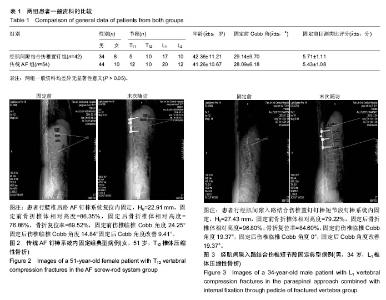
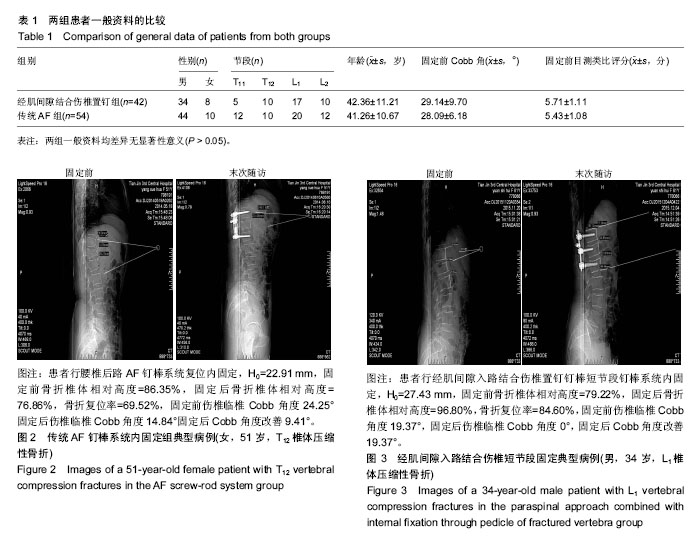
| [1] 魏富鑫,钟锐,崔尚斌,等.经伤椎置钉单椎间复位固定治疗创伤性胸腰椎骨折的远期疗效[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(9):760-764.[2] 冯睿,马信龙,马剑雄,等.伤椎置钉短节段内固定和传统短节段内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2014,30(6): 525-529.[3] 王根林,张福占,谢计乐,等.Wiltse肌间隙入路联合伤椎置钉治疗胸腰段骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(12):1047-1052.[4] Alanay A, Acaroglu E, Yazici M, et al. Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine. 2001;26(2): 213-217.[5] Alvine GF, Swain JM, Asher MA, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures with variable screw placement or Isola instrumentation and arthrodesis: case series and literature review. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(4):251-264.[6] Isaacs RE, Perez CM, Fessler RG, et al. Complications in the treatment of l1 burst fractures. techniques in neurosurgery. Thoracol Trauma. 2003;8(2):130-139.[7] Finkelstein JA, Wai EK, Jackson SS, et al. Single-level fixation of flexion distraction injuries. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003;16(2): 236-242.[8] 郭朝阳,陈云生,陈荣春.一期后路病灶清除植骨内固定治疗老年性胸腰椎结核[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(21):3620-3621.[9] 刘涛,申才良,唐开军,等.射频热凝术联合臭氧盘外注射治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效分析[J].天津医药,2015,43(12):1443-1446.[10] 王广辉,段维礼,郭坤营.椎管侧前方减压脊柱融合治疗胸腰椎骨折并脊髓损伤[J].实用骨科杂志,2003,9(2):107-108.[11] 唐康,张文志,段丽群,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉联合伤椎置钉治疗胸腰段脊椎骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(3):253-257.[12] 庞正宝,庞帮镭,汤优民,等.Wiltse入路治疗单节段胸腰椎骨折对多裂肌影响的研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(2):72-80.[13] Wiltse LL, Bateman JG, Hutchinson RH, et al. The paraspinal sacrospinalis-splitting approach to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968;50(5):919-926.[14] Cappuccio M, Amendola L, Pademi S, et al. Complications in minimally invasive percutaneous fixation of thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(6):E729-E734.[15] Tannous O, Shiu B, Koh EY. Minimally invasive spine surgery for thoracolumbar fractures: damage-control spine stabilization. Semin Spine Surg. 2013;25(3):170-175.[16] Dick JC, Jones MP, Zdeblick TA, et al. A biomechanical comparison evaluating the use of intermediate screws and cross-link-age in lumbar pedicle fixation. J Spine Disord. 1994; 7(5):402-407.[17] 袁强,田伟,张贵林,等.骨折椎垂直应力螺钉在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(4):217-222.[18] [林达生,郭林新,丁真奇,等.椎旁肌间隙入路经伤椎椎弓根植骨内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(2):125-129.[19] 江正康,林奇生,王一民,等.传统后路与附加伤椎固定治疗胸腰椎骨折比较[J].中华全科医学,2012,10(1):9-10. |