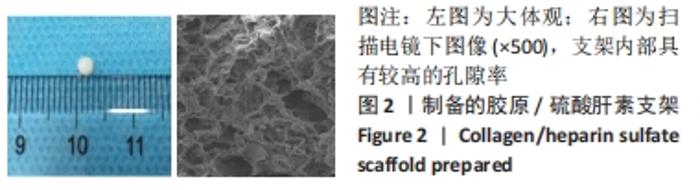
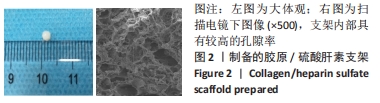
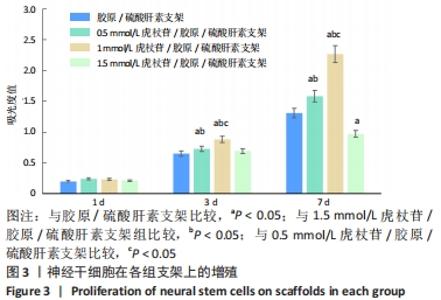
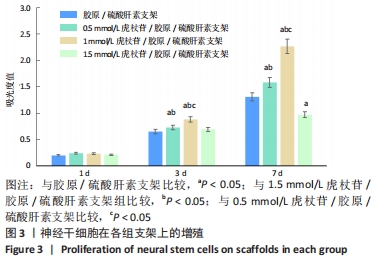
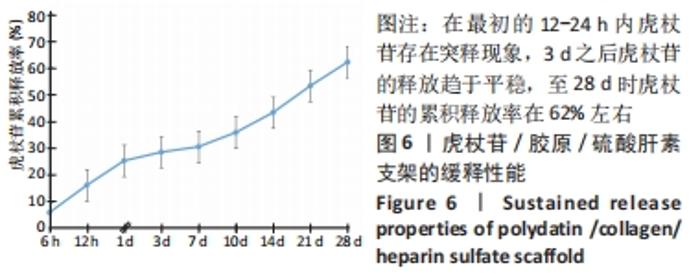
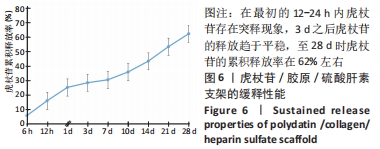
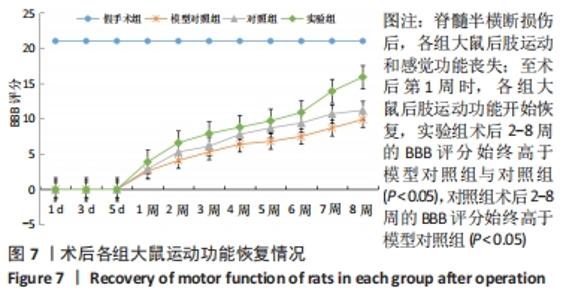
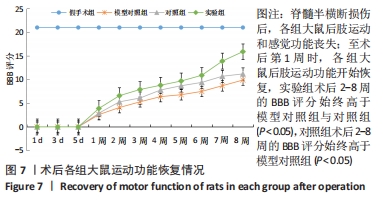
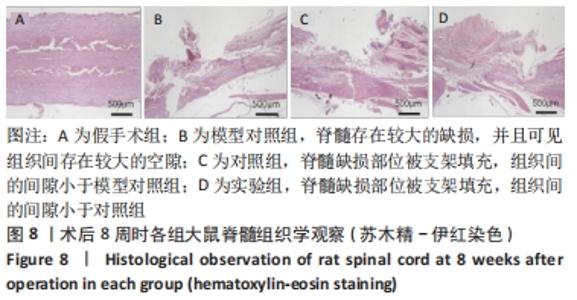
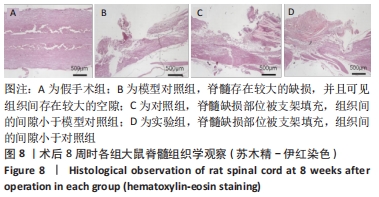
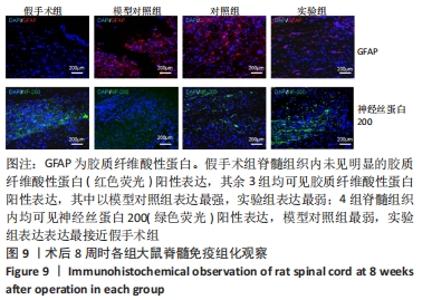
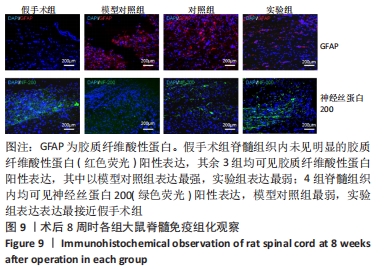
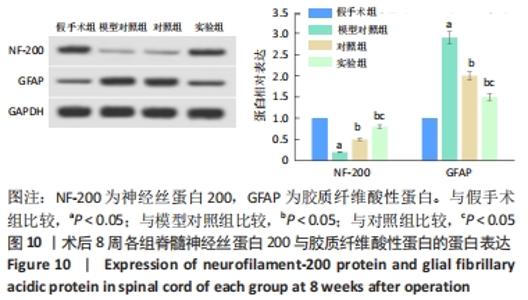
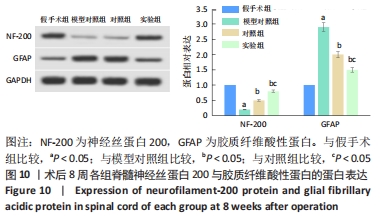
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (28): 4500-4506.doi: 10.12307/2022.305
Previous Articles Next Articles
Polydatin loaded collagen/heparin sulfate scaffold in the treatment of spinal cord injury in rats
Liu Kang1, Wang Yongping2, Zuo Kebin1, Yang Haitao1, Jia Bin1
- 1First Department of Orthopedics, Qingyang People’s Hospital, Qingyang 745000, Gansu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2021-02-25Accepted:2021-03-24Online:2022-10-08Published:2022-03-21 -
About author:Liu Kang, Associate chief physician, First Department of Orthopedics, Qingyang People’s Hospital, Qingyang 745000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, No. 20JR5RA369 (to WYP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Kang, Wang Yongping, Zuo Kebin, Yang Haitao, Jia Bin. Polydatin loaded collagen/heparin sulfate scaffold in the treatment of spinal cord injury in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4500-4506.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] ECKERT MJ, MARTIN MJ. Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury. Surg Clin North Am. 2017;97(5):1031-1045. [2] FAN B, WEI Z, YAO X, et al. Microenvironment Imbalance of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):853-866. [3] KARSY M, HAWRYLUK G. Modern Medical Management of Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(9):65. [4] VENKATESH K, GHOSH SK, MULLICK M, et al. Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, treatment strategies, associated challenges, and future implications. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;377(2):125-151. [5] PENG Y, XU J, ZENG Y, et al. Polydatin attenuates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice: Role of reverse cholesterol transport. Phytomedicine. 2019;62:152935. [6] AHMAD P, ALVI SS, IQBAL D, et al. Insights into pharmacological mechanisms of polydatin in targeting risk factors-mediated atherosclerosis. Life Sci. 2020;254:117756. [7] PARK B, JO K, LEE TG, et al. Polydatin Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome in Dry Eye Disease by Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting the NF-kappaB Pathway. Nutrients. 2019;11(11):2792. [8] 毕静,白晓雪,王超.虎杖苷通过激活Nrf2/HO-1信号抑制氧化应激诱导的心肌细胞损伤[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(2):407-409. [9] LIU LT, GUO G, WU M, et al. The progress of the research on cardio-vascular effects and acting mechanism of polydatin. Chin J Integr Med. 2012;18(9):714-719. [10] ZHAO X, YANG Y, YU H, et al. Polydatin inhibits ZEB1-invoked epithelial-mesenchymal transition in fructose-induced liver fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(22):13208-13222. [11] ZHAO XJ, YU HW, YANG YZ, et al. Polydatin prevents fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition through increasing miR-200a to