中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (19): 4111-4121.doi: 10.12307/2025.072
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
针刺联合神经干细胞修复脊髓损伤的科学依据
黄晓萌1,2,张芝兰1,尚文雅1,黄 靖1,韦慧麟1,李 冰2,任亚锋2
- 1河南中医药大学康复医学院,河南省郑州市 450046;2河南中医药大学第一附属医院,河南省郑州市 450000
-
收稿日期:2024-02-21接受日期:2024-04-27出版日期:2025-07-08发布日期:2024-09-13 -
通讯作者:任亚锋,博士,主任医师,硕士生导师,河南中医药大学第一附属医院,河南省郑州市 450000 -
作者简介:黄晓萌,女,1998年生,河南省周口市人,汉族,河南中医药大学在读硕士,主要从事脊髓损伤后常见功能障碍的康复治疗研究。 -
基金资助:河南省中医药科学研究专项课题(2022JDZX015,2021JDZY022),项目负责人:任亚锋
Scientific basis for acupuncture combined with neural stem cells for repairing spinal cord injury
Huang Xiaomeng1, 2, Zhang Zhilan1, Shang Wenya1, Huang Jing1, Wei Huilin1, Li Bing2, Ren Yafeng2
- 1School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-21Accepted:2024-04-27Online:2025-07-08Published:2024-09-13 -
Contact:Ren Yafeng, PhD, Chief physician, Master's supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Huang Xiaomeng, Master candidate, School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Special Project, Nos. 2022JDZX015, 2021JDZY022 (to RYF)
摘要:
文题释义:
神经干细胞:该细胞分布于神经系统,具有自我更新与复制潜能,并能分化成神经元、少突胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞等,具有易获得、分化潜力大及实验技术成熟等特点,在治疗脊髓损伤方面具有巨大的应用前景。脊髓损伤:是一种严重的神经系统损伤,通常发生在胸腰段。这种损伤会导致损伤平面以下的运动、感觉、括约肌和自主神经功能障碍,严重影响患者的日常生活和社会参与能力。
摘要
背景:脊髓损伤是由创伤性或非创伤性事件引起的一种神经系统疾病,常导致损伤节段以下严重功能障碍。近年来,神经干细胞移植被认为在调控脊髓损伤后的炎症反应、抑制胶质瘢痕的过度增生以及促进神经再生方面具有显著的治疗潜力。
目的:综述并讨论针刺及神经干细胞移植疗法在抑制脊髓损伤诱导的继发性损伤中的潜在作用机制,深入探讨其治疗脊髓损伤的科学依据。
方法:以“脊髓损伤,针刺,神经干细胞,SDF-1α/CXCR4轴”为中文检索词,以“Spinal cord injury,acupuncture,neural stem cells,SDF-1α/CXCR4 axis”为英文检索词,分别检索PubMed、Elsevier、万方及中国知网数据库,最终纳入96篇文献,汇总分析了针刺联合神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的相关研究成果,总结了这一联合疗法在治疗脊髓损伤后继发性损伤中的相关机制。
结果与结论:①基质细胞衍生因子1α(stromal-derived factor 1α,SDF-1α)/CXC趋化因子受体4(chemokine receptor 4,CXCR4)轴在神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤中扮演着至关重要的角色,该信号传导机制不仅影响神经干细胞的迁移、增殖和分化,更是决定干细胞归巢至损伤部位效率的关键因素。因此,针对该轴线的调控,对于提升脊髓损伤的治疗效果具有重要意义。②针刺作为一种传统中医疗法,在脊髓损伤的继发性损伤调控中展现出独特的优势,它能够通过调节炎症反应、抑制细胞凋亡、改善微循环、减少神经胶质瘢痕形成以及对抗氧化应激等多种途径,有效减轻脊髓损伤后的继发性损伤。③针刺还能够影响SDF-1α/CXCR4轴的表达与功能,从而增强神经干细胞的归巢和存活能力,促进神经再生和功能恢复。④结合针刺与干细胞移植的疗法,是一种创新且较好的脊髓损伤治疗策略,适用于修复神经环路,它结合了传统中医的智慧与现代生物技术的优势,为脊髓损伤患者提供了新的治疗选择。然而,目前这种联合疗法仍处于研究和探索阶段,其长期疗效和安全性尚需进一步验证。⑤综合而言,针刺及神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤具有巨大的临床应用潜力,但仍需深入研究和优化治疗方案。未来,期待通过更多的临床试验和机制研究,进一步揭示这一疗法的疗效机制和最佳适应证,为脊髓损伤患者带来更好的康复希望和更高效的治疗效果。
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-9926-8953 (黄晓萌)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄晓萌, 张芝兰, 尚文雅, 黄 靖, 韦慧麟, 李 冰, 任亚锋. 针刺联合神经干细胞修复脊髓损伤的科学依据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(19): 4111-4121.
Huang Xiaomeng, Zhang Zhilan, Shang Wenya, Huang Jing, Wei Huilin, Li Bing, Ren Yafeng. Scientific basis for acupuncture combined with neural stem cells for repairing spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4111-4121.
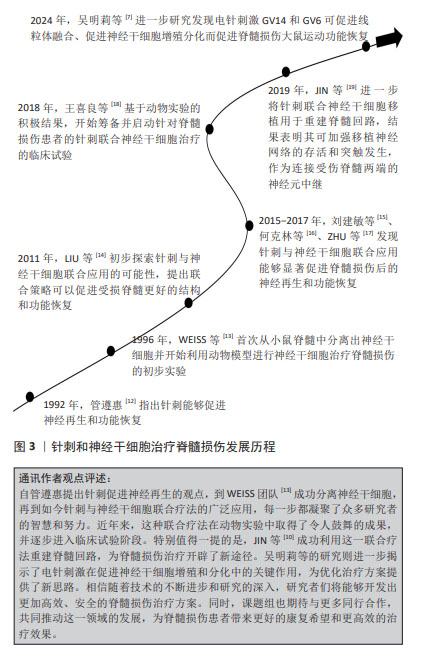
2.2 脊髓损伤治疗的关键环节:减轻继发性损伤以优化神经修复环境 在临床上,原发性损伤导致神经元立即死亡,无法治疗,而继发性损伤被认为是修复受损神经元的决定性因素[20]。这些继发性损伤包括血脊髓屏障的破坏、炎症性细胞的浸润以及细胞内离子稳态失衡,尤其是钙离子浓度的异常增加,这不仅加剧了脊髓损伤的程度,还严重影响了受损神经的修复与再生。此外,钙离子浓度的增加会激活钙依赖蛋白酶,进而导致线粒体功能障碍同时,兴奋性氨基酸的释放又会引发兴奋性毒性反应,最终导致神经元和胶质细胞的凋亡[6]。在脊髓损伤的后期,这些凋亡细胞会形成神经胶质瘢痕和囊腔,成为轴突再生的物理障碍[8]。因此,通过减轻继发性损伤的程度,为受损神经的修复创造更好的环境不仅是早期治疗脊髓损伤的关键,也是神经干细胞移植疗法的重要研究方向[21-28],见表1。
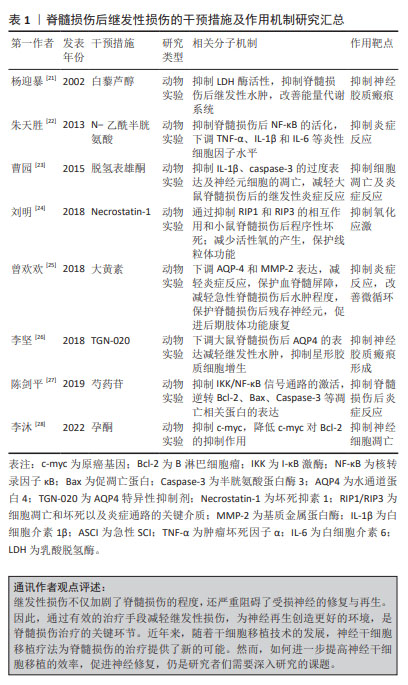
2.3 针刺改善脊髓损伤受损环境,促进神经再生
2.3.1 针刺缓解炎症反应,减少继发性损伤 RNA结合蛋白HuR,在神经再生、细胞凋亡和与中枢神经系统相关的各种疾病中起着关键作用[29]。研究表明,脊髓损伤后,HuR从细胞核转移到细胞质,并且正向调节星形胶质细胞中关键炎症递质的分泌[30]。通过抑制HuR,可以减少炎性细胞因子的分泌,进而减轻脊髓损伤后的炎症反应,这无疑为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了新的思路[29,31]。而HuR的下游因子锌指蛋白Krüppel样转录因子9(Krüppel-like factors,KLF9)在维持脊髓网络中的神经元敏化和疼痛所需突触变化方面的作用,进一步强调了HuR/KLF9轴在脊髓损伤过程中的重要性[32]。通过调控这一轴,可推测有可能在多个层面影响脊髓损伤的进展,包括减轻炎症、促进神经再生以及减少神经元凋亡[33-34]。此外,电针作为一种传统中医疗法,在调节HuR/KLF9轴方面的作用不容忽视。电针能够通过下调HuR和KLF9的表达,抑制促炎细胞因子和凋亡因子的产生,从而发挥抗炎、镇痛和促神经再生的作用[11]。此发现不仅为电针在脊髓损伤治疗中的应用提供了理论基础,也为其他中枢神经系统疾病的治疗提供了新的策略。除了HuR/KLF9轴外,NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3(NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3,NLRP3)炎症小体在中枢神经系统疾病中的作用也日益受到关注。通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体的激活,可以有效缓解神经炎症,进而改善疾病的进展[35]。而针刺在抑制NLRP3炎症小体通路方面的作用,为研究者们提供了一种非药物性的治疗选择,具有广阔的应用前景。因此,通过深入研究和应用电针等治疗方法,研究者们可以更有效地调节HuR/KLF9轴和NLRP3炎症小体,缓解炎症反应,为中枢神经系统疾病的治疗开辟新的途径。
