| [1] 王尚城,王冬梅,汪方,等.人骨拉伸和压缩力学的性能测试[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(7):1180-1184 [2] 董乐乐,连建强.生物学内固定原则在手术治疗长骨骨折不愈合中的应用[J]. 中医正骨,2013,25(3):73-74. [3] Thomas PR,William MM.骨折治疗的AO原则[M].北京:华夏出版社, 2003: 221-224. [4] 陈子华,徐国香.股骨近端解剖型钢板在股骨转子问骨折中应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(5):604-605. [5] 裴国献,任高宏. 长管状骨骨折治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2002,4(1):10-14. [6] Bishop JA,Rodriguez EK. Closed intramedullary nailing of the femur in the lateral decubitus position. Trauma. 2010 ;68: 231-235. [7] 徐文华,袁晓军,舒敏锐,等.探讨长骨骨干骨折内固定术后断裂及松动的原因[J].中国实用医药, 2012,7(31):36-37. [8] 王裕辉,黄俊文,胡曙荣,等.锁定加压钢板结合骨移植治疗四肢长骨骨干骨折术后骨不连35例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013, 28(5):491-492. [9] Müller ME. Manual of Internal Fixation.2nd ed. New York: Spinger-Verlag, 1979. [10] Walker M,Palumbo B,Badman B,et al.Humeral shaft fractures:a review.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5): 833-844. [11] Carroll EA,Schweppe M,Langfitt M, et al.Management of humeral shaftfractures. J Am Acad orthop Surg. 2012;20(7): 423-433. [12] Spiguel AR,Steffner RJ.Humeral shaft fractures.Curr Rev Musculoskeletmed. 2012;5(3):144-183. [13] 邱功名.交锁髓内钉与加压钢板内固定治疗肪骨干骨折的疗效对比[J].中国伤残医学, 2013;21(1):23-24. [14] 白达强,翟文亮.肱骨干骨折内固定治疗的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2013, 19(1):81-84. [15] Mulier T,Seligson D,Sioen W,et al.Operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 1997;63(3) : 170-177. [16] Bhandari M,Devereaux PJ,McKee MD,et al. Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures-a metaanalysis.Acta Orthop. 2006;77(2): 279-284. [17] 刘智,凌超,李连华. 肱骨干骨折内固定治疗临床研究与比较[J].国际骨科学杂志,2013,34(1):20-22. [18] 王照平,么红英,张远成,等.锁定加压钢板内固定治疗肱骨干合并肱骨近端骨折八例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(7):664- 665. [19] 吕诗武.股骨干骨折钢板固定并发症的防治[J].海南医学,2004; 15(7):92. [20] 张燕萍. LCP 结合自体髂骨植骨术治疗肱骨干骨折术后骨不连探讨[J].求医问药, 2012,10(10):267-277. [21] 张华俊,王树金,王遥伟,等. 锁定钢板联合自体髂骨植骨治疗肱骨干骨折术后骨不连[J].临床骨科杂志, 2013,16( 1):101-102. [22] 赵以甦.肌肉骨骼生物力学的历史回顾[J].中华骨科杂志,2006, 26 (2) :142-144. [23] 王辉亮,于东升,李吉艳,等.股骨干骨折钢板内固定失效36例治疗分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2008,8(27):6737-6738. [24] 王德印,李凤权.股骨干骨折钢板内固定失败原因分析[J].中国伤残医学,2008,16(4):37-38. [25] Heineman DJ, Poolman RW,Nork SE,et al.Plate fixation or intramedullary fixation of humeral shaft fractures.An updated meta-annlysis.Acta Orthopaed. 