Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (35): 5682-5687.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2927
Previous Articles Next Articles
Designing modified blocks based on Action Research Arm Test: evaluating the recovery potential of upper limb function in stroke patients
Shao Danli1, Xu Xuedi1, Gao Xiaoping1, Zhang Xu2
1Department of Rehabilitation, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China; 2Department of Electronic Science and Technology, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-24Revised:2020-02-29Accepted:2020-04-23Online:2020-12-18Published:2020-10-19 -
Contact:Gao Xiaoping, Master, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Shao Danli, Master candidate, Department of Rehabilitation, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 61771444
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shao Danli, Xu Xuedi, Gao Xiaoping, Zhang Xu. Designing modified blocks based on Action Research Arm Test: evaluating the recovery potential of upper limb function in stroke patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5682-5687.
share this article

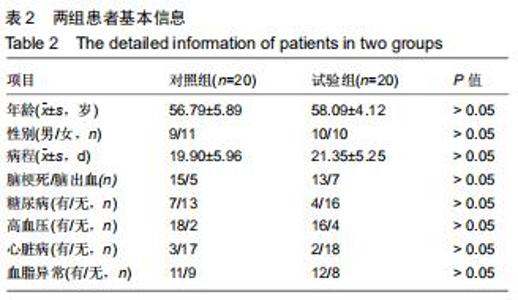
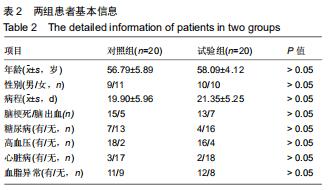
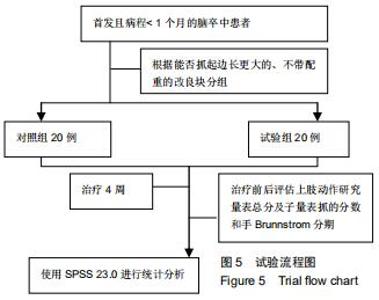
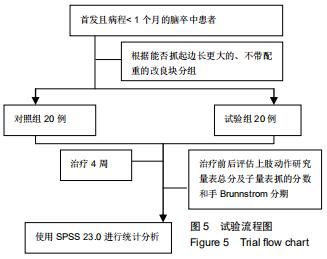
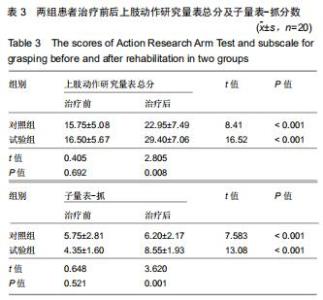
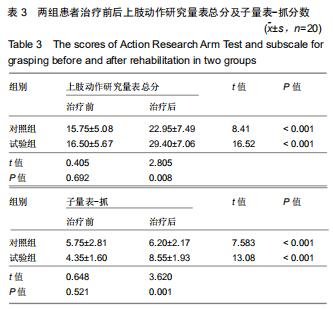
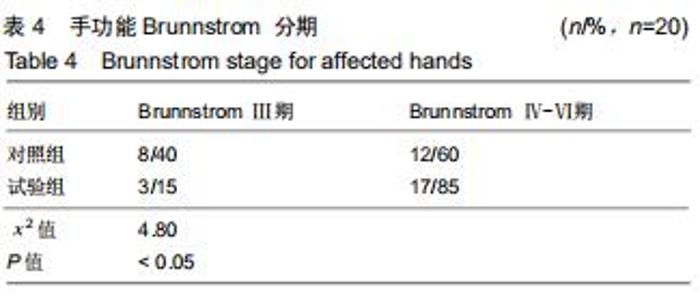
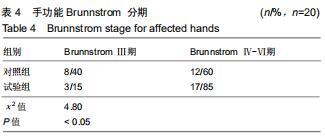
