Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4337-4346.doi: 10.12307/2026.103
Previous Articles Next Articles
Impact of Zi-Zhu ointment on the miRNA expression profile in mouse models of diabetic ulcers: a high-throughput sequencing analysis
Li Wenhui1, 2, Fan Weijing3, Liu Guobin3
- 1Collaborative Innovation Center, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China; 2School of Pharmacy, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China; 3Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
-
Received:2025-02-15Accepted:2025-06-10Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-11-27 -
Contact:Liu Guobin, PhD, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
About author:Li Wenhui, PhD, Associate professor, Collaborative Innovation Center, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China; School of Pharmacy, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Program), No. 81804096 (to LWH); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82274528 (to LGB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Wenhui, Fan Weijing, Liu Guobin. Impact of Zi-Zhu ointment on the miRNA expression profile in mouse models of diabetic ulcers: a high-throughput sequencing analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4337-4346.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
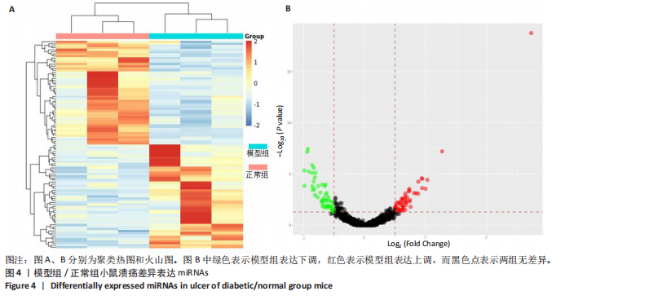
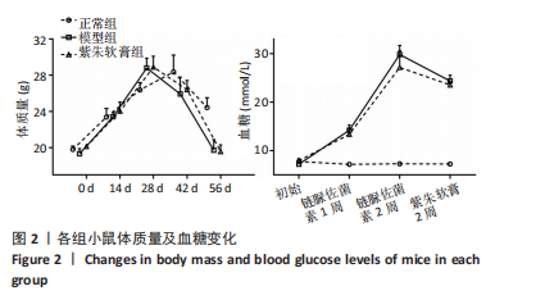
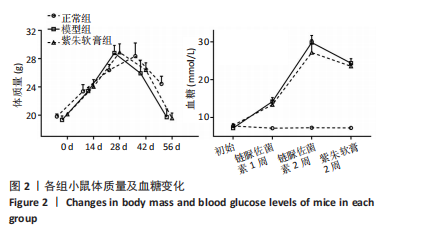
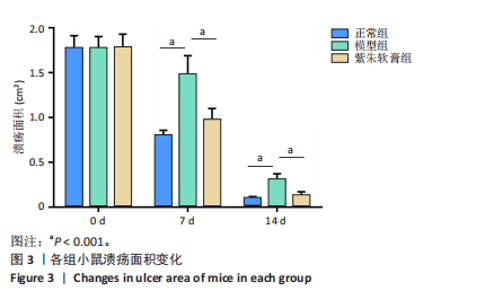
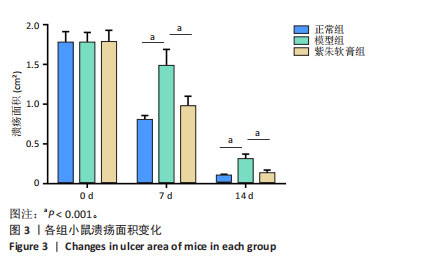
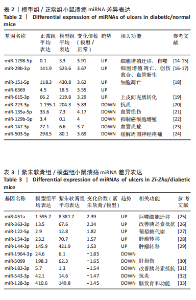
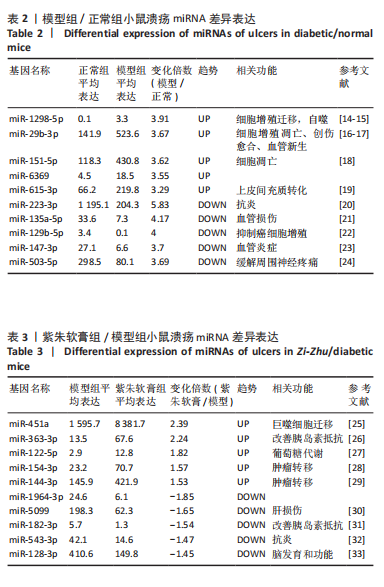
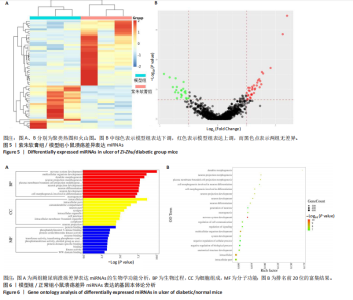
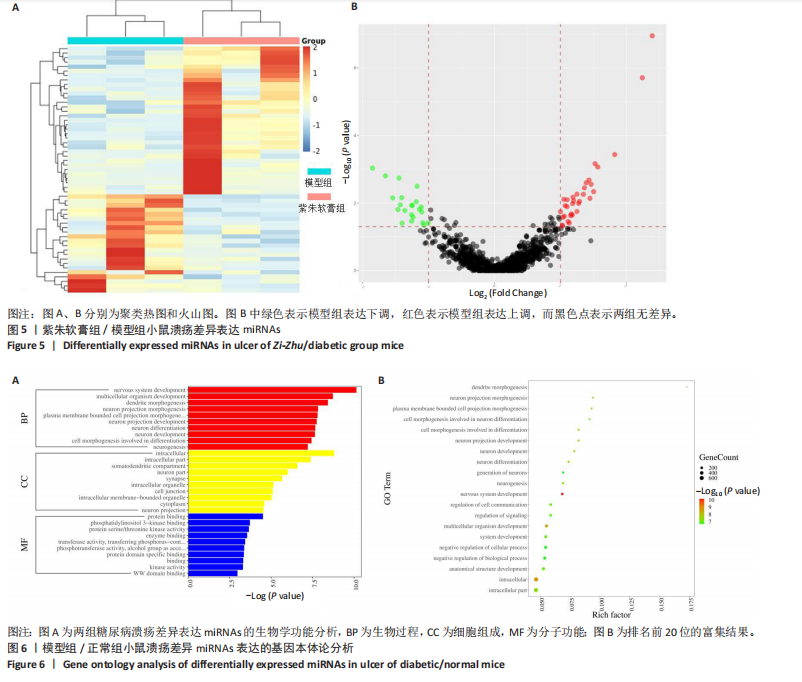
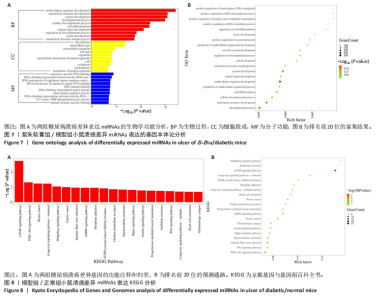
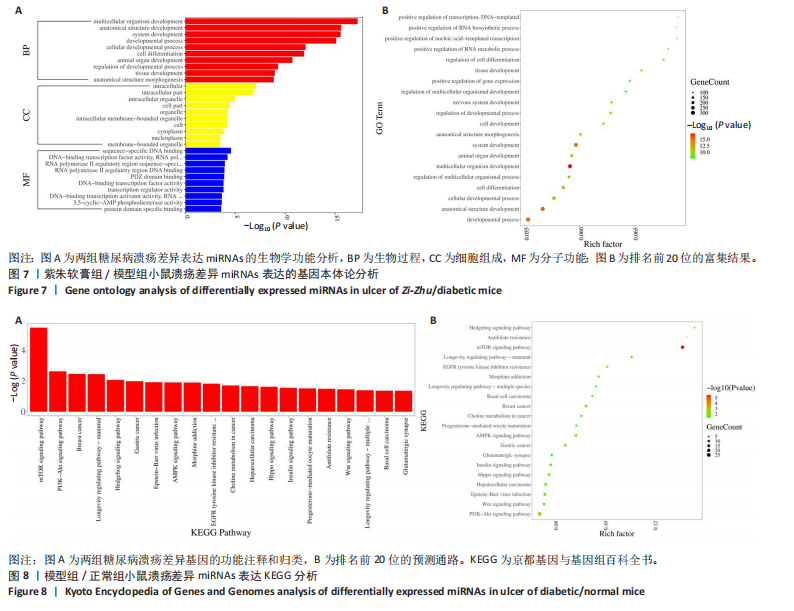
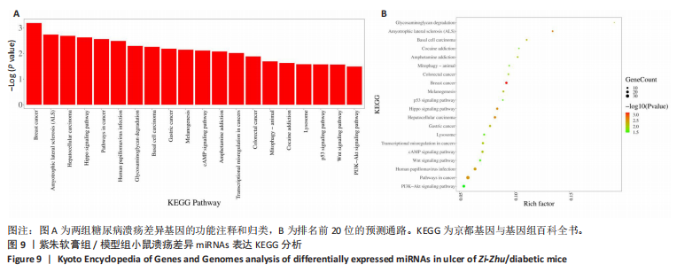
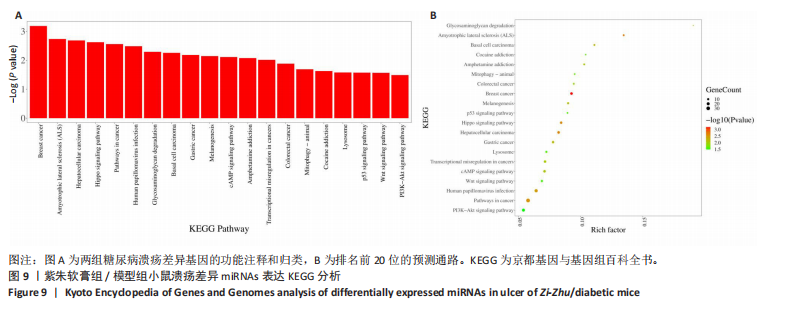
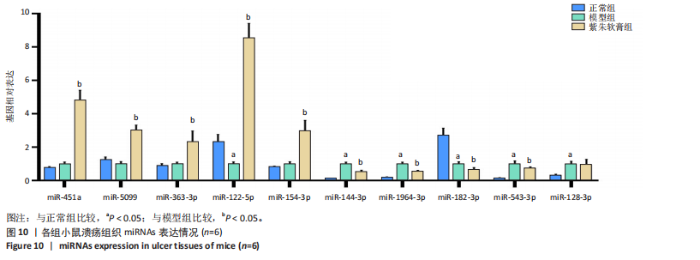
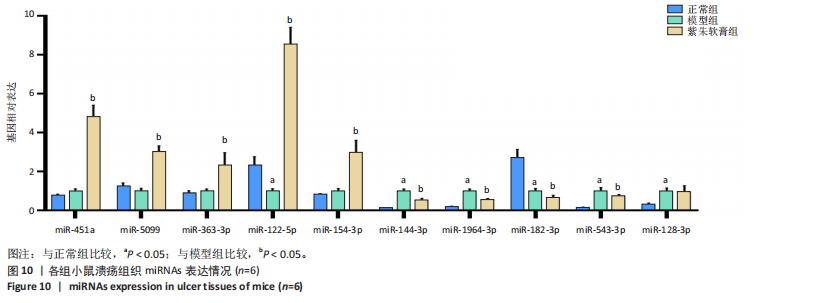
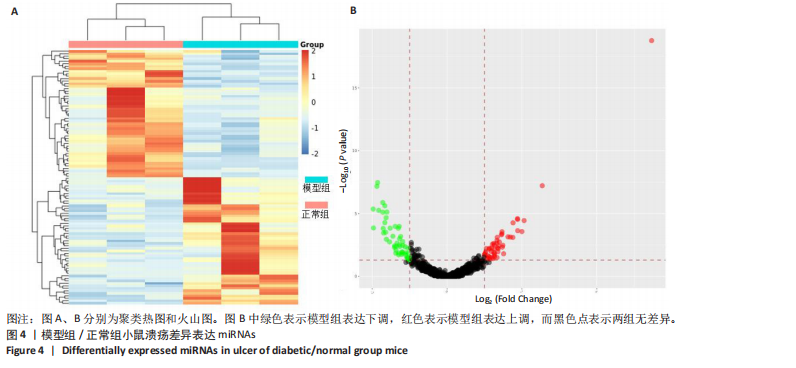