2010;81(2):216-223. [26] Lovald S,Mercer D,Hanson J,et al.Complications and hardware removal afteropen reduction and internal fixation of humeral fractures. J trauma. 2011;70(5):1273-1278. [27] Heineman DJ,Bhandari M,Nork SE,et al. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures-meta-analysis reupdated. Acta Orthopaed. 2010;81(4):517. [28] Meekers FS,Broos PL.Operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures.The Leuven experience. Acta Orthop Belg.2002;68: 462-470. [29] Sarmiento A,Waddell JP. Latter diaphyseal humeral fractures treatment options. Instr Course Lect. 2002;51:257-269. [30] 李丹,王刚,谷贵山,等.髓内钉与钢板治疗肱骨干骨折患者的疗效及安全性比较[J].吉林大学学报: 医学版, 2011,37(2):342-344. [31] 方军.经皮微创接骨板技术与髓内钉固定治疗肱骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].白求恩军医学院学报,2012,1(6):544-548. [32] 李军.锁定加压钢板微创固定治疗复杂肱骨干骨折[J].中外医疗, 2012, 31(35):70-71. [33] 张晓冬,曲铁兵,林源.成人肱骨干骨折髓内钉与钢板内固定两种方法的比较[J].北京医学,2007,29(6):334. [34] 陈志新, 梁晋, 郭成,等.数字散斑相关法在变形测量中的应用[J].光学精密工程, 2011,19(7):1480-1485. [35] 张亚莉,吴加权,廖经武,等.钢板治疗股骨干骨折断钉的生物力学研究[J].中国误诊学杂志,2009,9(4):774-775. [36] 刘亚双.数字散斑相关方法在实验力学中的适用性[J].成都大学学报:自然科学版, 2012,31(3):298-300. [37] 李爱洁,陈新民,徐祖杰,等.单端固定桥斜向受载三维位移的数字激光散斑技术研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2013,30(1):121- 125. [38] 叶丽晶,周轶平,邹庆峰.数字散斑法加载100N与500N测量胫骨干骨折内固定下的位移[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(17):3173-3076. [39] 吴邦国,阎甲,李仲铭,等.数字散斑法加载200-400N测量股骨干骨折髓内钉置入内固定下的形变[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复 , 2011,15(30):5552-5555. [40] 王志华,赵云伟,李静华,等.数字散斑法测量股骨干骨折内固定下的位移(英文) [J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(22):4019-4022. [41] 邹培,李主一,杨爱梅.股骨干骨折钢板内固定后钢板断裂并原位再折的生物力学分析[J].伤残医学杂志,2003,11(3):15-16. [42] Hasenoehler E,Rikli D,Babst R.Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture:a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury. 2007;38:365-370. [43] 齐金良,夏家年,吴刚,等.肱骨干骨折内固定失败16例原因分析[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2005,17(7):907. [44] 陈伟,江毅.微创钢板接骨术治疗肱骨干骨折进展[J].医学综述, 2013,19(6):1066-1068. [45] 罗世兴,董桂甫,陆春,等.前侧入路前内侧钢板内固定治疗肱骨干骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(3):274-275. |
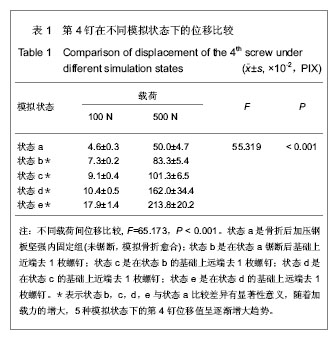
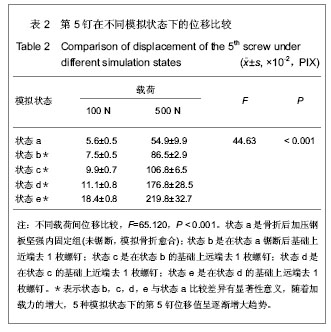
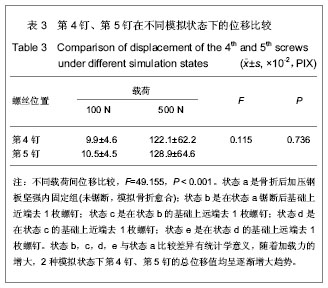
.jpg)
.jpg)