[1] SARTORETTO SC, SHIBLI JA, JAVID K, et al. Comparing the Long-Term Success Rates of Tooth Preservation and Dental Implants: A Critical Review. J Funct Biomater. 2023; 14(3):142.
[2] COSGAREA R, SCULEAN A, SHIBLI JA, et al.
Prevalence of peri-implant diseases - a critical review on the current evidence. Braz Oral Res. 2019;33(suppl 1):e063.
[3] ROMANDINI M, LIMA C, PEDRINACI I, et al. Prevalence and risk/protective indicators of peri-implant diseases: A university-representative cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2021;32(1):112-122.
[4] FOURMOUSIS I, VLACHOS M. Genetic Risk Factors for the Development of Periimplantitis. Implant Dent. 2019;28(2): 103-114.
[5] DARBY I. Risk factors for periodontitis & peri-implantitis. Periodontol 2000. 2022;90(1):9-12.
[6] ALVIM-PEREIRA F, MONTES CC, MIRA MT,
et al. Genetic susceptibility to dental implant failure: a critical review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(3):409-416.
[7] CHEN X, ZHAO Y. Genetic Involvement in Dental Implant Failure: Association With Polymorphisms of Genes Modulating Inflammatory Responses and Bone Metabolism. J Oral Implantol. 2019;45(4): 318-326.
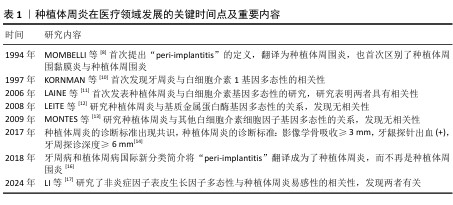
[8] MOMBELLI A, LANG NP. Microbial aspects of implant dentistry. Periodontol 2000. 1994;4:74-80.
[9] CHMIELEWSKI M, PILLONI A. Current Molecular, Cellular and Genetic Aspects of Peri-Implantitis Disease: A Narrative Review. Dent J (Basel). 2023;11(5):134-134.
[10] KORNMAN KS, CRANE A, WANG HY, et al. The interleukin-1 genotype as a severity factor in adult periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1997;24(1):72-77.
[11] LAINE ML, LEONHARDT A, ROOS-JANSÅKER AM, et al. IL-1RN gene polymorphism is associated with peri-implantitis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(4):380-385.
[12] LEITE MF, SANTOS MC, DE SOUZA AP, et al. Osseointegrated implant failure associated with MMP-1 promotor polymorphisms (-1607 and -519). Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(4):653-658.
[13] MONTES CC, ALVIM-PEREIRA F, DE CASTILHOS BB, et al. Analysis of the association of IL1B (C+3954T) and IL1RN (intron 2) polymorphisms with dental implant loss in a Brazilian population. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(2):208-217.
[14] JEPSEN S, CATON JG, ALBANDAR JM, et al.
Periodontal manifestations of systemic diseases and developmental and acquired conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 3 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45 Suppl 20:S219-S229.
[15] 李丛丛,于玢玢,范春,等.TNF-α、IL-6分子基因多态性与种植体周围炎相关性分析[J].中国现代医药杂志,2017,19(2):1-5.
[16] 郭淑娟,刘倩,丁一.牙周病和植体周病国际新分类简介[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2019,46(2):125-134.
[17] LI P, CHEN B, ZHAO L, et al. Correction: Correlations of FCGR2A 131R/H and FCGR3A 158V/F Polymorphisms with the Susceptibility of Peri-implantitis in Chinese Han Population. Mol Biotechnol. 2024;66(9):2677.
[18] DINARELLO CA. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol Rev. 2018;281(1):8-27.
[19] LAINE ML, LEONHARDT A, ROOS-JANSÅKER AM, et al. IL-1RN gene polymorphism is associated with peri-implantitis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(4):380-385.