1.4.2 改良块 众多研究表示,原始模型与使用3D打印的模型在外形、尺寸精度等方面具有一致性[13-14]。改良块是聚乳酸通过3D打印而成,每个改良块由5个面组成,其内中空[15]。通过测量,每个改良块的大小与相应的实木木块边长一致。由于材质问题,质量不一致,已通过测量进行配重添加模拟实木木块。每个改良块本身的质量及相应的配重可见表1。添加相应的可拆卸的配重的改良块与相应大小的原始实木木块在大小和质量上完全一致,结合上肢动作研究量表评分规则,可将添加相应配重的改良块视为原始实木木块的替代品。改良块的整体外观见图1。图2为添加530 g配重的10 cm大小的改良块,可替代10 cm大小的原始实木木块。图3显示了改良块的存储空间。图4显示部分可拆卸的配重,可置于不同的改良块内部,替代相应的原始木块。 "


1.4.2 改良块 众多研究表示,原始模型与使用3D打印的模型在外形、尺寸精度等方面具有一致性[13-14]。改良块是聚乳酸通过3D打印而成,每个改良块由5个面组成,其内中空[15]。通过测量,每个改良块的大小与相应的实木木块边长一致。由于材质问题,质量不一致,已通过测量进行配重添加模拟实木木块。每个改良块本身的质量及相应的配重可见表1。添加相应的可拆卸的配重的改良块与相应大小的原始实木木块在大小和质量上完全一致,结合上肢动作研究量表评分规则,可将添加相应配重的改良块视为原始实木木块的替代品。改良块的整体外观见图1。图2为添加530 g配重的10 cm大小的改良块,可替代10 cm大小的原始实木木块。图3显示了改良块的存储空间。图4显示部分可拆卸的配重,可置于不同的改良块内部,替代相应的原始木块。"


1.4.2 改良块 众多研究表示,原始模型与使用3D打印的模型在外形、尺寸精度等方面具有一致性[13-14]。改良块是聚乳酸通过3D打印而成,每个改良块由5个面组成,其内中空[15]。通过测量,每个改良块的大小与相应的实木木块边长一致。由于材质问题,质量不一致,已通过测量进行配重添加模拟实木木块。每个改良块本身的质量及相应的配重可见表1。添加相应的可拆卸的配重的改良块与相应大小的原始实木木块在大小和质量上完全一致,结合上肢动作研究量表评分规则,可将添加相应配重的改良块视为原始实木木块的替代品。改良块的整体外观见图1。图2为添加530 g配重的10 cm大小的改良块,可替代10 cm大小的原始实木木块。图3显示了改良块的存储空间。图4显示部分可拆卸的配重,可置于不同的改良块内部,替代相应的原始木块。"


1.4.2 改良块 众多研究表示,原始模型与使用3D打印的模型在外形、尺寸精度等方面具有一致性[13-14]。改良块是聚乳酸通过3D打印而成,每个改良块由5个面组成,其内中空[15]。通过测量,每个改良块的大小与相应的实木木块边长一致。由于材质问题,质量不一致,已通过测量进行配重添加模拟实木木块。每个改良块本身的质量及相应的配重可见表1。添加相应的可拆卸的配重的改良块与相应大小的原始实木木块在大小和质量上完全一致,结合上肢动作研究量表评分规则,可将添加相应配重的改良块视为原始实木木块的替代品。改良块的整体外观见图1。图2为添加530 g配重的10 cm大小的改良块,可替代10 cm大小的原始实木木块。图3显示了改良块的存储空间。图4显示部分可拆卸的配重,可置于不同的改良块内部,替代相应的原始木块。"

|
[1] LI Z, JIANG Y, LI H, et al. China's response to the rising stroke burden. BMJ. 2019;364:l879.
[2] ZENG W, GUO Y, WU G, et al. Mirror therapy for motor function of the upper extremity in patients with stroke: A meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2018;50(1):8-15.
