| [1] Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, et al. Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science.1999; 286(5446):1946-1949.
[2] Maeda T, Matsunuma A, Kurahashi I, et al. Induction of osteoblast differentiation indices by statins in MC3T3-E1 cells. J Cell Biochem 2004;92:458-471.
[3] 刘志强,周磊,邹剑曾,等.辛伐他汀对大鼠胫骨骨缺损修复作用的实验研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2010,26(4):214-217.
[4] Valentini P, Abensur D, Wenz B,et al.Sinus grafting withporous bone mineral (Bio-Oss) forimplant placement: a 5-year study on15 patients. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2000;20: 245-253.
[5] Maciel-Oliveira N, Bradaschia-Correa V, Arana-Chavez VE. Early alveolar bone regeneration in rats after topical administration of simvastatin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112(2):170-179.
[6] 荣小芳,吴琳,杨晓东,等.兔下颌骨临界骨缺损人工材料植入实验动物模型的建立[J].中国医科大学学报,2008,37(1):62-64.
[7] Rho JY, Hobatho MC, Ashman RB.Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med EngPhys.1995;17(5):347-355.
[8] Jensen S S, Aaboe M, Pinholt EM, et al. Tissue reaction and material characteristics of four bone substitutes. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants. 1996; 11(1): 55.
[9] Piattelli M, Favero GA, Scarano A, et al. Bone reactions to anorganic bovine bone (Bio-Oss) used in sinus augmentation procedures: a histologic long-term report of 20 cases in humans. The International journal of oral & maxillofacial implants. 1999;14(6): 835.
[10] Weibrich G, Trettin R, Gnoth S H, et al. Determining the size of the specific surface of bone substitutes with gas adsorption. Mund-, Kiefer-und Gesichtschirurgie: MKG, 2000; 4(3): 148.
[11] Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Healing around implants placed in bone defects treated with Bio-Oss: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res.1997;8:117-124.
[12] 邱立新,林野,王兴,等. Bio-Oss骨代用品同引导骨再生膜联合应用效果的观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2002,37(6):412-414.
[13] 方利华,平金良,孟祥勇,等.下颌骨缺损即刻修复的动物实验研究[J].上海口腔医学, 2008, 17(4): 405-410.
[14] 李春明,杨春艳,王鑫,等. bFGF基因修饰的骨髓基质细胞复合多孔矿化Bio-Oss胶原修复下颌骨缺损的实验研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2008, 24(4): 470-474.
[15] Zitzmann NU, Naef R, Schärer P. Resorbable versus nonresorbable membranes in combination with Bio-Oss for guided bone regeneration. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1997;12(6):844-852.
[16] Araújo MG, Carmagnola D, Berglundh T, et al. Orthodontic movement in bone defects augmented with Bio-Oss®. J Clin Periodontol. 2001;28(1):73-80.
[17] Duda M, Pajak J. The issue of bioresorption of the Bio-Oss xenogeneic bone substitute in bone defects[C]// AnnalesUniversitatisMariae Curie-Sklodowska.Sectio D: Medicina. 2004, 59(1): 269.
[18] Gielkens P F M, Schortinghuis J, De Jong J R, et al. Vivosorb®, Bio-Gide®, and Gore‐Tex® as barrier membranes in rat mandibular defects: an evaluation by microradiography and micro-CT. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008 May;19(5):516-521.
[19] Fayed MM, Pazera P, Katsaros C.Optimal sites for orthodonticmini-implant placement assessed by cone beam computed tomography. Angle Orthodontist. 2010;80(5): 939-951.
[20] Katsumata A, Nojiri M, Fujishita M, et al.Condylar head remodeling following mandibular setback osteotomy for prognathism:a comparative study of different imaging modalities.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101:505-514.
[21] Nair R, DeguchiSr T, Li X, et al.Quantitative analysis of the maxilla and the mandible in hyper-and hypodivergent skeletal class II pattern. Orthodontics & Craniofacial Res.2009;12(1): 9-13.
[22] Rho JY, Hobatho MC, Ashman RB.Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys.1995;17(5):347-355.
[23] 赵刚,尹蒙熔,李德超,等.纳米羟基磷灰石修复牙槽骨缺损后正畸牙齿移动的可行性研究[J].黑龙江医药科学, 2010,33(003): 10-11.
[24] 方利华,平金良,孟祥勇,等.下颌骨缺损即刻修复的动物实验研究[J].上海口腔医学, 2008, 17(4): 405-410.
[25] 蒋冰坤,吕松桧.不同比例Bio-oss与自体骨联合修复兔颌骨缺损的实验研究[J].黑龙江医药科学, 2008,31(4): 5-6.
[26] Nyan M, Sato D, Kihara H, et al. Effects of the combination with alpha -tricalcium phosphate and simvastatinonboneregeneration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(3):280-287.
[27] Ozec I, Kilic E, Gumus C,et al. Effect of local simvastatin application on mandibular defects. J Craniofac Surg. 2007; 18:546–550.