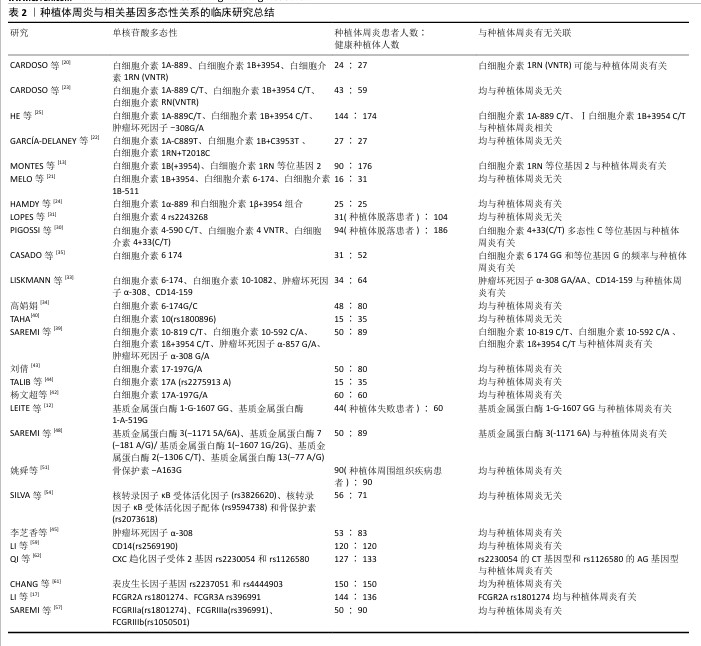
[20] CARDOSO JM, RIBEIRO AC, PROENÇA L,
et al. Analysis of the Association of IL-1A, IL-1B, and IL-1RN Genetic Polymorphisms with Peri-implantitis in a Portuguese Population. Int J Oral Maxillofacm Implants. 2024;39(4):103-111.
[21] MELO RF, LOPES BM, SHIBLI JA, et al. Interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 expression and gene polymorphisms in subjects with peri-implant disease. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012;14(6):905-914.
[22] GARCÍA-DELANEY C, SÁNCHEZ-GARCÉS MÁ, FIGUEIREDO R, et al. Clinical significance of interleukin-1 genotype in smoking patients as a predictor of peri-implantitis: A case-control study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2015;20(6):e737-e743.
[23] CARDOSO JM, RIBEIRO AC, BOTELHO J, et al.
The Influence of Genetic Polymorphisms on the Expression of Interleukin-1beta, Prostaglandin E2 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Peri-Implant Crevicular Fluid: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(1):651-651.
[24] HAMDY AA, EBRAHEM MA. The effect of interleukin-1 allele 2 genotype (IL-1a(-889) and IL-1b(+3954)) on the individual’s susceptibility to peri-implantitis: case-control study. J Oral Implantol. 2011;37(3): 325-334.
[25] HE K, JIAN F, HE T, et al. Analysis of the association of TNF-α, IL-1A, and IL-1B polymorphisms with peri-implantitis in a Chinese non-smoking population. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(2):693-699.
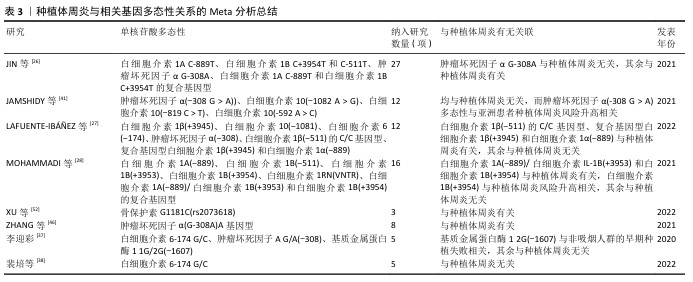
[26] JIN Q, TENG F, CHENG Z. Association between common polymorphisms in IL-1 and TNFα and risk of peri-implant disease: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2021; 16(10):e0258138.
