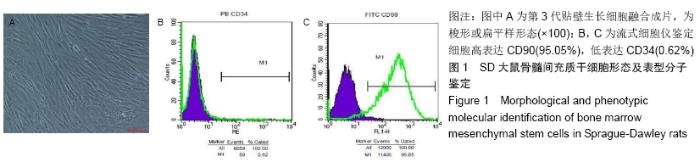
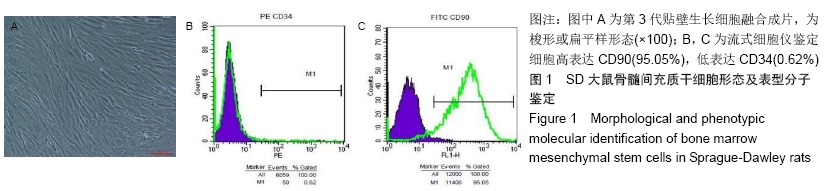
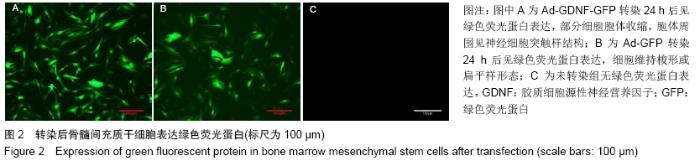
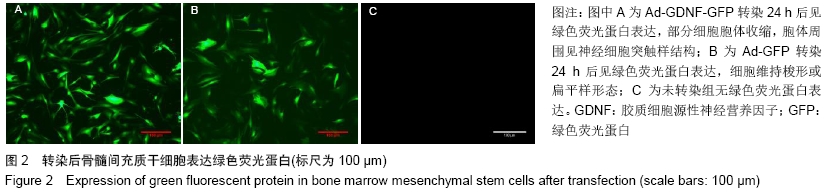
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 1037-1045.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2035
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor gene for spinal cord injury
Huang Cheng1, Liu Yuanbing1, Dai Yongping1, Wang Liangliang1, Cui Yihua1, Yang Jiandong2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Rugao People’s Hospital, Rugao 226500, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2019-08-09Revised:2019-08-14Accepted:2019-09-17Online:2020-03-08Published:2020-01-19 -
Contact:Yang Jiandong, Chief physician, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Spine Surgery, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Huang Cheng, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Rugao People’s Hospital, Rugao 226500, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81071466; the Science and Education Leading Talents Program for Invigorating Health of Yangzhou during 13th Five-Year Plan Period, No. LJRC20182; the Science and Technology Program of Rugao City, No. SRG(15) 3015
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Cheng, Liu Yuanbing, Dai Yongping, Wang Liangliang, Cui Yihua, Yang Jiandong. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor gene for spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1037-1045.
share this article
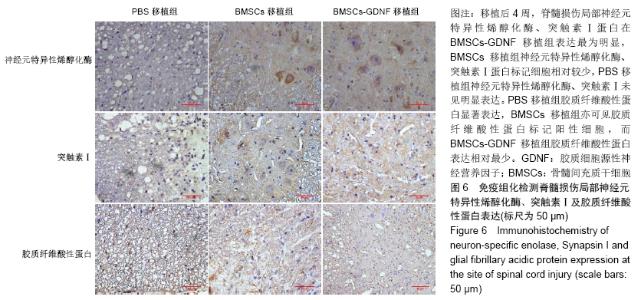
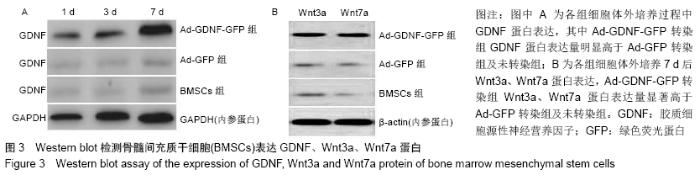
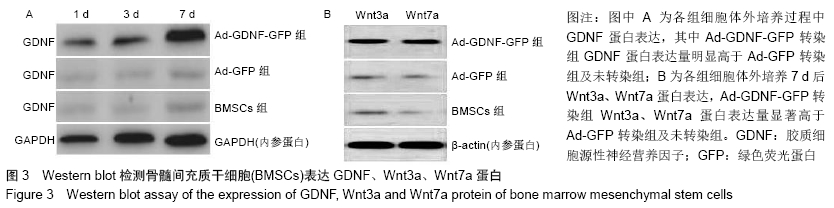
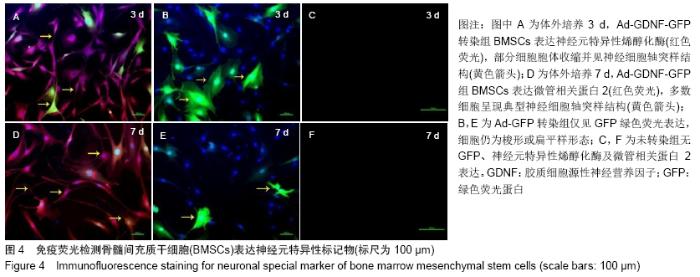
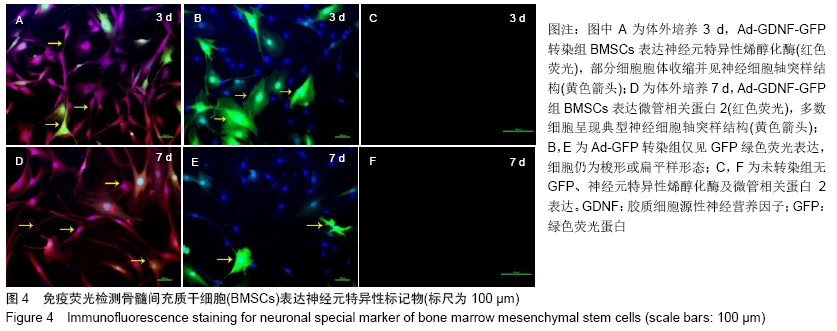
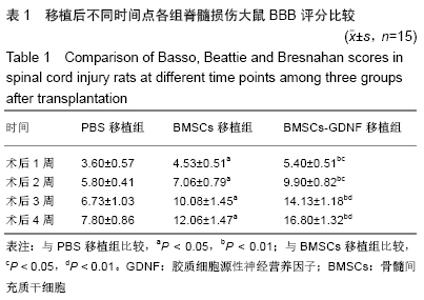
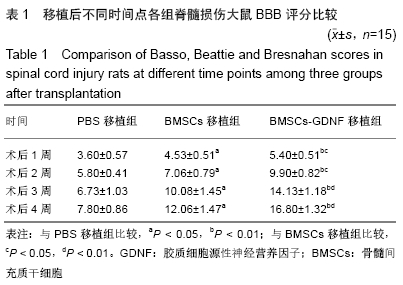
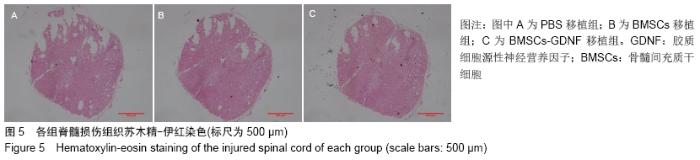
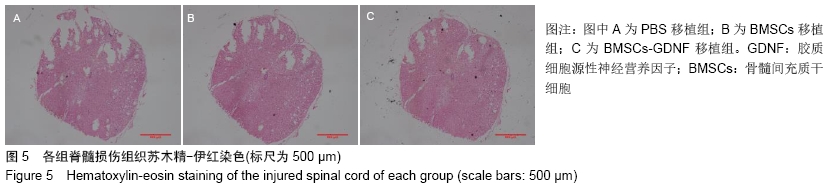
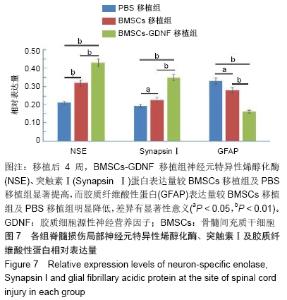
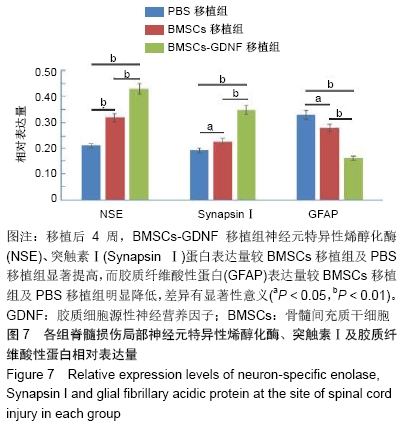
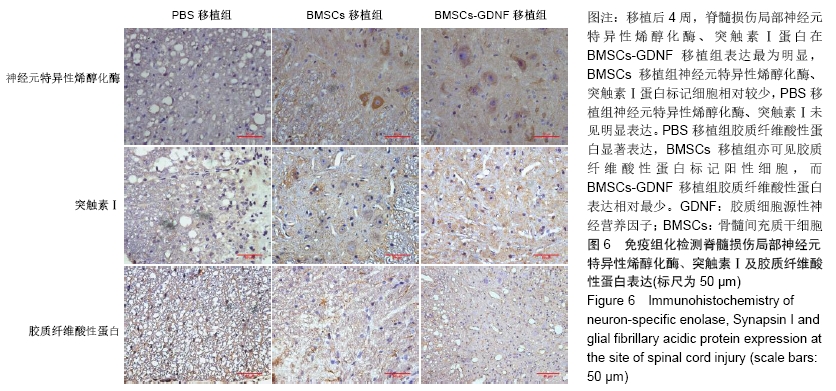
2.7 免疫组化检测脊髓损伤局部神经元特异性烯醇化酶、突触素Ⅰ及胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达 免疫组化染色结果显示BMSCs-GDNF移植治疗后4周脊髓损伤局部可见较多神经元特异性烯醇化酶阳性细胞分布,BMSCs移植组脊髓损伤局部亦可见神经元特异性烯醇化酶阳性细胞散在分布,但阳性细胞数较少,而PBS移植对照组未见明显阳性细胞。BMSCs-GDNF移植组与BMSCs移植组脊髓损伤局部可见棕褐色突触素Ⅰ蛋白表达,PBS移植组仅少许突触素Ⅰ蛋白表达,统计学分析比较各组神经元特异性烯醇化酶蛋白平均光密度值差异有显著性意义。另外,PBS移植组脊髓损伤局部可见棕褐色胶质纤维酸性蛋白阳性细胞大量分布,BMSCs移植组亦可见明显胶质纤维酸性蛋白阳性细胞分布,BMSCs-GDNF移植组脊髓损伤局部虽可见胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达但平均光密度值较PBS移植组、BMSCs移植组明显降低,差异有显著性意义,见图6,7。 "
| [1] MA Q, CAI M, SHANG JW, et al. In vitro neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells induced by hepatocyte growth factor and glial cell derived neurotrophic factor. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(22):4654-4663. [2] SHAHREZAIE M, MANSOUR RN, NAZARI B, et al. Improved stem cell therapy of spinal cord injury using GDNF-overexpressed bone marrow stem cells in a rat model. Biologicals. 