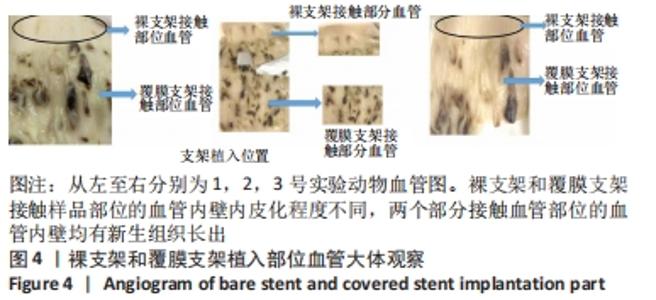
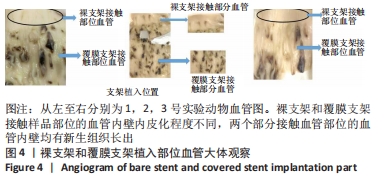
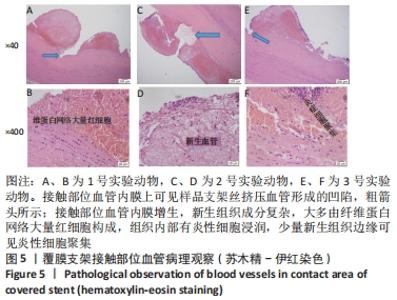
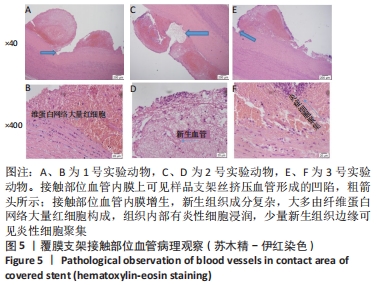
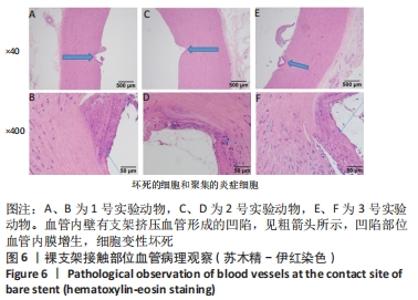
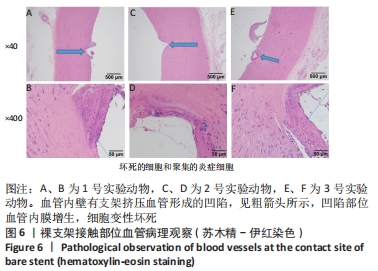
[1] BUNDHUN PK, SOOGUND MZS, PURSUN M, et al. Stent thrombosis and adverse cardiovascular outcomes observed between six months and five years with sirolimus-eluting stents and other drug-eluting stents in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(27):e4130.
[2] GB/T 16886.1-2011 医疗器生物学评价 第1部分:风险管理过程中的评价与实验.
[3] 许晶晶,袁晋青.不同时段支架血栓的风险预测及应对策略[J].中国循环杂志,2014(11):949-951.
[4] GB/T 16886.4-2003 医疗器械生物学评价 第 4 部分:与血液相互作用试验选择.
[5] International Organization for Standardization. ISO 10993-4 2017 Biological evaluation of medical devices–Part 4: Selection of tests for interactions with blood. 2017.
[6] DAKE MD, KATO N, MITCHELL RS, et al.Endovascular stent-graft placement for the treatment of acute aortic dissection.N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1546-1552.
[7] 葛静.Stanford B型主动脉夹层腔内修复术的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2020,49(11):1868-1874.
[8] 牛云茜,邓锡伟,罗建方.裸金属支架结合覆膜支架修复主动脉夹层二例报道[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2013,21(1):62-64.
[9] ITO N, TSUNODA T, NAKAMURA M, et al. Percutaneous bare Z-stent implantation as an alternative to surgery for acute aortic dissection with visceral ischemia. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2003;58(1):95-100.
[10] HOFFERBERTH SC, FOLEY PT, NEWCOMB AE, et al. Combined proximal endografting with distal bare-metal stenting for management of aortic dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93(1):95-102.
[11] NIENABER CA, KISCHE S, ZELLER T, et al. Provisional extension to induce complete attachment after stent-graft placement in type B aortic dissection: the PETTICOAT concept. J Endovasc Ther. 2006;13(6):738-746.