通过聚类热图和火山图表示3组样本之间的差异表达miRNAs,热图采用z-score算法表示两组样本差异miRNAs均值变化,红色表示表达偏高,蓝色表示表达偏低,提示组间存在明显差异。火山图亦为同理,其中绿色表示模型组表达下调,红色表示模型组表达上调,提示有部分miRNA呈显著高表达或低表达,而黑色点表示两组无差异,见图4,5。 2.5 GO功能分析 为进一步分析探讨紫朱软膏治疗糖尿病溃疡的差异表达miRNAs的生物学功能,对差异表达miRNAs进行基因本体论分析。结果显示,相比正常组,模型组生物过程主要涉及神经发育、细胞发育、树突形态等;细胞组成主要涉及细胞、细胞内在成分、细胞树突区细胞等;分子功能主要涉及蛋白结合、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(Phosphatidylinositol3-kinase,PI3K)、丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶(AKT Serine/Thre-onine Kinase 1,Akt)活性等。相比模型组,紫朱软膏组生物过程主要涉及多细胞发育、解剖结构、系统发育等;细胞组成主要涉及细胞、细胞内部分、细胞器等;分子功能主要涉及序列特异性 DNA 结合、DNA 结合转录因子活性、RNA 聚合酶Ⅱ调控区序列特异性等。排名前20位的富集结果见图6,7。 2.6 KEGG功能分析 通过KEGG pathway功能分析对差异基因进行功能注释和归类,与正常组相比,模型组功能注释与哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammaliantargetofrapamycin,mTOR)、PI3K-Akt、腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activatedproteinkinase,AMPK)、Wnt信号通路及癌症相关通路有关。紫朱软膏组相比模型组,与乳腺癌、肝癌相关通路和环腺苷酸(cyclic adenosine mono-phosphate,cAMP)、p53、Wnt、PI3K-Akt信号通路相关。图8,9为差异表达前20位的预测通路。 2.7 差异miRNAs验证结果 选取紫朱软膏组相对于模型组变化差异升高和降低前5位miRNAs进行qPCR验证,miR-451a、miR-363-3p、miR-122-5p、miR-154-3p、miR-144-3p为测序中紫朱软膏组明显高于模型组的miRNAs,验证结果与测序一致,且均有统计学差异(P < 0.05),见图10。其中正常组miR-154-3p测序表达是模型组的2.46倍(57/23.2),与验证结果亦一致。miR-1964-3p、miR-5099、miR-182-3p、miR-543-3p及miR-128-3p测序结果中紫朱软膏组较模型组明显降低,其中前4个有统计学差异(P < 0.05),正常组miR-1964-3p、miR-5099、miR-543-3p及miR-128-3p较模型组明显降低,亦与验证结果一致。证明测序结果正确可信。"
| [1] MATIJEVIĆ T, TALAPKO J, MEŠTROVIĆ T, et al. Understanding the multifaceted etiopathogenesis of foot complications in individuals with diabetes. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11(8):1669-1683. [2] CARUSO P, MAIORINO MI, MACERA M, et al. Antibiotic resistance in diabetic foot infection:how it changed with COVID-19pandemic in a tertiary care center. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021;175: 108797. [3] MELONI M, IZZO V, GIURATO L, et al. Prevalence, clinical aspects and outcomes in a large cohort of persons with diabetic foot disease: comparison between neuropathic and ischemic ulcers. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1780. [4] RENNAN MB, HESS TM, BARTLE B, et al. Diabetic foot ulcer severity predicts mortality among veterans with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31(3):556-561. [5] JIAO Y, CHEN X, NIU Y, et al. Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells embedded in PF-127 hydrogel plus sodium ascorbyl phosphate combination promote diabetic wound healing in type 2 diabetic rat. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):559. [6] ANURADHA U, MEHRA NK, KHATRI DK. Understanding molecular mechanisms and miRNA-based targets in diabetes foot ulcers. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):82. [7] ZAMPETAKI A, KIECHL S, DROZDOV I, et al. Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res. 2010;107(6):810-817. [8] XU J, WU W, ZHANG L, et al. The role of microRNA-146a in the pathogenesis of the diabetic wound-healing impairment: correction with mesenchymal stem cell treatment. Diabetes. 2012;61(11):2906-2912. [9] MADHYASTHA R, MADHYASTHA H, NAKAJIMA Y, et al. MicroRNA signature in diabetic wound healing: promotive role of miR-21 in fibroblast migration. Int Wound J. 2012;9(4):355-361. [10] CIECHOMSKA M, O’REILLY S, SUWARA M, et al. MiR-29a reduces TIMP-1 production by dermal fibroblasts via targeting TGF-β activated kinase 1 binding protein 1, implications for systemic sclerosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115596. [11] MATTICK JS, MAKUNIN IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15: R17-29. [12] 黄仁燕,王宏飞,王徐红,等.紫朱软膏对糖尿病溃疡小鼠创面炎症反应及上皮-间充质转化的影响[J].陕西中医,2023,44(12): 1673-1677. [13] 王丽翔,黄仁燕,柳国斌. 清筋术联合紫朱软膏外用治疗糖尿病足筋疽的临床疗效[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2023,50(7):102-105. [14] GAO S, GAO T, FENG L, et al. CircPKM2 aggravates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating MTDH via miR-1298-5p. Thorac Cancer. 2023;14(30):3020-3031. [15] LI X, ZHU M, ZHAO G, et al. MiR-1298-5p level downregulation induced by Helicobacter pylori infection inhibits autophagy and promotes gastric cancer development by targeting MAP2K6. Cell Signal. 2022; 93:110286. [16] ZHOU H, YAN Z, ZHU L, et al. miR-29b-3p’s Effects on Prostate Cancer. J Biomater Tiss Eng. 2022;12(4): 681-689. [17] QIN Z, WANG X, ZHOU Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-29b-3p alleviates coronary microembolization-induced myocardial injury via regulating BMF and GSK-3β. Apoptosis. 2023;28(1-2):210-221. [18] ZHOU F, CHEN L, XU S , et al. Upregulation of miR-151-5p promotes the apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells by targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor in ulcerative colitis mice. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(24): 2615-2626. [19] LEI B, WANG D, ZHANG M, et al. miR-615-3p promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer by targeting PICK1/TGFBRI axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):71. [20] 邓波,舒远,胡玲. 