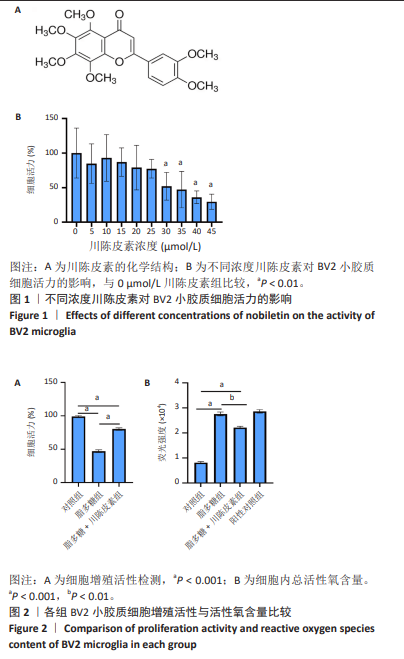
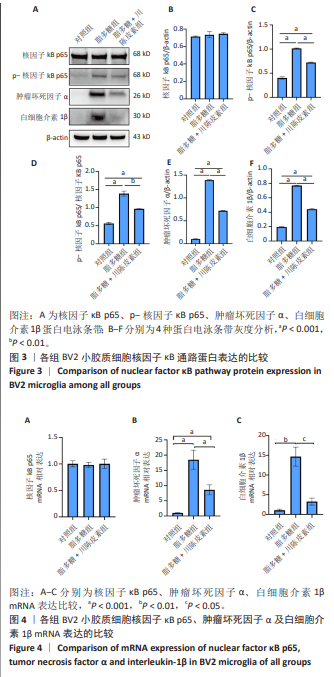
[1] ANJUM A, DA’IN YAZID M, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: Pathophysiology, Multimolecular Interactions, and Underlying Recovery Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533.
[2] STERNER RC, STERNER RM. Immune response following traumatic spinal cord injury: Pathophysiology and therapies. Front Immunol. 2023;13:1084101.
[3] KARSY M, HAWRYLUK G. Modern Medical Management of Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(9):65-72.
[4] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[5] ORR MB, GENSEL JC. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3): 541-553.
[6] GRAEBER MB, LI W, RODRIGUEZ ML. Role of microglia in CNS inflammation. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(23):3798-3805.
[7] YAN A, LIU Z, SONG L, et al. Idebenone Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Modulates Microglial Polarization in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Cells and MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:529.
[8] DING Y, CHEN Q. The NF-κB Pathway: a Focus on Inflammatory Responses in Spinal Cord Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(9): 5292-5308.
[9] LIU HT, ZHANG JJ, XU XX, et al. SARM1 promotes neuroinflammation and inhibits neural regeneration after spinal cord injury through NF-κB signaling. Theranostics. 2021;11(9):4187-4206.
[10] FAN L, DONG J, HE X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes reduce apoptosis and inflammatory response during spinal cord injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021;40(10):1612-1623.
[11] GUAN B, JIANG C. Design and development of 1,3,5-triazine derivatives as protective agent against spinal cord injury in rat via inhibition of NF-ĸB. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021;41:127964.
[12] ZHOU MM, ZHANG WY, LI RJ, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of Khayandirobilide A from Khaya senegalensis via NF-κB, AP-1 and p38 MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 and BV-2 cells. Phytomedicine. 2018;42: 152-163.
[13] WU X, SONG M, RAKARIYATHAM K, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of 4′-demethylnobiletin, a major metabolite of nobiletin. J Funct Foods. 2015;19(Pt A):278-287.
[14] MILEYKOVSKAYA E, YOO SH, DOWHAN W, et al. Nobiletin: Targeting the Circadian Network to Promote Bioenergetics and Healthy Aging. Biochemistry (Moscow). 2020;85(12-13):1554-1559.
[15] LIN Z, WU D, HUANG L, et al. Nobiletin Inhibits IL-1beta-Induced Inflammation in Chondrocytes via Suppression of NF-kappaB Signaling and Attenuates Osteoarthritis in Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:570.
[16] QI G, MI Y, FAN R, et al. Nobiletin Protects against Systemic Inflammation-Stimulated Memory Impairment via MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 2019; 67(18):5122-5134.
