Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (在线): 1-11.
Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment
Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia
- School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China
-
Online:2026-01-01Published:2025-07-01
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

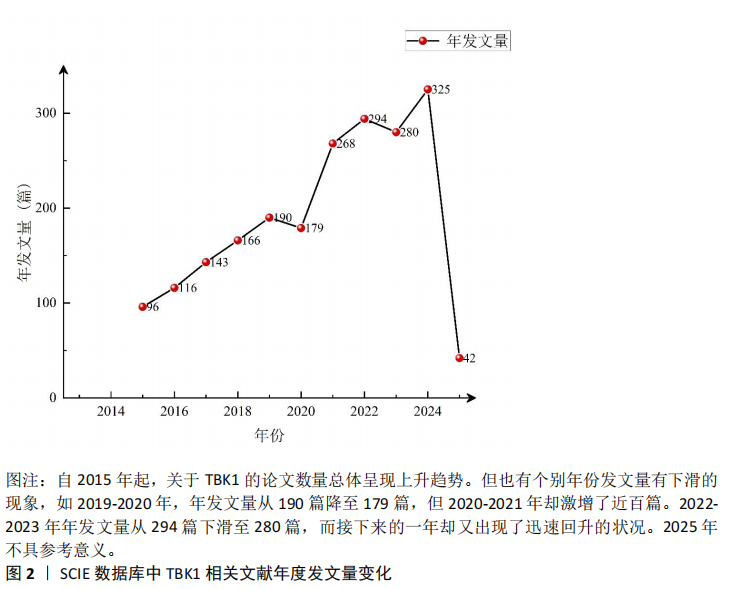
2.1 年度发文量分析 Web of Science数据库中共筛选出2099条记录,通过CiteSpace去除重复功能共得到2099条记录。其中Article为1933篇,Review Article为166篇。TBK1文献发文量年度变化见图2。其中2015-2019年TBK1相关的论文数量呈现阶梯状逐年上升的趋势,从原来的96篇升到了190篇。而在2019-2020年TBK1的研究热度有稍微下降的现象。但是在2020-2022年,发文量激增,由原来的179篇上升至294篇。2022-2023年迎来了第二个下坡路,年发文量从294篇降至280篇。2023-2024年,TBK1的发文量又迎来了转机,从280篇回升到325篇,可见TBK1逐渐成为学术界的新型研究热点。(由于此次检索时间截至到2025年2月,因此2025年年发文量不具有参考意义。)"

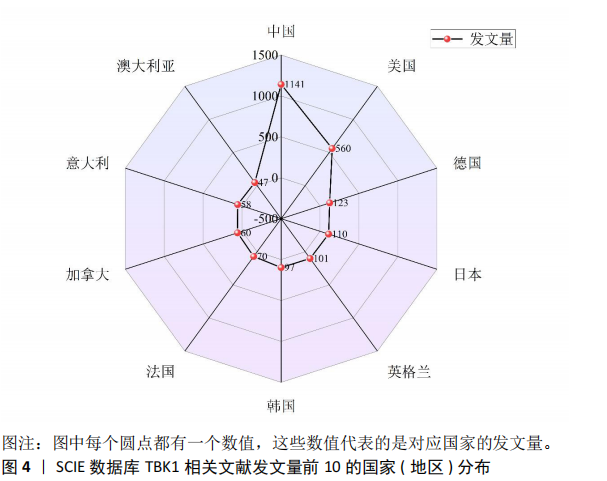
2.2 TBK1文献国家(地区)分析 在图3中,许多国家/地区都参与了TBK1的相关研究,国家之间的合作紧密,且呈现出多中心的特点。结合图4可知,发文量前5的国家分别是中国(1 141篇)、美国(560篇)、德国(123篇)、日本(110篇)、英格兰(101篇)。值得注意的是每个节点都有对应的中介中心值,而中介中心值代表了1个国家或者地区文章的影响力。其中高中心性的国家有美国(0.41)、英格兰(0.29)、中国(0.24)、法国(0.15)、德国(0.13)、韩国(0.12)、新加坡(0.11)、加拿大(0.1)。这表明国内的发文量占比最高,影响力也名列前茅,中国在TBK1的研究领域中发展潜力巨大。"


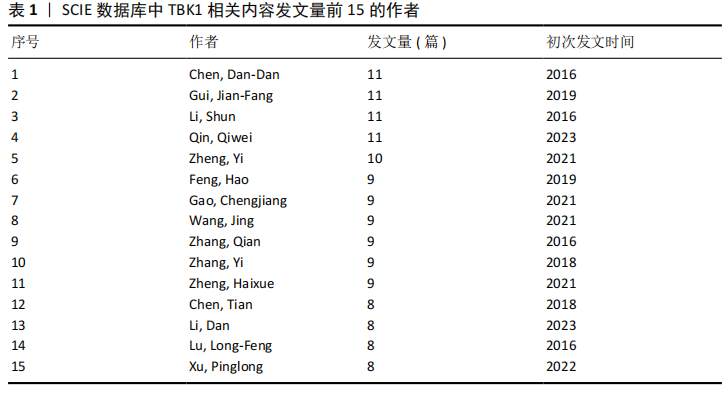
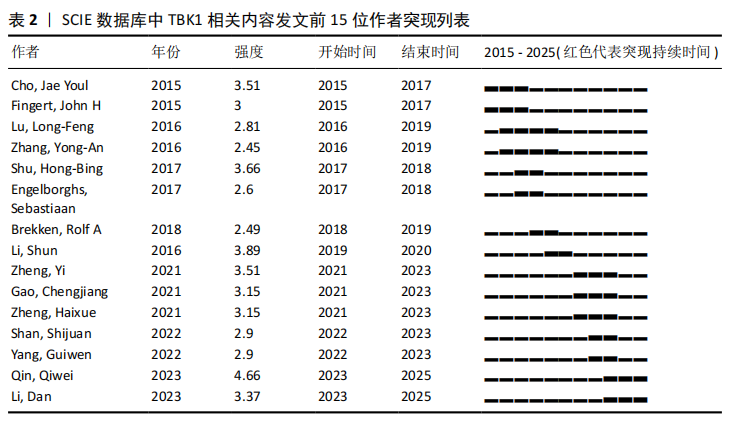
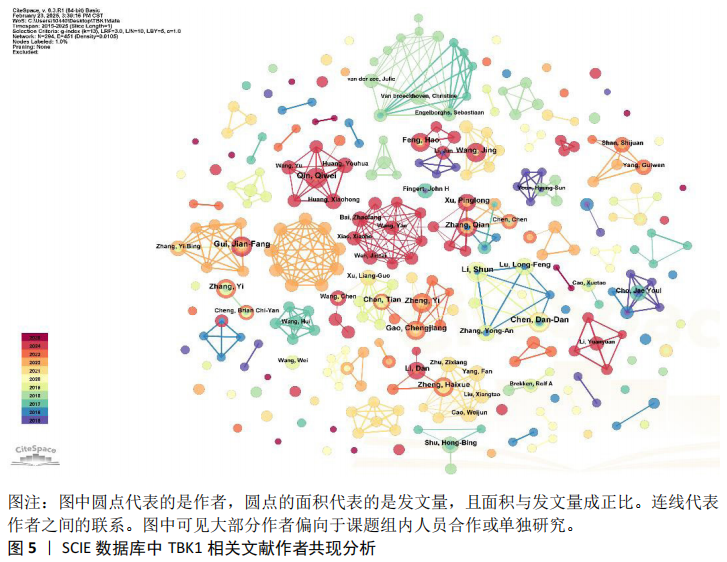
2.3 TBK1相关文献作者分析 共计294名作者参与了TBK1研究,从图5中可见作者与作者之间的联系并不紧密,更多是课题组内的人员合作,形成了一个个独立的研究团队。该文统计了作者的发文量,以及作者突现情况,如表1和表2所示,Qin,Qiwei发文量最多,达11篇,突现强度最强。Li,Shun持续时间很短,但是突现强度竟然高达3.89,文章也是11篇。这表明Qin,Qiwei和Li,Shun在该领域进行了较为深入的研究。许多作者尽管发文数量很多,但是突现强度不强。如Chen,Dan-Dan和Gui,Jian-Fang,发文量都是11篇,但突现强度排名在15名外。为了计算核心作者人数,该文利用核心作者最低发文公式N=0.749×ηmax1/2(ηmax指该领域中发文量最多的作者发文量)[14],ηmax=11,N≈3篇,核心作者有162人。"

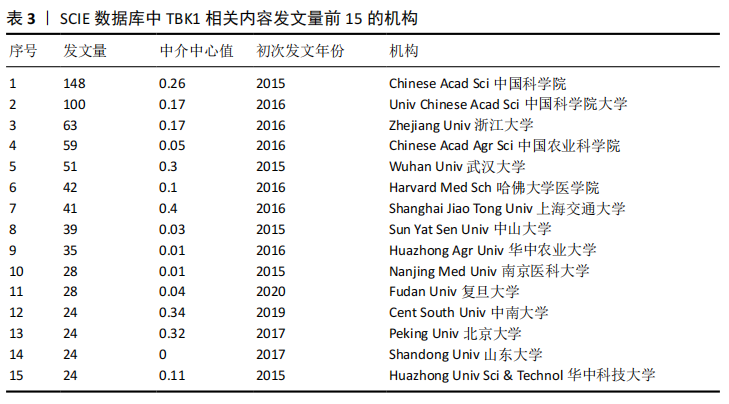
