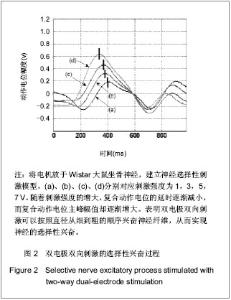
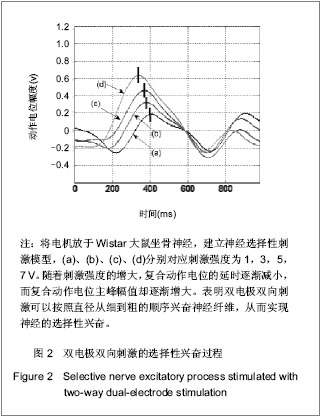
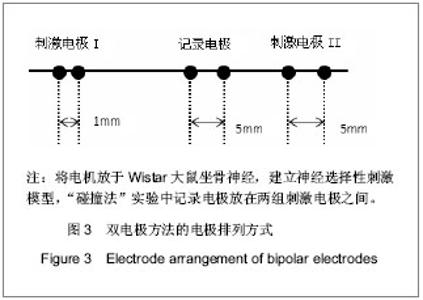
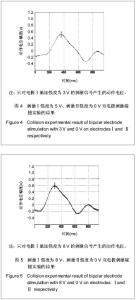
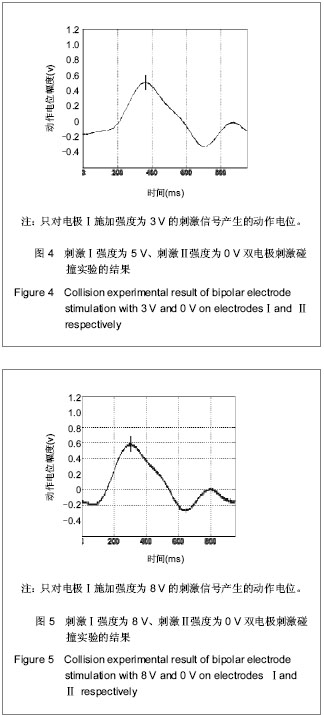
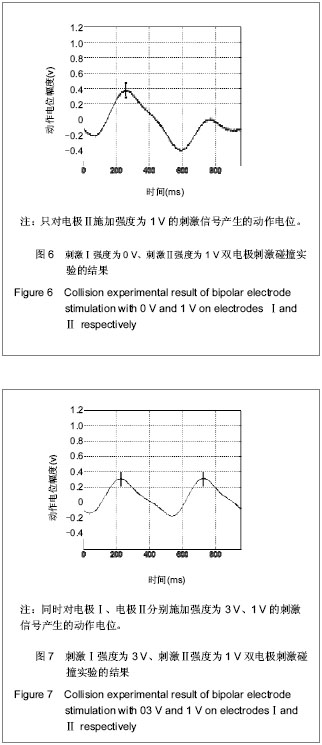
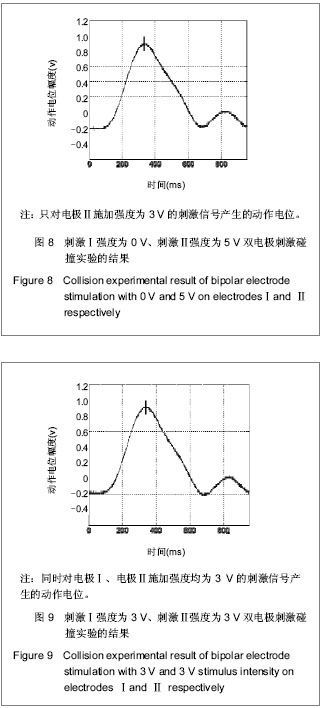
| [1] Blair EA, Erlanger JA. A comparison of the characteristics of axons through their individual electrical responses. Am J Physiol - Legacy Content.1933; 106(3): 524-564.[2] Koldewijn EL, Rijkhoff NJ, Van Kerrebroeck EV, et al. Selective sacral root stimulation for bladder control: Acute experiments in an animal model. J Urol. 1994;151(6): 1674-1679.[3] Tosato M, Yoshida K, Toft E, et al. Closed-loop control of the heart rate by electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve. Med Biol Eng Comput.2006;44(3): 161-169.[4] Zhou BH, Baratta R, Solomonow M. Manipulation of muscle force with various firing rate and recruitment control strategies. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng.1987;34(2): 128-139.[5] Solomonow M. External control of the neuromuscular system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng.1984;BME-31(12): 752-763.[6] Solomonow M, Eldred E, Lyman J, et al. Control of muscle contractile force through indirect high-frequency stimulation. Am J Phys Med.1983;62(2): 71-82.[7] Ishigooka M, Hashimoto T, Sasagawa I, et al. Modulation of the urethral pressure by high-frequency block stimulus in dogs. Eur Urol.1994;25(4): 334-337.[8] 沈强,刘雪良,蒋大宗,等. 利用双向方波脉冲刺激实现神经纤维选择性兴奋的双电极方法[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2001, 20(6): 533-540.[9] 沈强,邰常峰,蒋大宗.用双向脉冲作选择性神经刺激的研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,1999;(1):36-44.[10] 张旭,邰常峰,马斌荣. 用高频双向脉冲电刺激实现有髓神经传导阻断的仿真研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2006,25(3):280-284.[11] 于磊,陈安宇,任朝晖,等. 利用单电极不对称双向脉冲电刺激实现有髓神经传导阻断的仿真研究[J]. 北京生物医学工程,2008, 27(1):33-36. [12] 沈强,邰常峰,蒋大宗. 哺乳动物神经纤维的双向脉冲选择性刺激研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2000,34(2): 52-57.[13] 沈强,邰常峰,蒋大宗. 神经纤维双向选择性刺激方法仿真研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,1998,15(1):17-21. |