2.3.2 针刺抑制神经元凋亡,发挥神经保护作用 神经元凋亡是脊髓损伤的重要病理机制[36-37],其会阻断脊髓损伤后神经传导通路,加重继发性损伤。因此,抑制细胞凋亡是促进脊髓损伤恢复的关键[38]。在众多治疗手段中,针刺,特别是电针,展现出了在抑制神经元凋亡方面的独特优势。研究表明,电针可以通过调控凋亡相关因子的表达,如增加抗凋亡因子B淋巴细胞瘤2(B-cell lymphoma-2,Bcl-2)表达,同时下调凋亡因子caspase-3和Bax的表达,来有效地抑制脊髓神经元的凋亡过程[39]。这一发现不仅揭示了电针治疗脊髓损伤的内在机制,也为其在临床实践中的应用提供了坚实的理论基础。此外,电针还能够通过降低脊髓损伤大鼠模型损伤区域N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid,NMDA)亚基NR1和NR2A的表达,来减轻兴奋性氨基酸的毒性作用,从而进一步发挥神经保护作用[40-41]。这一发现不仅拓宽了研究者们对电针治疗脊髓损伤作用机制的认识,也为其在治疗其他神经系统疾病中的应用提供了启示。综上所述,针刺通过多种机制减少神经细胞凋亡,发挥神经保护作用,为其临床应用提供了科学依据。
2.3.3 针刺改善微循环功能障碍 在脊髓损伤后会出现一系列的病理变化,包括血管破裂、出血、血流量减少和毛细血管栓塞等,这些变化导致血-脊髓屏障受到破坏,引发炎症细胞浸润和脊髓组织水肿,进而导致微循环功能障碍[42-43]。针刺治疗在改善微循环方面发挥了重要作用。临床研究显示,针刺特定穴位能够显著调节毛细血管的直径和充盈程度,这对于改善微循环至关重要[44]。在动物实验中,针刺更是通过促进血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)、血管生成素1(angiopoietins
1,Ang-1)、血管生成素2(angiopoietins 2,Ang-2)等血管生长因子的表达,有效改善出血状况[45],从而缓解了脊髓损伤后的微循环障碍,这一过程与EphB4/EphrinB2介导的Src/PI3K信号通路的调节密切相关[46]。值得一提的是,针刺治疗改善微循环的机制并不仅限于对血管的直接作用。HONG等[47]的研究进一步揭示了针刺通过抑制炎症反应来调节微循环的新机制。细胞质磷脂酶A2(cytosolic phospholipase A2,cPLA2)活性和前列腺素E2(prostaglandin E2,PGE2)作为炎症反应中的关键因子,其活性的降低不仅有助于减轻炎症反应,更能有效地改善微循环,从而为神经细胞的存活和功能恢复创造更有利的环境。综上所述,针刺治疗在改善脊髓损伤后的微循环方面具有显著效果,其机制多样且深入。通过调节血管状态、促进血管生长因子表达以及抑制炎症反应等途径,针刺能够有效地改善微循环障碍,减少神经元的凋亡,促进功能的恢复。这为研究者们在未来研究和应用针刺治疗脊髓损伤提供了更为丰富的理论依据和实践指导。
2.3.4 针刺抑制神经胶质瘢痕形成,促进轴突再生 脊髓损伤后,星形胶质细胞增殖并分泌多种细胞外基质,形成神经胶质瘢痕。一方面,它将受伤的组织与健康组织隔开,限制病变扩张并保护周围组织;另一方面,它还通过分泌一些生长抑制因子,如硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖,形成化学屏障,限制了神经元再生,阻碍神经通路恢复[48-49]。针刺治疗作为一种传统的中医疗法,近年来在脊髓损伤治疗领域展现了其独特的优势。DING等[50-52]的研究发现,电针可以有效下调硫酸软骨素蛋白多糖蛋白这一星形胶质细胞的重要组成部分的表达,从而减少这种化学屏障的生成,为轴突的再生创造了有利条件。这不仅有助于减轻脊髓损伤后的病理改变,更能够促进神经功能的恢复,提高患者的生活质量。胶质纤维酸性蛋白不仅可以形成物理屏障隔离受损组织,同时也阻碍了轴突生长[53]。研究表明,火针针灸和电针可以降低胶质纤维酸性蛋白的表达,这有助于减少神经胶质瘢痕的形成,为轴突的生长创造有利条件[54]。同时,这些针刺方法还可以促进神经干细胞的分化,有助于损伤部位的修复和神经功能的恢复[55]。综上所述,针刺治疗可以通过多种机制调节神经胶质瘢痕的形成和神经干细胞的分化,为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了科学依据。
2.3.5 针刺减少活性氧产生,抑制氧化应激 脊髓损伤后,活性氧形成的增多及其随后的氧化应激成为神经元凋亡和功能障碍的关键诱因[56]。因此,针对脊髓损伤后的氧化应激损伤和抗氧化治疗构成了改善脊髓损伤继发性损伤策略的重要部分。脊髓内富含不饱和脂肪酸并拥有高活性的氧化代谢,然而,其神经元的抗氧化能力相对不足且再生能力受限。这种内在的脆弱性易导致氧化代谢产物的积累和抗氧化剂的过度消耗,从而加剧了脊髓损伤所介导的氧化应激损伤,这一过程进一步触发了小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的活化,以及炎性细胞因子的释放,最终导致神经元细胞的死亡[57-58]。研究表明,JNK/p66 Shc信号通路的激活可以促进活性氧的产生,而叉头转录因子(Forkhead box O3,FoxO3a)则能保护细胞免受氧化应激的损伤。然而,在脊髓损伤后,激活的JNK/p66Shc信号通路不仅促进了活性氧的生成,还抑制了FoxO3a的抗氧化作用,从而加剧了氧化应激损伤[59-60]。值得注意的是,针刺已被证实能够通过减弱p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase,p38MAPK)介导的小胶质细胞活化和炎症反应,以及抑制JNK/p66Shc介导的活性氧生成和氧化应激损伤,发挥神经保护作用[58]。
此外,脊髓损伤后炎症细胞会释放过量的活性氧和氮物质[61],这些物质能够造成DNA氧化损伤、蛋白质氧化和脂质过氧化[6],进而加剧神经元和神经胶质细胞的坏死和凋亡[62]。载脂蛋白E(apolipoprotein E,ApoE)具有抗炎、抗氧化和抗凋亡特性[63],ApoE的缺失会加剧炎症反应和氧化应激,增加神经凋亡,从而延缓脊髓损伤后运动和神经功能的恢复[64]。研究表明,ApoE能够诱导核转录因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2,Nrf2)的抗氧化信号激活,这在脊髓损伤后抗氧化过程中起着至关重要的作用[65]。然而,在脊髓损伤后,ApoE的水平下降会导致Nrf2和血红素氧合酶1(heme oxygenase-1,HO-1)的表达降低,进而增加氧化应激[64]。针刺不仅能够上调ApoE的表达,还能够通过激活Nrf2/HO-1抗氧化信号通路,增强细胞对氧化应激的抵抗能力。同时,针刺还能够抑制炎症相关因子如白细胞介素1β和核转录因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)的表达,从而减轻炎症反应,为神经元的再生和修复创造了更有利的环境[66-67]。综上所述,针刺作为一种有效的治疗手段,在脊髓损伤后的抗氧化和抗炎过程中发挥着重要作用,为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了新的思路和策略。见表2。
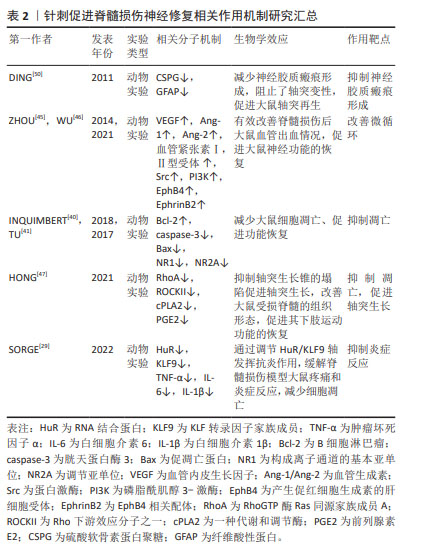

2.4 神经干细胞在脊髓损伤治疗中的神经保护与修复作用 脊髓损伤是由外力导致神经元回路的严重破坏,神经元数量大量减少,并且成年神经元的再生能力有限,从而造成脊髓神经功能缺损。在这种情况下,干细胞移植,尤其是神经干细胞移植,可以促进神经修复、减少神经功能的缺损,成为了治疗脊髓损伤的一种充满希望的方法。现代研究已经揭示了神经干细胞在神经保护方面的关键作用[68]。神经干细胞通过抑制炎症反应和细胞凋亡,为受损神经元提供必要的保护。此外,神经干细胞与内源性吞噬细胞之间的连接偶联有助于建立新的神经通路和清除受损部位的坏死组织,从而促进健康的神经细胞生长和修复,这种连接偶联为脊髓损伤患者带来了新的治疗希望。进一步的研究显示,神经干细胞不仅具有替代丢失的神经元和神经胶质细胞的潜力,而且能够促进轴突的双向生长和形成相互突触,这一过程在损伤后的脊髓分离节段之间建立新的中继连接,对于恢复神经系统的完整性和功能至关重要,为脊髓损伤患者提供了更好的康复前景[69]。
2.4.1 神经干细胞改善受损脊髓微环境,抑制炎症和神经元凋亡 神经干细胞在脊髓损伤治疗中的潜力已得到广泛认可。当神经干细胞迁移至病变区域时,它们能够显著改善受损脊髓的微环境。这一过程不仅通过调节免疫反应来降低炎症和神经元的凋亡,还抑制了继发性损伤,这为神经组织的修复创造了有利条件。此外,神经干细胞还能有效促进内源性神经干细胞的增殖和迁移,加速神经发生和增强神经再生,这些发现进一步证实了神经干细胞在脊髓损伤治疗中的积极作用[5]。CUSIMANO等[70]的研究进一步支持了神经干细胞移植在脊髓损伤治疗中的关键作用,他们发现,通过减少M1巨噬细胞和抑制炎症细胞浸润,神经干细胞有效地减轻了损伤部位的炎症反应,这为损伤脊髓的愈合创造了有利的环境。
2.4.2 神经干细胞促进神经元再生,抑制神经胶质瘢痕形成 神经干细胞移植在治疗脊髓损伤中展现出了巨大的潜力,其作用机制涉及多个层面。首先,神经干细胞能有效抑制神经胶质瘢痕的形成,这是脊髓损伤后阻碍轴突再生和神经功能恢复的关键病理改变,通过减少瘢痕组织的形成,神经干细胞为神经再生创造了更有利的环境。其次,神经干细胞能够替代受损的中枢神经系统神经元,促进新生神经元的生成,从而重建脊髓回路连接,减少凋亡,显著促进神经元的再生[71]。此外,神经干细胞还能改善微循环,为移植细胞的存活和分化提供良好的环境,进一步促进神经修复[72]。在炎症方面,神经干细胞具有抑制炎症的作用,有助于减轻脊髓损伤后的继发性损伤[70]。综上所述,神经干细胞移植通过抑制神经胶质瘢痕形成、促进神经元再生、改善微循环以及抑制炎症等多种机制,为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了新的思路和前景,有望成为未来脊髓损伤治疗的重要方向之一,为更多患者带来希望与康复,见表3。
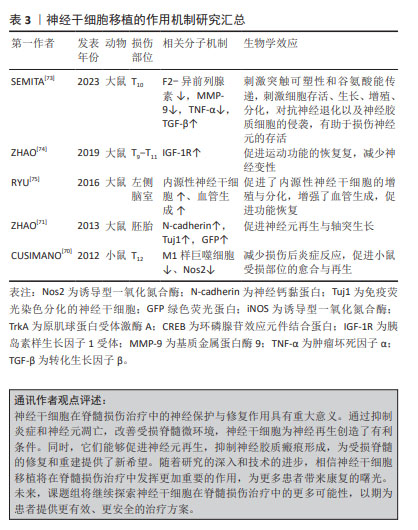
