structure of bone. Med Eng Phys. 1998;20(2):92-102. [17] 聂文忠.脊柱胸腰部的生物力学建模与应用研究[D].上海:上海交通大学, 2009. [18] 苏晋.腰椎有限元模型的建立与生物力学分析[D].大连:大连医科大学,2010. [19] 贾少薇,张顺心,范顺成,等.脊柱侧凸腰骶椎结构的有限元分析及其变形趋势[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(3):235-241. [20] GOEL VK, KONG W, HAN JS, et al. A Combined Finite Element and Optimization Investigation of Lumbar Spine Mechanics With and Without Muscles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(11):1531-1541. [21] ROHLMANN A, BOUSTANI HN, BERGMANN G, et al. Effect of a pedicle-screw-based motion preservation system on lumbar spine biomechanics: A probabilistic finite element study with subsequent sensitivity analysis. J Biomech. 2010;43(15): 2963-2969. [22] 国家技术监督局.成年人人体质心.中华人民共和国国家标准GB/T 17245-1998.1998. [23] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14(11):1256-1260. [24] BROWN T, HANSEN RJ, YORRA AJ. Some mechanical tests on the lumbosacral spine with particular reference to the intervertebral discs;a preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39(5):1135-1164. [25] HEUER F, SCHMIDT H, KLEZL Z, et al. Stepwise reduction of functional spinal structures increase range of motion and change lordosis angle. J Biomech. 2007; 40(2):271-280. [26] NACHEMSON AL, SCHULTZ AB, BERKSON MH. Mechanical properties of human lumbar spine motion segments. Influence of age, sex, disc level, and degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1979;4(1):1-8. [27] CHEN YC, TU YK, ZHUANG JY, et al. Evaluation of the parameters affecting bone temperature during drilling using a three-dimensional dynamic elastoplastic finite element model. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017;55(11):1949-1957. [28] 朱康平,祝建雯,曲恒磊.国外生物医用钛合金的发展现状[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2012,41(11):2058-2063. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Lü Qianyi, Chen Xinyi, Zheng Huie, He Haolong, Li Qilong, Chen Chutao, Tian Haomei. Stress and displacement of normal lumbar vertebra and posterior structure with different elbow pressing methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [4] | Bai Zixing, Cao Xuhan, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Chen Si, Wen Jianmin, Lin Xinxiao, Sun Weidong. Construction and biomechanical analysis of ankle joint finite element model in gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1362-1366. |
| [5] | Liu Feng, Feng Yi. Finite element analysis of different Kirschner wire tension bands on transverse patella fractures during gait cycle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [6] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [7] | Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [8] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [9] | Zheng Yongze, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Chen Xinmin, Li Musheng, Li Pengfei, Lin Ziling. Extended finite element modeling analysis of femoral neck fracture based on ABAQUS software [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 853-857. |
| [10] | Liu Yuhang, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Qu Xingyue, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Shaojie. Establishment and validation of finite element model of lower cervical spine in 6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 870-874. |
| [11] | Song Jiawei, Yang Yongdong, Yu Xing, Yang Jizhou, Wang Fengxian, Qu Yi, Bi Lianyong. Mid-term effect of Isobar EVO non-fusion dynamic fixation in the treatment of adjacent segment disease after lumbar fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 908-913. |
| [12] | Duan Chao, Shang Xiaoqiang, Duan Xianglin, Yang Ping, Tao Shengxiang. Stability of patellar claw versus loop plate combined with patellar claw for the treatment of comminuted fractures of the lower pole of the patella [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 934-937. |
| [13] | Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 567-572. |
| [14] | Li Yanting, Chen Jian, Liu Menglan, Ren Manman, Zhong Weihong, Chen Changxing. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of Daogaijinbei manipulation on lumbar intervertebral disc biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 340-343. |
| [15] | Chen Jinmin, Chen Suisheng, Ding Jing, Xia Baoquan, Luo Xiaojia, Lu Chenghai. Stability of balloon dilation with injectable calcium sulfate cement for tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 414-418. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||