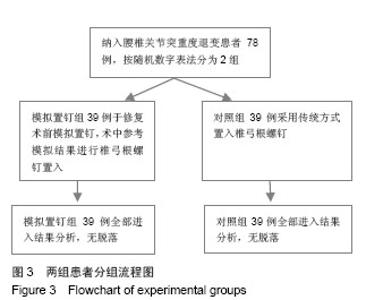
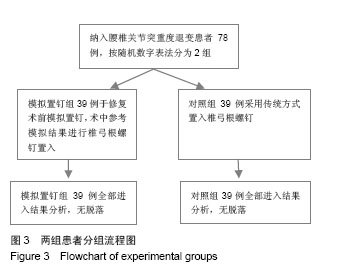
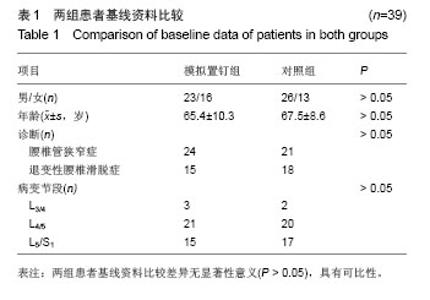
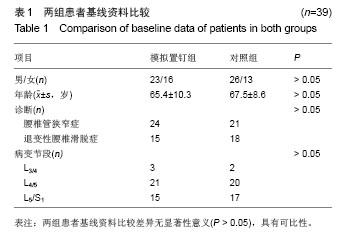
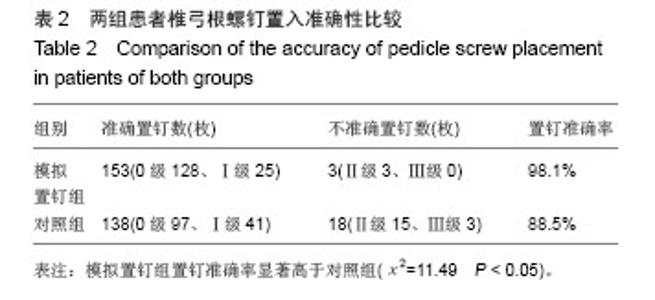
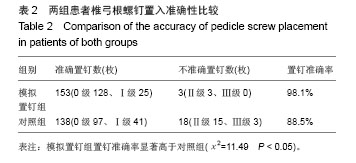
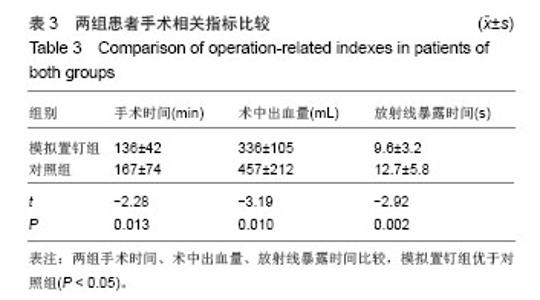
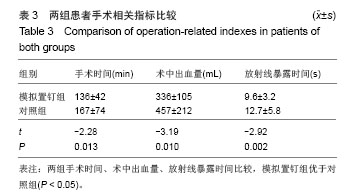
| [1]杨惠林,唐天驷,朱国良,等.胸腰椎骨折经椎弓根内固定治疗中的失误和并发症的分析[J].中华骨科杂志,1996,16(6): 356-358.
[2]Boucher HH. A method of spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959;41-B:248-259.
[3]Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Spengler D, et al. Spinal pedicle fixation: reliability and validity of roentgenogram-based assessment and surgical factors on successful screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988;13:1012-1018.
[4]Roy-Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;203:7-17.
[5]Tischer T, Aktas T, Milz S, et al. Detailed pathological changes of human lumbar facet joints L1-L5 in elderly individuals. Eur Spine J. 2006;15:308-315.
[6]李响,李春志,唐光才,等.多层螺旋CT腰椎三维成像在椎弓根螺钉置入术中的应用[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2011,19(8): 580-584.
[7]于海龙,刘军,陈语,等.腰椎骨折伤椎置钉中椎弓根螺钉可视化技术的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(4):547-552.
[8]Fujiwara A, Tamai K, Yamato M, et al. The relationship between facet joint osteoarthritis and disc degeneration of the lumbar spine: an MRI study. Eur Spine J. 1999;8:396-401.
[9]杜心如,赵玲秀,张一模,等.腰椎人字嵴顶点椎弓根螺钉进钉方法的解剖学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2002,20(2):86-88.