[17] NAKAJIMA A, YAMAKUNI T, HARAGUCHI M, et al. Nobiletin, a Citrus Flavonoid That Improves Memory Impairment, Rescues Bulbectomy-Induced Cholinergic Neurodegeneration in Mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 2019;105(1):122-126.
[18] DAI XJ, LI N, YU L, et al. Activation of BV2 microglia by lipopolysaccharide triggers an inflammatory reaction in PC12 cell apoptosis through a toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015;20(2):321-331.
[19] HE GB, HE YB, NI HW, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuroinflammation and microglia activation in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglia cells through targeting circ-Shank3/miR-140-3p/TLR4 axis. Eur J Histochem. 2023;67(3):3766.
[20] XIAO DM, YANG R, GONG L, et al. Plantamajoside inhibits high glucose-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and extracellular matrix accumulation in rat glomerular mesangial cells through the inactivation of Akt/NF-κB pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2021;41(1):45-52.
[21] YI LJ, LU Y, YU S, et al. Formononetin inhibits inflammation and promotes gastric mucosal angiogenesis in gastric ulcer rats through regulating NF-κB signaling pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2022;42(1):16-22.
[22] HE Y, RUGANZU JB, ZHENG Q, et al. Silencing of LRP1 Exacerbates Inflammatory Response Via TLR4/NF-κB/MAPKs Signaling Pathways in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(9):3727-3743.
[23] CHEONG MH, LEE SR, YOO HS, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Polygala tenuifolia root through inhibition of NF-κB activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;137(3):1402-1408.
[24] HAN Q, YUAN Q, MENG X, et al. 6 Shogaol attenuates LPS induced inflammation in BV2 microglia cells by activatin. Oncotarget. 2017;8(26): 42001-42006.
[25] TIMMERMAN R, BURM SM, BAJRAMOVIC JJ. Tissue-specific features of microglial innate immune responses. Neurochem Int. 2021;142: 104924.
[26] YANG X, XU S, QIAN Y, et al. Resveratrol regulates microglia M1/M2 polarization via PGC-1α in conditions of neuroinflammatory injury. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;64:162-172.
[27] YOU ZJ, YANG ZZ, CAO S, et al. The Novel KLF4/BIG1 Regulates LPS-mediated Neuro-inflammation and Migration in BV2 Cells via PI3K/Akt/NF-kB Signaling Pathway. Neuroscience. 2022;488:102-111.
[28] WALSH CM, WYCHOWANIEC JK, BROUGHAM DF, et al. Functional hydrogels as therapeutic tools for spinal cord injury: New perspectives on immunopharmacological interventions. Pharmacol Ther. 2022; 234:108043.
[29] JENDELOVA P. Therapeutic Strategies for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(10):3200-3202.
[30] XU S, WANG J, ZHONG J, et al. CD73 alleviates GSDMD‐mediated microglia pyroptosis in spinal cord injury through PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e269.
[31] ZHENG Y, QI S, WU F, et al. Chinese Herbal Medicine in Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(7):1593-1616.
[32] JIANG S, BABA K, OKUNO T, et al. Go-sha-jinki-Gan Alleviates Inflammation in Neurological Disorders via p38-TNF Signaling in the Central Nervous System. Neurotherapeutics. 2020;18(1):460-473.
[33] MARK PETRASH J, SHIEH B, AMMAR DA, et al. Diabetes-Independent Retinal Phenotypes in an Aldose Reductase Transgenic Mouse Model. Metabolites. 2021;11(7):450-460.
[34] WU A, YANG Z, HUANG Y, et al. Natural phenylethanoid glycosides isolated from Callicarpa kwangtungensis suppressed lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory response via activating Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages cell. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;258:112857.
[35] JIA R, LI Y, CAO L, et al. Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects of resveratrol on oxidative stress-induced liver damage in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2019;215: 56-66.
[36] LI BJ, WANG MM, CHEN S, et al. Baicalin Mitigates the Neuroinflammation through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglia. Biomed Res Int. 2022: 2022:3263446.
[37] YANG GL, LI SM, YUAN L, et al. Effect of nobiletin on the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in the synovial membrane of rats with arthritis induced by collagen. Food Funct. 2017;8(12):4668-4674.
[38] LI SY, LI X, CHEN FY, et al. Nobiletin mitigates hepatocytes death, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in a murine model of NASH through modulating hepatic oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Nutr Biochem. 2022; 100:108888. |