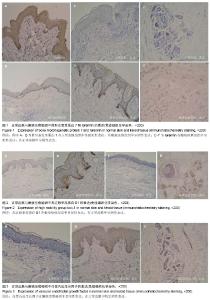
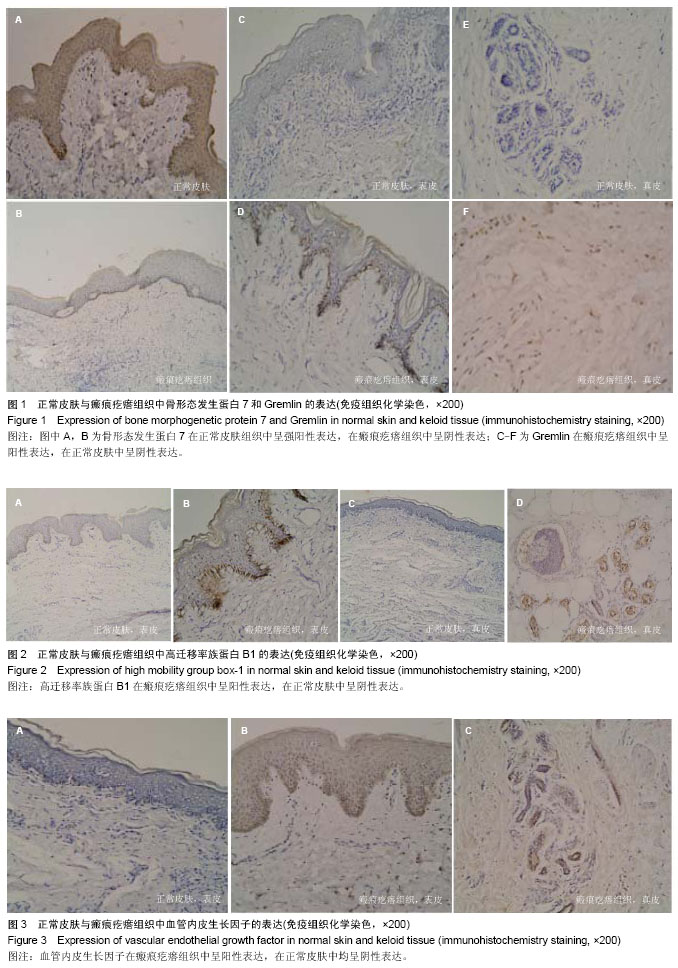
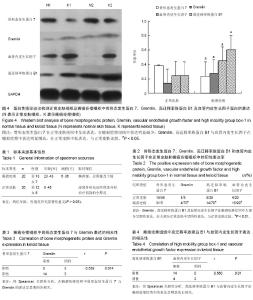
| [1] Namazi MR, Fallahzadeh MK, Schwartz RA. Strategies for prevention of scars. what can we learn from fetal skin? Int J Dermatol.2011;50(1):85-93.
[2] Ogawa R. The most current algorithms for the treatment and prevention of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Plast Reconstr Surg.2010;125(2):557-568.
[3] 潘丽,张选奋.Smads介导转化生长因子β1信号转导通路与病理性瘢痕[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(50):9485-9490.
[4] Yang T, Chen SL, Lu XJ, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 7 suppresses the progression of hepatic fibrosis and regulates the expression of gremlin and transforming growth factorβ1. Mol Med Report.2012;6(1):246-252.
[5] Pegorier S, Campbell GA, Kay AB,et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)-4 and BMP-7 regulate differentially Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-β1 in normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLF).Respir Res. 2010;11(85):1-11.
[6] Nguyen TQ, Goldschmeding R. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-7 and Connective Tissue Growth Factor: Novel Targets for Treatment of Renal Fibrosis.Pharm Res. 2008;25(10): 2416-2426.
[7] Yang G, Zhu Z, Wang Y, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.Toxicol Lett. 2013;220(2):103-108.
[8] Wang S, Hirschberg R. Y-box protein-1 is a transcriptional regulator of BMP7. Cell Biochem.2011;112(4):1130-1137.
[9] Wang S, Hirsehberg R. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 signals opposing transforming growth factor beta in mesangial cell. Biol Chem.2004;279(22):23200-23206.
