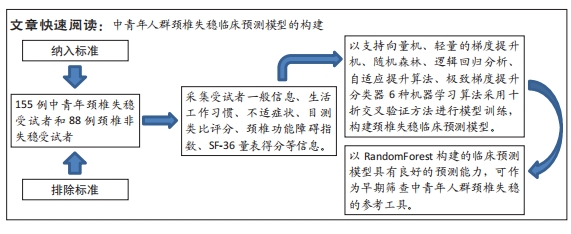
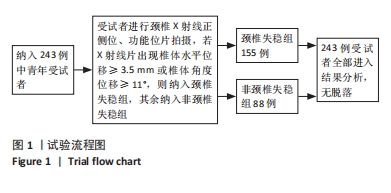
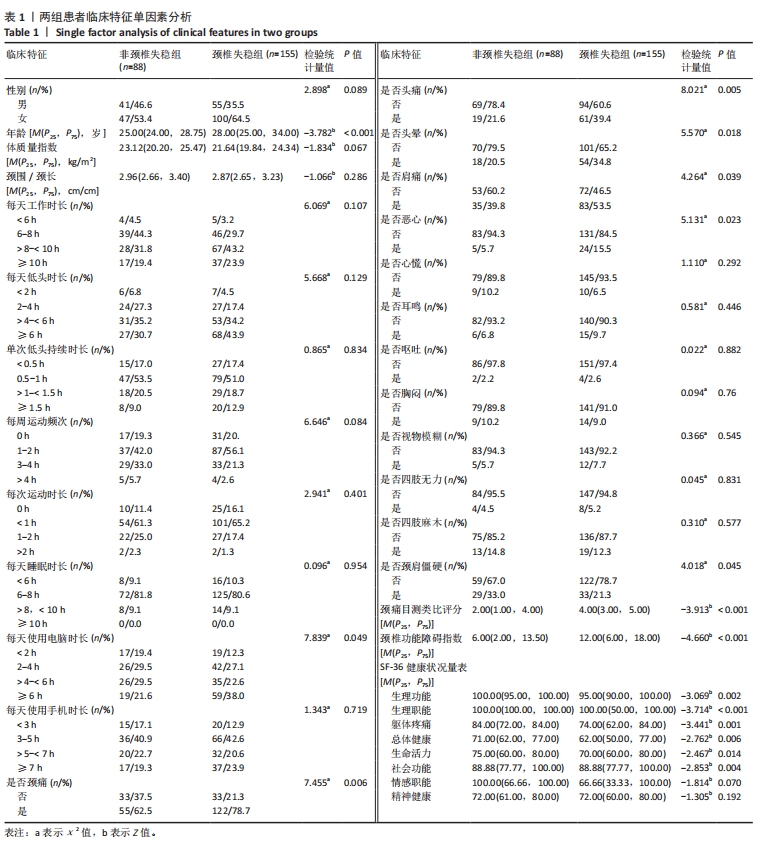
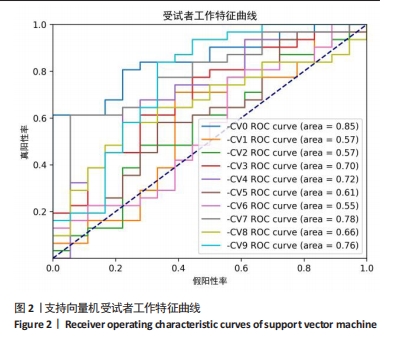
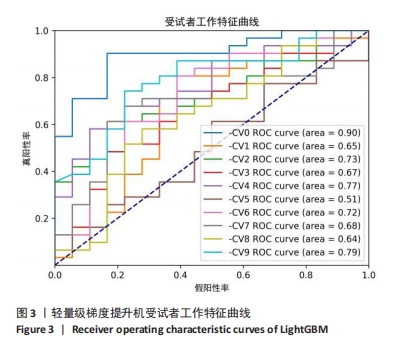
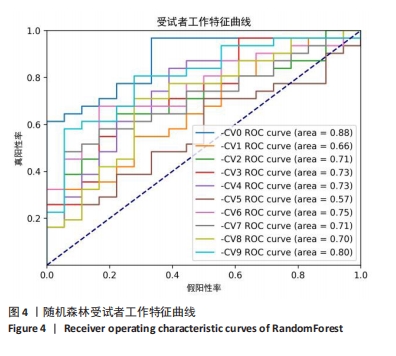
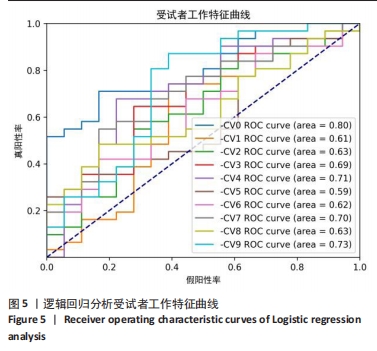
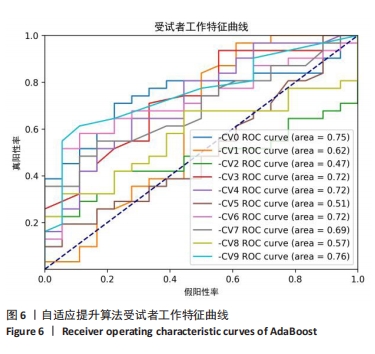
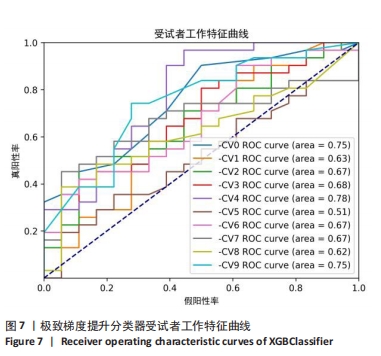
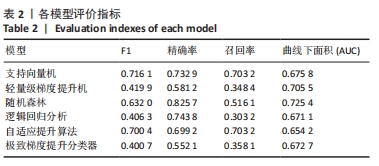
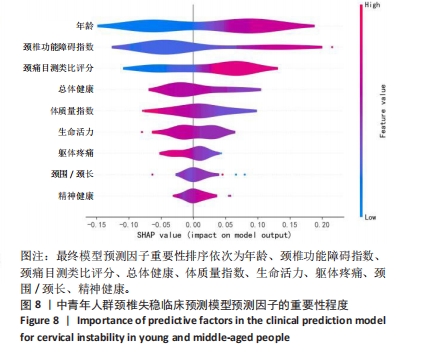
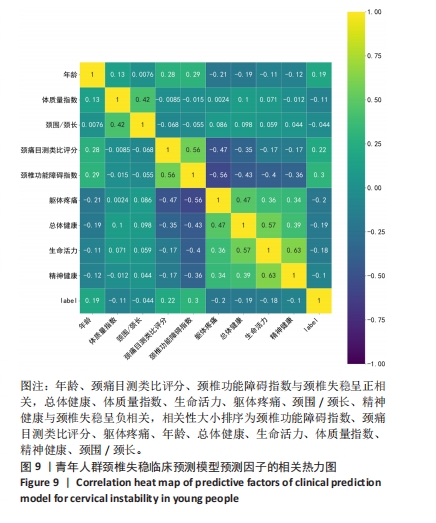
[1] GUI L, SAVINI R, MARTUCCI E, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of cervical instability. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1982;8(2):131-144.
[2] 曾恒,周红海.颈椎生物力学平衡变化的研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2008(2):62-63.
[3] 李帅林,吴嘉容,孔令军.退行性下颈椎失稳症的临床诊疗进展[J].河北中医,2017,39(10):1592-1596.
[4] ZHUANG L, WANG L, XU D, et al. Association between excessive smartphone use and cervical disc degeneration in young patients suffering from chronic neck pain. J Orthop Sci. 2021;26(1):110-115.
[5] BRAITMAN LE, DAVIDOFF F. Predicting clinical states in individual patients. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125(5):406-412.