2017;50: 73-80. [3] YUAN J, HUANG G, XIAO Z, et al. Overexpression of β-NGF promotes differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neurons through regulation of AKT and MAPK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;383(1-2):201-211. [4] LIU Q, CHENG G, WANG Z, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into nerve-like cells in vitro after transfection with brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015;51(3):319-327. [5] ROSICH K, HANNA BF, IBRAHIM RK, et al. The Effects of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor after Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(24):3311-3325. [6] LI R, SHANG J, ZHOU W, et al. Overexpression of HIPK2 attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by modulating apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 103:127-134. [7] MIYASHITA T, KODA M, KITAJO K, et al. Wnt-Ryk signaling mediates axon growth inhibition and limits functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(7):955-964. [8] PARK JH, MIN J, BAEK SR, et al. Enhanced neuroregenerative effects by scaffold for the treatment of a rat spinal cord injury with Wnt3a-secreting fibroblasts. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013;155(5): 809-816. [9] CISTERNAS P, HENRIQUEZ JP, BRANDAN E, et al. Wnt signaling in skeletal muscle dynamics: myogenesis, neuromuscular synapse and fibrosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;49(1): 574-589. [10] YANG JD, CHENG-HUANG, WANG JC, et al. The isolation and cultivation of bone marrow stem cells and evaluation of differences for neural-like cells differentiation under the induction with neurotrophic factors. Cytotechnology. 2014;66(6):1007-1019. [11] KAKABADZE Z, KIPSHIDZE N, MARDALEISHVILI K, et al. Phase 1 Trial of Autologous Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:6768274. [12] OH SK, CHOI KH, YOO JY, et al. A Phase III Clinical Trial Showing Limited Efficacy of Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Neurosurgery. 2016;78(3): 436-447. [13] PU Y, MENG K, GU C, et al. Thrombospondin-1 modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) promote neurite outgrowth and functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury. Oncotarget. 2017;8(56):96276-96289. [14] YOU K, CHANG H, ZHANG F, et al. Cell-seeded porous silk fibroin scaffolds promotes axonal regeneration and myelination in spinal cord injury rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019; 514(1):273-279. [15] LIN GL, WANG H, DAI J, et al. Upregulation of UBAP2L in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Functional Recovery in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Med Sci. 2018;38(6): 1081-1089. [16] 周燕,王琳,裴双,等.骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体可减少脊髓损伤后A1型星形胶质细胞的活化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(21): 3294-3301. [17] BROCK JH, GRAHAM L, STAUFENBERG E, et al. Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Intraspinal Transplants Fail to Improve Motor Outcomes in a Severe Model of Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2016;33(12):1103-1114. [18] OLIVERI RS, BELLO S, BIERING-SØRENSEN F. Mesenchymal stem cells improve locomotor recovery in traumatic spinal cord injury: systematic review with meta-analyses of rat models. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;62:338-353. [19] AIZAWA-KOHAMA M, ENDO T, KITADA M, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow stromal cell-derived neural precursor cells ameliorates deficits in a rat model of complete spinal cord transection. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(9):1613-1625. [20] AZIM K, FISCHER B, HURTADO-CHONG A, et al. Persistent Wnt/β-catenin signaling determines dorsalization of the postnatal subventricular zone and neural stem cell specification into oligodendrocytes and glutamatergic neurons. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(5):1301-1312. [21] LI Q, YANG C, ZHANG B, et al. Wnt3a Ectopic Expression Interferes Axonal Projection and Motor Neuron Positioning During the Chicken Spinal Cord Development. J Mol Neurosci. 2018; 64(4):619-630. [22] FU S, YANG L, HONG H, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling is involved in the Icariin induced proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Tradit Chin Med. 2016;36(3):360-368. [23] PENG RJ, JIANG B, DING XP, et al. Effect of TNF-α Inhibition on Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Neurological Function Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury via the Wnt Signaling Pathway in a Rat Model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2): 743-752. [24] 阎文柱,秦书俭,刘学政,等.体外培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化: Wnt3 信号分子的诱导作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(14):2476-2480. [25] UDEH A, DVORIANTCHIKOVA G, CARMY T, et al. Wnt signaling induces neurite outgrowth in mouse retinal ganglion cells. Exp Eye Res. 2019;182:39-43. [26] BELEMA BEDADA F, TECHNAU A, EBELT H, et al. Activation of myogenic differentiation pathways in adult bone marrow-derived stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(21):9509-9519. [27] STANGANELLO E, ZAHAVI EE, BURUTE M, et al. Wnt Signaling Directs Neuronal Polarity and Axonal Growth. iScience. 2019;13: 318-327. [28] SUN X, XIONG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Harpagoside attenuates MPTP/MPP⁺ induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration and movement disorder via elevating glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurochem. 