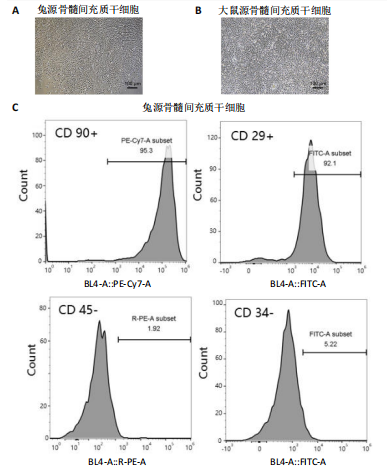
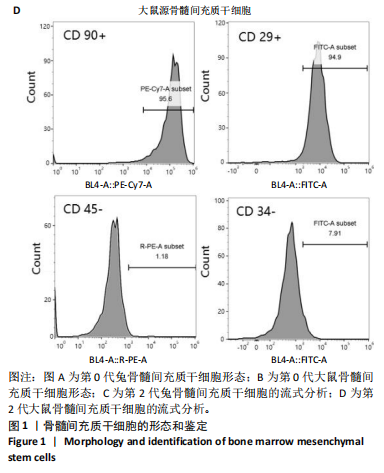
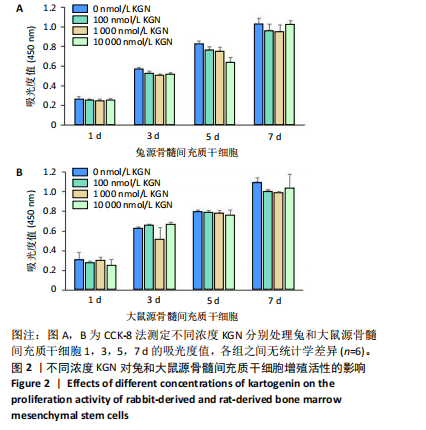
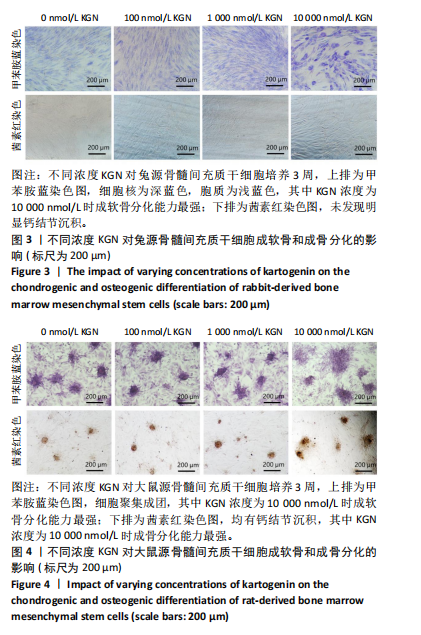
[1] HOU M, TIAN B, BAI B, et al. Dominant role of in situ native cartilage niche for determining the cartilage type regenerated by BMSCs. Bioact Mater. 2021;13:149-160.
[2] WANG Y, KONG B, CHEN X, et al. BMSC exosome-enriched acellular fish scale scaffolds promote bone regeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):444.
[3] JIA R, SUN T, ZHAO X, et al. DEX-Induced SREBF1 Promotes BMSCs Differentiation into Adipocytes to Attract and Protect Residual T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells After Chemotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(19):e2205854.
[4] ZHONG G, YAO J, HUANG X, et al. Injectable ECM hydrogel for delivery of BMSCs enabled full-thickness meniscus repair in an orthotopic rat model. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):871-879.
[5] ZHANG Q, LI J, WANG C, et al. N6-Methyladenosine in Cell-Fate Determination of BMSCs: From Mechanism to Applications. Research (Wash D C). 2024;7:0340.
[6] BIANCO P, ROBEY PG, SIMMONS PJ. Mesenchymal stem cells: revisiting history, concepts, and assays. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(4): 313-319.
[7] LI J, MA J, FENG Q, et al. Building Osteogenic Microenvironments with a Double-Network Composite Hydrogel for Bone Repair. Research (Wash D C). 2023;6:0021.
[8] LIU J, TANG C, HUANG J, et al. Nanofiber Composite Microchannel-Containing Injectable Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(31):e2302293.
[9] WANG L, GUAN C, ZHANG T, et al. Comparative effect of skeletal stem cells versus bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on rotator cuff tendon-bone healing. J Orthop Translat. 2024;47:87-96.
[10] LIU F, WU M, WU X, et al. TGM2 accelerates migration and differentiation of BMSCs by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):168.
[11] XU X, LIANG Y, LI X, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of kartogenin for chondrogenesis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120539.
[12] SHIMOYAMA M, SMITH JR, BRYDA E, et al. Rat Genome and Model Resources. ILAR J. 2017;58(1):42-58.
[13] DENG S, ZHU F, DAI K, et al. Harvest of functional mesenchymal stem cells derived from in vivo osteo-organoids. Biomater Transl. 2023;4(4):270-279.
[14] WANG X, MA Y, CHEN J, et al. A novel decellularized matrix of Wnt signaling-activated osteocytes accelerates the repair of critical-sized parietal bone defects with osteoclastogenesis, angiogenesis, and neurogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2022;21:110-128.
