Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (48): 7757-7762.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.48.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zero-P implant versus traditional interbody fusion with titanium plate in the repair of nerve root cervical spondylosis: 2-year follow-up of efficacy and imaging
Hu Wei, Li Lei, Liu Yan-lu, Wu Yan-sheng, Huang Yi-fei, Zhang Bin
- Department of Spine, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2014-10-16Online:2014-11-26Published:2014-11-26 -
Contact:Zhang Bin, Master, Chief physician, Second Department of Spine, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Hu Wei, M.D., Associate chief physician, Second Department of Spine, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2013211A116
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Wei, Li Lei, Liu Yan-lu, Wu Yan-sheng, Huang Yi-fei, Zhang Bin. Zero-P implant versus traditional interbody fusion with titanium plate in the repair of nerve root cervical spondylosis: 2-year follow-up of efficacy and imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(48): 7757-7762.
share this article
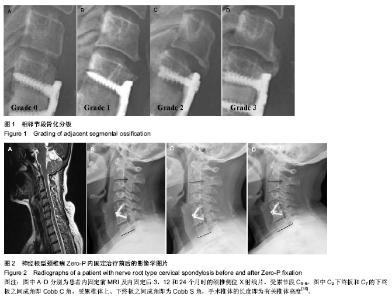
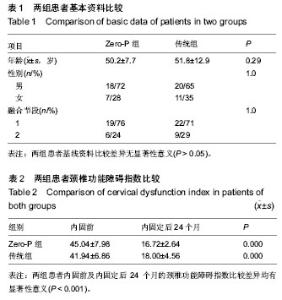
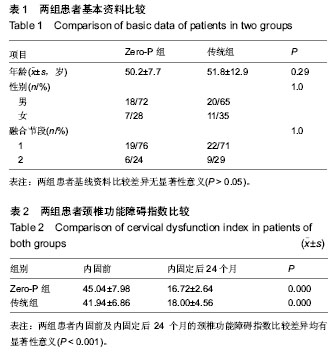
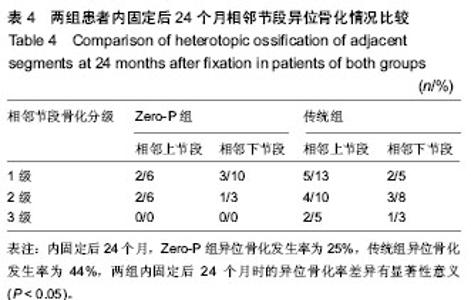
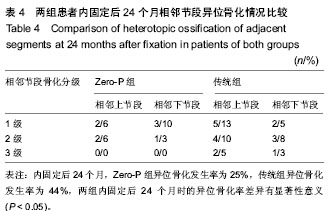
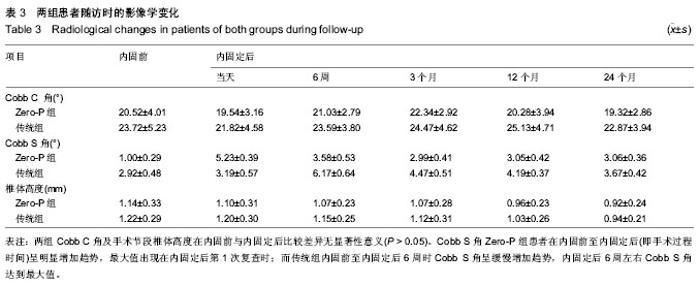
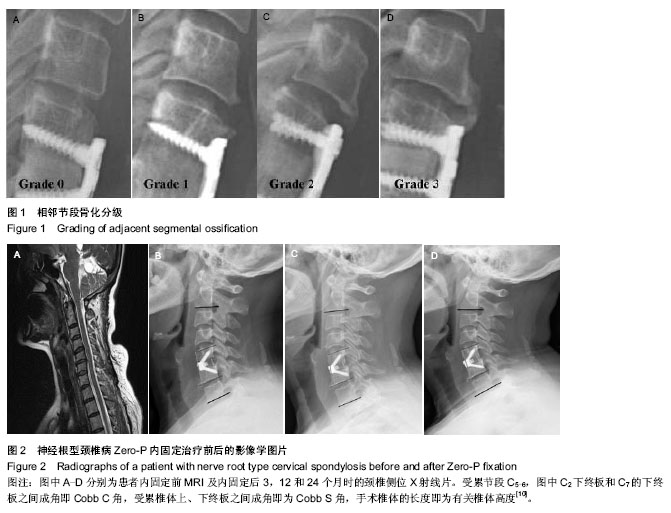
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,纳入行颈椎前路内固定患者56例,根据内固定方案分为两组,Zero-P组25例,传统组31例。全部进入结果分析,无脱落。 2.2 基线资料比较 两组患者基线资料比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 两组患者内固前、内固定后观测指标比较 Zero-P组共25例患者共计31个手术处理节段,传统组共31例患者共计40个手术处理节段。两组患者手术节段均位于C4-C7,所有患者手术过程顺利、无异常情况发生,两组患者内固前及内固定后24个月的颈椎功能障碍指数比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.00 1),内固定治疗效果良好(见表2);Zero-P组内固定后早期均发现1例吞咽困难患者,内固定后24个月随访时症状消失,吞咽困难发生率为4%;传统组内固定后发生吞咽困难有2例,内固定后24个月随访时仍有1例觉吞咽不适,其发生率为7%;两组术后吞咽困难发生率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 内固前及内固定后行X射线片检查,测量结果显示:Zero-P组与传统组在内固前及内固定后各个时间点,Cobb C角均较低,同时,Zero-P组内固前及内固定后(3个月)随访测得的Cobb C角未见明显变化(P=0.062),随着时间的延长(24个月时)Cobb C也未证明有所变化(P=0.083);Zero-P组患者在内固定后3个月时Cobb C角值增至最大,然后逐渐降低至内固前水平;Zero-P组患者Cobb S角在内固前至内固定后(即手术过程时间)呈明显增加趋势,最大值出现在内固定后第1次复查时,后逐渐下降、稳定;而传统组内固前至内固定后6周时Cobb S角呈缓慢增加趋势,内固定后6周左右Cobb S角达到最大值,后逐渐下降、稳定;两组手术节段在内固前及内固定后各个时间点椎体高度差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),两组手术节段椎体高度随时间延长逐渐下降,但降幅度较小;内固定后24个月时复查椎体高度值仍是内固前的95%左右,未见明显椎体高度变化;Cobb C、Cobb S及椎体高度在各个时间点的变化情况见表3。 2.4 两组内固定后骨性愈合及异位骨化情况比较 内固定后24个月随访检查显示:Zero-P组患者手术节段均达到了牢固骨性融合(稳定),稳定率为100%,而传统组31例患者中有30例达到牢固骨性融合(稳定),仅有1例为可能稳定,稳定率为97%,两组内固定后24个月时手术节段稳定情况比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 内固定后24个月,Zero-P组手术处理节段上下共有5个1级、3个2级异位骨化,异位骨化发生率为25%,其中上位节段发生率12%,下位阶段发生率为13%,重度异位骨化(2级或3级)率为9%;而传统组手术处理节段上下共有7个1级、7个2级和3个3级异位骨化,异位骨化发生率为"
| [1] Smith GW, Robinson RA. The treatment of certain cervical spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1958; 40: 607- 624. [2] Jacobs W, Willems PC, Kruyt M, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration: systematic review of anterior interbody fusion techniques for single and double level cervical degenerative disc disease. Spine. 2011;14:E950-960. [3] Vanek P, Bradac O, DeLacy P, et al. Comparison of three fusiontechniques in the treatment of the degenerative cervical spine. Is autograft really “the golden standard”? Spine. 2012; 37:1645-1651. [4] Kao FC,Niu CC, Chen LH.Maintenance of interbody space in one- and two-level anterior cervical interbody fusion: comparison of the effectiveness of autograft, allograft and cage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 430: 108-116. [5] McAfee PC, Capuccino A, Cunningham BW, et al. Lower incidence of dysphagia with cervical arthroplasty compared with ACDF in a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010; 23:1-7. [6] Pitzen TR, Chrobok J, Stulik J, et al. Implant complications, Psion, loss of lordosis and outcome after anterior cervical plating with dynamic or rigid plates. Spine. 