2.4 TBK1文献机构分析 发文量是一个研究机构学术能力的重要体现。该文统计了近10年研究TBK1的机构发文情况,如图6和表3所示。发现共有276个机构参与了TBK1的研究。根据发文量,该文统计了排名前10的机构,分别如下:中国科学院(148篇)、中国科学院大学(100篇)、浙江大学(63篇)、中国农业科学院(59篇)、武汉大学(51篇)、哈佛大学医学院(42篇)、上海交通大学(41篇)、中山大学(39篇)、华中农业大学(35篇)、南京医科大学(28篇)。图6中可见机构之间有联系但不算紧密。因此国家与国家之间、机构与机构之间应尽力消除学术壁垒,加强沟通合作,实现学术共赢,合力推动TBK1的深入研究。"


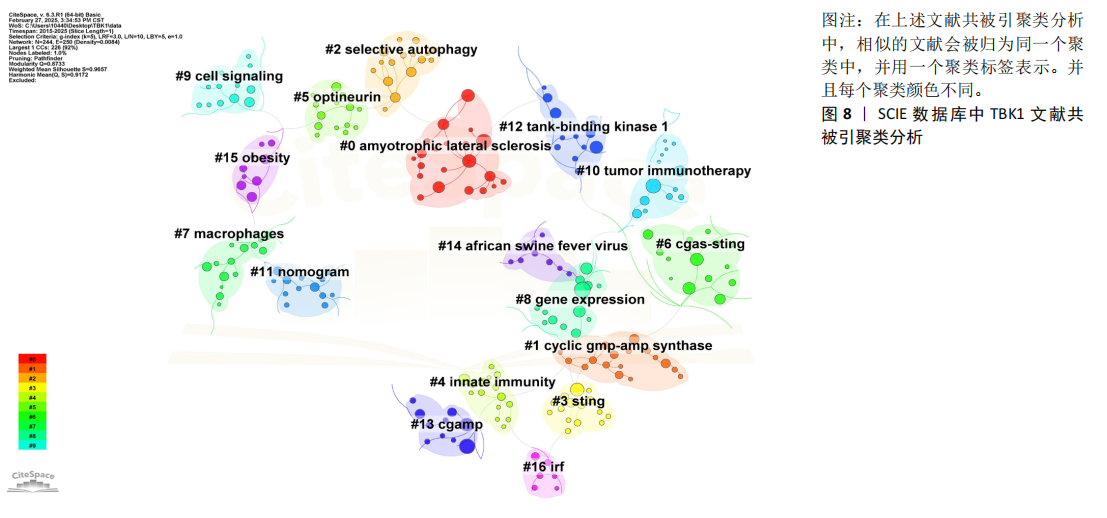
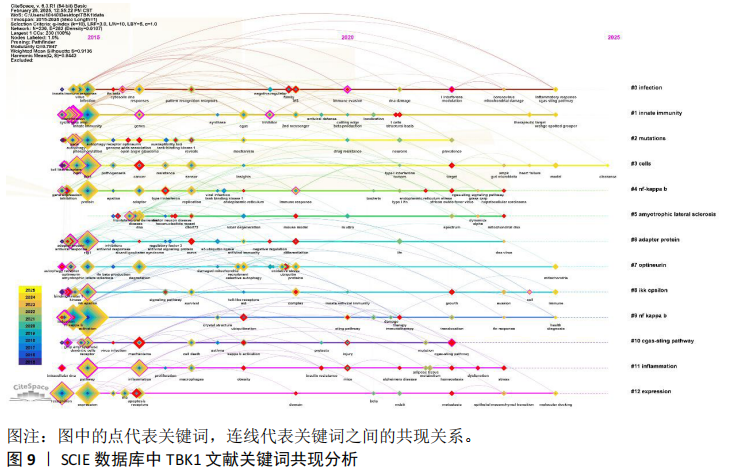
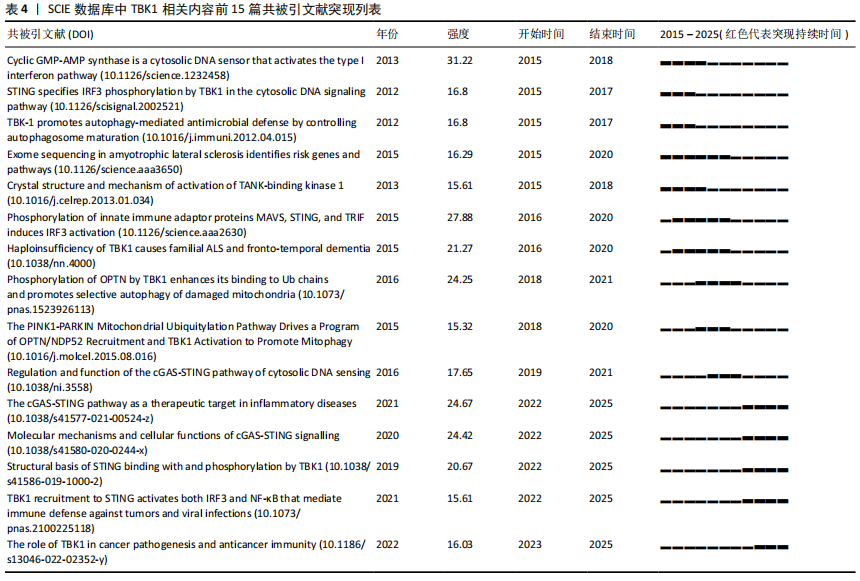
2.5 TBK1文献共被引分析 文献共被引分析是文献计量学的一种独特的计量方法,能够用于研究文献之间和各领域之间的影响力和联系。共被引次数是反映一篇文章影响力的重要指标。值得注意的是由于引用延迟以及Citespace软件只能对Web of Science等有限的几个数据库进行文献共被引分析,而中国知网、万方等数据库的文章不能纳入研究,因此共被引次数只能代表特定数据库和特定时期某篇文章的影响力。尽管如此,文献共被引次数还是可以用于探析研究动态、趋势以及该领域的热点。 该文总结了2015-2025年2月在Web of Science上发表的所有关于TBK1文献共被引数据,见图7和表4。其中共被引频数最高的文章是Zhang等[15]于2019年发表在《Nature》上的Structural basis of STING binding with and phosphorylation by TBK1(121次),突现强度为20.67。他们发现STING的C端尾部呈β链状构象,能够插入TBK1二聚体中一个亚基的激酶结构域与第二个亚基的支架和二聚化结构域之间的沟槽中,但是STING尾部的磷酸化位点Ser366无法到达结合的TBK1的激酶域活性位点。鉴于此,他们成功验证了在环二核苷酸(cyclic GMP-AMP,cGAMP)诱导下STING和TBK1的高阶寡聚化导致STING被TBK1磷酸化的模型。 2015年Liu等[16]发表在《Science》的Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS,STING,and TRIF induces IRF3 activation文章共被引频数排名第二(108次),突现强度高达27.88。研究发现线粒体抗病毒蛋白(MAVS)和STING 含有两个保守的Ser和Thr簇,在受到刺激时会被激酶IKK和/或TBK1磷酸化。磷酸化的MAVS和STING会与干扰素调节因子3(IRF3)带正电荷的表面结合,从而招募IRF3使其磷酸化并被TBK1激活。进一步研究发现,Toll样受体信号转导中的β干扰素TIR结构域衔接蛋白也通过类似的磷酸化依赖机制激活IRF3。 共被引频数排名第三的是Freischmidt等[17]发表在《Nature Neuroscience》的Haploinsufficiency of TBK1 causes familial ALS and fronto- temporal dementia(102次),突现强度为21.27。他们对252例家族性肌萎缩性脊髓侧索硬化症患者和827例对照个体进行了外显子组测序实验,发现单倍体TBK1缺乏会导致肌萎缩性脊髓侧索硬化症和额颞叶痴呆症。 Hopfner等[18]发表在《Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology》的Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling文章共被引频次排到了第4位(96次),突现强度为24.42。这篇文章以综述的形式回顾了cGAS-STING激活与信号传导的分子机制和细胞功能。