丹皮酚上调miR-223-3p减轻高糖诱导的小鼠心肌微血管内皮细胞损伤的研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2023,31(9): 697-702. [21] XIE K, LI C, WANG M, et al. miR-135a-5p overexpression in peripheral blood-derived exosomes mediates vascular injury in type 2 diabetes patients. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1035029. [22] ZHENG L, QI Y, LIU S, et al. miR-129b suppresses cell proliferation in the human lung cancer cell lines A549 and H1299. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(4). doi: 10.4238/gmr15048367. [23] VLACIL AK, VOLLMEISTER E, BERTRAMS W, et al. Micrornas Mir-147-3p And Mir-298-5p Are Nod-Driven Regulators Of Endothelial Cytokine Expression. Atherosclerosis. 2019;287:e98. [24] GUO Y, ZENG J, ZHUANG Y, et al. MiR-503-5p alleviates peripheral neuropathy-induced neuropathic pain in T2DM mice by regulating SEPT9 to inhibit astrocyte activation. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):14361. [25] LIU X, ZHANG D, WANG H, et al. MiR-451a enhances the phagocytosis and affects both M1 and M2 polarization in macrophages. Cell Immunol. 2021:365:104377. [26] 姚婷婷,李涛,吕红艳,等.运动通过上调肥胖小鼠肝脏miR-363-3p影响AKT/mTOR通路而减轻肝脏胰岛素抵抗[J].中国病理生理杂志,2023,39(2):297-304. [27] ZHANG J, LI K, GAO L, et al. Glucose metabolism disorder related to follicular fluid exosomal miR-122-5p in cumulus cells of endometriosis patients. Reproduction. 2024;168(4):e240028. [28] SUN K, LU T, HU C, et al. LINC00115 regulates lung adenocarcinoma progression via sponging miR-154-3p to modulate Sp3 expression. Mol Cell Probes. 2023:68:101909. [29] XIU C, DENG X, DENG D, et al. miR-144-3p Targets GABRB2 to Suppress Thyroid Cancer Progression In Vitro. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024;82(4):3585-3595. [30] YANG R, YANG F, HUANG Z, et al. Serum microRNA-122-3p, microRNA-194-5p and microRNA-5099 are potential toxicological biomarkers for the hepatotoxicity induced by Airpotato yam. Toxicol Lett. 2017; 280:125-132. [31] RAO J, CHEN Y, HUANG J, et al. Inhibiting miR-182-3p Alleviates Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle. Balkan Med J. 2022;39(2):121-129. [32] NEAMAH WH, SINGH NP, ALGHETAA H, et al. AhR Activation Leads to Massive Mobilization of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells with Immunosuppressive Activity through Regulation of CXCR2 and MicroRNA miR-150-5p and miR-543-3p That Target Anti-Inflammatory Genes. J Immunol. 