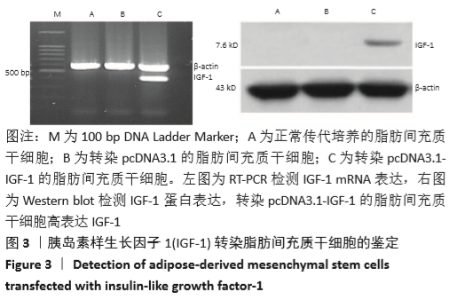
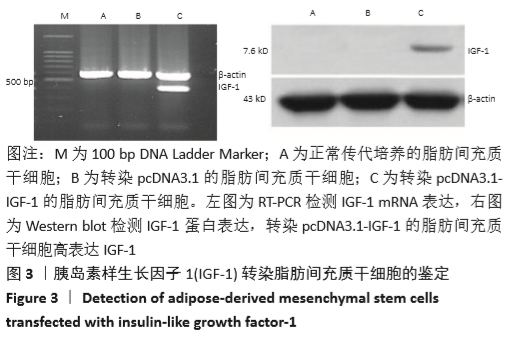
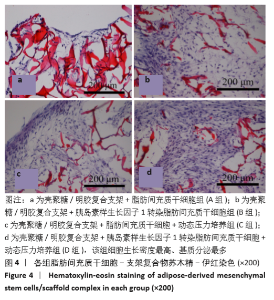
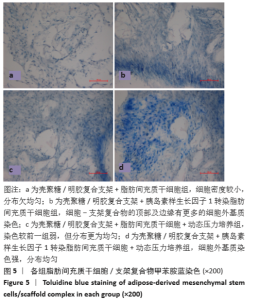
[1] BACAKOVA L, ZARUBOVA J, TRAVNICKOVA M, et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells - a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(4): 1111-1126.
[2] WANG T, LAI JH, YANG F. Effects of Hydrogel Stiffness and Extracellular Compositions on Modulating Cartilage Regeneration by Mixed Populations of Stem Cells and Chondrocytes In Vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(23-24):1348-1356.
[3] GU X, LI C, YIN F, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells in articular cartilage regeneration: current concepts and optimization strategies. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(7):639-653.
[4] AN C, CHENG Y, YUAN Q, et al. IGF-1 and BMP-2 induces differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes-like cells. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010; 38(4): 1647-1654.
[5] 张传辉,杨军,李建军.调控脂肪间充质干细胞成软骨分化基因Sox-9和低氧诱导因子1α的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(45):6766-6773.
[6] VAINIERI ML, WAHL D, ALINI M, et al. Mechanically stimulated osteochondral organ culture for evaluation of biomaterials in cartilage repair studies. Acta Biomater. 2018;81:256-266.
[7] JUNG Y, KIM SH, KIM YH, et al. Cartilaginous tissue formation using a mechano-active scaffold and dynamic compressive stimulation. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2008;19:61-74.
[8] CHEN CH, KUO CY, CHEN JP. Effect of Cyclic Dynamic Compressive Loading on Chondrocytes and Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Co-Cultured in Highly Elastic Cryogel Scaffolds. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):370.
[9] 杨军,张传辉,李建军,等.动态压力联合胰岛素样生长因子1基因转染促进兔脂肪间充质干细胞低氧诱导因子1α的表达[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(45):3220-3224.
[10] SAWATJUI N, LIMPAIBOON T, SCHROBBACK K, et al. Biomimetic scaffolds and dynamic compression enhance the properties of chondrocyte- and MSC-based tissue-engineered cartilage. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(5):1220-1229.
[11] AISENBREY EA, BILOUSOVA G, PAYNE K, et al. Dynamic mechanical loading and growth factors influence chondrogenesis of induced pluripotent mesenchymal progenitor cells in a cartilage-mimetic hydrogel. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(12):5388-5403.
[12] LI Z, KUPCSIK L, YAO SJ, et al. Mechanical load modulates chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through the TGF-beta pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(6A):1338-1346.
[13] ANDERSON DE, JOHNSTONE B. Dynamic Mechanical Compression of Chondrocytes for Tissue Engineering: A Critical Review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:76.
[14] ZHANG Y, TANG CL, CHEN WJ, et al. Dynamic compression combined with exogenous SOX-9 promotes chondrogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in PLGA scaffold. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(14):2671-2678.
[15] JIMI E, HUANG F, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275.
[16] SONO T, AKIYAMA H, MIURA S, et al. THRAP3 interacts with and inhibits the transcriptional activity of SOX9 during chondrogenesis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2018;36(4):410-419.
[17] OLNEY RC. Mechanisms of impaired growth: effect of steroids on bone and cartilage. Horm Res. 2009;72 Suppl 1:30-35.
[18] TIAN F, WANG Y, BIKLE DD. IGF-1 signaling mediated cell-specific skeletal mechano-transduction. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):576-583.
[19] 杨自权,赵永亮,冯军宇,等.动态压力对间充质干细胞定向成软骨分化的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016,33(11):2602.
[20] 李昆朋,张雯,李忠,等.动态压应力促进软骨前体干细胞Sox9和细胞外基质表达的实验研究[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2016, 22(3):189-193.
[21] ZHOU Y, LV M, LI T, et al. Spontaneous calcium signaling of cartilage cells: from spatiotemporal features to biophysical modeling. FASEB J. 2019;33(4):4675-4687.
[22] GUILAK F, ZELL RA, ERICKSON GR, et al. Mechanically induced calcium waves in articular chondrocytes are inhibited by gadolinium and amiloride. J Orthop Res. 1999;17(3):421-429.
[23] LV M, ZHOU Y, CHEN X, et al. Calcium signaling of in situ chondrocytes in articular cartilage under compressive loading: Roles of calcium sources and cell membrane ion channels. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):730-738.
|