Gui等[19]在《Nature》发表的文章共被引频次达到了85次,排名第5,这篇文章名为Autophagy induction via STING trafficking is a primordial function of the cGAS pathway。作者们报告了STING能通过一种独立于TBK1激活和干扰素诱导的机制激活自噬。STING与cGAMP结合后,会转位到内质网-高尔基体中间区室和高尔基体,这一过程依赖于COP-II复合物和ARF GTP酶。含STING的内质网-高尔基体中间区室是微管相关蛋白1轻链3脂化的膜源,而微管相关蛋白1轻链3脂化是自噬体生物生成的关键步骤。cGAMP诱导微管相关蛋白1轻链3脂化的途径依赖于结合蛋白WD重复结构域磷酸肌醇互作蛋白2和自噬相关基因5,但独立于自噬相关蛋白ULK和VPS34-beclin激酶复合物。此外,他们还发现cGAMP诱导的自噬对清除细胞质中的DNA和病毒非常重要。 TBK1文献共被引聚类分析图(图8)中发现有244个节点、250条连线。Modularity Q=0.873 3 > 0.3,这表明该聚类图具有合理性。Weighted Mean Silhouette S=0.965 7 > 0.5这代表同质性也是合理的。在这些共被引文献中,相似的文献会被归为同一个聚类中,并用一个聚类标签表示。在这个聚类图中,主要的聚类如下:#0 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis(肌萎缩侧索硬化);#1cyclic gmp-amp synthase(环状GMP-AMP合成酶);#2 selective autophagy(选择性自噬);#3 sting(干扰素基因刺激蛋白);#4 innate immunity(天然免疫);#5 optineurin(选择性自噬受体);#6 cgas-sting(cGAS-STING 信号通路);#7 macrophages(巨噬细胞);#8 gene expression(基因表达);#9 cell signaling(细胞信号);#10 tumor immunotherapy(肿瘤免疫治疗);#11 nomogram(诺谟图);#12 tank-binding kinase 1(TBK1);#13 cGAMP(环二核苷酸);#14 african swine fever virus(非洲猪瘟病毒);#15 obesity(肥胖症) #16 irf(干扰素调节因子)。 2.6 TBK1文献关键词分析 关键词作为一篇文章的精髓,能够快速准确地反映一篇文章的研究主题。关键词的出现频次、突现强度以及关键词时间轴共同反映了某领域某时间段的研究热点。结合高共被引文献的内容、共被引文献聚类分析结果、关键词共现图(图9),总结出TBK1领域的研究热点包括TBK1在先天免疫系统中的作用、cGAS-STING-TBK1信号通路或TBK1与NF-κB的上下游关系、TBK1基因在肌萎缩侧索硬化的作用、TBK1与开角型青光眼的相关研究和TBK1因子的激活途径与表达等。许多高频次关键词如innate immune response、innate immunity、nf kappa b、activation、recognition、expression等在2015年已经是高频次关键词,且这些关键词热度甚至持续到2025年(图10)。 "


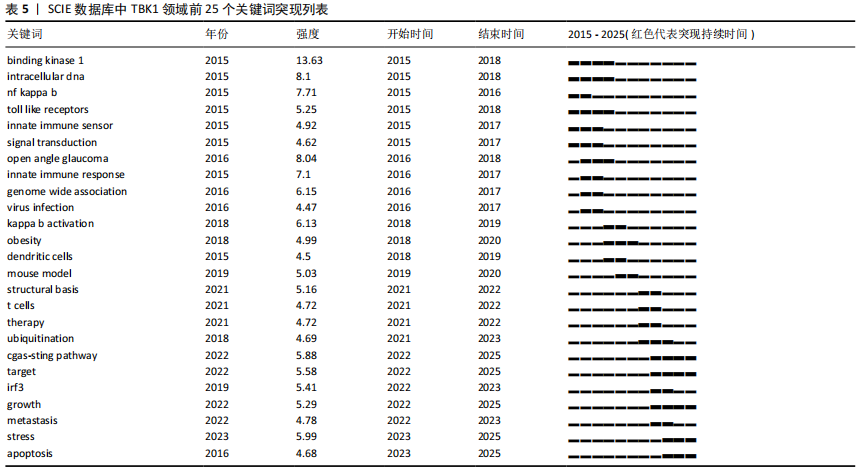
关键词突现表(表5)能够直观地反映各关键词在TBK1领域中的突现强度以及热度持续时间。该文根据突现强度总结了近10年TBK1研究关键词的突现排名。其中binding kinase 1突现强度最强,达到13.63,而且突现时间也达到了4年之长。intracellular dna的热度也持续了4年,突现强度达到了8.1。open angle glaucoma突现强度排名第三,强度高达8.04。自nf kappa b被发现与TBK1存在上下游关系后,突现强度上升到7.71。