2019;203(7):1830-1844. [33] KIEL K, KRÓL SK, BRONISZ A, et al. MiR-128-3p - a gray eminence of the human central nervous system. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024; 35(1):102141. [34] COFFEY L, MAHON C, GALLAGHER P. Perceptions and experiences of diabetic foot ulceration and foot care in people with diabetes: A qualitative meta-synthesis. Int Wound J. 2019;16(1):183-210. [35] ASVHNER P, KARURANGA S, JAMES S, et al. The international diabetes federation’s guide for diabetes epidemiological studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021:172(2):108630. [36] ARMSTRONG DG, TAN TW, BOULTON AJM, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(1):62-75. [37] EMING SA, MARTIN P, TOMIC-CANIC M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(265):265sr6. [38] ZIMMET P, ALBERTI KG, MAGLIANO DJ, et al. Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: facts and fallacies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(10):616-622. [39] 黄仁燕,樊炜静,柳国斌.中药油膏治疗糖尿病足溃疡用药规律研究[J].海南医学院学报,2021,27(4):302-306. [40] HO PTB, CLARK LM, LE CTT. MicroRNA-Based Diagnosis and Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7167. [41] WANG L, WANG C, HUANG C, et al. Role of microRNAs in diabetic foot ulcers: Mechanisms and possible interventions. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024;217:111858. [42] ZHAO X, XU M, TANG Y, et al. Changes in miroRNA-103 expression in wound margin tissue are related to wound healing of diabetes foot ulcers. Int Wound J. 2023;20(2):467-483. [43] AMIN KN, UMAPATHY D, ANANDHARAJ A, et al. miR-23c regulates wound healing by targeting stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α/CXCL12) among patients with diabetic foot ulcer. Microvasc Res. 2020;127:103924. [44] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YU T, et al. Inhibition of circulating exosomal microRNA-15a-3p accelerates diabetic wound repair. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(10):8968-8986. [45] RODRIGUES BT, VANGAVETI VN, URKUDE R, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of lower limb amputations in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022;16(2):102397. [46] CHEN L, SUN S, GAO Y, et al. Global mortality of diabetic foot ulcer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(1):36-45. [47] GUO J, LIN Q, SHAO Y, et al. miR-29b promotes skin wound healing and reduces excessive scar formation by inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad/CTGF signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;95(4):437-442. [48] LIU X, GUO B, LI Q, et al. mTOR in metabolic homeostasis and disease. Exp Cell Res. 2024;441(2):114173. [49] SOLINAS G, BECATTINI B. PI3K and AKT at the Interface of Signaling and Metabolism. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022; 436:311-336. [50] JIN T. Current understanding on role of the Wnt signaling pathway effector TCF7L2 in glucose homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 2016;37(3):254-277. |
| [1] | Li Zhifei, Han Bin, Liu Qiuli, Zhang Zhanming, Wei Haokai, Zuo Kuangshi, Zhang Yisheng. Cervical motion characteristics in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy based on motion capture technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2286-2293. |
| [2] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [3] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [4] | Cao Xinyan, Yu Zifu, Leng Xiaoxuan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation on motor function and gait in children with cerebral palsy: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1539-1548. |
| [5] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [6] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [7] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [8] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [9] | Zhang Jiuxuan, Zhang Jinnan, Sui Xiaofan, Pei Xiaxia, Wei Jianhong, Su Qiang, Li Tian. Effects of ammonia poisoning on cognitive behavior and hippocampal synaptic damage in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1122-1128. |
| [10] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [11] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [12] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [13] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [15] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||