[3] HOU S, IVANHOE C, LI S. Botulinum Toxin Injection for Spastic Scapular Dyskinesia After Stroke: Case Series. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(32):e1300.
[4] 王海桥,鲍春龄,李鹤,等.针刺联合运动想象对脑卒中软瘫上肢精细动作的影响[J].中国针灸,2015,35(6):534-538.
[5] BHAKTA BB, HARTLEY S, HOLLOWAY I, et al. The DARS (Dopamine Augmented Rehabilitation in Stroke) trial: protocol for a randomised controlled trial of Co-careldopa treatment in addition to routine NHS occupational and physical therapy after stroke. Trials. 2014;15:316.
[6] 瓮长水,王军,王刚,等.上肢动作研究量表在脑卒中患者中的信度[J].中国康复理论与实践,2007,13(9):868-869.
[7] 瓮长水,王军,潘小燕,等.上肢动作研究量表在脑卒中患者中的效度[J].中国康复理论与实践,2008,14(1):53-54.
[8] LYLE RC. A performance test for assessment of upper limb function in physical rehabilitation treatment and research. Int J Rehabil Res. 1981;4(4):483-492.
[9] CARROLL D. A quantitative test of upper extremity function. J Chronic Dis. 1965;18:479-491.
[10] YOZBATIRAN N, DER-YEGHIAIAN L, CRAMER SC. A standardized approach to performing the action research arm test. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2008;22(1):78-90.
[11] HUANG CY, LIN GH, HUANG YJ, et al. Improving the utility of the Brunnstrom recovery stages in patients with stroke: Validation and quantification. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95(31):e4508.
[12] CHEN CL, CHEN CY, CHEN HC, et al. Responsiveness and minimal clinically important difference of Modified Ashworth Scale in patients with stroke. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019; 55(6):754-760.
[13] 贾朋,孙峰,薛世峰,等.基于3D打印的复杂井筒模拟岩样制作[J].实验室研究与探索,2019,38(7):73-76.
[14] 徐伟业,陈维平,金枫,等.基于数值模拟和砂型3D打印的机匣整体重力铸造工艺研究[J].铸造,2019,68(8):905-910.
[15] LI N, LI Y, LIU S. Rapid prototyping of continuous carbon fiber reinforced polylactic acid composites by 3D printing. Journal of Materials Processing Technology. 2016;238:218-225. [16] AMANO S, UMEJI A, UCHITA A, et al. Clinimetric properties of the action research arm test for the assessment of arm activity in hemiparetic patients after stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2020;27(2):127-136.
[17] KLAUER C, FERRANTE S, AMBROSINI E, et al. A patient-controlled functional electrical stimulation system for arm weight relief. Med Eng Phys. 2016;38(11):1232-1243.
[18] MOFTAH M, JADAVJI NM. Role of behavioral training in reducing functional impairments after stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(9):1507-1508.
[19] NELSON CM, MURRAY WM, DEWALD JPA. Motor Impairment-Related Alterations in Biceps and Triceps Brachii Fascicle Lengths in Chronic Hemiparetic Stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2018;32(9):799-809.
[20] ZHENG Y, SHIN H, HU X. Muscle Fatigue Post-stroke Elicited From Kilohertz-Frequency Subthreshold Nerve Stimulation. Front Neurol. 2018;9:1061.
[21] SHI D, LI Z, YANG J, et al. Symptom Experience and Symptom Burden of Patients Following First-Ever Stroke Within 1 Year: A Cross-Sectional Study Neural Regen Res. 2018 ;13(11): 1907-1912.
[22] HATHIDARA MY, SAINI V, MALIK AM. Stroke in the Young: a Global Update. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(11):91.
[23] FEIGIN VL, KRISHNAMURTHI R, BARKER-COLLO S, et al. Measuring stroke and transient ischemic attack burden in New Zealand: Protocol for the fifth Auckland Regional Community Stroke Study (ARCOS V). Int J Stroke. 2019. doi: 10.1177/1747493019884528. [Epub ahead of print]
[24] SHAQIRI A, DANCKERT J, BURNETT L, et al. Statistical Learning Impairments as a Consequence of Stroke. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018;12:339.
