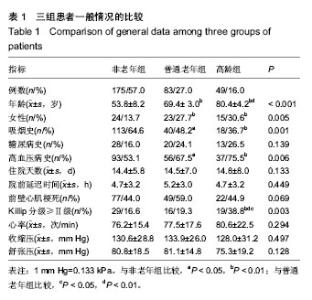
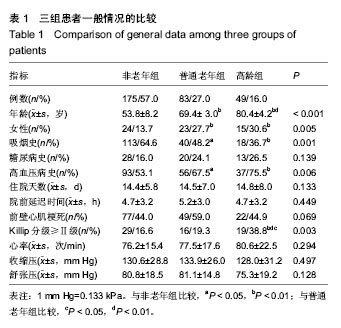
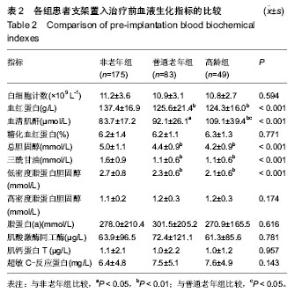
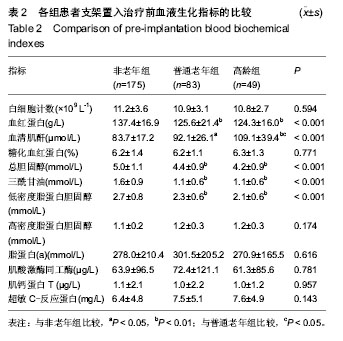
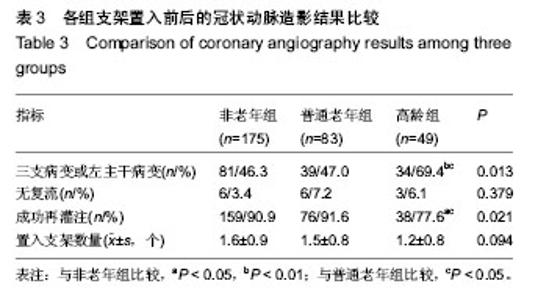
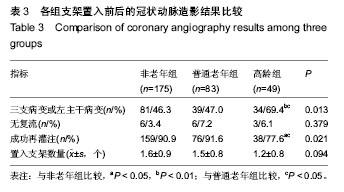
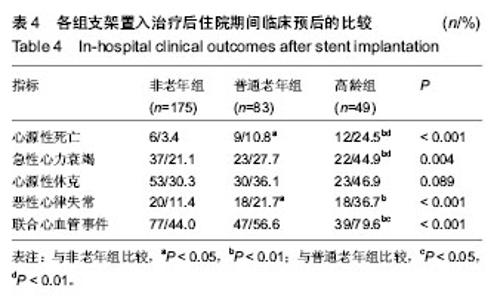
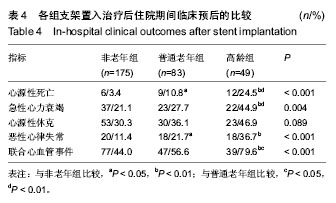
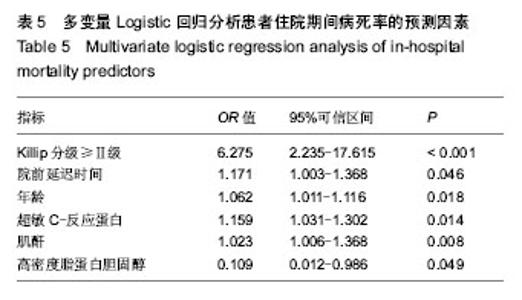
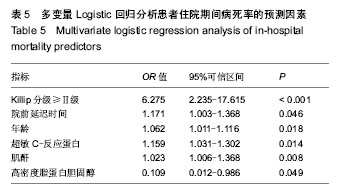
| [1] Antman EM,Anbe DT,Armstrong PW,et al.ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Revise the 1999 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction). Circulation.2004;110:282-292.
[2] Andersen HR,Nielsen TT,Rasmussen K,et al. A comparison of coronary angioplasty with fibrinolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction.N Engl J Med. 2003;349:733-742.
[3] Mehta RH,Granger CB. Reperfusion strategies for acute myocardial infarction in the elderly: benefits and risks.J Am Coll Cardiol.2005;45(4):471-478.
[4] Henry TD,Sharkey SW,Burke MN,et al.A regional system to provide timely access to percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2007;116: 721-728.
[5] Newell MC,Henry JT,Henry TD,et al.Impact of age on treatment and outcomes in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am Heart J.2011;161(4):664-672.
[6] Mehta RH,Rathore SS,Radford MJ,et al. Acute myocardial infarction in the elderly: difference by age.J Am Coil Cardiol. 2001;38:736-741.
[7] Gharacholou SM,Lopes RD,Alexander KP,et al. Age and Outcomes in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Treated With Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Arch Intern Med.2011;171(6):559-567.
[8] Park JS,Kim YJ,Shin DG,et al.Gender differences in clinical features and in-hospital outcomes in ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction: from the Korean acute myocardial infarction registry(KAMIR)study.Clin Cardiol. 2010;33:1-6.
[9] Trigo J,Mimoso J,Gago P,et al.Female gender: an independent factor in ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Rev Port Cardiol.2010;29:1383-1394.
[10] Rathore SS,Mehta RH,Wang Y,et al.Effects of age on the quality of care provided to older patients with acute myocardial infarction.Am J Med.2003;114(4):307-315.
[11] Denke MA.Weighting before the fight low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol versus apoolipoprotein B as the best predictor for coronary heart disease and the best measure of therapy. Circulation. 2005;112:3368-3370.
[12] 徐燕华,傅明德,徐勇霞,等.冠心病患者血脂水平与血清高密度脂蛋白亚类组成关系的研究[J].临床心血管病杂志,2003,19(10): 581-584.
[13] Wennberg DE,Makenka DJ,Sengupta A,et al.Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty in the elderly: epidemiology, clinical risk factors, and in-hospital outcomes. The Northern New England Cardiovascular Disease Study Group.Am Heart J. 2007;137:639.
[14] Singh M,Mathew V,Garratt KN,et al.Effect of age on the outcome of angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction among patients treated at the Mayo Clinic.Am J Med.2000;108(3): 187-192.
[15] Celik T,Turhan H,Kursaklioglu H,et al.Impact of metabolic syndrome on myocardial perfusion grade after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction.Coron Artery Dis.2006;17:39.
[16] Gottlieb S,Behar S,Schwartz R,et al.Age differences in the adherence to treatment guidelines and outcome in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011;52(1):118-124.
[17] Juliard JM,Golmard JL,Himbert D,et al. Comparison of Hospital Mortality During ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in the Era of Reperfusion Therapy in Women Versus Men and in Older Versus Younger Patients.Am J Cardiol. 2013;111(12):1708-1713.
[18] Boucher JM,Racine N,Thanh TH,et al.Age related differences in in-hospital mortality and the use of thrombolytic therapy for a acute myocardial infarction. CMAJ. 2001;164:1285-1291.
[19] Christiansen EC,Wickstrom KK,Henry TD,et al. Comparison of Functional Recovery Following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Three Age Groups (< 70, 70 to 79, and ≥80 Years). Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(3):330-335.
[20] Maid AR,Rafique S,Tarin SM.Age-related in-hospital mortality among patients with acute myocardial infarction.J Coil Physicians Surg Pak.2004;14(5): 262-266. |