[10] Oyama Y, Hashiguchi T, Taniguchi N, et al. High-mobility group box-1 prote in promotes granulomatous nephritis in adenine-induced nephropathy.Lab Invest.2010;90(6): 853-866.
[11] He Y, Zhou X, Zheng X,et al. Exogenous high-mobility group box 1 protein prevents postinfarction adverse myocardial remodeling through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.2013;114(7):1634-1641.
[12] Wang FP, Li L, Li J, et al. High mobility group box-1 promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatic stellate cells via TLR4-dependent signal pathways of PI3K/Akt and JNK. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64373.
[13] Chen BL, Peng J, Li QF,et al. Exogenous bone morphogenetic protein-7 reduces hepatic fibrosis in Schistosoma japonicum -infected mice via transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19(9):1405-1415.
[14] Wang S,Hirsehberg R.BMP-7 antagonizes TGF-β dependent fibrogenesis in mesangial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;284(5):1006-1013.
[15] Djamali A, Samaniego M. Fibrogenesis in kidney transplantation: potential targets for prevent ion and therapy. Transplantation.2009;88 (10):1149-1156.
[16] Weiskirchen R, Meurer SK. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 in focus:A member of the transforming growth factor-superfamily is implicated in the maintenance of liver health. Hepatology. 2007;45(5):1324-1325.
[17] Sun J, Zhuang FF, Mullersman JE, et al.BMP4 activation and secretion are negatively regulated by an intracellular gremlin-BMP4 interaction. Biol Chem.2006;281(39) : 29349-29356.
[18] Zeisberg M, Kalluri R.Reversal of experimental renal fibrosis by BMP7 provides insights into novel therapeutic strategies for chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol.2008;23(9) : 1395-1398.
[19] Zhang LQ,Loato M,Munona P, et al. Normal and hypertrophic scars: qualification and localization of messenger RNAs for type I, and collangens.Br J Dermartol.1994;20(2):130-453.
[20] Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia:role of the HIF system. Nat Med.2003;9(6):677-684.
[21] Sims GP, Rowe DC, Rietdijk ST,et al.HMGB1 and RAGE in inflammation and cancer.Annu Rev Immunol. 2010;28(11): 367-388.
[22] Leemans JC, Butter LM, Pulskens WP, et al. The role of Tol-l like receptor 2 in inflammation and fibrosis during progressive renal in jury. PLoS One.2009;4(5):5704-5712.
[23] DcAgati V, SchmidtA M. RAGE and the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease. N atRev Nephro.2010;6(6):352-360.
[24] Liu T, He YW. Protective effect of recombinant HMGB1 A box protein in mouse with acute hepatic failure. Zhong hua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.2010;18(3):222-226.
[25] Dardenne AD, Wulff BC, Wilgus TA. The alarmin HMGB-1 influences healing outcomes in fetal skin wounds.Wound Rep Reg.2013;21(3):282-291.
[26] Kitahara T, Takeishi Y, Harada M, et al. High-mobility group box1 restores cardiac function after myocardial infarction in transgenic mice.Cardiovasc Res. 2008;80(1):40-46.
[27] Urbonaviciute V, Furnrohr BG, Meister S, et al. Induction of inflammatory and immune responses by HMGB1 nucleosome complexes: implications for the pathogenesis of SLE. J Exp Med.2008;205(13):3007-3018.
[28] Goldin A,Beckman JA,Schmidt AM,et al. Advanced glycation end products:sparking the development of diabetic vascular injury.Circulation.2006;114(6):597-605.
[29] Straino S, DiCarlo A, Mangoni A, et al. High-mobility group box 1 protein in human and murine skin: involvement in wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128(6):1545-1553.
[30] Zhang Q, O’Hearn S, Kavalukas SL, et al. Role of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in wound healing. J Surg Res. 2011;176(4):343-347.
[31] Ranzato E, Patrone M, Pedrazzi M, et al. HMGb1 promotes wound healing of 3T3 mouse fibroblasts via RAGEHMGB dependent ERK1/2 activation. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2010; 57(2):9-17. |