2.5 神经干细胞移植的关键因素——SDF-1α/CXCR4轴 神经干细胞是一种具有自我更新能力的多能干细胞,具有分化为神经元、星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞的潜力,足以提供大量神经组织细胞,为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了可能[76]。将神经干细胞移植到损伤部位,可以发挥多方面的治疗作用。首先,神经干细胞能够促进巨噬细胞的极化,从而有效调节炎症和免疫微环境[77];其次,神经干细胞能够分泌神经营养因子,改善受损神经的微环境,并刺激受损轴突实现再生[8];此外,神经干细胞还可以分化为少突胶质细胞,有助于髓鞘的形成,从而促进神经系统的修复和功能恢复[78]。这些作用机制以协同的方式增强神经干细胞移植后受损脊髓的可塑性和组织再生能力。因此,神经干细胞移植在脊髓损伤治疗中具有广阔的应用前景,有望为脊髓损伤患者带来更好的治疗结果。
神经发生是一个复杂的过程,涉及神经干细胞的增殖和分裂,以及定向祖细胞的生成。这些祖细胞会逐渐迁移到功能区域,经历可塑性变化,并与其他神经元建立突触联系,从而发挥神经功能。在这一过程中,SDF-1α/CXCR4信号传导起到了至关重要的作用[8]。SDF-1表达的增加能够促进神经干细胞向损伤部位的迁移,并维持其干细胞特性;此外,神经干细胞能够表达CXCR4,使其沿着SDF-1α的趋化因子梯度进行迁移,在这个过程中,神经干细胞可以与血管、胼胝体和胶质细胞形成支架,进而参与轴突生长、模式形成、突触功能以及重塑的调节[79]。
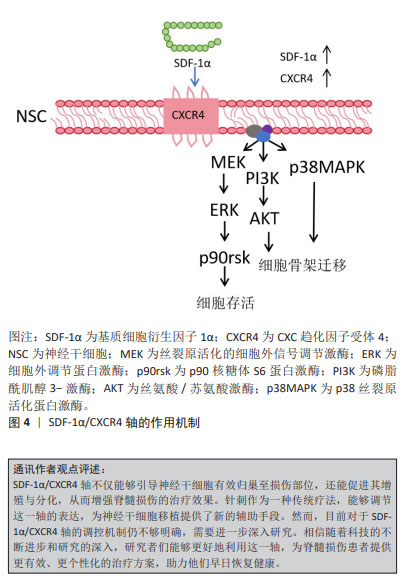
这些发现为深入理解神经干细胞在脊髓损伤修复中的作用提供了重要的理论依据。尽管神经干细胞移植在脊髓损伤治疗中具有巨大的潜力,但其归巢到损伤部位的效率不理想是限制治疗效果的主要瓶颈[80-81]。因此,提高干细胞归巢效率是干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的关键切入点。有研究显示,针刺能够调节SDF-1α/CXCR4轴,进而促进神经球的增殖、迁移和形成[82]。当SDF-1α与CXCR4结合后,引发细胞内信号转导,包括MAPK级联反应的激活,在这个级联反应中,MEK(MAPK/ERK激酶)首先被激活,进而磷酸化并激活其下游的ERK(细胞外信号调节激酶),激活的ERK随后磷酸化并激活P90核糖体S6蛋白激酶(RSK),这一过程涉及细胞存活、凋亡抑制和细胞周期调控,从而有助于神经干细胞的存活和增殖,并增强其归巢至损伤部位的能力。此外,神经干细胞表达的CXCR4是SDF-1α的特异性受体,大量的SDF-1α表达可能作为“路标”,通过二者之间的相互作用动员和引导神经干细胞的归巢[83]。
综上所述,通过深入研究SDF-1α/CXCR4信号传导机制以及如何通过针刺等手段调节这一机制,研究者们可以为脊髓损伤的治疗提供新的策略和思路,有望在未来实现更有效的神经再生和功能恢复,见图4。
2.6 针刺联合神经干细胞移植疗法治疗脊髓损伤潜力巨大 单纯针刺或神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤都具有巨大的潜力,而当这两种方法联合应用时,其治疗效果更是值得期待。目前,针刺联合神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤已经有了初步的探索性研究,主要集中在以下几个方面:抑制炎性反应、促进神经营养因子的表达、抑制神经细胞凋亡、提高神经干细胞的分化及治疗效率等。
2.6.1 针刺联合神经干细胞的研究进展 有研究显示,针刺与神经干细胞联合治疗确实能产生显著的效果[84]。这一创新策略不仅通过调控凋亡相关蛋白的表达,有效减少了神经细胞的凋亡,还通过改善受损组织的微环境,促进了神经元的再生和轴突的生长[85]。而LI等[86]进一步发现,电针能够促进从人类胚胎干细胞分化而来的内侧神经节隆起神经祖细胞的存活,并显著减轻脑缺血大鼠的学习和记忆障碍。这一积极效果部分归因于肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的表达受到抑制,以及海马体中血管内皮生长因子的表达增加和血管密度的增大,这些改变可以促进血管生成并抑制炎症反应,从而有助于移植的神经祖细胞的存活,并进一步提升移植治疗的疗效。值得一提的是,当针刺应用于受损的脊髓时,它可以诱导NT-3的合成与分泌,这一过程不仅可以显著增强移植到损伤或移植部位的TrkC过表达的神经干细胞和间充质干细胞的存活、分化和迁移能力,还能促使它们与现有的神经元回路进行整合,这一整合过程能够替换受伤的宿主神经元,改善受伤组织周围的微环境,刺激神经纤维的再生和髓鞘的形成;最终,这些改变会增强皮质运动诱发电位,从而恢复瘫痪肢体的运动功能[87-88]。综上所述,将针刺与干细胞移植相结合是脊髓损伤治疗的一种创新策略,具有巨大的临床应用潜力,值得进一步开发与测试。
2.6.2 针刺联合神经干细胞移植疗法的协同机制 神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的核心在于其分化成神经元以修复受损的神经环路。电针作为传统物理疗法,通过穴位刺激可调节机体的神经内分泌系统,进而促进内源性神经干细胞的增殖与分化,与神经干细胞移植结合时,电针能够进一步激活移植部位的微环境,为神经干细胞的存活、增殖和分化创造有利条件。ZHAO等[89]研究发现,当与神经干细胞移植结合时,电针能够进一步激活移植部位的微环境,为神经干细胞的存活和分化提供了必要的营养和生长因子。这种联合作用加速了神经干细胞向神经元的分化,更有效地补充了受损脊髓部位的神经元,促进了神经环路的重建。此外,电针还能改善损伤部位的血液循环,减轻炎症反应和水肿,为神经干细胞的移植和分化提供稳定环境,并促进移植的神经干细胞与宿主组织的融合及神经再生。同时,电针调节神经递质释放,改善神经传导功能,与神经干细胞移植结合,共同促进新神经环路的形成和受损脊髓功能的恢复。卫哲[90]研究发现,早期电针刺激能够促进星形胶质细胞的活化,发挥其神经保护作用;而在后期,电针能够抑制胶质纤维酸性蛋白的免疫反应性,促进神经功能的重塑,进一步改善神经传导和运动功能。JIN等[19]研究发现,电针治疗可以通过增加NT-3水平,并激活NT-3/TRKC/AKT通路来增强神经元的存活、神经元分化和突触连接;当电针联合神经干细胞治疗时,这种效果更为明显。这种联合治疗能够促进宿主轴突再生进入损伤/移植部位,重建与移植神经网络的突触连接,这有助于部分恢复脊髓神经回路,最终改善脊髓的神经传导以及瘫痪后肢的运动功能。
综上所述,电针联合神经干细胞治疗的协同机制在于通过电针调节神经内分泌系统、改善局部微环境和神经传导功能,结合神经干细胞移植直接补充受损神经元,共同促进神经环路的重建和功能恢复。这种联合治疗方法充分发挥了两者的优势,为脊髓损伤患者提供了更有效的康复策略。
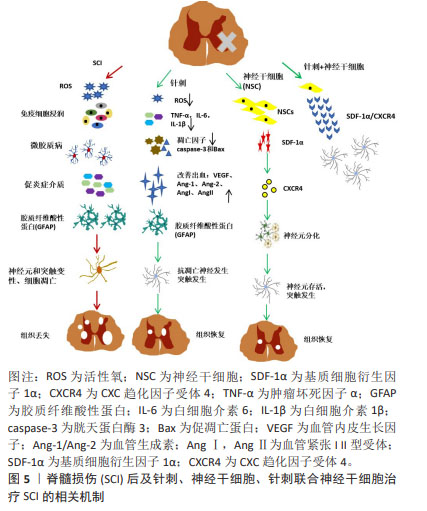
2.6.3 针刺增强SDF-1α/CXCR4轴作用,促进神经干细胞移植和分化效率 SDF-1α/CXCR4轴在神经干细胞移植过程中发挥关键作用,能够促进神经干细胞迁移至病变部位[8],对于其的深入研究可以作为提高神经干细胞移植效率的切入点。脊髓损伤模型相关研究发现,针刺可通过激活SDF-1α/CXCR4轴促进外源性神经干细胞迁移至损伤组织,提高神经干细胞移植的治疗效率[91]。还有相关基础研究表明,电针可通过调控SDF-1α/CXCR4轴改善脊髓损伤模型大鼠的神经功能,促进神经干细胞迁移分化[83]。如果在神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的早期介入针刺疗法,针刺可以激活脊髓损伤损伤部位中星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞,促进SDF-1在神经干细胞中的聚集,从而增强神经干细胞表达的CXCR4的梯度迁移,这可以发挥靶向治疗作用,促进轴突生长和突触功能的重塑,进一步提高单纯神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的效率及临床转化能力。总体来说,针刺通过调节SDF-1α/CXCR4轴促进干细胞的归巢作用,发挥干细胞自身的修复功能。这不仅能抑制损伤部位的继发性损伤级联反应、降低星形胶质细胞的活化、减少小胶质细胞的激活、调节炎性因子的表达、抑制炎性信号通路,还能促进神经细胞的修复、降低神经元和神经胶质的凋亡。这一科学依据为针刺联合神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤提供了有力的支持,见图5。
2.6.4 针刺联合神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的临床应用前景 近年来,针刺治疗脊髓损伤的临床应用逐渐受到医学界的关注,其独特的疗效已在多项研究中得到证实。针刺作为传统中医疗法,其疗效在脊髓损伤治疗中得到了多方面的验证。无论是芒针还是毫针,亦或是超声引导下的电针刺激,都展现出了在促进神经功能恢复方面的显著效果[92-93]。通过刺激穴位,针刺能够调节机体的神经内分泌系统,进而促进神经干细胞的增殖与分化,加速损伤部位的神经再生。与此同时,神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的研究也取得了长足进展。从人类神经干/祖细胞到中枢神经系统干细胞,这些细胞移植治疗不仅显示了良好的安全性和耐受性,还有助于受损脊髓的神经功能恢复,这些研究成果为脊髓损伤的修复提供了新的希望[94-95]。值得注意的是,当针刺与神经干细胞移植联合应用时,二者能够发挥协同效应,进一步提高治疗效果。这种联合疗法不仅加速了神经干细胞的增殖和分化,还促进了移植细胞的存活和与宿主组织的融合,从而更有效地补充了受损脊髓部位的神经元,促进了神经环路的重建[7,96]。然而,尽管针刺对神经干细胞增殖分化的影响已有较多研究,但关于神经干细胞联合针刺治疗脊髓损伤的研究仍然较少。因此,日后研究应该侧重于针刺联合神经干细胞移植的临床应用细节、疗效评估指标、并发症和长期转归等,以期为患者提供更有效、更安全的治疗方法,促进他们的神经修复和功能恢复。

