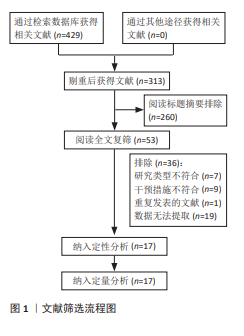
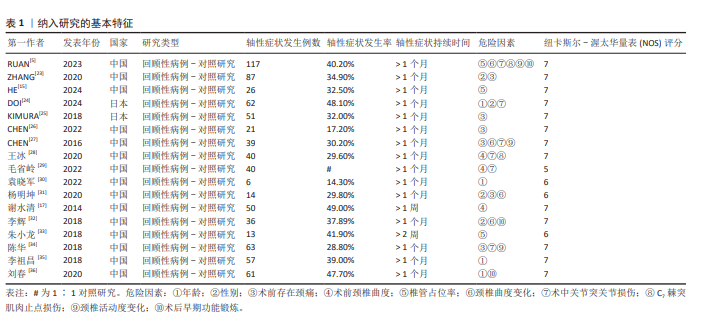
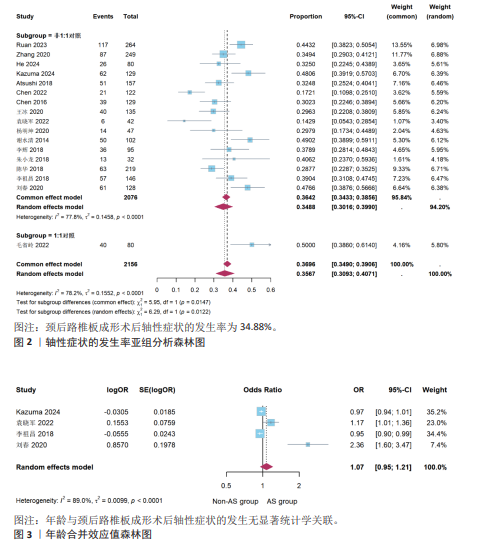
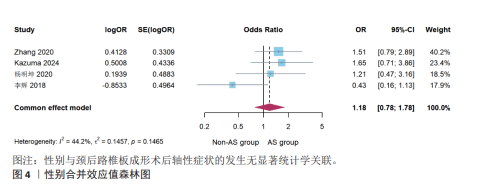
[1] STEPHENS BF, RHEE JM, NEUSTEIN TM, et al. Laminoplasty Does not Lead to Worsening Axial Neck Pain in the Properly Selected Patient With Cervical Myelopathy: A Comparison With Laminectomy and Fusion. Spine. 2017;42(24):1844-1850.
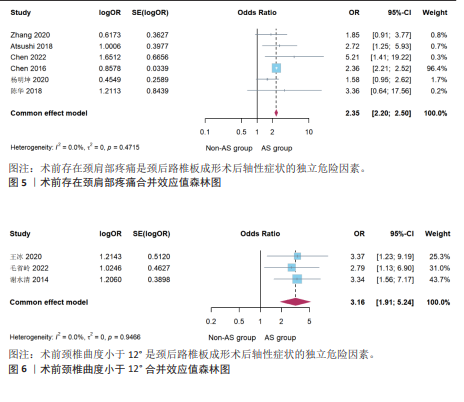
[2] ZHANG X, GAO Y, GAO K, et al. Factors associated with postoperative axial symptom after expansive open-door laminoplasty: retrospective study using multivariable analysis. Eur Spine J. 2020; 29(11):2838-2844.
[3] HOSONO N, YONENOBU K, ONO K. Neck and shoulder pain after laminoplasty. A noticeable complication. Spine. 1996; 21(17):1969-1973.
[4] ZHENG B, GUO C, ZHAO C, et al. Global Tendencies and Frontier Topics in Cervical Laminoplasty: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1982 to 2023. World Neurosurg. 2024;191: 91-101.