当研究人员发现TBK1是先天免疫系统的重要成员后,innate immune response逐渐成为了2016年-2017年的研究热点,虽然持续时间短,但是爆发力强,突现强度达到7.1。cGAS-STING与TBK1的通路关系研究虽然起步较晚,从2022年才开始研究,但突现强度高达5.88,而且截至目前为止,该信号通路的相关研究仍在继续,提示cGAS-STING与TBK1可能成为免疫相关疾病领域的研究热点。 该文总结了近10年来Web of Science关于TBK1研究的关键词,并以聚类图(图11)形式展现。研究人员对TBK1主要开展了以下方面的研究:#0 infection(感染);#1 innate immunity (天然免疫);#2 mutations (突变);#3 cells(细胞);#4 nf-kappa b (核因子κB,NF-κB);#5 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis(肌萎缩侧索硬化);#6 adapter protein(衔接蛋白);#7 optineurin(选择性自噬受体);#8 IKK epsilon(与TBK1结构相似的激酶);#9 nf kappa b(NFκb);#10 cgas-sting pathway(cGAS-STING信号通路);#11 inflammation(炎症);#12 expression (表达)。这表明近10年来TBK1的研究主要集中在先天性免疫反映、炎症反映、信号通路、TBK1基因表达等方面。 "

| [1] 胡芳茴, 李丽蔚, 杨霞, 等. 抑制TBK1通过调节mTORC1信号通路减轻肺泡巨噬细胞中NLRP3介导的细胞焦亡[J/OL]. 中国免疫学杂志, 1-10[2025-02-24]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/22.1126.R.20250124.1616.006.html. [2] RUNDE A P, MACK R, S J PB, et al. The role of TBK1 in cancer pathogenesis and anticancer immunity [J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 135. [3] MIRANDA A, SHIRLEY C A, JENKINS R W. Emerging roles of TBK1 in cancer immunobiology [J]. Trends Cancer, 2024, 10(6): 531-540. [4] ZHANG M, ZOU Y, ZHOU X, et al. Inhibitory targeting cGAS-STING-TBK1 axis: emerging strategies for autoimmune diseases therapy [J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 954129. [5] 王悦宸, 侯亚威, 王振国. 基于文献计量学的丹参研究现状与热点分析[J]. 中草药, 2025, 56(4): 1318-1337. [6] 江宇慧, 朱明玉, 张景景, 等. 基于文献计量学分析近10年药用植物组织培养的研究趋势[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2025, 27(1): 98-109. [7] 李进鹏, 曹妍, 赵奕雯, 等. 基于文献计量学的国内外药食同源及食疗领域研究热点分析[J]. 护理研究, 2024, 38(19): 3457-3467. [8] 张建, 杨卫华, 刘萍, 等. 海洋固碳研究进展—基于Citespace的可视化分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报(中英文), 2024, 46(4): 135-142. [9] 朱格格, 黄安书, 覃盈盈. 