| [1] 刘培培,贾露露,牛向宝,等.温阳通利灸联合膀胱功能训练治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱尿潴留临床研究[J].实用中医内科杂志, 2023,37(9):152-156. [2] 郭宁,秦合伟,李彦杰,等.近5年电针治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱机制研究进展[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022,29(9):153-156. [3] 毛治杰,罗珊,刘蓉,等.针刺治疗脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱随机对照试验Meta分析[J].亚太传统医药,2023,19(3):149-156. [4] HOSSEII SM, BORYS B, KARIMI-ABDOLZAEE S. Neural stem cell therapies for spinal cord injury repair: an update on recent preclinical and clinical advances. Brain. 2024;147(3):766-793. [5] 何宛俞,程乐平.干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的策略与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(19):3090-3096. [6] AHUJA CS, NORI S, TETREAULT L, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury-repair and regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S9-S22. [7] 吴明莉,段昭远,常文涛,等.电针督脉对脊髓损伤大鼠脊髓组织线粒体融合及神经干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].针刺研究,2024, 49(2):119-126. [8] 吴成林,郭德华,许洋,等.基于JAK2/STAT3信号通路探讨补阳还五汤联合骨髓间质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脊髓损伤的机制[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(7):1543-1546. [9] 刘成贺,刘强,王攀,等.SDF-1α/CXCR4轴在脊髓损伤干细胞治疗中的作用研究进展[J].山东医药,2023,63(19):107-110. [10] JU D, DONG C. The combined application of stem cells and three-dimensional bioprinting scaffolds for the repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1751-1758. [11] ZHANG J, XU J, LI S, et al. Electroacupuncture relieves HuR/KLF9-mediated inflammation to enhance neurological repair after spinal cord injury. eNeuro. 2023;10(11):ENEURO.0190-23.2023. [12] 管遵惠.针刺治疗脊髓损伤3则[J].云南中医学院学报,1992(1): 17-19. [13] WEISS S, DUNNE C, HEWSON J, et al. Multipotent CNS stem cells are present in the adult mammalian spinal cord and ventricular neuroaxis. J Neurosci. 1996;16(23):7599-7609. [14] LIU Z, DING Y, ZENG YS. A new combined therapeutic strategy of governor vessel electro-acupuncture and adult stem cell transplantation promotes the recovery of injured spinal cord. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(33):5165-5171. [15] 刘建敏,王福川,周亚净,等.电针刺激对神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤大鼠后肢功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(50): 8132-8138. [16] 何克林,孙连珠,张柳娟,等.夹脊电针对急性脊髓损伤大鼠神经干细胞分化趋势的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2016,34(12): 2849-2851. [17] ZHU Y, WU Y, ZHANG R. Electro-acupuncture promotes the proliferation of neural stem cells and the survival of neurons by downregulating miR-449a in rat with spinal cord injury. Excli J. 2017;16:363-374. [18] 王喜良,赵岩,肖宇龙.神经干细胞移植治疗人脊髓损伤的临床应用研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(30):14-15, 17. [19] JIN H, ZHANG YT, YANG Y, et al. Electroacupuncture facilitates the integration of neural stem cell-derived neural network with transected rat spinal cord. Stem Cell Reports. 2019;12(2):274-289. [20] LI F, WANG H, CHEN H, et al. Mechanism of ferroptosis and its role in spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. 2022;13:926780. [21] 杨迎暴,朴英杰.白藜芦醇对脊髓损伤后继发性脊髓水肿,乳酸脱氢酶及ATP酶活性的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2002,18(5):539-543. [22] 朱天胜,金伟,倪红斌,等.N-乙酰半胱氨酸对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后继发性脊髓损伤的保护作用[J].江苏医药,2013,39(10):1124-1126, 1112. [23] 曹园,易成腊,潘睿,等.脱氢表雄酮对大鼠脊髓损伤后继发性炎症反应的影响及其机制[J].山东医药,2015,55(13):22-24. [24] 刘明,杭春华,蔡智基,等.Necrostatin-1在小鼠脊髓损伤后继发性损伤中的作用[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2018,23(6):419-422. [25] 曾欢欢,黄英如,李子健,等.大黄素对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后继发脊髓水肿的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(4):378-384. [26] 李坚,李刚,郭卫东,等.TGN-020对大鼠脊髓损伤后继发性水肿和星形胶质细胞增生的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2018, 39(5):685-690,718. [27] 陈剑平,廖祥萍,李正南,等.芍药苷基于IKK/NF-κB信号通路对大鼠脊髓损伤后继发性损害的保护作用[J].广东医学,2019,40(18): 2578-2582. [28] 李沐,郭燕春,洪伟达.孕酮对脊髓外伤动物模型的治疗作用及其调控c-myc以拮抗脊髓外伤后继发性损伤[J].中国处方药,2022, 20(3):19-22. [29] SORGE RE, SI Y, NORIAN LA, et al. Inhibition of the RNA regulator HuR by SRI-42127 attenuates neuropathic pain after nerve injury through suppression of neuroinflammatory responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(5):1649-1661. [30] KWAN T, FLOYD CL, PATEL J, et al. Astrocytic expression of the RNA regulator HuR accentuates spinal cord injury in the acute phase. Neurosci Lett. 2017;651:140-145. [31] BORGONETTI V, GALEOTTI N. Intranasal delivery of an antisense oligonucleotide to the RNA-binding protein HuR relieves nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Pain. 2021;162(5):1500-1510. [32] MAMET J, KLUKINOV M, HARRIS S, et al. Intrathecal administration of AYX2 DNA-decoy produces a long-term pain treatment in rat models of chronic pain by inhibiting the KLF6, KLF9 and KLF15 transcription factors. Mol Pain. 2017;13:1744806917727917. [33] QU R, LIU J, FENG L, et al. Down-regulation of KLF9 ameliorates LPS-caused acute lung injury and inflammation in mice via reducing GSDMD expression. Autoimmunity. 