[12] DONG Z, FU W, WANG Y,et al.Stent graft-induced new entry after endovascular repair for Stanford type B aortic dissection. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52(6):1450-1457.
[13] 董智慧,符伟国,王玉琦,等.胸主动脉腔内修复术后支架源性新破口——从支架力学损伤角度的思考[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2011,18(10):1031-1038.
[14] ISO 10993-4:2017, Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 4: Selection of Tests for Interactions with Blood.
[15] 马嘉丽,于振华,朱明,等.镍钛合金血管支架性能研究综述[J].金属功能材料,2015,22(2):56-59.
[16] 郑利萍,贾莉芳,袁暾,等.新型可降解聚合物血管支架的体内血栓形成评价[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2019,36(2):232-237.
[17] 侯丽,乔春霞,赵增琳.解读ISO 10993-4:2017《医疗器械生物学评价第4部分:与血液相互作用试验选择》[J].中国医疗设备, 2018(11):1-6.
[18] 谭利兰,罗勇,肖晨,等.低剪切应力与动脉粥样硬化形成研究新进展[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2019,27(5):432-438.
[19] 杜庆霞,王春晓,李栋,等.剪切力对大鼠肺微血管内皮细胞细胞骨架的影响[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2013,51(9):13-16.
[20] WENAWESER P, REY C, EBERLI FR, et al. Stent thrombosis following bare-metal stent implantation: success of emergency percutaneous coronary intervention and predictors of adverse outcome. Eur Heart J. 2005;26(12):1180-1187.
[21] WENAWESER P, DAEMEN J, ZWAHLEN M, et al. Incidence and correlates of drug-eluting stent thrombosis in routine clinical practice. 4-year results from a large 2-institutional cohort study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52(14):1134-1140.
[22] FUJII K, CARLIER SG, MINTZ GS, et al. Stent underexpansion and residual reference segment stenosis are related to stent thrombosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: an intravascular ultrasound study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45(7):995-998.
[23] 赵宏伟,王贵学,戴传云.血管内支架和支架内皮化[J].生物技术通讯,2005,16(6):684-686.
[24] 席亚东,黄玉华,杜若林,等.血管内支架植入后的内皮损伤及其修复策略[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2018,35(2):307-313.
[25] KAZEMIAN MR, SOLOUK A, TAN A, et al. Preventing in-stent restenosis using lipoprotein (a), lipid and cholesterol adsorbent materials. Med Hypotheses. 2015;85(6):986-988.
[26] PAPAFAKLIS MI, CHATZIZISIS YS, NAKA KK, et al. Drug-eluting stent restenosis: effect of drug type, release kinetics, hemodynamics and coating strategy. Pharmacol Ther. 2012;134(1):43-53.
[27] LAN H, WANG Y, YIN T, et al. Progress and prospects of endothelial progenitor cell therapy in coronary stent implantation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016;104(6):1237-1247.
[28] FOIN N, TORII R, MATTESINI A, et al. Biodegradable vascular scaffold: is optimal expansion the key to minimising flow disturbances and risk of adverse events? EuroIntervention. 2015;10(10):1139-1142.
[29] CARMONT MR, PATRICK JH, CASSAR-PULLICINO VN, et al. Sequential metatarsal fatigue fractures secondary to abnormal foot biomechanics. Mil Med. 2006; 171(4):292-297.
[30] LIU JL, KADDOUR N, CHOWDHURY S, et al. Role of CCN5 (WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2) in pancreatic islets. J Diabetes. 2017;9(5):462-474.
[31] 曹雪飞.剪切力对血管内皮功能影响及机制研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016(10):956-958.
[32] CHENG M, GUAN X, LI H, et al. Shear stress regulates late EPC differentiation via mechanosensitive molecule-mediated cytoskeletal rearrangement. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e67675.
[33] 陈满军,洪文娟,洪志鹏.血液剪切力诱导的血管内皮细胞形态学变化和信号通路[J].山东医药,2014(40):99-102.
[34] 古冬金,苏小康,王帅,等.切应力对脑血管内皮细胞Notch通路表达的影响[J].山西医科大学学报,2020,51(6):541-545. |