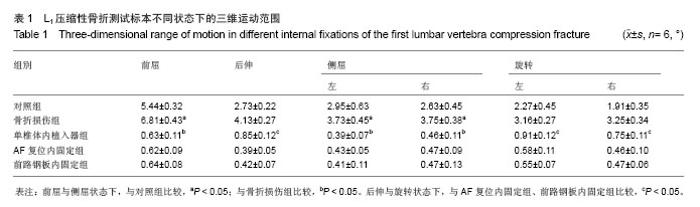
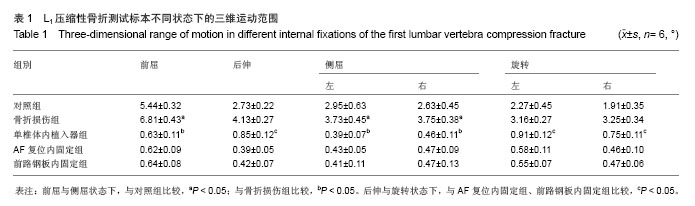
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (9): 1350-1355.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.09.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Primary development and biomechanics of single vertebrae internal fixation system for thoracolumbar compression fracture
Li Ji-cai1, Liu Ping-jun1, He Yong-li1, Zhao Wei-dong2, Liang Dong-zhu2, Mao Bing-yan1
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, Simen Hospital Affiliated to Changsha Medical School, Changde 415300, Hunan Province, China; 2 Key Laboratory of Biomechanics, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2014-02-26Published:2014-02-26 -
Contact:Liu Ping-jun, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Simen Hospital Affiliated to Changsha Medical School, Changde 415300, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Li Ji-cai, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Simen Hospital Affiliated to Changsha Medical School, Changde 415300, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Project of Hunan Provincial Health Department, No. B2009134
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ji-cai, Liu Ping-jun, He Yong-li, Zhao Wei-dong, Liang Dong-zhu, Mao Bing-yan. Primary development and biomechanics of single vertebrae internal fixation system for thoracolumbar compression fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(9): 1350-1355.
share this article
| [1]贺用礼,刘平均,王长青,等.胸腰椎影像学测量及其临床意义[J].中国现代医药杂志,2012,14(9):7-10.[2]Wilson DR, Myers ER, Mathis JM,et al. Effect of augmentation on the mechanics of vertebral wedge fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(2):158-165.[3]魏富鑫,刘少喻,赵卫东,等.单节段与双节段椎弓根螺钉固定胸腰椎单椎体骨折的生物力学比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2007, 17(1):46-50.[4]Korovessis P, Baikousis A, Zacharatos S,et al. Combined anterior plus posterior stabilization versus posterior short-segment instrumentation and fusion for mid-lumbar (L2-L4) burst fractures.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(8): 859-868.[5]Pintar FA, Yoganandan N, Maiman DJ,et al. Thoracolumbar spine fractures in frontal impact crashes.Ann Adv Automot Med. 2012;56:277-283.[6]Jun W, Yi-Jun K, Fei C. Application of a crescent-shaped PMMA strut in anterior spinal reconstruction of thoracolumbar and lumbar burst fractures: a new technique.Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22(2):161-166.[7]黄刚,陈海云,刘卓勋,等.经皮椎体成形术与经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].南方医科大学学报,2010, 30(12):2729-2732.[8]Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK,et al. Initial outcome and efficacy of "kyphoplasty" in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1631-1638.[9]郑召民,李佛保.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术-问题与对策[J].中华医学杂志,2006,86(27):1878-1880.[10]Hulme PA, Krebs J, Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17):1983-2001.[11]Chen B, Li Y, Xie D,et al. Comparison of unipedicular and bipedicular kyphoplasty on the stiffness and biomechanical balance of compression fractured vertebrae.Eur Spine J. 2011;20(8):1272-1280.[12]Kim YY, Rhyu KW. Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(11):1907-1912. [13]Heo DH, Chin DK, Yoon YS, et al.Recollapse of previous vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty.Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(3):473-480.[14]Bouza C, López T, Magro A,et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review.Eur Spine J. 2006;15(7): 1050-1067. [15]Dupuy DE, Palmer WE, Rosenthal DI.Vertebral fluid collection associated with vertebral collapse.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 167(6):1535-1538.[16]Fribourg D, Tang C, Sra P,et al. Incidence of subsequent vertebral fracture after kyphoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(20):2270-2276.[17]Frankel BM, Monroe T, Wang C. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation: an elevation in adjacent-level fracture risk in kyphoplasty as compared with vertebroplasty.Spine J. 2007; 7(5):575-582.[18]Garfin SR, Buckley RA, Ledlie J,et al. Balloon kyphoplasty for symptomatic vertebral body compression fractures results in rapid, significant, and sustained improvements in back pain, function, and quality of life for elderly patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19):2213-2220.[19]Tzermiadianos MN, Renner SM, Phillips FM,et al. Altered disc pressure profile after an osteoporotic vertebral fracture is a risk factor for adjacent vertebral body fracture.Eur Spine J. 2008;17(11):1522-1530. [20]Berlemann U, Franz T, Orler R,et al. Kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective non-randomized study.Eur Spine J. 2004;13(6):496-501. [21]Boszczyk BM, Bierschneider M, Hauck S,et al. Transcostovertebral kyphoplasty of the mid and high thoracic spine.Eur Spine J. 2005;14(10):992-999. [22]Grohs JG, Matzner M, Trieb K,et al. Minimal invasive stabilization of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective nonrandomized comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(3):238-242.