[28] 许莹莹.载辛伐他汀磷酸钙骨水泥/聚乳酸—聚羟基乙酸新型材料对剩余牙槽嵴骨修复影响的实验研究[D].吉林大学,2010.
[29] Gutierrez GE, Lalka D, Garrett IR,et al.. Transdermal application of lovastatin to rats causes profound increases in bone formation and plasma concentrations. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(7):1033-42.
[30] Maritz FJ, Conradie MM, Hulley PA, et al. Effect of statins on bone mineral density and bone histomorphometry in rodents. Arterioscler ThrombVascBiol.2001;21(10):1636-1641.
[31] Ma B, Clarke SA, Brooks RA, et al.The effect of simvastatin on bone formation and ceramic resorption in a peri-implant defect model.ActaBiomater. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(1): 149-155.
[32] Calixto JC, Lima CE, Frederico L, et al. The influence of local administration of simvastatin in calvarial bone healing in rats. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011;39(3):215-220.
[33] Anbinder AL, Junqueira JC, Mancini MN,et al. Influence of simvastatin on bone regeneration of tibial defects and blood cholesterol level in rats. Braz Dent J. 2006;17(4):267-273..
[34] Yin H,LiJ,YuX,et al.Effects of Simvastatin on Osseointegration in a Canine Total Hip ArthroplastyModel:An Experimental Study. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1534-1539. |
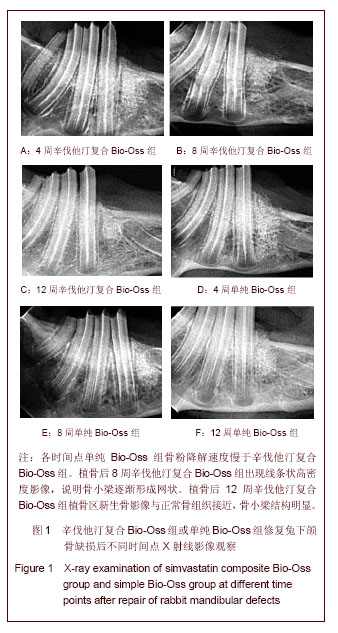
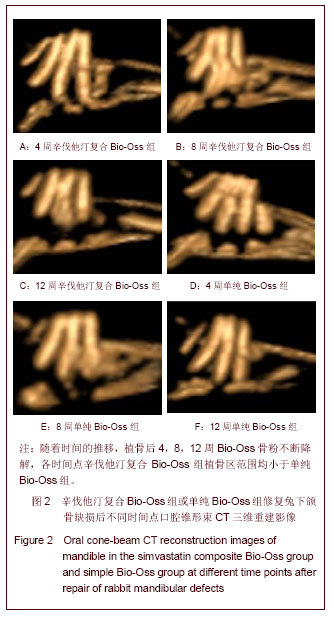
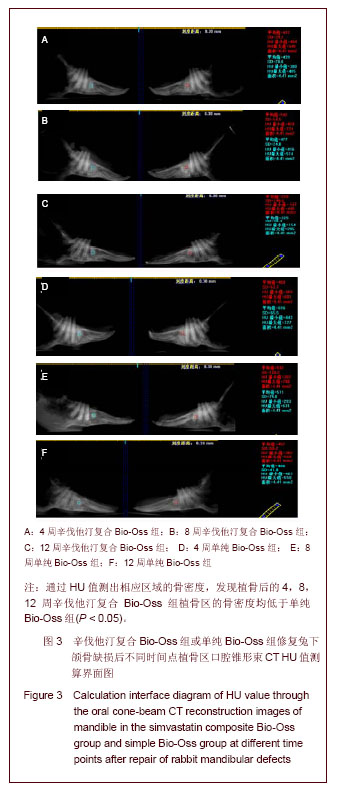
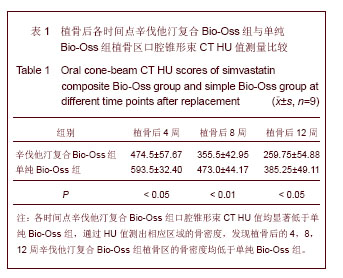
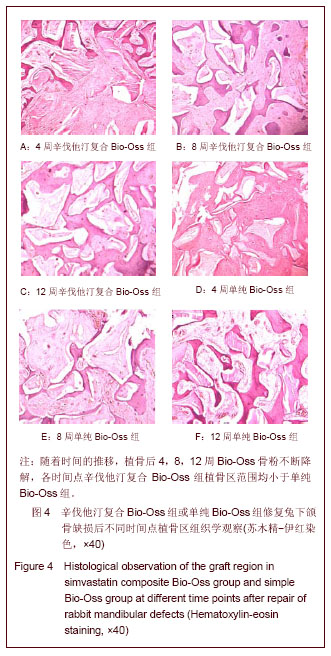
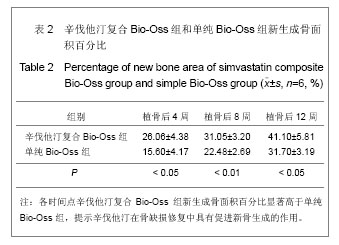
.jpg)