基于Web of Science的国际红树林研究发展态势分析[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 42(5): 1-12. [10] 徐灿丽, 何文星, 汪磊, 等. 肝脏类器官研究的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. [11] 谭令, 龙霖梓, 邓秘, 等. 抗血小板活化的文献计量学及可视化分析[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2022, 24(1): 195-208. [12] 王晗, 李春辉, 孙海玮. 远隔缺血适应相关研究的文献计量学和可视化分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2025, 22(2): 89-98. [13] 王勇, 李宏宇, 刘雨航, 等. 股骨头坏死手术治疗知识图谱:2005-2024数据的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(33): 7250-7260. [14] 郭萌, 吴文, 李敬文, 等. 基于文献计量学的“结核”主题高被引文献特征分析[J]. 中国防痨杂志, 2024, 46(5): 567-577. [15] ZHANG C, SHANG G, GUI X, et al. Structural basis of STING binding with and phosphorylation by TBK1 [J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7748): 394-398. [16] LIU S, CAI X, WU J, et al. Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation [J]. Science, 2015, 347(6227): aaa2630. [17] FREISCHMIDT A, WIELAND T, RICHTER B, et al. Haploinsufficiency of TBK1 causes familial ALS and fronto-temporal dementia [J]. Nat Neurosci, 2015, 18(5): 631-636. [18] HOPFNER K P, HORNUNG V. Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling [J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2020, 21(9): 501-521. [19] GUI X, YANG H, LI T, et al. Autophagy induction via STING trafficking is a primordial function of the cGAS pathway [J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7747): 262-266. [20] REVACH O Y, LIU S, JENKINS R W. Targeting TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) in cancer [J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2020, 24(11): 1065-1078. [21] HU L, ZHANG Q. Mechanism of TBK1 activation in cancer cells [J]. Cell Insight, 2024, 3(5): 100197. [22] HUANG X, HUO