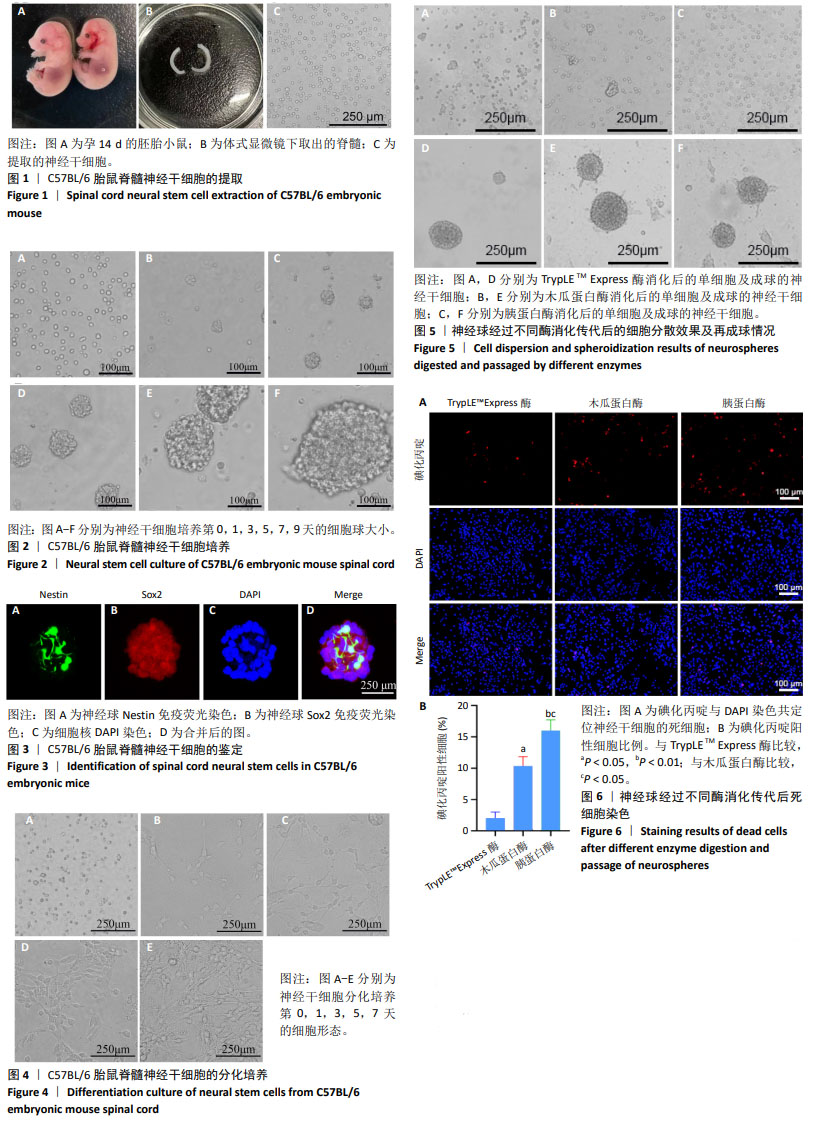
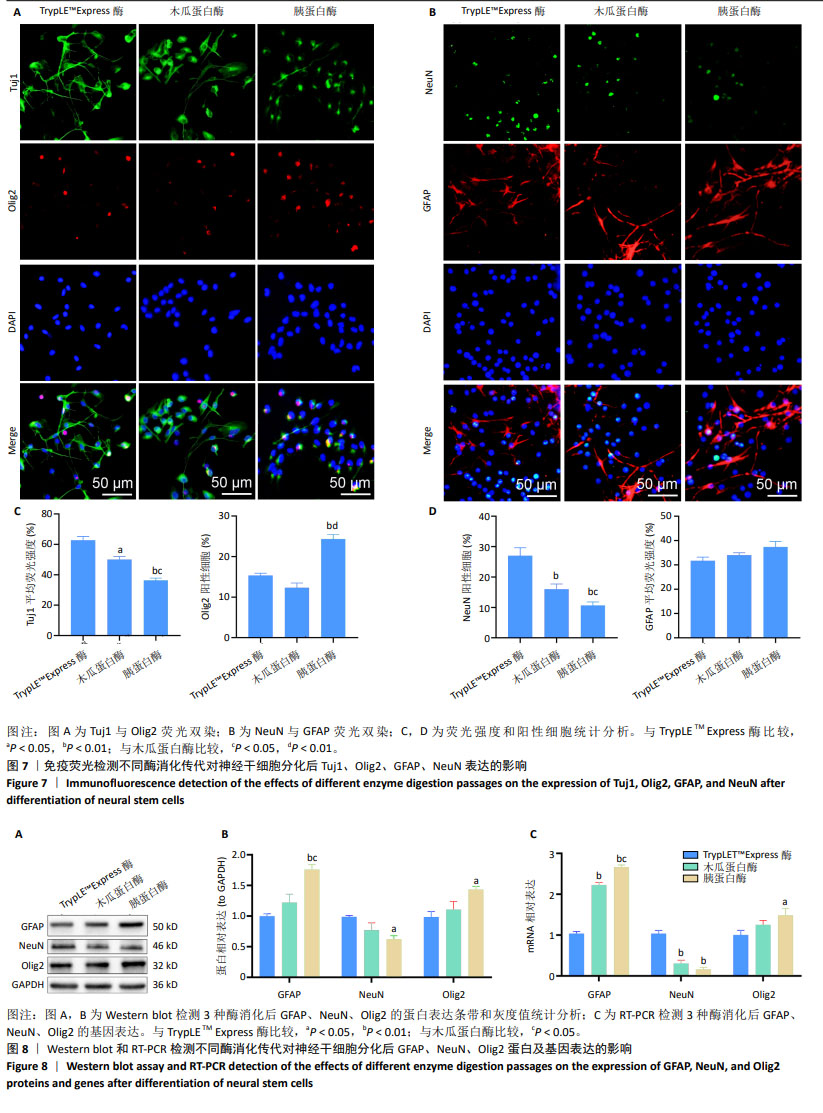
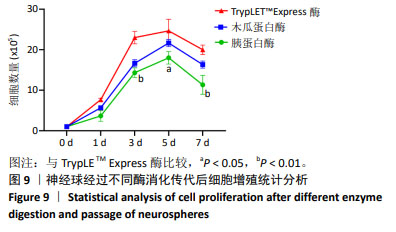
[1] HU X, XU W, REN Y, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):245.
