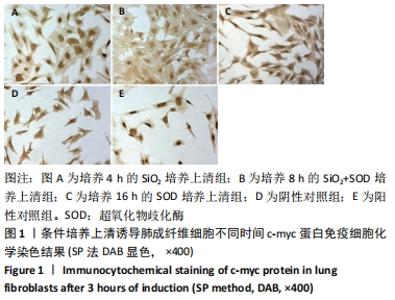
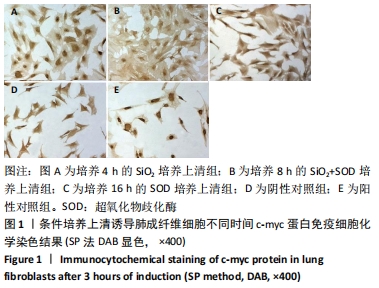
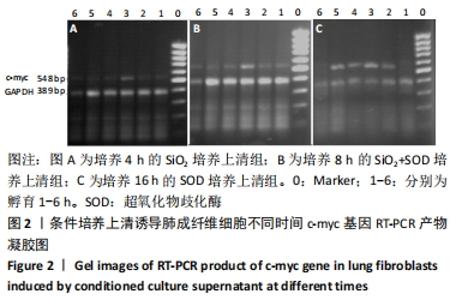
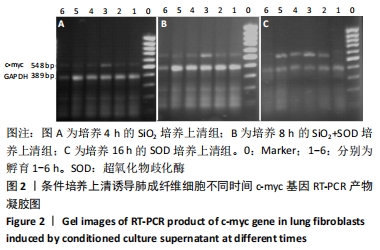
[1] YANG X, WANG J, ZHOU Z, et al. Silica-induced initiation of circular ZC3H4 RNA/ZC3H4 pathway promotes the pulmonary macrophage activation. FASEB J. 2018;32(6):3264-3277.
[2] LI C, LU Y, DU S, et al. Dioscin Exerts Protective Effects Against Crystalline Silica-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Theranostics. 2017;7(17):4255-4275.
[3] CAO Z, XIAO Q, DAI X, et al. circHIPK2-mediated σ-1R promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pulmonary fibroblasts exposed to silica. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(12):3212.
[4] MOSSMAN BT, CHURG A. Mechanisms in the pathogenesis of asbestosis and silicosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.1998;157(5):1666-1680.
[5] BARSYTE-LOVEJOY D, LAU SK, BOUTROS PC, et al. The c-Myc oncogene directly induces the H19 noncoding RNA by allele-specific binding to potentiate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2006;66(10):5330-5337.
[6] KUBOTA S, TOKUNAGA K, UMEZU T, et at. Lineage-specific RUNX2 super-enhancer activates MYC and promotes the development of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1653.
[7] XU L, HAO H, HAO Y, et al. Aberrant MFN2 transcription facilitates homocysteine-induced VSMCs proliferation via the increased binding of c-Myc to DNMT1 in atherosclerosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(7): 4611-4626.
[8] CAO L, XU C, XIANG G, et al. AR-PDEF pathway promotes tumour proliferation and upregulates MYC-mediated gene transcription by promoting MAD1 degradation in ER-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):136.
[9] 李雪, 伍艳平, 周铁军,等.宫颈鳞癌组织中miRNA-451、c-myc、E-cadherin、Vimentin的表达变化及其意义[J]. 山东医药,2020, 60(36):50-53.
[10] 熊敏涵, 秦恩杰, 袁炜,等. C-myc过表达促进宫颈上皮内瘤变的Meta分析[J].中国医药生物技术,2020,15(6):89-93.
[11] 陈玉惠, 周伟光, 高晶,等.牛外周血单核巨噬细胞的分离、培养与鉴定[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学,2013,34(5):21-22.
[12] 尹红玲. 肥大细胞与肺成纤维细胞共育的形态学观察[J]. 解剖学报, 1998,29(1):81-84.
[13] 陈非, 邓鸿业, 龙振洲. 肺泡巨噬细胞因子与肺纤维母细胞[J]. 国外医学.免疫学分册,1991,14(2):82-85.
[14] BARLUCCHI L, LERI A, DOSTAL DE, et al. Canine ventricular myocytes possess a renin-anigiotensin system that is upregulated with heart failure. Circ Res. 2001;88(3):298-304.
[15] 卢圣栋. 现代分子生物学实验技术[M]. 2版.北京: 中国协和医科大学出版社,1999:458-481.
[16] HOU J, SHI J, CHEN L, et al. M2 macrophages promote myofibroblast differentiation of LR-MSCs and are associated with pulmonary fibrogenesis. BioMed Central. 2018;16(1):89.
[17] 张元元, 薄存香, 张放. 肺泡巨噬细胞在矽肺发病机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国职业医学,2020,47(1):110-113.
[18] ACQUAVIVA C, FERRAVA P, BOSSIS G, et al. Degradation of celluar and viral Fos proteins. Biochimie. 2001;83(3-4):357-362.
[19] 孙镜洁, 肖敏, 周志祥. 锰超氧化物歧化酶(MnSOD)表达与活性调控及其与肿瘤的关系[J]. 生理科学进展,2019,50(2):117-121.
[20] LIU J, FENG W, LIU M, et al. Stomach-specific c-Myc overexpression drives gastric adenoma in mice via AKT/mTOR signaling.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Nov 19. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.
|