L, XIAO B, et al. Activating STING/TBK1 suppresses tumor growth via degrading HPV16/18 E7 oncoproteins in cervical cancer [J]. Cell Death Differ, 2024, 31(1): 78-89. [23] ALAM M, HASAN G M, HASSAN M I. A review on the role of TANK-binding kinase 1 signaling in cancer [J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 183: 2364-2375. [24] ZHAO C, ZHAO W. TANK-binding kinase 1 as a novel therapeutic target for viral diseases [J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2019, 23(5): 437-446. [25] LAN J, DENG Z, WANG Q, et al. Neuropeptide substance P attenuates colitis by suppressing inflammation and ferroptosis via the cGAS-STING signaling pathway [J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2024, 20(7): 2507-2531. [26] DU S S, CHEN G W, YANG P, et al. Radiation Therapy Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immune Cloaking via PD-L1 Upregulation Induced by cGAS-STING Activation [J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2022, 112(5): 1243-1255. [27] 龙昊, 吴怡林, 龚建平. TBK1在炎症性疾病发生机制中的作用[J]. 重庆医学, 2020, 49(20): 3472-3475+3480. [28] DUAN Q Q, WANG H, SU W M, et al. TBK1, a prioritized drug repurposing target for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: evidence from druggable genome Mendelian randomization and pharmacological verification in vitro [J]. BMC Med, 2024, 22(1): 96. [29] ZHAO X, CAO Y, LU R, et al. Phosphorylation of AGO2 by TBK1 Promotes the Formation of Oncogenic miRISC in NSCLC [J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(15): e2305541. [30] GAO CQ, CHU ZZ, ZHANG D, et al. Serine/threonine kinase TBK1 promotes cholangiocarcinoma progression via direct regulation of β-catenin [J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(18): 