[27] LAFUENTE-IBÁÑEZ DMI, SETIEN-OLARRA A, GARCÍA-DE LFA, et al. Role of proinflammatory mutations in peri-implantitis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Implant Dent. 2022;8(1):2-2.
[28] MOHAMMADI H, ROOCHI MM, SADEGHI M, et al. Association between Interleukin-1 Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Dental Peri-Implant Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Pathogens. 2021;10(12):1600-1600.
[29] BROWN MA, HURAL J. Functions of IL-4 and Control of Its Expression. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):181-212.
[30] PIGOSSI SC, ALVIM-PEREIRA F, ALVIM-PEREIRA CC, et al. Association of interleukin 4 gene polymorphisms with dental implant loss. Implant Dent. 2014;23(6):723-731.
[31] LOPES TF, SOUZA CM, REICHOW AM, et al. Analysis of the association of IL4 polymorphisms with orthodontic mini-implant loss. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;48(7):982-988.
[32] 张海英.白细胞介素-6及其受体基因多态性与中国西北人群慢性牙周炎的关联研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2011.
[33] LISKMANN S, VIHALEMM T, SALUM O, et al. Correlations between clinical parameters and interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in saliva from totally edentulous patients with peri-implant disease. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2006;21(4):543-550.
[34] 高娟娟.白介素6基因多态性与种植体周围组织疾病的相关性研究[D].沈阳: 中国医科大学,2020.
[35] CASADO PL, VILLAS-BOAS R, DE MELLO W, et al. Peri-implant disease and chronic periodontitis: is interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism the common risk factor in a Brazilian population? Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(1):35-43.
[36] PETKOVIC-CURCIN A, ZELJIC K, CIKOTA-ALEKSIC B, et al. Association of Cytokine Gene Polymorphism with Peri-implantitis Risk. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017; 32(5):e241-e248.
[37] 李迎彩.IL-6 G/C(-174)、TNFA G/A(-308)和MMP-1 1G/2G(-1607)基因多态性与种植体周围炎易感性的meta分析[D].长春:吉林大学,2020.
[38] 裴培,姬晓伟,韩祥祯.IL-6-174 G/C基因多态性与种植体周围病易感性的Meta分析[J].新疆医学,2022,52(11):1271-1275.
[39] SAREMI L, SHAFIZADEH M, ESMAEILZADEH E, et al. Assessment of IL-10, IL-1ß and TNF-α gene polymorphisms in patients with peri-implantitis and healthy controls. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(3):2285-2290.
[40] TAHA GI. Involvement of IL-10 gene polymorphism (rs1800896) and IL-10 level in the development of periimplantitis. Minerva Dent Oral Sci. 2024;73(5):264-271.
[41] JAMSHIDY L, TADAKAMADLA SK, CHOUBSAZ P, et al. Association of IL-10 and TNF-α Polymorphisms with Dental Peri-Implant Disease Risk: A Meta-Analysis, Meta-Regression, and Trial Sequential Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(14):7697-7697.
[42] 杨文超,吴静静.口腔种植体周围炎与IL-17A、IL-17A-197G/A基因多态性、TNF-α的相关性分析[J].中国卫生检验杂志, 2023,33(14):1754-1757.
[43] 刘倩.白细胞介素17基因多态性与种植体周围炎相关性研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2021.
[44] TALIB EQ, Taha GI. Involvement of interlukin-17A (IL-17A) gene polymorphism and interlukin-23 (IL-23) level in the development of peri-implantitis. BDJ Open. 2024;10(1):12.
[45] 李芝香,黄英.TNF-α水平及基因多态性与种植体周围炎相关性分析[J].中国医药导刊,2023,25(1):67-70.
[46] ZHANG X, ZHU X, SUN W. Association Between Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (G-308A) Polymorphism and Chronic Periodontitis, Aggressive Periodontitis, and Peri-implantitis: A Meta-analysis. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2021;21(3):101528.