[10]Youkilis AS, Quint DJ, McGillicuddy JE, et al. Stereotactic navigation for placement of pedicle screws in the thoracic spine. Neurosurgery. 2001;48:771-778, 778-779.
[11]Magerl FP. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;189:125-141.
[12]杜心如,赵玲秀,张一模,等.腰椎人字嵴顶点毗邻结构的观察及其临床意义[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2001,11(2):89-91.
[13]崔新刚,丁自海,蔡锦方.胸腰椎棘突上缘根部与椎弓根关系的放射解剖学研究及意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2004,12(2): 95-97.
[14]刘金龙,毛广平,李洋,等.以关节突关节面及棘突为参照定位腰椎椎弓根的解剖学研究[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(4):277-281.
[15]覃柳生.腰椎关节突关节退变的影像学表现及意义[J]. 实用医学影像杂志, 2014,15(5):357-359.
[16]金胡日查,崔志明.腰椎关节突关节退变的影像学研究进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2013,7(8):3577-3579.
[17]Vaccaro AR, Kepler CK, Rihn JA, et al. Anatomical relationships of the anterior blood vessels to the lower lumbar intervertebral discs: analysis based on magnetic resonance imaging of patients in the prone position. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:1088-1094.
[18]Hicks JM, Singla A, Shen FH, et al. Complications of pedicle screw fixation in scoliosis surgery: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35:E465-470.
[19]韩今华,马德春,白淼,等.腰椎椎弓根螺钉进钉点的个体化定位[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(48):9066-9069.
[20]Tian NF, Huang QS, Zhou P, et al. Pedicle screw insertion accuracy with different assisted methods: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:846-859.
[21]Verma R, Krishan S, Haendlmayer K, et al. Functional outcome of computer-assisted spinal pedicle screw placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 23 studies including 5,992 pedicle screws. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19:370-375.
[22]田伟,刘亚军,刘波,等.计算机导航在脊柱外科手术应用实验和临床研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2006, 26(10):671-675.
[23]Arand M, Hartwig E, Hebold D, et al. [Precision analysis of navigation-assisted implanted thoracic and lumbar pedicled screws. A prospective clinical study]. Unfallchirurg. 2001; 104: 1076-1081.
[24]柯雨洪,尹东,昌耘冰,等.CT三维重建在脊柱半椎体畸形矫正手术中的价值[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(1):52-55.
[25]Cui G, Watanabe K, Hosogane N, et al. Morphologic evaluation of the thoracic vertebrae for safe free-hand pedicle screw placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a CT-based anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;34: 209-216.
[26]于海龙,项良碧,刘军,等.CT三维重建技术在手术治疗胸腰段椎体骨折中应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(2):157-159.
[27]严斌,张国栋,吴章林,等. 3D打印导航模块辅助腰椎椎弓根螺钉精确植入的实验研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,32(3): 252-255.
[28]张强,赵昌松,袁征,等.导板导航在复杂腰椎椎弓根螺钉置入手术中的初步应用[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(24): 11574-11577.
[29]杨波,方世兵,尹飚,等.三维重建腰椎椎弓根螺钉置入的精确性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13):2333-2338.
[30]陈昆,刘爱刚,蔡惠民,等.腰椎椎弓根螺钉置入内固定前三维测量的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(39):6914-6919.
[31]肖进,尹庆水,张美超,等. Mimics软件重建脊柱三维骨骼数据基础上快速成型的脊柱畸形模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(35):6835-6838.
[32]Yang M, Zeng C, Guo S, et al. Digitalized design of extraforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a computer-based simulation and cadaveric study. PLoS One. 2014;9(8): e105646.
[33]Marulanda GA, Nayak A, Murtagh R, et al. A cadaveric radiographic analysis on the effect of extreme lateral interbody fusion cage placement with supplementary internal fixation on indirect spine decompression. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014; 27(5):263-270.
[34]Wang MY, Vasudevan R, Mindea SA. Minimally invasive lateral interbody fusion for the treatment of rostral adjacent-segment lumbar degenerative stenosis without supplemental pedicle screw fixation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(6):861-866.
[35]Nayak AN, Gutierrez S, Billys JB, et al. Biomechanics of lateral plate and pedicle screw constructs in lumbar spines instrumented at two levels with laterally placed interbody cages. Spine J. 2013;13(10):1331-1338.
[36]Wasinpongwanich K, Paholpak P, Tuamsuk P, et al. Morphological study of subaxial cervical pedicles by using three-dimensional computed tomography reconstruction image. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(9):736-745.
[37]Lee JY, Lee JW, Pang KM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of magnesium-based resorbable metallic screw system in a bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy model using three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(2):402. |