1492-1507. [31] QIAN Y, YAO W, YANG T, et al. aPKC-ι/P-Sp1/Snail signaling induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and immunosuppression in cholangiocarcinoma [J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(4): 1165-1182. [32] YANG S, IMAMURA Y, JENKINS RW, et al. Autophagy Inhibition Dysregulates TBK1 Signaling and Promotes Pancreatic Inflammation [J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2016, 4(6): 520-30. [33] SIDDIQUI AJ, JAMAL A, ZAFAR M, et al. Identification of TBK1 inhibitors against breast cancer using a computational approach supported by machine learning [J]. Front Pharmacol, 2024, 15: 1342392. [34] ZHU L, LI Y, XIE X, et al. TBKBP1 and TBK1 form a growth factor signalling axis mediating immunosuppression and tumourigenesis [J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2019, 21(12): 1604-1614. [35] CAI H, YAN L, LIU N, et al. IFI16 promotes cervical cancer progression by upregulating PD-L1 in immunomicroenvironment through STING-TBK1-NF-kB pathway [J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 123: 109790. [36] JIANG Y, CHEN S, LI Q, et al. TANK-Binding Kinase 1 (TBK1) Serves as a Potential Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Enhancing Tumor Immune Infiltration [J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 612139. [37] VAN DAELE SH, MOISSE M, VAN VUGT JJFA, et al. Genetic variability in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Brain, 2023, 146(9): 3760-3769. [38] GURFINKEL Y, POLAIN N, SONAR K, et al. Functional and structural consequences of TBK1 missense variants in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2022, 174: 105859. [39] CIRULLI ET, LASSEIGNE BN, PETROVSKI S, et al. Exome