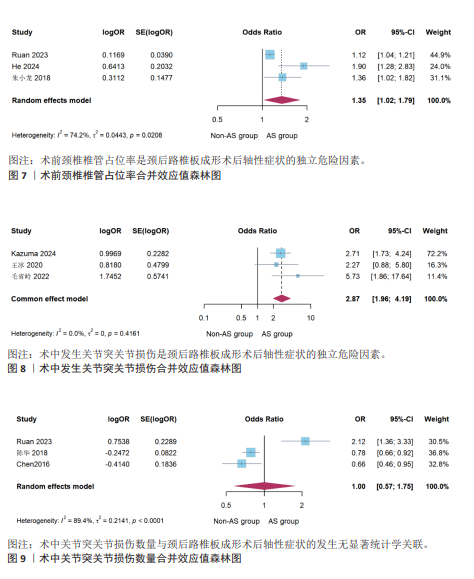
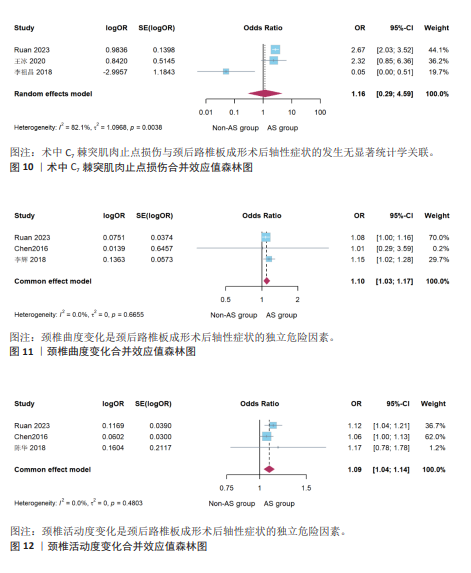
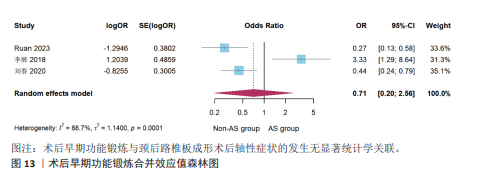
[5] RUAN C, JIANG W, LU W, et al. Analysis of risk factors for axial symptoms after posterior cervical open-door laminoplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):954.
[6] CHIBA K, OGAWA Y, ISHII K, et al. Long-term results of expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy--average 14-year follow-up study. Spine. 2006;31(26): 2998-3005.
[7] LIN CR, TSAI SHL, TSAI PA, et al. What is the best strategy for C3 in open-door laminoplasty: laminectomy versus laminoplasty-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2025;25(7):1440-1454.
[8] 仇子叶, 马昱堃, 俞兴, 等. 颈椎术后轴性症状与影像学评价指标相关性的研究进展[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2023,20(1):80-84.
[9] 单杰. 颈椎单开门术后轴性症状的危险因素分析[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学, 2023.
[10] LIU FJ, DING XK, CHAI Y, et al. Influence of fixed titanium plate position on the effectiveness of open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):297.
[11] DU W, WANG S, WANG H, et al. Cervical alignment and clinical outcome of open-door laminoplasty vs. laminectomy and instrumentation in kyphotic multilevel cervical degenerative myelopathy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(3): 1429-1440.
[12] LI Z, LIANG Q, LI H, et al. Fatty infiltration of the cervical multifidus musculature and its clinical correlation to cervical spondylosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):613.
[13] ZHENG B, ZHU Z, LIANG Y, et al. Cervical Subcutaneous Fat Thickness and Its Association with Sagittal Parameters and Clinical Outcomes Following Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. World Neurosurg. 2025;199:124069.
[14] JIANG Z, FU X, DU W, et al. Changes in cervical sagittal parameters and the impact on axial symptoms after two types of posterior single-door cervical decompression surgeries. J Clin Neurosci. 2025;137:111293.
[15] HE W, PAN J. Influencing factors for axial symptoms after modified expansive open-door laminoplasty. Ceska a Slovenska Neurologie a Neurochirurgie. 2024;87(4): 264-268.
[16] KIM AH, AVENDANO JP, GREENBERG M, et al. The Impact of Cervical Laminoplasty and Cervical Foraminotomy on Axial Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2025;15(6): 21925682251319544.
[17] 谢水清, 孙天威, 田融, 等. 脊髓型颈椎病单开门椎板成形术后轴性症状的危险因素分析[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(5):620-624.
[18] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010; 25(9):603-605.
[19] LI C, TANG X, ZHENG X, et al. Global Prevalence and Incidence Estimates of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156(2):172-181.
[20] PETIT CB, HUSSAIN ZB, MCPHERSON A, et al. Graft Failure in Pediatric Patients After Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone, Hamstring Tendon, or Quadriceps Tendon Autograft ACLR: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Orthop J Sports Med. 2024;12(11):23259671241289140.
[21] ZHAO H, QI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Correlation between uric acid levels and bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025;16:1415550.
[22] HUANG T, LI C, CHEN F, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of osteosarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2023;23(1):369.
[23] ZHANG X, GAO Y, GAO K, et al. Factors associated with postoperative axial symptom after expansive open-door laminoplasty: retrospective study using multivariable analysis. Eur Spine J. 2020; 29(11):2838-2844.
[24] DOI K, OKAZAKI T, TANI S, et al. The new proposal of the relationship between axial pain and hinge fracture and facet involvement after open-door laminoplasty with titanium spacers. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2024;15(3):321-325.
[25] KIMURA A, SHIRAISHI Y, INOUE H, et al. Predictors of Persistent Axial Neck Pain After Cervical Laminoplasty. Spine. 2018;43(1): 10-15.
[26] CHEN K, YU J, NIE C, et al. Preoperative dynamic quantitative sensory testing in remote pain-free areas is associated with axial pain after posterior cervical spinal surgeries. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1): 409.
[27] CHEN H, LIU H, DENG Y, et al. Multivariate Analysis of Factors Associated With Axial Symptoms in Unilateral Expansive Open-Door Cervical Laminoplasty With Miniplate Fixation. Medicine. 2016;95(2):e2292.
