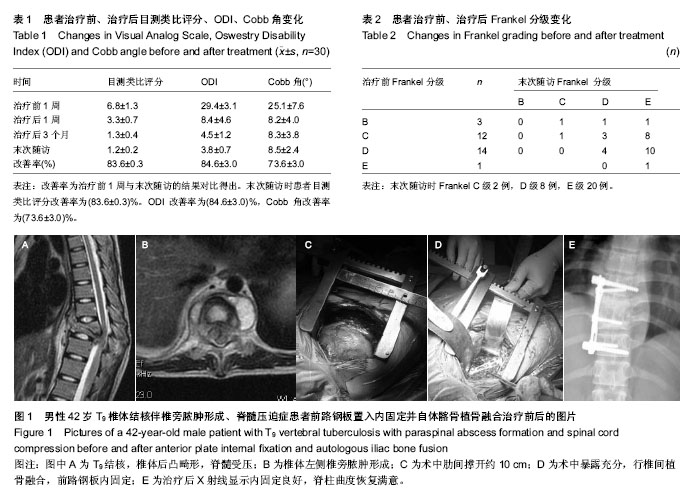
| [1] 刘志辉,罗一鲁.结核病实验诊断现状及展望[J].中国防痨杂志, 2003, 25(1): 38.
[2] Garg RK, Somvantion DS. Spinal tuberculosis:a review. Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34(5): 440-454.
[3] 吴兴彪,张曦,吕正祥,等.经胸一期病灶清除植骨融合内固定术治疗胸椎结核并截瘫[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(6):613-616.
[4] Jain AK. Tubeerculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(7):905-913.
[5] 金大地.脊柱结核治疗若干问题探讨[J].脊柱外科杂志,2005,6(3): 186.
[6] 李承球.脊柱结核的诊断和治疗进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,1999,20(3): 161-163.
[7] 金大地,陈建庭,张浩,等.一期前路椎体间植骨并内固定治疗胸腰椎结核[J].中华外科杂志,2000,38(12):900-902.
[8] 谢富荣,林春博,杨渊,等.不断肋并保留肋骨经肋间隙入路治疗胸椎疾患的体会[J].广西医科大学学报,2010,27(2):303-304.
[9] 李树林,李章红,江柏青,等.改良胸后外侧切口在胸外科的应用[J].微创医学,2006,1(4):250-252.
[10] 刘茂林,杨勇.腋下不中断肋骨小切口在胸外手术中的应用[J].中华临床医药,2004,5(2):3.
[11] 余雨,王群波,邵高海.前路钉棒系统在多发下胸椎结核手术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(19):1595-1598.
[12] 候树勋,邱贵兴,金大地,等.脊柱外科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2005:1151-1182.
[13] 张巍巍,张怀学,余华伟,等.前路钉-棒系统在手术治疗胸椎结核中的应用[J].脊柱外科杂志,2006,4(1):46-47.
[14] 瞿东滨,金大地,陈建庭,等.脊柱结核的一期手术治疗[J].中华医学杂志,2003,83(2):110-113.
[15] 张宏其,龙文荣,邓展生,等.影响一期手术治疗脊柱结核并截瘫患者疗效的相关因素[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(12): 720-723.
[16] 余雨,李波,邵高海.侧前路单钉棒系统内固定治疗多发胸椎结核[J].四川医学,2008,29(12):1641-1643.
[17] 林宏,李康宁,向勇.胸腰椎结核伴截瘫的前路手术治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(1):23-24.
[18] 李涛,杨述华,刘国辉,等.钛网植骨侧前路钉棒系统内固定治疗脊柱结核伴截瘫[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2007, 15(5): 274-276.
[19] 陈云生,游辉,陈荣春. 胸腔镜辅助下前路病灶清除植骨内固定治疗胸椎结核[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(3):184-186.
[20] 张忠民,付忠泉,尹刚辉,等.胸椎结核外科治疗的长期临床随访[J].脊柱外科杂志,2014,10(4):198-201.
[21] 范俊,秦世炳,董伟杰.胸椎结核术后常见并发症的临床分析[J].北京医学,2014,36(3):184-187.
[22] 朱定川,高峰,曾建成.胸椎结核经前路病灶清除融合单钉棒固定术的疗效观察[J].华西医学,2014, 29(1):26-29.
|