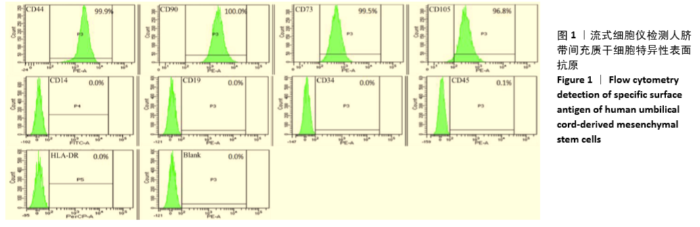
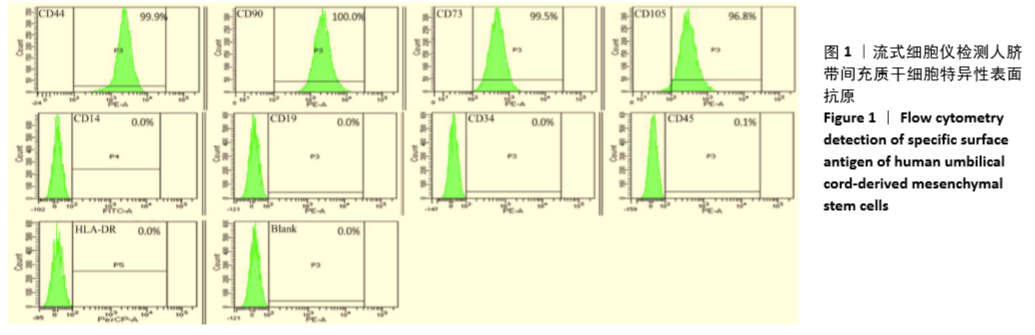
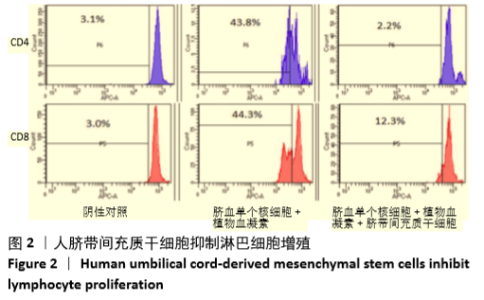
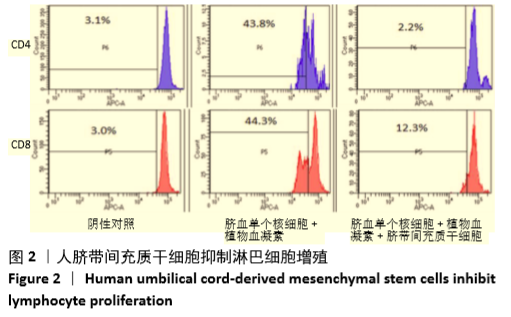
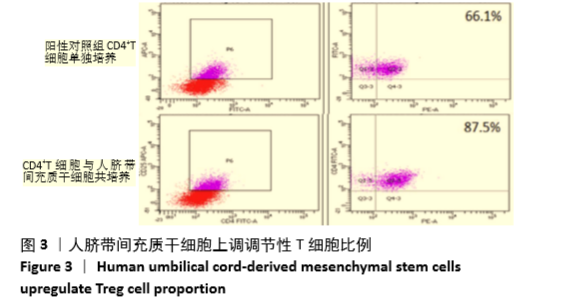
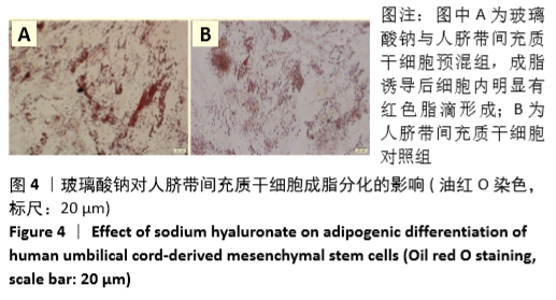
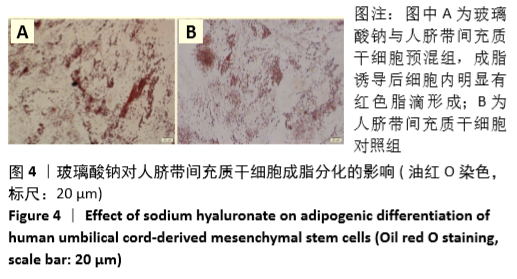
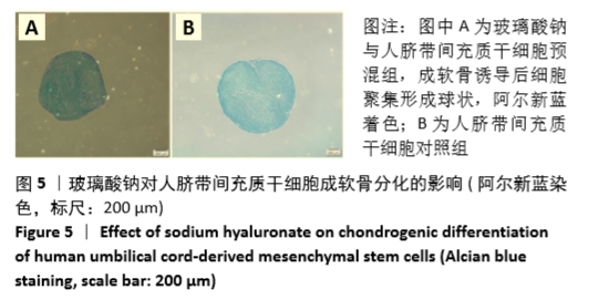
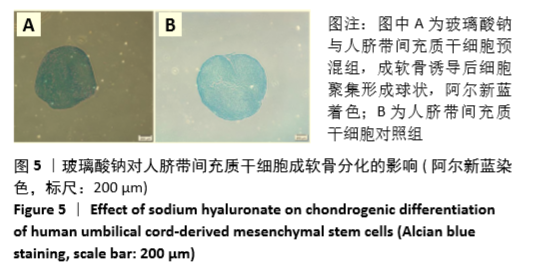
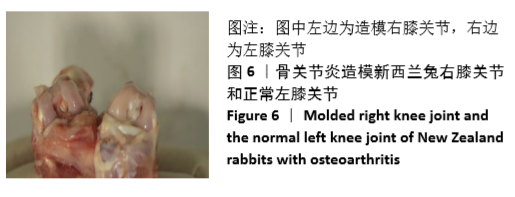
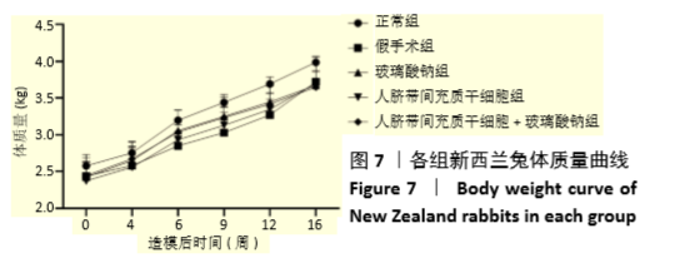
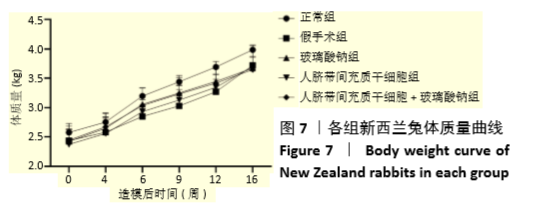
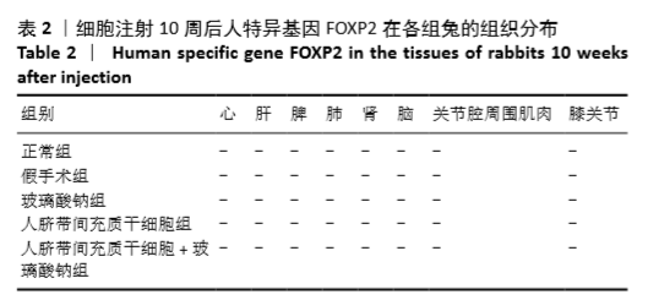
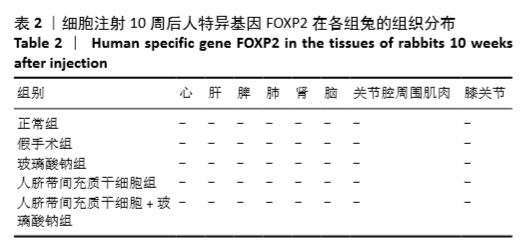
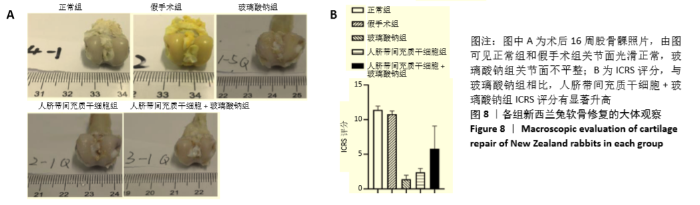
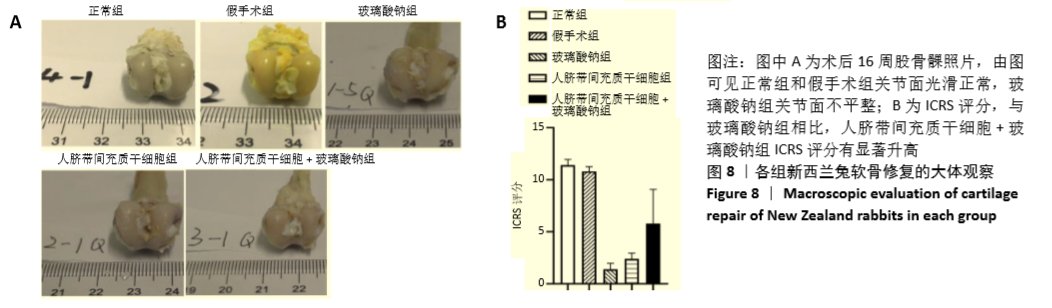
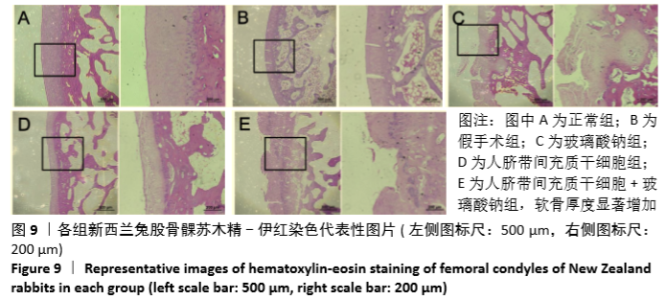
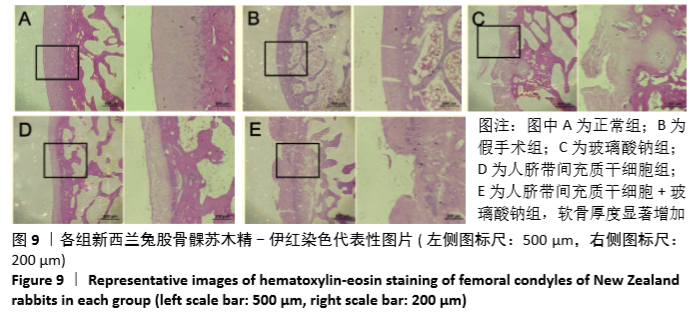
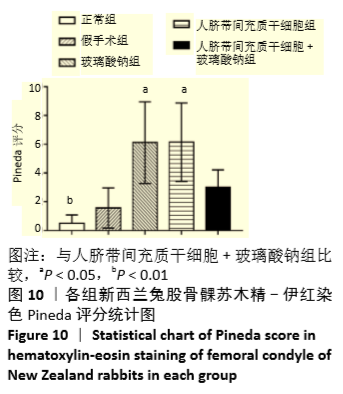
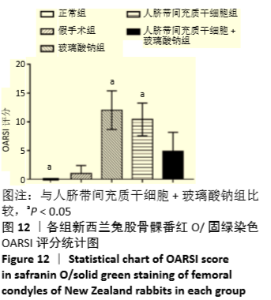
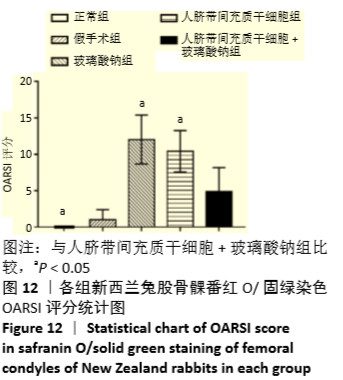
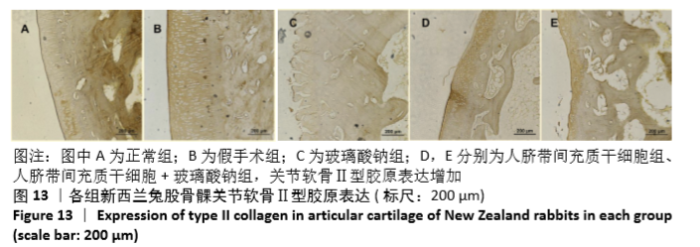
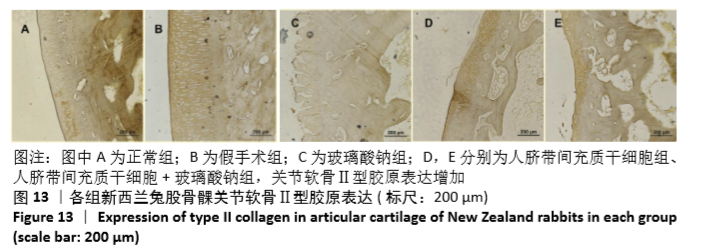
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (31): 4956-4963.doi: 10.12307/2021.136
Previous Articles Next Articles
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with sodium hyaluronate injection
Cui Xiaoyan
- Shanghai Best Year Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201615, China
-
Received:2020-05-10Revised:2020-05-14Accepted:2020-09-05Online:2021-11-08Published:2021-04-25 -
About author:Cui Xiaoyan, MD, Engineer, Shanghai Best Year Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201615, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cui Xiaoyan. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with sodium hyaluronate injection[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4956-4963.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] OROZCO L, MUNAR A, SOLER R, et al. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with autologous mesenchymal stem cells: a pilot study. Transplantation. 2013;95(12):1535-1541. [2] 赵志宏,王锐,国宇,等.膝关节骨关节炎患病率及与骨质疏松症相关性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(14):870-875. [3] 周思齐,李皓桓.氨基葡萄糖联合关节腔内注射透明质酸钠治疗膝骨关节炎的Meta分析[J].疑难病杂志,2018,17(10):1156-1160. [4] 哈承志,李伟,任少达,等.