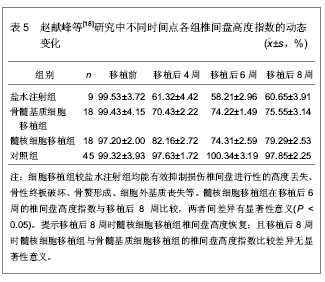
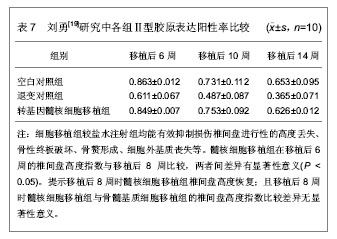
| [1] Karppinen J, Shen FH, Luk KD, et al. Management of degenerative disk disease and chronic low back pain. Orthop Clin North Am.2011;42(4):513-528.[2] Samartzis D, Cheung KM. Lumbar intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4):xi-xii.[3] Adams MA, Roughley PJ.What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2151-2161.[4] Chung SA, Khan SN, Diwan AD. The molecular basis of intervertebral disk degeneration.Orthop Clin North Am. 2003;34(2):209-219.[5] Brisby H. Pathology and possible mechanisms of nervous system response to disc degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:68-71.[6] Bae WC, Masuda K. Emerging technologies for molecular therapy for intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4):585-601.[7] 彭宝淦,施杞.退变椎间盘的组织病理学变化[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1996,4(6):52-55.[8] 胡有谷.腰椎间盘突出症[M].第二版.北京:人民卫生出版社,1995: 118-136.[9] Inoue N, Espinoza Orías AA. Biomechanics of intervertebral disk degeneration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2011;42(4): 487-499.[10] Gan JC, Ducheyne P, Vresilovic EJ, et al. Intervertebral disc tissue engineering II: cultures of nucleus pulposus cells. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(411):315-324.[11] 万方数据库.万方医学网[DB/OL].2013-09-21. https://med.wanfangdata.com.cn[12] Medline.Pubmed[DB/OL].2013-09-21.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/[13] 张兴凯,曹鹏,王君,等.多次胶原酶消化法培养小鼠椎间盘髓核细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(28):5136-5140.[14] 程洪涛.兔髓核细胞的体外培养及髓核细胞移植抑制椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].江苏:东南大学,2004:1.[15] 宁斌,刘海飞,龚维明,等.成人退变髓核细胞微载体旋转立体培养对细胞外基质合成的影响[J].中华外科杂志,2013,51(5): 432-436.[16] 满孝旭,马迅,关晓明,等.肝细胞生长因子对体外培养的人退变髓核细胞生物学活性影响[J].中华临床医学杂志(电子版),2011, 5(24):7226-7231.[17] Gruber HE, Johnson T, Norton HJ, et al. The sand rat model for disc degeneration. Radiologic characterization of age-ralated changes:cross-sectional and prospective analyses. Spine.2002;27(3):230-234.[18] 赵献峰,刘浩,丰干均,等.髓核细胞与骨髓基质细胞移植对受损椎间盘退变的影响[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2009,40(3): 472-477.[19] 刘勇.转基因CTGF和TIMP1髓核细胞移植阻逆兔腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].山东:山东大学,2011:4-40.[20] 宋希元,彭圣智.TGF-β3修饰退变髓核细胞移植修复兔退变椎间盘的效果观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(7): 790-795.[21] 王月秋,陈伯华.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2009,24(4):369-370,372.[22] Iwashina T, Mochida J, Sakai D, et al. Feasibility of using a human nucleus pulposus cell line as a cell source in cell transplantation therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(11):1177-1186.[23] Matsuzaki H, Wakabayashi K, Ishihara K, et al. Allografting intervertebral discs in dogs: a possible clinical application. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(2):178-183.[24] Okuma M, Mochida J, Nishimura K, et al. Reinsertion of stimulated nucleus pulposus cells retards intervertebral disc degeneration:an in vitro and in vivo experimental study. J Orthop Res.2000;18(6):988-997.[25] Nomura T, Mochida J, Okuma M, et al. Nucleus pulposus allograft retards intervertebral disc degeneration.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(389):94-101.[26] Watanabe K, Mochida J, Nomura T, et al. Effect of reinsertion of activated nucleus pulposus on disc degeneration: an experimental study on various types of collagen in degenerative discs.Connect Tissue Res. 2003;44(2):104-108.[27] Ganey T, Libera J, Moos V, et al.Disc chondrocyte transplantation in a canine model: a treatment for degenerated or damaged intervertebral disc.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(23):2609-2620. [28] 于占革,杨威,温莹,等.兔不同节段椎间盘髓核细胞培养特性的比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(8):689-693.[29] 马凯歌,邵增务,王佰川,等.自噬参与压力诱导兔髓核细胞退变的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(2):354-357.[30] 陶海鹰,贺斌,卫爱林,等.羧甲基壳聚糖对体外培养大鼠椎间盘髓核细胞增殖、细胞周期及细胞外基质分泌的影响[J].中国实验外科杂志,2013,30(10):2165-2168. |