[2] TIAN T, ZHANG S, YANG M. Recent progress and challenges in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Protein Cell. 2023;14(9):635-652.
[3] GILBERT EAB, LAKSHMAN N, LAU KSK, et al. Regulating Endogenous Neural Stem Cell Activation to Promote Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Cells. 2022;11(5):846.
[4] GONZALEZ R, HAMBLIN MH, LEE JP. Neural Stem Cell Transplantation and CNS Diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2016;15(8):881-886.
[5] DE FRERIA CM, VAN NIEKERK E, BLESCH A, et al. Neural Stem Cells: Promoting Axonal Regeneration and Spinal Cord Connectivity. Cells. 2021;10(12):3296.
[6] GUO W, ZHANG X, ZHAI J, et al. The roles and applications of neural stem cells in spinal cord injury repair. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022; 10:966866.
[7] XUE W, FAN C, CHEN B, et al. Direct neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells for spinal cord injury repair. Stem Cells. 2021;39(8):1025-1032.
[8] 金元植,戎鑫,刘浩.外伤性脊髓损伤不同时期行干细胞移植治疗的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(6):721-726.
[9] 杨昊南,刘玲,于才勇,等.神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的临床研究现状及存在的问题[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(9):846-851.
[10] GUO JJ, SU RB, WU HT, et al. New Insights into the Role of Mild Hypoxia in Regulating Neural Stem Cell Characteristics. Stem Cells Dev. 2024;33(13-14):333-342.
[11] CHO SK, GWON S, KIM HA, et al. Abnormal Development of Neural Stem Cell Niche in the Dentate Gyrus of Menkes Disease. Int J Stem Cells. 2022;15(3):270-282.
[12] APÓSTOLO N, DE WIT J. Compartmentalized distributions of neuronal and glial cell-surface proteins pattern the synaptic network. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2019;57:126-133.
[13] DENG Q, TAN YS, CHEW LY, et al. Msps governs acentrosomal microtubule assembly and reactivation of quiescent neural stem cells. EMBO J. 2021;40(19):e104549.
[14] 张玲娣,赵亮,由涌,等.新生SD大鼠原代海马组织中神经干细胞的培养和鉴定[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2023,49(3):795-801.
[15] HUGNOT JP. Isolate and culture neural stem cells from the mouse adult spinal cord. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1059:53-63.
[16] PARK D, XIANG AP, MAO FF, et al. Nestin is required for the proper self-renewal of neural stem cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28(12):2162-2171.
[17] DARABI S, TIRAIHI T, RUINTAN A, et al. Polarized neural stem cells derived from adult bone marrow stromal cells develop a rosette-like structure. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013;49(8):638-652.
[18] SOMREDNGAN S, THEERAKITTAYAKORN K, NGUYEN HT, et al. The Efficiency of Neurospheres Derived from Human Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury Regeneration in Rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):3846.
[19] MARQUES BL, MACIEL GF, BRITO MR JÚNIOR, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of stem cell differentiation: Biotechnological applications for neurogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023;144:11-19.
[20] KAHROBA H, RAMEZANI B, MAADI H, et al. The role of Nrf2 in neural stem/progenitors cells: From maintaining stemness and self-renewal to promoting differentiation capability and facilitating therapeutic application in neurodegenerative disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;65:101211.
[21] BRISCOE J, NOVITCH BG. Regulatory pathways linking progenitor patterning, cell fates and neurogenesis in the ventral neural tube. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008;363(1489):57-70.
[22] ZHOU QZ, ZHANG G, LONG HB, et al. Effect of spinal cord extracts after spinal cord injury on proliferation of rat embryonic neural stem cells and Notch signal pathway in vitro. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7(7):562-567.
[23] 董龙家,丁家秀,史学形,等.脊髓损伤后内源性神经干细胞增殖与Bcl-2的相关性研究[J].贵州医药,2018,42(3):259-262.
[24] 李孔平,彭林辉,左夏林,等.神经干细胞移植在缺血性卒中治疗中的作用[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2022,19(11):778-782.
[25] 李瑞鑫,苏刚,刘骥飞,等.干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤神经保护作用的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(10): 1634-1640.
[26] 郭文文,赵亚,白敏,等.神经干细胞移植在神经退行性疾病中的研究进展[J].中国实验动物学报,2022,30(2):274-282.
[27] KIM SW, WOO HJ, KIM EH, et al. Neural stem cells derived from human midbrain organoids as a stable source for treating Parkinson’s disease: Midbrain organoid-NSCs (Og-NSC) as a stable source for PD treatment. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;204:102086. |