富血小板血浆联合间充质干细胞治疗膝骨关节炎的疗效[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2018,12(5):644-652. [5] 吴毅.老年膝骨关节炎的康复治疗[J].老年医学与保健,2019,25(5):554-556. [6] BROWN GA. AAOS clinical practice guideline: treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: evidence-based guideline, 2nd edition. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(9):577-579. [7] HOLZER LA, LEITHNER A, HOLZER G. Surgery versus physical therapy for meniscal tear and osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(7):677. [8] JEVSEVAR DS, BROWN GA, JONES DL, et al. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons evidence-based guideline on: treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee, 2nd edition. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(20):1885-1886. [9] BRITTBERG M, LINDAHL A, NILSSON A, et al. Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(14):889-895. [10] KNUTSEN G, ENGEBRETSEN L, LUDVIGSEN TC, et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation compared with microfracture in the knee. A randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(3):455-464. [11] VERSIER G, DUBRANA F, FRENCH ARTHROSCOPY SOCIETY. Treatment of knee cartilage defect in 2010. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(8 Suppl): S140-153. [12] SATO M, UCHIDA K, NAKAJIMA H, et al. Direct transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells into the knee joints of Hartley strain guinea pigs with spontaneous osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(1):R31. [13] JO CH, LEE YG, SHIN WH, et al. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells. 2014;32(5):1254-1266. [14] AGGARWAL S, PITTENGER MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815-1822. [15] 张斌斌,赵英杰,杨雪枝,等.新鲜和冷冻人脐带来源间充质干细胞对大鼠骨关节炎的治疗作用比较[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2019, 24(10):1092-1100. [16] LIU TM, MARTINA M, HUTMACHER DW, et al. Identification of common pathways mediating differentiation of bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived human mesenchymal stem cells into three mesenchymal lineages. Stem Cells. 