[47] CHECCHI V, MARAVIC T, BELLINI P, et al. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Periodontal Disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(14):4923-4923.
[48] SAREMI L, SHAHBAZI S, GHAFFARI ME, et al. The Association of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1,-2,-3,-7and-13Gene Polymorphisms with Peri-Implantitis in an Iranian Population: A Case-Control Study. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2024;10(6):e70049.
[49] YASUDA H, SHIMA N, NAKAGAWA N, et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95(7):3597-3602.
[50] EGUIA DEL VALLE A, LÓPEZ-VICENTE J, MARTÍNEZ-CONDE R, et al. Current understanding of genetic polymorphisms as biomarkers for risk of biological complications in implantology. J Clin Exp Dent. 2018;10(10):e1029-e1039.
[51] 姚舜,刘倩,邓巍.骨保护素(OPG)基因多态性与种植体周围组织疾病的相关性研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2021, 37(4):525-529.
[52] XU M, ZHANG C, HAN Y, et al. Association between Osteoprotegerin rs2073618 polymorphism and peri-implantitis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):598.
[53] RIBEIRO R, MELO R, TORTAMANO NP, et al. Polymorphisms of Il-10 (-1082) and RANKL (-438) Genes and the Failure of Dental Implants. Int J Dent. 2017;2017:3901368.
[54] SILVA R, REIS M, ARID J, et al. Association between Genetic Polymorphisms in RANK, RANKL and OPG and Peri-Implant Diseases in Patients from the Amazon Region. Braz Dent J. 2020;31(1):63-68.
[55] VAN SORGE NM, VAN DER POL WL, VAN DE WINKEL JG. FcgammaR polymorphisms: Implications for function, disease susceptibility and immunotherapy. Tissue Antigens. 2003;61(3):189-202.
[56] CASTRO-DOPICO T, CLATWORTHY MR. IgG and Fcγ Receptors in Intestinal Immunity and Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:805.
[57] SAREMI L, ESMAEILZADEH E, GHORASHI T, et al. Association of Fc gamma-receptor genes polymorphisms with chronic periodontitis and Peri-Implantitis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(7):12010-12017.
[58] CIESIELSKA A, MATYJEK M, KWIATKOWSKA K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(4):1233-1261.
[59] LI J, QIAO X, SHANG J. Association analysis between CD14 gene polymorphisms and peri-implantitis susceptibility in a Chinese population. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024;12(4):e1230.
[60] ANGIERO F, UGOLINI A, CATTONI F, et al. Evaluation of bradykinin, VEGF, and EGF biomarkers in gingival crevicular fluid and comparison of PhotoBioModulation with conventional techniques in periodontitis: a split-mouth randomized clinical trial. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;35(4):965-970.
[61] CHANG Z, JIANG D, ZHANG S, et al. Genetic association of the epidermal growth factor gene polymorphisms with peri-implantitis risk in Chinese population. Bioengineered 2021;12(1):8468-8475.
[62] QI Y, LI C, DU Y, et al. Chemokine Receptor 2 (CXCR2) Gene Polymorphisms and Their Association with the Risk of Developing Peri-Implantitis in Chinese Han Population. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:1625-1631.
[63] WANG J, ZHANG Y, CAO J, et al. The role of autophagy in bone metabolism and clinical significance. Autophagy. 2023;19(9): 2409-2427.
[64] OZKOCER O, OZKOCER SE, GULER B, et al.
Immunohistochemical analysis with apoptosis and autophagy markers in periodontitis and peri-implantitis: Clinical comparative study. J Periodontal Res. 2023; 58(2):456-464.
[65] CHENG Y, JIN W, ZHENG L, et al. The role of autophagy in SIM mediated anti-inflammatory osteoclastogenesis through NLRP3 signaling pathway. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024;12(1):e1145. |