Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (29): 4625-4629.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.29.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Differentiation of HaCaT cells infected with lentivirus
Hou Na1, Hou Bin-bin2, Wang Xiu-li3, Liu Yu-fang1, Guo Xin4, Lin Mao2, Xu Xue-zhu2
- 1Department of Dermatology, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Dermatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116027, Liaoning Province, China; 3College of Basic Medical Science, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China; 4Group 1802, Department of Biotechnology, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian 116021, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-11Online:2014-07-09Published:2014-07-09 -
Contact:Xu Xue-zhu, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Dermatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116027, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Hou Na, Master, Physician, Department of Dermatology, Zhongshan Hospital Affiliated to Dalian University, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171489
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hou Na, Hou Bin-bin, Wang Xiu-li, Liu Yu-fang, Guo Xin, Lin Mao, Xu Xue-zhu. Differentiation of HaCaT cells infected with lentivirus[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(29): 4625-4629.
share this article
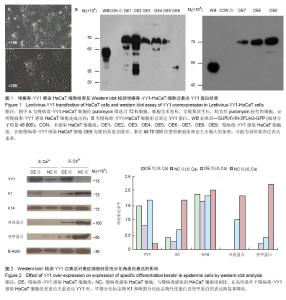
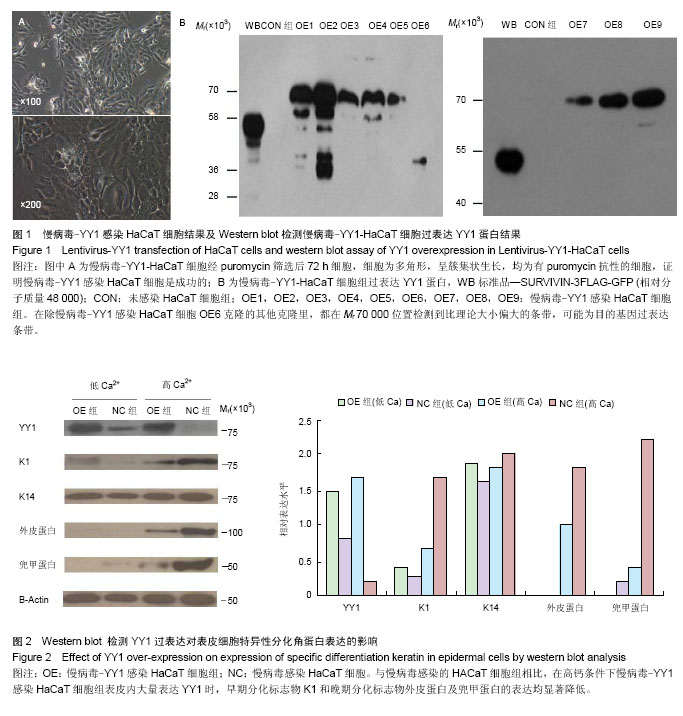
2.1 慢病毒-YY1感染HaCaT细胞结果 慢病毒-YY1- HaCaT细胞经puromycin筛选后72 h细胞,细胞为多角形,呈簇集状生长,状态良好,均为有puromycin抗性的细胞,证明慢病毒-YY1感染HaCaT细胞是成功的(图1A)。 2.2 慢病毒-YY1-HaCaT细胞组过表达YY1蛋白 与对照组相比,慢病毒-YY1感染HACaT细胞组细胞合成大量的YY1蛋白,说明慢病毒-YY1感染HaCaT细胞是成功的。慢病毒-YY1感染HaCaT细胞组OE1、OE2、OE4单克隆细胞内检测到理论大小位置有条带,判断为目的条带,但在条带附近有杂带;在除慢病毒-YY1感染HaCaT细胞OE6克隆的其他克隆里,都在Mr 70 000位置检测到比理论大小偏大的条带,可能为目的基因过表达条带(图1B)。 2.3 YY1过表达对表皮细胞特异性分化角蛋白表达的影响 Western blot法结果显示:与慢病毒感染的HaCaT细胞组相比,在高钙条件下慢病毒-YY1感染HaCaT细胞组表皮内大量表达YY1时,早期分化标志物K1和晚期分化标志物外皮蛋白及兜甲蛋白的表达均显著降低(P < 0.05),而基底层角质形成细胞标志物K14的表达在两组中差异无显著性意义(图2)。"
| [1] Proksch E,Brandner JM,Jensen JM.The skin: an indispensable barrier.Exp Dermatol.2008;17(12):1063-1072. [2] Ramms L, Fabris G, Windoffer R,et al.Keratins as the main component for the mechanical integrity of keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2013;110(46):18513-18518. [3] Pellegrini G,Rama P,Mavilio F,et al.Epithelial stem cells in comeal regeneration and epidermal gene therapy. J Pathol. 2009;217(2):217-228. [4] Rubinson DA, Dillon CP, Kwiatkowski AV, et al.A lentivirus-based system to functionally silence genes in primary mammalian cells, stem cells and transgenic mice by RNA interference. Nat Genet.2003;33(3):401-406. [5] Xu X,Kawachi Y,Nakamura Y, et al.Yin-Yang-1 negatively regulates the Differentiation-Specific transcription of mouse loricrin gene in undifferentiated keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol.2004;123:1120-1126. [6] Regnier M, Vaigot P, Darmon M, et al.Onset of epidermal differentiation in rapidly proliferating basal keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol.1986;87:472-476. [7] Yoshimi N, Imai Y, Kakuno A, et al. Epithelial keratin and filaggrin expression in seborrheic keratosis: evaluation based on histopathological classification. Int J Dermatol. 