2022;55(8):587-596. [34] APARA A, GALVAO J, WANG Y, et al. KLF9 and JNK3 Interact to Suppress Axon Regeneration in the Adult CNS. J Neurosci. 2017;37(40):9632-9644. [35] ZHANG HM, LUO D, CHEN R, et al. Research progress on acupuncture treatment in central nervous system diseases based on NLRP3 inflammasome in animal models. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1118508. [36] ABBASZADEH F, FAKHRI S, KHAN H. Targeting apoptosis and autophagy following spinal cord injury: therapeutic approaches to polyphenols and candidate phytochemicals. Pharmacol Res. 2020;160:105069. [37] SHI Z, YUAN S, SHI L, et al. Programmed cell death in spinal cord injury pathogenesis and therapy. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(3):e12992. [38] 赵继荣,蔡毅,陈文,等.中药治疗脊髓损伤相关机制研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2021,39(8):5-9. [39] 许明,艾坤,卓越,等.电针对骶上脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱大鼠尿流动力学及脊髓组织ERK/CREB/Bcl-2通路表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2024,31(4):100-105. [40] INQUIMBERT P, MOLL M, LATREMOLIERE A, et al. NMDA receptor activation underlies the loss of spinal dorsal horn neurons and the transition to persistent pain after peripheral nerve injury. Cell Rep. 2018;23(9):2678-2689. [41] TU WZ, CHEN WC, XIA W, et al. The regulatory effect of electro-acupuncture on the expression of NMDA receptors in a SCI rat model. Life Sci. 2017;177:8-14. [42] 李建花,罗林钊,邓强,等.中药治疗脊髓损伤后血-脊髓屏障功能障碍机制的研究进展[J].中医研究,2023,36(12):84-88 [43] 周逸敏,李宗洋,许翰勋,等.中药改善脊髓微环境修复血-脊髓屏障的机制研究进展[J].中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(9):80-83. [44] YEH BY, CHAO YL, CHEN YS, et al. Effect of acupuncture on capillary refill time in healthy adults: a clinical study. Microvasc Res. 2021;135: 104135. [45] ZHOU HJ, TANG T, ZHONG JH, et al. Electroacupuncture improves recovery after hemorrhagic brain injury by inducing the expression of angiopoietin-1 and -2 in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:127. [46] WU Y, HU R, ZHONG X, et al. Electric acupuncture treatment promotes angiogenesis in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion through EphB4/EphrinB2 mediated Src/PI3K signal pathway. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;30(3):105165. [47] HONG ES, YAO HH, MIN YJ, et al. The mechanism of electroacupuncture for treating spinal cord injury rats by mediating Rho/Rho-associated kinase signaling pathway. J Spinal Cord Med. 2021;44(3):364-374. [48] 潘志鹏,李思成,姚黎清.星形胶质细胞演变及相关信号通路对脊髓损伤后胶质瘢痕调节作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2022, 62(16):104-107. [49] TRAN AP, WARREN PM, SILVER J. The biology of regeneration failure and success after spinal cord injury. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(2):881-917. [50] DING Y, YAN Q, RUAN JW, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and electroacupuncture downregulate the inhibitor molecules and promote the axonal regeneration in the transected spinal cord of rats. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(4):475-491. [51] 尚文雅,任亚锋,李冰,等.脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡调控机制及治疗策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(11):1772-1779. [52] 吴永萌,马宁,李国婧,等.胶质纤维酸性蛋白在脑损伤中作用的研究进展[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2024,22(5):852-856. [53] 杨成,谭程方,杨祝歆,等.电针联合细胞移植对脊髓损伤大鼠轴突再髓鞘化的作用及神经调节蛋白Nrg1的影响[J].针刺研究, 2021,46(12):987-995. [54] ZHANG M, DAI Q, LIANG D, et al. Involvement of adenosine A1 receptor in electroacupuncture-mediated inhibition of astrocyte activation during neuropathic pain. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2018;76(11):736-742. [55] XU J, CHENG S, JIAO Z, et al. Fire needle acupuncture regulates Wnt/ERK multiple pathways to promote neural stem cells to differentiate into neurons in rats with spinal cord injury. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(3):245-255. [56] 赵继荣,蒋鹏,薛旭,等.人参皂苷抗脊髓损伤作用机制的研究进展[J/OL].