regulate Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Redox Biol. 2018;18:124-137. [12] TANG J, LI Y, WANG J, et al. Polydatin suppresses the development of lung inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting activation of the NACHT domain-, leucine-rich repeat-, and pyd-containing protein 3 inflammasome and the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway after Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10137-10144. [13] FU Y, YAN M, XIE C, et al. Polydatin relieves paraquat-induced human MRC-5 fibroblast injury through inhibiting the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(12):765. [14] HUANG B, LIU J, MENG T, et al. Polydatin Prevents Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Parkinson’s Disease via Regulation of the AKT/GSK3beta-Nrf2/NF-kappaB Signaling Axis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2527. [15] SHAH FA, KURY LA, LI T, et al.Polydatin Attenuates Neuronal Loss via Reducing Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rat MCAO Models. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:663. [16] LV R, DU L, LIU X, et al. Polydatin alleviates traumatic spinal cord injury by reducing microglial inflammation via regulation of iNOS and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;70:28-36. [17] 陈露露,祁佐良.虎杖苷对丙酮醛诱导施万细胞损伤的干预作用[J].山东医药,2020,60(32):1-4. [18] 曹宗锐,郑博,钟琳,等.胶原/硫酸肝素支架联合神经干细胞促进脊髓损伤后运动功能的恢复[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(34): 5454-5461. [19] 陈丹莹,张立新.超短波对脊髓损伤后内源性神经干细胞存活和分化的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(4):390-397. [20] ORR MB, GENSEL JC. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):541-553. [21] BRADBURY EJ, BURNSIDE ER. Moving beyond the glial scar for spinal cord repair. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3879. [22] NOCERA AD, COMÍN R, SALVATIERRA NA, et al. Development of 3D printed fibrillar collagen scaffold for tissue engineering. Biomed Microdevices. 2018;20(2):26. [23] BAM P, BHATTA A, KRISHNAMOORTHY G. Design of biostable scaffold based on collagen crosslinked by dialdehyde chitosan with presence of gallic acid. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;130:836-844. [24] 温玉莹,钟燕南,梁佳欣,等.红景天苷-胶原蛋白海绵支架的构建及其对大鼠皮肤创伤的修复作用[J].广西医学,2020,42(13): 1669-1673. [25] 陈明祥,陈金联,陆金来,等.N-去硫酸肝素对胃癌碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因表达和血管形成的影响[J].中华医学遗传学杂志, 2008,2(1):78-81. [26] 刘秋庭,胡丹,涂鄂文,等.虎杖苷对脑缺血再灌注大鼠海马凋亡相关蛋白表达的影响[J].国际中医中药杂志,2017,39(3):230-233. [27] GAO Y, CHEN T, LEI X, et al. Neuroprotective effects of polydatin against mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in the rat cerebral cortex following ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(6):5481-5488. [28] 阮玲娟,崔戈,顾旭东,等.虎杖苷联合生长因子诱导人脐带间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化的研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2015, 30(1):284-287. [29] 詹吉恒,栾继耀,罗丹,等.虎杖苷促进骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化治疗脊髓损伤机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(5): 2628-2633. [30] ZHAN J, LI X, LUO D, et al. Polydatin promotes the neuronal differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of Nrf2 signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):5317-5329. [31] MOLINA-GONZALEZ I, MIRON VE. Astrocytes in myelination and remyelination. Neurosci Lett. 2019;713:134532. [32] OKADA S, HARA M, KOBAYAKAWA K, et al. Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res. 2018;126:39-43. [33] SONG HH, SONG TC, YANG T, et al. High mobility group box 1 mediates inflammatory response of astrocytes via cyclooxygenase 2/prostaglandin E2 signaling following spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(9):1848-1855. [34] KUHN S, GRITTI L, CROOKS D, et al. Oligodendrocytes in Development, Myelin Generation and Beyond.Cells. 2019;8(11):1424. [35] PAJOOHESH-GANJI A, MILLER RH. Targeted Oligodendrocyte Apoptosis in Optic Nerve Leads to Persistent Demyelination. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(3):580-590. [36] HUANG H, JIANG J, ZENG C, et al. Transplanted adipose-derived stem cells promote the expression of deleted in colorectal cancer (DCC) and neurofilament-200 (NF-200) in peri-infarct cortex of rats. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;35(5):399-404. [37] WANG J, LI H, CHEN L, et al. mRNA Profiling for miR-124-mediated Repair in Spinal Cord Injury. Neuroscience. 2020;438:158-168. [38] ANDERSON J, PATEL M, FORENZO D, et al. A novel mouse model for the study of endogenous neural stem and progenitor cells after traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2020;325:113119. [39] DIXON KJ, THEUS MH, NELERSA CM, et al. Endogenous neural stem/progenitor cells stabilize the cortical microenvironment after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2015;32(11):753-764. [40] NIIMI Y, LEVISON SW. Pediatric brain repair from endogenous neural stem cells of the subventricular zone. Pediatr Res. 2018;83(1-2):385-396. |
| [1] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1286-1292. |
| [2] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [3] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [4] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [5] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [6] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [7] | Wang Ruanbin, Cheng Liqian, Chen Kai. Application and value of polymer materials in three-dimensional printing biological bones and scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 610-616. |
| [8] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [9] | Tan Guozhong, Tu Xinran, Guo Liyang, Zhong Jialin, Zhang Yang, Jiang Qianzhou. Biosafety evaluation of three-dimensional printed gelatin/sodium alginate/58S bioactive glass scaffolds for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 521-527. |
| [10] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [11] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [12] | Lu Yunan, Zhang Xinzhao, Lin Binbin, Xu Gan, Chen Jingdi, Chen Shunyou. Naringin-chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite scaffold in repair of rat skull defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4441-4445. |
| [13] | Wu Li, Huang Wei, Li Xuetao, Li Panpan, Zhang Kaihang, Shen Zhiyuan. Analysis of adhesion and permeability of bone scaffold with Voronoi architecture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4472-4476. |
| [14] | Liu Ming, Wang Kai. Chitosan/alginate composite scaffold combined with hawthorn leaf flavonoids for spinal cord injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4466-4471. |
| [15] | Zhang Jiaying, Suo Hairui, Xu Mingen, Wang Ling. 3D printed collagen/chitosan scaffolds crosslinked by genipin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4477-4482. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||