2013;20: 1365-4632. [8] Rothnagel JA, Meherl T, Idler WW,et al. The gene for mouse epidermal filaggrin precursor. Its partial characterization, expression, and sequence of a repeating filaggrin unit. J Biol Chem.1987;262:15643-15648. [9] Guo BR, Sun LD, Cui Y, et al. Progressive symmetrical erythrokeratoderma: report of two Chinese families and evaluation for mutations in the loricrin, connexin 30.3 and connexin 31 genes. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38(8):925-927. [10] Atchison L, Ghias A, Wilkinson F, et al. Transcription factor YYI flinaions as a PcG protein in vivo. Embo J.2003;22: 1347-1358. [11] Brown JL, Mucci D, Whiteley M, et al. The Drosophila Polycomb group gene pleiohomeotic encodes aDNA binding protein with homology to the transcription factor YYI. Molecular Cell.1998;1:1057-1064. [12] Fisher C, Haydock PV, Dale BA. Localization of profilaggrin mRNA in newborn rat skin by in situ hybridization. J Invest Dermatol.1987;88:661-664. [13] Rice RH, Green H. Presence in human epidermal cells of a soluble protein precursor of the cross-linked envelope: activation of the cross-linking by calcium ions. Cell.1979;18: 681-694. [14] 陈彩云,刘亚京,牛忠英.慢病毒载体的研究进展及应用[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2012,13(2):117-120. [15] Engelbert D, Schnerch D, Baumgarten A, et al. The ubiquitin ligase APC (Cdh1) is required to maintain genome integrity in primary human cells.Oncogene. 2008;27(7):907-917. [16] Hizi A, Herschhorn A. Retroviral reverse transcriptases fother than those of HIV-1 and murine leukemia virus): a comparison of their molecular and biochemical properties. Virus Res. 2008; 134(1-2):203-220. [17] Masurier C,Boutin S,Veron P,et al.Enhanced lentiviral transduction of monocyte—derived dendritic cells in the presence of conditioned medium from dying monocytes. Hum Gene Ther. 2007;18(2):161-170. [18] Taguchi S, Kawachi Y, Ishitsuka Y, et al.Overexpression of the transcription factor Yin-Yang-1 suppresses differentiation of HaCaT cells in three-dimensional cell culture. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131(1):37-45 [19] Gordon S, Akopyan G, Garban H, et al.Transcription factor YY1: structure, function, and therapeutic implication in cancer biology. Oncogene.2006;25:1125-1142. [20] Castellano G, Torrisi E, Ligresti G, et al. The involvement of the transcription factor Yin Yang 1 in cancer development and progression. Cell Cycle.2009;8(9):1367-1372. [21] Sui G, Affar B, Shi Y,et al. Yin Yang 1 is a negative regulator of p53. Cell. 2004;117:859-872. [22] Vega MI, Jazirehi AR, Huerta-Yepez S,et al. Rituximab-induced inhibition of YY1 and Bcl-xLexpression in Ramos non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cell line via inhibition of NF-kappa B activity: role of YY1 and Bcl-xL in Fas resistance and chemoresistance, respectively. J Immunol.2005;175: 2174-2183. [23] Walowitz JL, Bradley ME, Chen S,et al. Proteolytic regulation of the zinc finger transcription factor YY1, a repressor of muscle-restricted gene expression. J Biol Chem.1998;273: 6656-6661. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||