[23]Ledlie JT, Renfro M.Balloon kyphoplasty: one-year outcomes in vertebral body height restoration, chronic pain, and activity levels.J Neurosurg. 2003;98(1 Suppl):36-42.[24]Phillips FM, Ho E, Campbell-Hupp M,et al. Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(19):2260-2265.[25]Suzuki N, Ogikubo O, Hansson T. Previous vertebral compression fractures add to the deterioration of the disability and quality of life after an acute compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(4):567-574.[26]Schultheiss M, Hartwig E, Sarkar M,et al. Biomechanical in vitro comparison of different mono- and bisegmental anterior procedures with regard to the strategy for fracture stabilisation using minimally invasive techniques.Eur Spine J. 2006; 15(1):82-89. [27]Verheyden AP, Hoelzl A, Lill H,et al.The endoscopically assisted simultaneous posteroanterior reconstruction of the thoracolumbar spine in prone position.Spine J. 2004;4(5): 540-549.[28]Schultheiss M, Hartwig E, Kinzl L,et al.Thoracolumbar fracture stabilization: comparative biomechanical evaluation of a new video-assisted implantable system.Eur Spine J. 2004;13(2):93-100. [29]Verheyden AP, Katscher S, Gonschorek O,et al. Endoscopically assisted minimally invasive reconstruction of the anterior thoracolumbar spine in prone position. Unfallchirurg. 2002;105(10):873-880.[30]Steib JP, Charles YP, Aoui M. In situ contouring technique in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures.Eur Spine J. 2010;19 Suppl 1:S66-68.[31]Wood KB, Bohn D, Mehbod A. Anterior versus posterior treatment of stable thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit: a prospective, randomized study.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18 Suppl:S15-23.[32]Mahar A, Kim C, Wedemeyer M,et al.Short-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(14):1503-1507.[33]Ringel F, Stoffel M, Stüer C,et al. Endoscopy-assisted approaches for anterior column reconstruction after pedicle screw fixation of acute traumatic thoracic and lumbar fractures.Neurosurgery. 2008;62(5 Suppl 2):ONS445-452. [34]Arand M, Kinzl L, Hartwig E.Combined posterior and anterior endoscopic supported instrumentation of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Arguments, concepts and first clinical results. Zentralbl Chir. 2002;127(6):490-496.[35]陈祥和,李孔嘉.应用钛合金椎体植入物行椎体重建的临床报告及其生物力学分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10):908-912.[36]Lee KS, Cho YJ, Choi JH, et al. A small amount of bone cement injected vertebroplasty utilizing percutaneous vertebral body access (PVBA) technique for osteoporotic vertebral fractures.Korean J Spine. 2005;2(4):333-341.[37]Beisse R.Video-assisted techniques in the management of thoracolumbar fractures.Orthop Clin North Am. 2007;38(3): 419-429.[38]Beisse R, Mückley T, Schmidt MH, et al.Surgical technique and results of endoscopic anterior spinal canal decompression.J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(2):128-136.[39]明江华,郑慧锋,赵奇,等.Sextant经皮椎弓根钉棒微创系统治疗胸腰椎骨折:随访评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(48): 8343-8348.[40]刘涛,李长青,周跃,等.新型经皮椎弓根螺钉系统的设计与生物力学测试[J] .中华骨科杂志,2010,30(6):594-599.[41]Schmidt OI, Strasser S, Kaufmann V, et al. Role of early minimal-invasive spine fixation in acute thoracic and lumbar spine trauma. Indian J Orthop. 2007;41(4):374-380. [42]Wang HW, Li CQ, Zhou Y, et al. Percutaneous pedicle screw Fixation through the pedicle of fractured vertebra in the treatment of type A thoracolumbar fractures using Sextant system: an analysis of 38 cases. Chin J Traumatol. 2010; 13(3): 137-145.[43]Briem D, Windolf J, Lehmann W,et al.Bone grafts endoscopically applied to the spine Ergebnisse der anterioren Fusion und therapeutische Konsequenzen.Unfallchirurg. 2004; 107(12):1152-1161.[44]Olinger A, Vollmar B, Hildebrandt U,et al. Experimental development and validation of a technique for lumboendoscopic anterior fusion of lumbar spine fractures: comparison of endoscopic and open surgery in a live porcine model.Surg Endosc. 2000;14(9):844-848.[45]Olinger A, Hildebrandt U, Vollmar B,et al. Laparoscopic- transperitoneal and lumboscopic-retroperitoneal surgery of the spine. Developments from animal experiments for use in clinical practice. Zentralbl Chir. 1999;124(4):311-317. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [6] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [7] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [8] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [9] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [10] | Tan Jiachang, Yuan Zhenchao, Wu Zhenjie, Liu Bin, Zhao Jinmin. Biomechanical analysis of elastic nail combined with end caps and wire fixation for long oblique femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 334-338. |
| [11] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [12] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [13] | Li Kun, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Gao Shang, Sun Hao, Yang Xi, Wang Xing, Dai Lina . A 4-year-old child model of occipito-atlanto-axial joints established by finite element dynamic simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3773-3778. |
| [14] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||