2012;120(6):1072-1083. [29] MUKHAMEDSHINA YO, GARANINA EE, MASGUTOVA GA, et al. Assessment of Glial Scar, Tissue Sparing, Behavioral Recovery and Axonal Regeneration following Acute Transplantation of Genetically Modified Human Umbilical Cord Blood Cells in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Contusion. PLoS One. 2016;11(3): e0151745. [30] LIN W, LI M, LI Y, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells promote neurite outgrowth of spinal motor neurons by means of neurotrophic factors in vitro. Neurol Sci. 2014;35(3):449-457. [31] LU Y, GAO H, ZHANG M, et al. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Transfected Placenta-Derived Versus Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Cells for Treating Spinal Cord Injury. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:1800-1811. [32] 黄成,冯新民,杨建东,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子基因修饰后间充质干细胞的生长与分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45): 7932-7938. [33] GONG Y, WANG H, XIA H. Stable transfection into rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by lentivirus-mediated NT-3. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(1):367-373. [34] LUO H, XU C, LIU Z, et al. Neural differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with human brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified in functionalized self-assembling peptide hydrogel in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3):2828-2835. [35] ZHOU CL, ZHAO L, SHI HY, et al.Combined acupuncture and HuangDiSan treatment affects behavior and synaptophysin levels in the hippocampus of senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 after neural stem cell transplantation.Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(3):541-548. [36] HAN X, CHEN Y, LIU Y, et al. HIF-1α promotes bone marrow stromal cell migration to the injury site and enhances functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. J Gene Med. 2018;20(12): e3062. [37] SANTOS MV, PAGNUSSAT AS, MESTRINER RG, et al. Motor Skill Training Promotes Sensorimotor Recovery and Increases Microtubule-Associated Protein-2 (MAP-2) Immunoreactivity in the Motor Cortex after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in the Rat. ISRN Neurol. 2013;2013:159184. [38] WANG L, PEI S, HAN L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Reduce A1 Astrocytes via Downregulation of Phosphorylated NFκB P65 Subunit in Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1535-1559. [39] LIDDELOW SA, BARRES BA. Reactive Astrocytes: Production, Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Immunity. 2017;46(6): 957-967. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [5] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [6] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [7] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [8] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [9] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [10] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [11] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [14] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [15] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||