[28] 王冰, 刘涛. 单开门椎板成形钢板内固定术后轴性疼痛相关因素分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2020,41(1):26-28.
[29] 毛省岭, 肖江岭. 多节段脊髓型颈椎病患者后路单开门椎管扩大成形术后发生颈椎轴性痛的影响因素分析[J]. 四川解剖学杂志,2022,30(2):11-13.
[30] 袁晓军, 徐文华, 林军明, 等. 多裂肌萎缩与颈后路单开门术后轴性症状发生的相关性研究[J]. 宜春学院学报,2022, 44(12):48-51.
[31] 杨明坤, 张旭, 刘川, 等. 改良椎管扩大成形术术后发生轴性症状的危险因素分析[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2020,41(5): 318-322.
[32] 李辉, 郝定均, 刘鹏, 等. 颈后路单开门椎板成形术后轴性症状的危险因素分析[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2018,3(30): 99-102.
[33] 朱小龙, 徐卫星, 丁伟国, 等. 颈椎单开门椎板成形术术后轴性症状的影响因素分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2018,31(11): 1022-1026.
[34] 陈华, 刘浩, 龚全, 等. 颈椎单开门椎管扩大椎板成形微型钢板内固定术后轴性疼痛的危险因素[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2018,28(2):111-117.
[35] 李祖昌, 蒋继乐, 田伟, 等. 颈椎后路双开门椎管成形术后发生轴性症状的危险因素分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(16): 1009-1015.
[36] 刘春, 亢志强, 杨辉, 等. 慢性压迫性颈脊髓病患者行C3-C7单开门椎板成形术后发生轴性症状影响因素分析[J]. 中国药物与临床,2020,20(15):2509-2513.
[37] YOSHIDA M, TAMAKI T, KAWAKAMI M, et al. Does reconstruction of posterior ligamentous complex with extensor musculature decrease axial symptoms after cervical laminoplasty? Spine. 2002; 27(13):1414-1418.
[38] PINTER ZW, MIKULA AL, REED R, et al. Is Severe Neck Pain a Contraindication to Performing Laminoplasty in Patients With Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy? Clin Spine Surg. 2023;36(3):127-133.
[39] WANG H, XU H, WANG X, et al. Imbalance of Muscles Around the Cervical Spine in Patients with Degenerative Cervical Spondylotic Kyphosis and Myelopathy. World Neurosurg. 2025;195:123605.
[40] 张黎龙, 邵睿, 耿彦南, 等. 术前C7/T1椎间孔面积对后路单开门椎管扩大成形术治疗脊髓型颈椎病疗效的影响[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2024,34(5): 458-462.
[41] WANG LN, WANG L, SONG YM, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcome of unilateral open-door laminoplasty with alternative levels centerpiece mini-plate fixation for cervical compressive myelopathy: a five-year follow-up study. Int Orthop. 2016; 40(6):1267-1274.
[42] KOBAYASHI H, NIKAIDO T, WATANABE K, et al. Impact of Cervical Micro-Endoscopic Laminotomy on Postoperative Neck Pain and Range of Motion: A Case-Control Study. Spine. 2025. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000005305.
[43] 崔致尧, 闫景龙, 姬烨. 颈椎椎管扩大成形术的研究进展[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2021,27(9):811-814+858.
[44] 江仲超, 韩晓辉, 袁宇飞, 等. 颈椎单开门椎管扩大成形术中重建伸肌附着点及保留C7棘突开槽式减压的临床疗效观察[J]. 科学技术与工程,2022,22(19): 8248-8252.
[45] SHANGGUAN Z, CHEN G, LIU W, et al. Clinical outcomes of modified versus traditional expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: A single-institution experience. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2023;31(3):10225536231209556.
[46] 王晓岩, 徐公平, 王新涛, 等. C2穹隆减压术联合棘突悬吊椎管扩大成形术治疗颈椎高位后纵韧带骨化症[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2024,17(12):1057-1062.
[47] COHEN SP, HUANG JH, BRUMMETT C. Facet joint pain--advances in patient selection and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013; 9(2):101-116.
[48] MACHINO M, YUKAWA Y, HIDA T, et al. Cervical alignment and range of motion after laminoplasty: radiographical data from more than 500 cases with cervical spondylotic myelopathy and a review of the literature. Spine. 2012;37(20):E1243-1250.
[49] YU Q, REN Y, WANG Z, et al. The Effect of a Cervical Brace on Postoperative Axial Symptoms Following Single-level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. Clin Spine Surg. 2025;38(3):E181-E185.
[50] TAKEUCHI K, YOKOYAMA T, ABURAKAWA S, et al. Axial symptoms after cervical laminoplasty with C3 laminectomy compared with conventional C3-C7 laminoplasty: a modified laminoplasty preserving the semispinalis cervicis inserted into axis. Spine. 2005;30(22):2544-2549. |