中华中医药学刊,1-14[2024-04-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R.20240307.1045.010.html. [57] HAMANN K, SHI R. Acrolein scavenging: a potential novel mechanism of attenuating oxidative stress following spinal cord injury. J Neurochem. 2009;111(6):1348-1356. [58] CHENG M, WU X, WANG F, et al. Electro-acupuncture inhibits p66Shc-mediated oxidative stress to facilitate functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Mol Neurosci. 2020;70(12):2031-2040. [59] 尹刚,申国明,江爱娟,等.基于PKCβ/P66shc信号通路探讨针刺干预肥胖糖尿病大鼠氧化应激的作用机制[J].针刺研究,2021, 46(8):642-648, 678. [60] 张仙宏,魏萌萌,袁冬冬,等.转录因子FOXOs家族调控肿瘤生物学功能的研究进展[J].生理学报,2022,74(5):843-855. [61] WANG C, ZHANG L, NDONG JC, et al. Progranulin deficiency exacerbates spinal cord injury by promoting neuroinflammation and cell apoptosis in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):238. [62] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic spinal cord injury: an overview of pathophysiology, models and acute injury mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282. [63] 杨语晗,许明军,穆敬平.电针通过调节Notch3信号通路改善大脑中动脉闭塞小鼠海马神经元凋亡的作用机制[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2023,21(24):4530-4535. [64] YANG X, CHEN S, SHAO Z, et al. Apolipoprotein E deficiency exacerbates spinal cord injury in mice: inflammatory response and oxidative stress mediated by NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018; 12:142. [65] MOLAGODA IMN, LEE KT, CHOI YH, et al. Anthocyanins from hibiscus syriacus l. inhibit oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(1):42. [66] DAI N, TANG C, LIU H, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on inhibition of inflammatory response and oxidative stress through activating ApoE and Nrf2 in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Brain Behav. 2021;11(9):e2328. [67] LI X, YIN C, HU Q, et al. Nrf2 Activation mediates antiallodynic effect of electroacupuncture on a rat model of complex regional pain syndrome type-i through reducing local oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:8035109. [68] 王素平,钟亮,兰小磊,等.hUC-MSCs源性神经干细胞样细胞对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].青岛大学学报(医学版), 2023,59(5):709-713. [69] LU P, KADOYA K, TUSZYNSKI MH. Axonal growth and connectivity from neural stem cell grafts in models of spinal cord injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014;27:103-109. [70] CUSIMANO M, BIZIATO D, BRAMBILLA E, et al. Transplanted neural stem/precursor cells instruct phagocytes and reduce secondary tissue damage in the injured spinal cord. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 2):447-460. [71] ZHAO J, SUN W, CHO HM, et al. Integration and long distance axonal regeneration in the central nervous system from transplanted primitive neural stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(1):164-168. [72] 岳倩文,夏铂.神经干细胞在脊髓损伤修复机制中的实验研究进展[J].贵州医药,2020,44(6):859-862. [73] SEMITA IN, UTOMO DN, SUROTO H, et al. The mechanism of human neural stem cell secretomes improves neuropathic pain and locomotor function in spinal cord injury rat models: through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-matrix degradation, and neurotrophic activities. Korean J Pain. 2023;36(1):72-83. [74] ZHAO XM, HE XY, LIU J, et al. Neural stem cell transplantation improves locomotor function in spinal cord transection rats associated with nerve regeneration and IGF-1 R expression. Cell Transplant. 2019; 28(9-10):1197-1211. [75] RYU S, LEE SH, KIM SU, et al. Human neural stem cells promote proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells and enhance angiogenesis in ischemic rat brain. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(2): 298-304. [76] 仇静茹,林志,霍桂桃,等.神经干细胞移植治疗神经系统疾病的研究进展[J].药物评价研究,2023,46(12):2724-2728. [77] JI Z, JIANG X, LI Y, et al. Neural stem cells induce M2 polarization of macrophages through the upregulation of interleukin-4. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):148. [78] SANKAVARAM SR, HAKIM R, COVACU R, et al. Adult neural progenitor cells transplanted into spinal cord injury differentiate into oligodendrocytes, enhance myelination, and contribute to recovery. Stem Cell Reports. 2019;12(5):950-966. [79] SANCHEZ AB, MEDDERS KE, MAUNG R, et al. CXCL12-induced neurotoxicity critically depends on NMDA receptor-gated and L-type Ca2+ channels upstream of p38 MAPK. J Neuroinflammation. 2016; 13(1):252. [80] NI W, RAMALINGAM M, LI Y, et al. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effect of neural stem/progenitor cells in the central nervous system. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(4):866-885. [81] SONG AT, SINDEAUX RHM, LI Y, et al. Developmental role of macrophages modeled in human pluripotent stem cell-derived intestinal tissue. Cell Rep. 2024;43(1):113616. [82] 王泽然,巴特,桑博默,等.针灸干预神经干细胞治疗缺血性脑卒中机制探析[J].针灸临床杂志,2023,39(1):1-5. [83] STEWART AN, KENDZIORSKI G, DEAK ZM, et al. Co-transplantation of mesenchymal and neural stem cells and overexpressing stromal-derived factor-1 for treating spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2017;1672:91-105. [84] 介小素,侯玉晋.针刺联合神经干细胞移植对脑性瘫痪幼鼠模型的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(45):7309-7313. [85] 饶芳,林斌,钟伟平.穴位针刺和神经干细胞联合治疗实验性大脑中动脉闭塞性脑缺血损伤的机制研究[J].黑龙江医学,2020,44(7): 886-888. [86] LI J, CHEN L, LI D, et al. Electroacupuncture promotes the survival of the grafted human mge neural progenitors in rats with cerebral ischemia by promoting angiogenesis and inhibiting inflammation. Neural Plast. 2021;2021:4894881. [87] ZHANG YT, JIN H, WANG JH, et al. Tail nerve electrical stimulation and electro-acupuncture can protect spinal motor neurons and alleviate muscle atrophy after spinal cord transection in rats. Neural Plast. 2017;2017:7351238. [88] ZENG YS, DING Y, XU HY, et al. Electro-acupuncture and its combination with adult stem cell transplantation for spinal cord injury treatment: a summary of current laboratory findings and a review of literature. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28(5):635-647. [89] ZHAO L, LIU JW, KAN BH, et al. Acupuncture accelerates neural regeneration and synaptophysin production after neural stem cells transplantation in mice. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(12):1576-1590. [90] 卫哲.电针对脊髓损伤后小鼠神经功能重塑的机制研究[J].上海针灸杂志,2017,36(5):608-613. [91] CHEN Y, WEI Y, LIU J, et al. Chemotactic responses of neural stem cells to SDF-1α correlate closely with their differentiation status. J Mol Neurosci. 2014;54(2):219-233. [92] 张灿,全仁夫,柴乐,等.芒针针刺秩边、水道对脊髓损伤患者尿潴留的影响[J].中国针灸,2019,39(4):359-363. [93] SONG XZ, CHU XL, LIU T, et al. Case report: ultrasound-guided multi-site electroacupuncture stimulation for a patient with spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. 2022;13:903207. [94] SHIN JC, KIM KN, YOO J, et al. Clinical trial of human fetal brain-derived neural stem/progenitor cell transplantation in patients with traumatic cervical spinal cord injury. Neural Plast. 2015;2015:630932. [95] LEVI AD, OKONKWO DO, PARK P, et al. Emerging safety of intramedullary transplantation of human neural stem cells in chronic cervical and thoracic spinal cord injury. Neurosurgery. 2018;82(4):562-575. [96] DENG Q, MA L, YANG Y, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture stimulation on proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells in rats with spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(2):635-645. |
| [1] | 赵济宇, 王少伟. 叉头框转录因子O1信号通路与骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | 迟文鑫, 张存鑫, 高 凯, 吕超亮, 张科峰. 川陈皮素抑制BV2小胶质细胞炎症反应的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [3] | 赵瑞华, 陈思娴, 郭 杨, 石 磊, 吴承杰, 吴 毛, 杨光露, 张昊恒, 马 勇. 温肾通督方促进小鼠脊髓损伤的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [4] | 贺光辉, 原 杰, 柯燕琴, 丘小婷, 张晓玲. Hemin调控小鼠软骨细胞氧化应激的线粒体途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [5] | 何 波, 陈 文, 马岁录, 何志军, 宋 渊, 李金鹏, 刘 涛, 魏晓涛, 王威威, 谢 婧. 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的发病机制及治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [6] | 支 芳, 朱满华, 熊 伟, 林星镇. 腰椎间盘突出症模型大鼠疼痛的针刺干预[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [7] | 王荣荣, 黄玉珊, 李湘淼, 白金柱. 创伤性脊髓损伤急性期前列腺素E1对血管相关因子的调节和微循环功能的保护[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 958-967. |
| [8] | 逯冉冉, 周 旭, 张利杰, 杨新玲. 富马酸二甲酯减轻帕金森病模型鼠神经损伤的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [9] | 王瑜茹, 李思源, 徐 烨, 张雨蒙, 刘 杨, 郝慧琴. 汉黄芩素对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠关节炎症影响的内质网应激途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [10] | 杨 彬, 陶广义, 杨 顺, 许俊杰, 黄俊卿. 人工智能在脊髓神经损伤与修复领域研究热点的可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [11] | 郑伊桐, 汪永新, 刘 文, 阿木吉特, 秦 虎. 神经内镜下人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体鞘内移植修复脊髓损伤的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [12] | 司马鑫利, 刘丹平, 綦 惠. 二甲双胍修饰骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体调节软骨细胞的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [13] | 郭 佳, 任亚锋, 李 冰, 黄 靖, 尚文雅, 杨溢珂, 刘慧瑶. 负载miRNA间充质干细胞源外泌体改善脊髓损伤的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7827-7838. |