2009; 34: 641-646. [7] Shimamoto N, Cunningham BW, Dmitriev AE, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of stand-alone interbody fusion cage in the cervical spine. Spine. 2001;26: 432-436. [8] Barbagallo GM, Romano D, Certo F,et al. Zero-P: a new zero-pro?le cage-plate device for single and multilevel ACDF. A single Institution series with four years maximum follow-up and review of the literature on zero-pro?le devices. J Eur Spine. 2013;22:868-878. [9] 缪锦浩,匡勇,陈德玉,等.颈前路减压零切迹椎间植骨融合内固定系统治疗颈椎病的早期疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012, 22(6):536-540. [10] 王治栋,朱若夫,杨惠林,等. 路减压Zero-p椎间融合器与传统钛板联合cage融合内固定治疗脊髓型颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(5):440-444. [11] Vermon H, Mior S. The neck disability index: a study of reliability and validity. J Manip Physiol Ther. 1991; 14: 409-415. [12] Odom GL,Finney W, Woodhall B. Cervical disc lesions. J Am Med Assoc.1958;166: 23-28. [13] Vanek P, Bradac O, DeLacy P, et al. Anterior Interbody Fusion of the Cervical Spine With Zero-P Spacer. Spine. 2013;38: E792-797. [14] Park JB, Cho YS, Riew KD. Development of adjacent-level ossi?cation in patients with an anterior cervical plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:558-563. [15] Lee DH, Lee JS, Yi JS, et al. Anterior cervical plating technique to prevent adjacent-level ossi?cation development. Spine J. 2013;13: 823-829. [16] Bohler J, Gaudernak T. Anterior plate stabilization for fracture dislocations of Loir cervical spine. J Trauma.1980; 20: 203-205. [17] Lowery GI, McDonough RF. The signi?cance of hardware failure in anterior cervical plate ?xation. Patient with two to seven-year follow-up. Spine.1998; 23: 181-186. [18] Gof?n J, van Loon J, Van Calenbergh F, et al. Long-term resultsafter anterior cervical fusion and osteosynthetic stabilization for fractures and/or dislocations of the cervical spine. J Spinal Disord. 1995;8:500-508; discussion 499. [19] Park JB, Cho YS, Riew KD. Development of adjacent-level ossi?cation in patients with an anterior cervical plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:558-563. [20] Matge G. Cervical cage fusion with ?ve different implants: 250 cases. Acta Neurochirurg. 2002; 144: 539-549. [21] Vavruch L, Hedlund R, Javid D, et al. A prospective randomized comparison between the Cloward procedure and a carbon ?brecage in the cervical spine: a clinical and radiologic study. Spine. 2002;27: 1694-1701. [22] Fernández-Fairen M, Sala P, Dufoo M Jr, et al. Anterior cervical fusion with tantalum implant: a prospective randomized controlled study.Spine. 2008; 33: 465-472. [23] Hacker RJ. A randomised prospective study of an anterior cervical fusion device with minimum two years follow-up results.J Neurosurg. 2000; 93: 222-226. [24] Peolsson A, Vavruch L, Hedlund R. Long-term randomised comparison between a carbon ? bre cage and the Cloward procedure in the cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2007;16: 173-178. [25] Scholz M, Reyes PM, Schleicher P, et al. A new stand-alone cervical anterior interbody fusion. Biomechanical comparison with established anterior cervical ?xation device. Spine. 2009; 34: 156-160. [26] Barsa P, Suchomel P. Factor affecting sagittal malalignment due to cage subsidence in stand-alone cage assisted anterior cervical fusion.Eur Spine J. 2007; 16: 1395-1400. [27] Song KJ, Teghavi CE, Lee KB, et al. The ef?cacy of plate construct augmentative versus stand-alone in anterior cervical Psion. Spine. 2009;34: 2886-2892. [28] Miao J, Shen Y, Kuang Y, et al. Early follow-up outcomes of new Zero-pro?le implant used in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(5):E193-197 |
