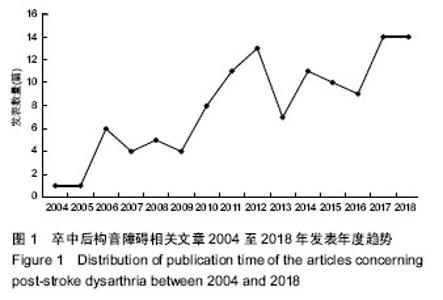
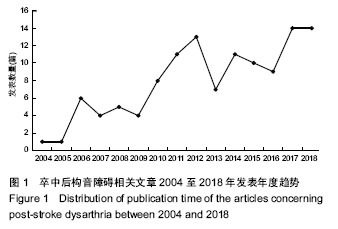
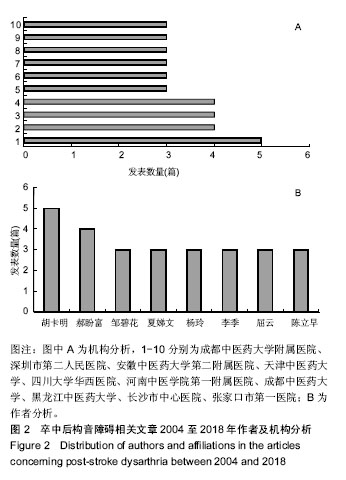
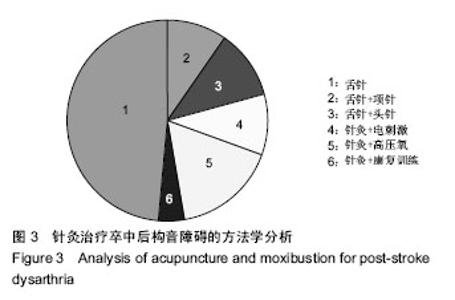
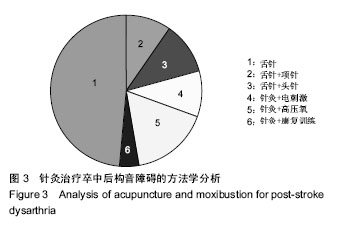
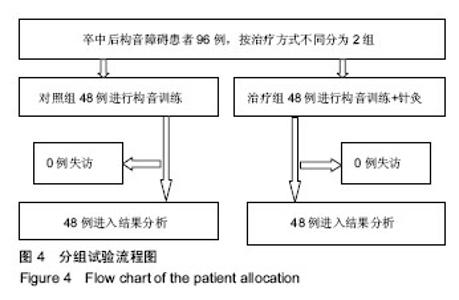
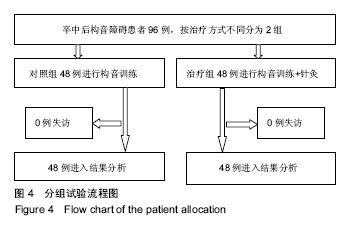
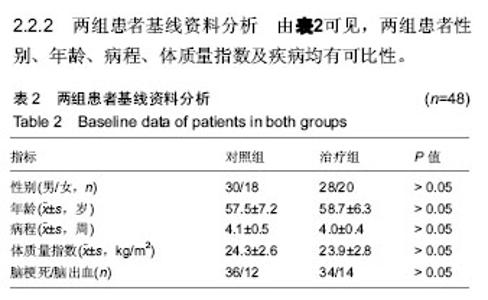
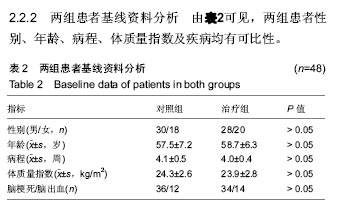
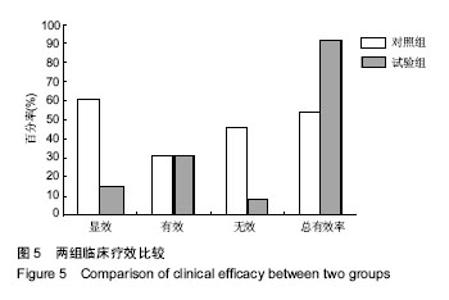
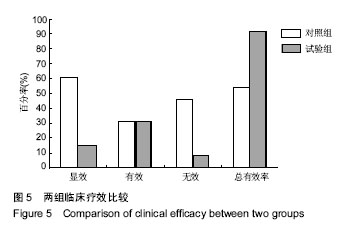
| [1] Kwon YG, Do KH, Park SJ, et al.Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Patients With Dysarthria After Subacute Stroke.Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(5):793-799.[2] Kim G, Min D, Lee EO, et al.Impact of Co-occurring Dysarthria and Aphasia on Functional Recovery in Post-stroke Patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(6):1010-1017.[3] 金梅,刘晓加.基底神经节的语言功能[J].中国行为医学科学, 2003,12(04):119-121.[4] Netsell R.Speech aeromechanics and the dysarthrias: implications for children with traumatic brain injury.J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2001; 16(5):415-425.[5] Mackenzie C, Muir M, Allen C, et al.Non-speech oro-motor exercises in post-stroke dysarthria intervention: a randomized feasibility trial.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2014; 49(5): 602-617.[6] Mackenzie C, Lowit A.Improved status following behavioural intervention in a case of severe dysarthria with stroke aetiology.Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2012;14(4):318-328.[7] Mahler LA, Ramig LO.Intensive treatment of dysarthria secondary to stroke.Clin Linguist Phon. 2012;26(8):681-694.[8] 梁猛军, 蔡永亮.脑卒中后构音障碍治疗研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志,2011,23(12):1136-1137.[9] 杨孝芳,施杨婉琳,崔瑾,等.针刺结合康复训练对脑卒中后假性球麻痹患者构音障碍影响的研究[J].贵阳中医学院学报,2012, 34(5):42-44.[10] 路飞,张连城. 中医治疗脑卒中后构音障碍研究[J].长春中医药大学学报,2012,28(2):253-254.[11] 潘巍一,张捷洪,柯秀君,等.头部督脉穴联合舌三针改善脑卒中后构音障碍的临床症状及Frenchay评分情况观察[J].首都食品与医药,2016,(10):71-72. [12] 武志佳,胡卡明,郭耀光,等.针刺结合言语康复训练治疗脑卒中后痉挛性构音障碍:多中心随机对照研究(英文)[J].世界针灸杂志, 2014,24(4):12-16.[13] 王雅青,刘芳, 王晓芳,等.舌下放血合舌部操治疗脑卒中假性延髓麻痹构音障碍32例[J].福建中医药大学学报,2013,23(3): 63-64.[14] 刘丽丽,董赟,郝盼富.针刺配合言语康复训练治疗脑卒中后构音障碍临床研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志,2013,25(11): 1038-1039.[15] 贾力,白洁,刘东,等.舌体分区多针点刺配合言语训练治疗脑卒中后运动性构音障碍30例[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2016, 14(2):44-46.[16] 缪鸿石,朱镛连.脑卒中的康复评定和治疗[M].北京:华夏出版社, 1996.[17] 缪鸿石.康复医学理论与实践(上册)[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2000.[18] 柳金英,常静玲.脑卒中后基底核构音障碍的脑机制研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(10):987-990.[19] 王红,陈卓铭.脑卒中后遗构音障碍的诊断与治疗[J].新医学, 2006,37(11):717-719,738.[20] 刘莉,邵伟波.脑卒中所致痉挛型构音障碍的康复训练方法及疗效[J].中国康复理论与实践,2008,14(10):925-926. |