2007;25(3):750-760. [17] AL-NAJAR M, KHALIL H, AL-AJLOUNI J, et al. Intra-articular injection of expanded autologous bone marrow mesenchymal cells in moderate and severe knee osteoarthritis is safe: a phase I/II study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):190. [18] SONG Y, DU H, DAI C, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis: a pilot study with long-term follow-up and repeated injections. Regen Med. 2018;13(3):295-307. [19] LI M, LUO X, LV X, et al. In vivo human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell tracking after intra-articular delivery in a rat osteoarthritis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):160. [20] WANG W, HE N, FENG C, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells engraft into rabbit articular cartilage. Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16(6):12076-12091. [21] 程文丹,徐生林,吴小三,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞复合富血小板血浆治疗早期膝关节骨关节炎疗效观察[J].中华全科医学,2019,17(10): 1652-1655. [22] LI M, HAO M, JIANG D, et al. In Vivo Tracking of Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Rat Knee Osteoarthritis Model with Fluorescent Lipophilic Membrane Dye. J Vis Exp. 2017;(128):56273. [23] MELLO TG, ROSADO-DE-CASTRO PH, CAMPOS RMP, et al. Intravenous Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Administration in Models of Moderate and Severe Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(9):586-598. [24] SAULNIER N, VIGUIER E, PERRIER-GROULT E, et al. Intra-articular administration of xenogeneic neonatal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells early after meniscal injury down-regulates metalloproteinase gene expression in synovium and prevents cartilage degradation in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(1):122-133. [25] 何继晨,严君逸,程琢玉,等.诱导多能干细胞来源间充质干细胞对大鼠骨关节炎的治疗作用[J].安徽医药,2019,23(8):1496-1500. [26] MAGRI C, SCHRAMME M, FEBRE M, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of single versus repeated intra-articular injection of allogeneic neonatal mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of osteoarthritis of the metacarpophalangeal/metatarsophalangeal joint in horses: A clinical pilot study. PLoS One. 2019;14(8):e0221317. [27] DILOGO IH, CANINTIKA AF, HANITYA AL, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treating osteoarthritis of the knee: a single-arm, open-label study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(5):799-807. [28] MUSHAHARY D, SPITTLER A, KASPER C, et al. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A. 2018; 93(1):19-31. [29] KIM YS, KOH YG. Comparative Matched-Pair Analysis of Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy With Versus Without an Injection of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Varus Knee Osteoarthritis: Clinical and Second-Look Arthroscopic Results. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(11):2669-2677. [30] XIANG A, DENG H, CHENG K, et al. Laser photobiomodulation for cartilage defect in animal models of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;35(4):789-796. [31] 谢文鹏,徐龙进,王象鹏,等.p38 MAPK信号通路在膝关节骨性关节炎中医药诊疗中的作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(8):219-225. [32] 刘献祥,李西海,周江涛.改良Hulth造模法复制膝骨性关节炎的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2005,25(12):1104-1108. [33] MURPHY JM, FINK DJ, HUNZIKER EB, et al. Stem cell therapy in a caprine model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(12):3464-3474. [34] MORILLE M, TOUPET K, MONTERO-MENEI CN, et al. PLGA-based microcarriers induce mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis and stimulate cartilage repair in osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 2016;88:60-69. [35] WU KC, CHANG YH, LIU HW, et al. Transplanting human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronate hydrogel repairs cartilage of osteoarthritis in the minipig model. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;31(1):11-19. [36] MATAS J, ORREGO M, AMENABAR D, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (mscs) for knee osteoarthritis: repeated msc dosing is superior to a single MSC dose and to Hyaluronic Acid in a Controlled Randomized Phase I/II Trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(3):215-224. [37] PLATZER H, NEES TA, REINER T, et al. Impact of Mononuclear Cell Infiltration on Chondrodestructive MMP/ADAMTS Production in Osteoarthritic Knee Joints-An Ex Vivo Study. J Clin Med. 2020;9(5):1279. [38] DAMIA E, CHICHARRO D, LOPEZ S, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Are They a Good Therapeutic Strategy for Osteoarthritis? Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):1926. [39] ELMORSY S, FUNAKOSHI T, SASAZAWA F, et al. Chondroprotective effects of high-molecular-weight cross-linked hyaluronic acid in a rabbit knee osteoarthritis model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(1):121-127. [40] KOSINSKA MK, LUDWIG TE, LIEBISCH G, et al. Articular Joint Lubricants during Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Display Altered Levels and Molecular Species. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125192. [41] BAND PA, HEETER J, WISNIEWSKI HG, et al. Hyaluronan molecular weight distribution is associated with the risk of knee osteoarthritis progression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(1):70-76. [42] ALTMAN RD, MANJOO A, FIERLINGER A, et al. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:321. [43] ZHU J, MARCHANT RE. Design properties of hydrogel tissue-engineering scaffolds. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2011;8(5):607-626. [44] MARA CS, DUARTE AS, SARTORI A, et al. Regulation of chondrogenesis by transforming growth factor-beta 3 and insulin-like growth factor-1 from human mesenchymal umbilical cord blood cells. J Rheumatol. 2010; 37(7):1519-1526. [45] CHOI YS, IM MW, KIM CS, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived multilineage progenitor cells in atelocollagen. Cytotherapy. 2008;10(2):165-173. [46] GAUTHAMAN K, FONG CY, VENUGOPAL JR, et al. Propagation and differentiation of human Wharton’s jelly stem cells on three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffolds. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1058:1-23. [47] CHEN H, ZHANG Y, YANG Z, et al. Human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly-derived oligodendrocyte precursor-like cells for axon and myelin sheath regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(10):890-899. [48] FONG CY, SUBRAMANIAN A, GAUTHAMAN K, et al. Human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly stem cells undergo enhanced chondrogenic differentiation when grown on nanofibrous scaffolds and in a sequential two-stage culture medium environment. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012;8(1):195-209. [49] WALTER GJ, FLESKENS V, FREDERIKSEN KS, et al. Phenotypic, Functional, and Gene Expression Profiling of Peripheral CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ CD4+CD25+CD127(low) Treg Cells in Patients With Chronic Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(1):103-116. [50] 刘登榜,邓江.TGF-β3在关节软骨组织工程的研究进展[J].山东医药, 2016,56(18):103-106. [51] 李华杰,邱波.间充质干细胞源性外泌体参与修复骨关节炎退变软骨的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2018,22(7):493-496. [52] WANG Y, YU D, LIU Z, et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):189. [53] 张志强.X线、超声及MRI影像诊断膝骨关节炎临床价值比较[J].泰山医学院学报,2018,39(1):90-91. |
| [1] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [2] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [3] | Li Chaojie, Gulati•Maitirouzi, Aierxiding•Abulaiti, Zheng Hui, Tu Hudi. Finite element analysis of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction at different flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1359-1364. |
| [4] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [5] | Shan Jiaxin, Zhang Yilong, Wu Hongtao, Zhang Jiayuan, Li Anan, Liu Wengang, Xu Xuemeng, Zhao Chuanxi. Changes in muscle strength and pain in patients receiving Jianpi Yiqi Huoxue Formula after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1378-1382. |
| [6] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [7] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [8] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [9] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [10] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [11] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [12] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [13] | Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan. Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 905-910. |
| [14] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [15] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||