| [14] | 刘 璇, 丁雨晴, 夏若寒, 汪献旺, 胡淑娟. 运动防治胰岛素抵抗:Keap1/核因子E2相关因子2信号通路的作用与分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [15] | 张晓宇, 韦善文, 方佳炜, 倪 莉. 普鲁士蓝纳米粒子抗氧化恢复退变髓核细胞线粒体功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
近年来,随着干细胞疗法的兴起,特别是神经干细胞的应用,为脊髓损伤的治疗带来了新的希望。干细胞的多能性、自我更新能力以及富含营养因子的特性,使其在治疗脊髓损伤方面展现出显著的治疗潜力。尽管目前仍受限于多种因素,如干细胞的种类、移植方式、剂量、移植时间以及归巢效率等,但在基础研究中的应用表明,其在未来具有巨大的发展潜力[7-9]。
提高干细胞移植的治疗效率是促进其治疗脊髓损伤临床转化和应用的关键。在此背景下,文章创新性地将针刺疗法与神经干细胞移植相结合,探讨二者在脊髓损伤治疗中的协同作用。神经干细胞具有易获得、分化潜力大、实验技术成熟等特点,可为损伤部位提供新的细胞来源[10]。而针刺作为传统中医的瑰宝,已经在脊髓损伤的治疗中展现出其独特的优势,通过调节机体的内环境,针刺能够促进神经再生和功能恢复[11]。与已有的研究相比,文章不仅深入探讨了针刺和神经干细胞在脊髓损伤治疗中的机制,还重点分析了二者联合应用的潜力和优势。
通过综述相关文献,文章旨在揭示针刺在提高神经干细胞移植效率方面的作用,为脊髓损伤的临床治疗提供新的思路和策略。此外,文章还关注了基质细胞衍生因子1α(stromal-derived factor 1α,SDF-1α)/CXC趋化因子受体4(chemokine receptor 4,CXCR4)轴在神经干细胞移植中的关键作用,以及脊髓损伤后的继发性损伤级联反应对恢复过程的影响。通过综合分析针刺在调控这些过程中的作用,文章进一步阐明了针刺联合神经干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的可行性和有效性。
综上所述,文章的创新性在于将传统中医的针刺疗法与现代生物技术的神经干细胞移植相结合,为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了一种新的、有潜力的治疗策略。通过深入分析二者的作用机制和协同效果,文章旨在为脊髓损伤的临床治疗提供科学依据和理论支持。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年1月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时间范围重点为2010年1月至2024年1月,同时纳入少数远期经典及特别相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Elsevier、Springer Link、万方数据和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“脊髓损伤,针刺,神经干细胞,SDF-1α/CXCR4轴”为中文检索词,以“Spinal cord injury,acupuncture,neural stem cells,SDF-1α/ CXCR4 axis”为英文检索词分别进行检索。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述及荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 对于文献中的高价值参考文献,先阅读文题,再以标题进行检索,阅读摘要或全文。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed 数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初检文献4 593篇,其中PubMed数据库84篇,Elsevier数据库2 178篇,Springer Link数据库1 829篇,万方数据库159篇,中国知网数据库343篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 针刺与神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤相关研究。
1.2.2 排除标准 文献内容与主题无关的文章和重复性研究。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 初步检索获得4 593篇文章,其中英文文献4 091篇、中文文献502篇,排除重复文献及与文章相关性低的文献,结合手工检索及远期经典文献,最终纳入96篇文献进行综述分析,包括中文文献39篇、英文文献57篇,其中PubMed数据库49篇,Elsevier数据库5篇,Springer Link数据库3篇,万方数据库5篇,中国知网数据库34篇,见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 在文献检索过程中作者发现,神经干细胞移植被国内外大量学者广泛应用于脑出血、帕金森病、免疫、神经科学等领域,但在脊髓损伤领域中的研究较少,而且尚无全面、系统的文章将针刺联合神经干细胞移植在脊髓损伤领域的研究成果进行综合分析。该综述不仅关注了神经干细胞移植和针刺在脊髓损伤中的治疗作用,还深入探讨了它们对脊髓损伤后炎症、凋亡、微循环、神经胶质瘢痕和氧化应激等方面的影响。通过对这些关键病理过程的综合分析,文章更加全面、深入地阐述了针刺联合神经干细胞在脊髓损伤发病机制领域的应用,为理解脊髓损伤的发病机制和寻求新的治疗方法提供了重要的参考。此外,文章还注重分析了针刺及神经干细胞在脊髓损伤中相关的基因表达、细胞内信号通路以及调控网络的变化。这些深入分析有助于揭示针刺联合神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的分子机制,为未来的研究提供了方向。该文章是首篇对针刺联合神经干细胞移植在脊髓损伤中的研究进展进行综述的文献。
3.3 综述的局限性 尽管针刺治疗在脊髓损伤领域已展现出确切的疗效和安全性,通过减少继发性损伤的机制发挥神经保护作用,但针刺联合干细胞移植疗法目前仍处于初步探索阶段,亟待更深入的研究和验证。针刺能够增加SDF-1α的分泌,进而促进神经干细胞的靶向迁移,对脊髓损伤后的继发性损伤产生积极的影响,这为联合疗法的探索提供了新的视角和思路。然而文章仍存在一些未解决的问题:首先,当前的研究文献尚不全面,可能存在未被充分发掘的关键信息;其次,尽管近年来神经干细胞移植在脑出血等多种疾病中的研究逐渐受到关注,但其在针刺联合疗法中治疗脊髓损伤的应用仍显不足,研究深度和广度均有待加强;此外,由于篇幅所限,文章未能详尽列举所有相关的调节因子,也未深入探讨针刺联合神经干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的除继发性损伤以外的其他作用机制;同时,关于具体的操作手段和实际应用中的注意事项也未作详细阐述。
3.4 综述的重要意义 由于脊髓损伤发病机制较为复杂,目前临床上并没有确切的诊断标准与治疗手段。与此同时,随着干细胞移植技术的逐步发展与应用,将其应用于脊髓损伤相关研究,推动了人们对于脊髓损伤相关发病机制的认识和深入了解。神经干细胞移植的快速发展极大地促进了脊髓损伤研究中对于神经元再生与分子机制的理解。在这篇综述中,主要回顾分析近5年针刺联合神经干细胞在脊髓损伤中的应用,为脊髓损伤的诊断、预后和靶向治疗提供更多的循证医学依据。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 尽管目前神经干细胞移植技术仍存在局限性和挑战性,但其在中枢神经系统疾病中已经取得了一定的研究成果,专家组建议下一步应致力于提高神经干细胞的移植效率,并结合中医传统治疗手段,如针刺、艾灸和中药等,开展更为深入和系统的研究。首先,优化针刺联合神经干细胞移植的治疗方案,包括穴位选择、神经干细胞来源、培养方法和移植时机等,以提升疗效和患者舒适度。同时,针对不同患者亚群,研究其对该疗法的临床响应,为个体化治疗提供依据。此外,综合多种治疗手段,如药物治疗及物理治疗等,可望取得更好的疗效和生活质量提升。总之,针刺联合神经干细胞移植疗法具有临床转化的可行性和巨大潜力。未来应致力于优化治疗方案、规范操作流程、研究不同患者亚群的临床响应,推动该疗法在实际应用中的完善和发展,为脊髓损伤患者带来康复希望。随着技术改进和中医传统治疗手段的结合,对脊髓损伤发病机制的认知将更深入,个性化治疗方案和分子机制为基础的治疗策略将推动疾病治疗手段的进步。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
神经干细胞:该细胞分布于神经系统,具有自我更新与复制潜能,并能分化成神经元、少突胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞等,具有易获得、分化潜力大及实验技术成熟等特点,在治疗脊髓损伤方面具有巨大的应用前景。#br# 脊髓损伤:是一种严重的神经系统损伤,通常发生在胸腰段。这种损伤会导致损伤平面以下的运动、感觉、括约肌和自主神经功能障碍,严重影响患者的日常生活和社会参与能力。#br##br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
脊髓损伤是由创伤性或非创伤性事件引起的一种神经系统疾病,常导致损伤节段以下严重功能障碍。近年来,神经干细胞移植被认为在调控脊髓损伤后的炎症反应、抑制胶质瘢痕的过度增生以及促进神经再生方面具有显著的治疗潜力。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||