| [1] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [2] | Pu Xingyu, Luo Wenyuan, Qian Yaowen, Cai Liyang, Zhang Chao, Chen Shaolong, Wang Yue, Zhang Wei . Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial compartmental knee osteoarthritis in young and middle-aged patients: a short-term follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1161-1166. |
| [3] | Fu Jiaxin, Xiao Lianping, Wang Shusen, Li Xiaodong, Han Liqiang, Wang Tonghao. Therapeutic effects of paraspinal approach combined with internal fixation through pedicle of fractured vertebra versus traditional AF screw-rod system for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1177-1181. |
| [4] | Qiu Zhongpeng, Li Ke, Li Gang, Liu Keyu, Du Xinhui, Meng Defeng, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan. Different treatments for two-part and three-part proximal humeral fractures by Neer classification: follow-up results analyzed using clinical economics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1188-1195. |
| [5] | Chen Xiaokang, Wu Zhengjie, Zhou Bingxue, Zhou Jiansheng, Hong Shi. Semi-restrictive total elbow arthroplasty for complex distal humeral fractures in the older adults: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1168-1171. |
| [6] | Ke Wei, Li Ke, Wang Sibo, Du Xinhui, Qiu Zhongpeng, Kang Zhilin, Wang Weishan, Li Gang . Open reduction and plate fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation for distal radius fractures: scores and linear regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1196-1202. |
| [7] | Liang Long, Wei Xu, Zhu Liguo, Yin He, Yu Jie, Feng Minshan, Chen Lin. Cervical posterior single-door laminoplasty versus double-door laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1299-1306. |
| [8] | Fan Zhirong, Peng Jiajie, Zhong Degui, Zhou Lin, Su Haitao, Huang Yongquan, Wu Jianglin, Liang Yihao. Suture anchor combined with open reduction and internal fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for ankle fracture combined with deltoid ligament injury: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1307-1312. |
| [9] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [10] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [11] | Yin Hao, Zhou Enchang, Pan Zhengjun, Chen Guang, Jiang Hua. Finite element analysis of the four and three cannulated screws combined with buttress plate fixation for the treatment of Pauwels III femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5133-5137. |
| [12] |
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming.
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3924-3930.
|
| [13] | Hao Liang, Zhang Zhonglin, Wang Baodong, Bi Zhenggang. Intertrochanteric fracture of the femur: improvement of internal fixation device, surgical changes and related disputes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2927-2935. |
| [14] | Zhang Xiang1, Qian Yuzhang1, Xie Lin2, 3, Kang Ran2, 3 . Technological methods and result evaluation of establishing the animal models of vertebral artery type of cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2427-2435. |
| [15] | Yao Liquan, Ling Qinjie, Li Jiaying, Zhong Letian, Zhou Xingping, Liu Jintao, He Erxing, Yin Zhixun. Antibiotic artificial bone implantation for treating pyogenic spondylodiscitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2133-2139. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||