[15] QIN W, GAO J, YAN J, et al. Microarray analysis of signalling interactions between inflammation and angiogenesis in subchondral bone in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Biomater Transl. 2024;5(2):175-184.
[16] GUO J, WANG F, HU Y, et al. Exosome-based bone-targeting drug delivery alleviates impaired osteoblastic bone formation and bone loss in inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4(1):100881.
[17] KANG N, LIU X, GUAN Y, et al. Effects of co-culturing BMSCs and auricular chondrocytes on the elastic modulus and hypertrophy of tissue engineered cartilage. Biomaterials. 2012;33(18):4535-4544.
[18] CAI JY, ZHANG L, CHEN J, et al. Kartogenin and Its Application in Regenerative Medicine. Curr Med Sci. 2019;39(1):16-20.
[19] TIAN X, ZHANG Y, SHEN L, et al. Kartogenin-enhanced dynamic hydrogel ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via restoration of local redox homeostasis. J Orthop Translat. 2023;42:15-30.
[20] LIU G, GUO Q, LIU C, et al. Cytomodulin-10 modified GelMA hydrogel with kartogenin for in-situ osteochondral regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2023;169:317-333.
[21] ZHANG J, WANG JH. Kartogenin induces cartilage-like tissue formation in tendon-bone junction. Bone Res. 2014;2:14008.
[22] WANG Y, CHEN G, YAN J, et al. Upregulation of SIRT1 by Kartogenin Enhances Antioxidant Functions and Promotes Osteogenesis in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018; 2018:1368142.
[23] JOHNSON K, ZHU S, TREMBLAY MS, et al. A stem cell-based approach to cartilage repair. Science. 2012;336(6082):717-721.
[24] ZHANG S, HU P, LIU T, et al. Kartogenin hydrolysis product 4-aminobiphenyl distributes to cartilage and mediates cartilage regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(24):7108-7121.
[25] WANG H, PENG T, WU H, et al. In situ biomimetic lyotropic liquid crystal gel for full-thickness cartilage defect regeneration. J Control Release. 2021;338:623-632.
[26] WEI J, RAN P, LI Q, et al. Hierarchically structured injectable hydrogels with loaded cell spheroids for cartilage repairing and osteoarthritis treatment. Chem Eng J. 2022;430:132211.
[27] CHEN YR, YAN X, YUAN FZ, et al. Kartogenin-Conjugated Double-Network Hydrogel Combined with Stem Cell Transplantation and Tracing for Cartilage Repair. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(35):e2105571.
[28] JANG Y, JUNG H, NAM Y, et al. Centrifugal gravity-induced BMP4 induces chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells via SOX9 upregulation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):184.
[29] ZHANG W, XUE W, JIA Z, et al. Photo-driven dynamic hydrogel modulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells behavior for enhanced cartilage regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2024;484:149689.
[30] XUE JX, GONG YY, ZHOU GD, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced by acellular cartilage sheets. Biomaterials. 2012;33(24):5832-5840.
[31] CAO L, YANG F, LIU G, et al. The promotion of cartilage defect repair using adenovirus mediated Sox9 gene transfer of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(16):3910-3920.
[32] DUFFY DJ, KRSTIC A, HALASZ M, et al. Retinoic acid and TGF-β signalling cooperate to overcome MYCN-induced retinoid resistance. Genome Med. 2017;9(1):15.
[33] LEFEBVRE V, BEHRINGER RR, DE CROMBRUGGHE B. L-Sox5, Sox6 and Sox9 control essential steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9 Suppl A:S69-75.
[34] TUAN RS, BOLAND G, TULI R. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and cell-based tissue engineering. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5(1):32-45.
[35] WEHRLI BM, HUANG W, DE CROMBRUGGHE B, et al. Sox9, a master regulator of chondrogenesis, distinguishes mesenchymal chondrosarcoma from other small blue round cell tumors. Hum Pathol. 2003;34(3):263-269.
[36] VAN GASTEL N, STEGEN S, EELEN G, et al. Lipid availability determines fate of skeletal progenitor cells via SOX9. Nature. 2020;579(7797): 111-117.
[37] SHI H, ZHOU K, WANG M, et al. Integrating physicomechanical and biological strategies for BTE: biomaterials-induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. Theranostics. 2023;13(10):3245-3275.
[38] BAHARLOU HOUREH A, MASAELI E, NASR-ESFAHANI MH. Chitosan/polycaprolactone multilayer hydrogel: A sustained Kartogenin delivery model for cartilage regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;177:589-600.
[39] YAN H, YU T, LI J, et al. Kartogenin Improves Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Autophagy. Stem Cells Int. 2022; 2022:1278921.
[40] MENG X, LI L, HUANG C, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anabolic biphasic scaffold facilitates osteochondral tissue regeneration in osteoarthritic joints. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2023;156:20-31.
[41] 田鑫,刘滔,杨惠林,等.甲基丙烯化明胶微球缓释Kartogenin修复髓核退变的体外评估[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(5):724-730. |