[6] 高永祥,张晋昕.Logistic回归分析的样本量确定[J].循证医学,2018, 18(2):122-124.
[7] WHITE AA, JOHNSON RM, PANJABI MM, et al. Biomechanical analysis of clinical stability in the cervical spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975; 109(1):85-96.
[8] HE S, RENNE A, ARGANDYKOV D, et al. Comparison of an Emoji-Based Visual Analog Scale With a Numeric Rating Scale for Pain Assessment. JAMA. 2022;328(2):208-209.
[9] VAISHNAV AS, GANG CH, IYER S, et al. Correlation between NDI, PROMIS and SF-12 in cervical spine surgery. Spine J. 2020;20(3):409-416.
[10] WARE JE JR, SHERBOURNE CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30(6):473-483.
[11] ALBA AC, AGORITSAS T, WALSH M, et al. Discrimination and Calibration of Clinical Prediction Models: Users’ Guides to the Medical Literature. JAMA. 2017;318(14):1377-1384.
[12] STEYERBERG EW, VICKERS AJ, COOK NR, et al. Assessing the performance of prediction models: a framework for traditional and novel measures. Epidemiology. 2010;21(1):128-138.
[13] GBD 2021 NECK PAIN COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of neck pain, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024;6(3):e142-e155.
[14] SHIM GY, CHOI J, KIM HJ, et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Spine Pain, 1990-2019: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2024;105(3):461-469.
[15] 王向阳,高晔,龚福太,等.不同牵引角度治疗青少年颈椎失稳症120例[J].陕西医学杂志,2019,48(1):80-82.
[16] 张丽蓉,连红强,郝莹.慢性非特异性颈痛疼痛机制研究进展[J].医学研究与战创伤救治,2023,36(9):978-981.
[17] ZHUANG L, WANG L, XU D, et al. Association between excessive smartphone use and cervical disc degeneration in young patients suffering from chronic neck pain. J Orthop Sci. 2021;26(1):110-115.
[18] 王宏岩,何亮亮,窦智,等.颈源性头痛发病机制和诊断的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2023,29(9):685-690.
[19] ZHANG Y, ZHOU F, SUN Y. Assessment of health-related quality of life using the SF-36 in Chinese cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients after surgery and its consistency with neurological function assessment: a cohort study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015;13:39.
[20] BATTISTELLI M, MAZZUCCHI E, MUSELLI M, et al. The Role of Psychosomatic Traits in Tailored Workup for Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion-A Case Series. J Pers Med. 2024;14(5):454.
[21] TRELEAVEN J. The Role of the Cervical Spine in Dizziness. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2024 1;48(4):1-10.
[22] AZODI CB, TANG J, SHIU SH. Opening the black box: interpretable machine learning for geneticists. Trends Genet. 2020;36:442-455.
[23] WANG C, TIAN F, ZHOU Y, et al. The incidence of cervical spondylosis decreases with aging in the elderly, and increases with aging in the young and adult population: a hospital-based clinical analysis. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:47-53.
[24] MATSUMOTO M, OKADA E, TOYAMA Y, et al. Tandem age-related lumbar and cervical ntervertebral disc changes in asymptomatic subjects. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(4):708-713.
[25] 刘承鑫,李翔宇,王宇,等.不同年龄颈椎病患者颈椎椎间盘退行性变与颈椎矢状位参数之间的关系[J].脊柱外科杂志,2022, 20(2):116-120.
[26] 夏凌,李交杰,顾一伟,等.颈围和体质指数与颈肌强度的相关性[J].解放军预防医学杂志,2013,31(5):432-433.
[27] BLIZZARD L, GRIMMER KA, DWYER T. Validity of a measure of the frequency of headaches with overt neck involvement, and reliability of measurement of cervical spine anthropometric and muscle performance factors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2000;81(9):1204-1210.
[28] WU Y, WU J, QIN T, et al. Cervical facet joint degeneration, facet joint angle and paraspinal muscle degeneration are correlated with degenerative cervical spondylolisthesis at C4/5: a propensity score-matched study. Spine J. 2024:S1529-9430(24)00920-3. |