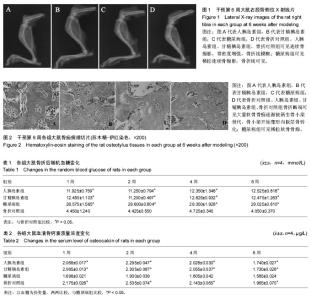
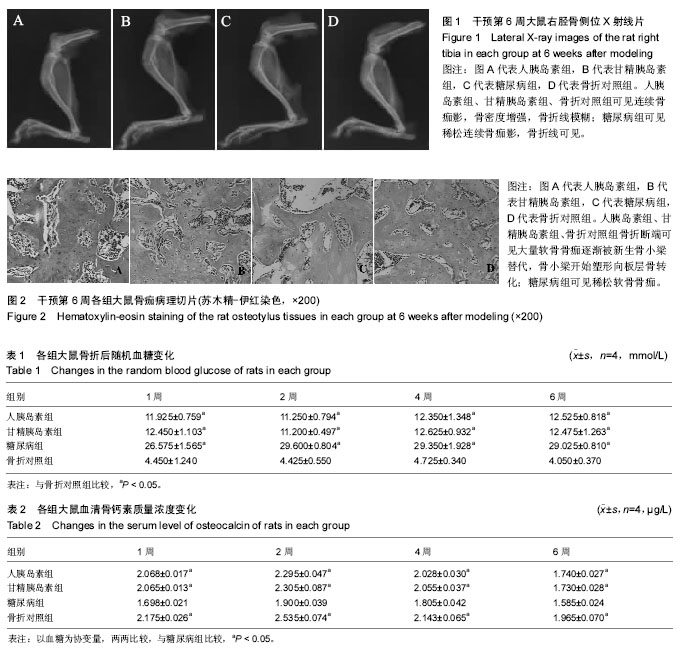
| [1] Kurtzhals P, Schäffer L, Sørensen A, et al. Correlations of receptor binding and metabolic and mitogenic potencies of insulin analogs designed for clinical use. Diabetes. 2000;49(6): 999-1005.[2] 林心君,王麒又,辛金钟,等. 高成模率和高稳定性的糖尿病大鼠模型制备——高脂高糖膳食+STZ体重联合体表面积法构建糖尿病大鼠模型[J].中国老年学杂志, 2013,33(9): 2051-2054.[3] 唐立群,宫明智,刘中浩,等. 糖尿病大鼠骨折愈合过程中骨钙素的变化[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2006, 23(4):617-618.[4] Moseley KF. Type 2 diabetes and bone fractures. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012;19(2): 128-135.[5] Yamagishi S. Role of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in osteoporosis in diabetes. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12(14): 2096-2102.[6] Graves DT, Kayal RA. Diabetic complications and dysregulated innate immunity. Front Biosci. 2008;13:1227-1239.[7] Yamaguchi T. [Bone metabolism in dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome]. Clin Calcium. 2011;21(5): 677-682.[8] 宫明智,邢德国,刘中浩,等. 糖尿病大鼠骨折后骨形态发生蛋白-2、胰岛素样生长因子-1的变化[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2007,23(12):945-948.[9] Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(7): 505-518.[10] Smith U, Gale EA. Does diabetes therapy influence the risk of cancer? Diabetologia.2009;52(9): 1699-1708.[11] Shukla A, Grisouard J, Ehemann V, et al. Analysis of signaling pathways related to cell proliferation stimulated by insulin analogs in human mammary epithelial cell lines. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009;16(2): 429-441.[12] Bronsveld HK, ter Braak B, Karlstad Ø, et al. Treatment with insulin (analogues) and breast cancer risk in diabetics; a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro, animal and human evidence. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17: 100.[13] 李裕明,邓波,李丽华,等.葡萄糖、胰岛素对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2009, 89(36): 2583-2585.[14] Wang Y, Menendez A, Fong C, et al. IGF-I Signaling in Osterix-Expressing Cells Regulates Secondary Ossification Center Formation, Growth Plate Maturation, and Metaphyseal Formation During Postnatal Bone Development. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(12): 2239-2248.[15] Ren G, Ali T, Chen W, et al. The role of selenium in insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) expression and regulation of apoptosis in mouse osteoblasts. Chemosphere. 2016; 144: 2158-2164.[16] 梁立阳,杜敏联,夏焱,等.胰岛素对长骨成骨细胞的影响及受体后机制的研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2006,22(11):2251-2255.[17] 李溪,向盈盈,龚跃昆,等.糖尿病骨折大鼠骨痂组织中成骨细胞增殖和骨钙素表达与骨形态发生蛋白2干预的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(20):3857-3861.[18] 王德亮,邢德国,王亮,等. 胰岛素样生长因子-1基因转染骨髓间质干细胞移植对糖尿病大鼠骨折愈合的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012, 29(3):518-520.[19] 王德亮,邢德国,王亮,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞移植对糖尿病大鼠骨折愈合的影响[J].中华创伤杂志, 2012, 28(11):1042-1045.[20] Celil AB, Campbell PG. BMP-2 and insulin-like growth factor-I mediate Osterix (Osx) expression in human mesenchymal stem cells via the MAPK and protein kinase D signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(36): 31353-31359.[21] Bolli GB, Hahn AD, Schmidt R, et al. Plasma exposure to insulin glargine and its metabolites M1 and M2 after subcutaneous injection of therapeutic and supratherapeutic doses of glargine in subjects with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(12): 2626-2630. |