[25] 赵春善,张悦琪,李医华,等.吉林地区老年人脑卒中高危目标人群筛查现状及危险因素[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(10): 2926-2928.
[26] KARUBE N, SASAKI A, HONDOH F, et al. Quality of Life in Physical and Psychological Health and Social Environment at Posthospitalization Period in Patients with Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25(10):2482-2487.
[27] TWARDZIK E, CLARKE P, ELLIOTT MR, et al. Neighborhood Socioeconomic Status and Trajectories of Physical Health-Related Quality of Life Among Stroke Survivors. Stroke. 2019;50(11):3191-3197.
[28] TOGLIA J, ASKIN G, GERBER LM, et al. Participation in Younger and Older Adults Post-stroke: Frequency, Importance, and Desirability of Engagement in Activities. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1108.
[29] KATZAN IL, THOMPSON NR, UCHINO K, et al. The most affected health domains after ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2018;90(16):e1364-e1371. [30] HILDEBRANDT J, BEZAMA A, THRÄN D. Cascade use indicators for selected biopolymers: Are we aiming for the right solutions in the design for recycling of bio-based polymers? Waste Manag Res. 2017;35(4):367-378. |
| [1] | Luo Lin, Song Naiqing, Huang Jin, Zou Xiaodong. Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1270-1276. |
| [2] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [3] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [4] | Huang Maomao, Hu Yue, Wang Binchuan, Zhang Chi, Xie Yujie, Wang Jianxiong, Wang Li, Xu Fangyuan. Bibliometric and visual analysis of international literature addressing ischemic stroke rehabilitation in recent 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3725-3733. |
| [5] | Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi. Ferroptosis and stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739. |
| [6] | Lin Dongxin, Huang Xuecheng, Qin Qingguang, Yang Yang, Deng Yuping, Tan Jinchuan, Wang Mian, Su Weiwei, Huang Tao, Huang Wenhua. Comparison of motion range of cervical spine after two cervical manipulations based on motion capture technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3281-3285. |
| [7] | Bao Sairong, Lin Lihua, Shan Sharui, Yang Xingping, Liu Chunlong. Effect of electrical deep muscle stimulate on muscle tone, elasticity, and stiffness of biceps brachii in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3138-3143. |
| [8] | Lu Yi, Deng Wenchong. Regulation and difference of different exercise styles on brain structure and cognitive function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3252-3258. |
| [9] | Bao Sairong, Zhang Qiming, Yang Xingping, Liu Chunlong. Immediate effects of extracorporeal shock wave on muscle tone, stiffness, and elasticity of wrist flexor in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 228-231. |
| [10] | Li Xiangze, Bu Xianmin, Li Dongmei, Chi Yulei, Su Qiang, Jin Xintong, Zhao Jian, Zhang Gaotian, Wu Bin, Meng Chunyang . Stem cells, cytokines, hormones, neuropeptides and genes in traumatic brain trauma to promote fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3057-3063. |
| [11] | Wang Donghui, Wu Xin, Sun Ningning, Zhang Han, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the expression of synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampi of mice with radiation-induced brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2205-2210. |
| [12] | Fan Feiyan, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine for replenishing qi and promoting blood combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in promoting angiogenesis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2060-2069. |
| [13] | Lin Yi, Feng Jierong, Luo Xingwen. Mobilization with movement facilitates early functional recovery after fixed-bearing posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1842-1846. |
| [14] | Cao Haixin, Wang Xiaomei . Aerobic exercise protects the rat brain against senile dementia induced by amyloid beta protein 1-42 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1675-1681. |
| [15] | Wang Liqun, Li Yuxi, Jin Rongjiang, Wang Wenchun, Pang Richao, Zhang Anren. Application of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in the study of depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1799-1804. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||