sequencing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis identifies risk genes and pathways [J]. Science, 2015, 347(6229): 1436-41. [40] WEINREICH M, SHEPHEARD SR, VERBER N, et al. Neuropathological characterization of a novel TANK binding kinase (TBK1) gene loss of function mutation associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol, 2020, 46(3): 279-291. [41] AHMAD L, ZHANG SY, CASANOVA JL, et al. Human TBK1: A Gatekeeper of Neuroinflammation [J]. Trends Mol Med, 2016, 22(6): 511-527. [42] LI Q, LIU Y, XIA X, et al. Activation of macrophage TBK1-HIF-1α-mediated IL-17/IL-10 signaling by hyperglycemia aggravat es the complexity of coronary atherosclerosis: An in vivo and in vitro study [J]. FASEB J, 2021, 35(5): e21609. [43] ZHAO P, SUN X, LIAO Z, et al. The TBK1/IKKε inhibitor amlexanox improves dyslipidemia and prevents atherosclerosis [J]. JCI Insight, 2022, 7(17): e155552. [44] SUN Y, REVACH O Y, ANDERSON S, et al. Targeting TBK1 to overcome resistance to cancer immunotherapy [J]. Nature, 2023, 615(7950): 158-167. [45] MAAN M, JAISWAL N, LIU M, et al. TBK1 reprograms metabolism in breast cancer: an integrated omics approach [J]. J Proteome Res, 2025, 24(1): 121-133. [46] MA X, JIA S, WANG G, et al. TRIM28 promotes the escape of gastric cancer cells from immune surveillance by increasing PD-L1 abundance [J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 246. [47] MAAN M, AGRAWAL NJ, PADMANABHAN J, et al. Tank Binding Kinase 1 modulates spindle assembly checkpoint components to regulate mitosis in breast and lung cancer cells [J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2021, 1868(3): 118929. [48] LEFRANC J, SCHULZE VK, HILLIG RC, et al. Discovery of BAY-985, a Highly Selective TBK1/IKKε Inhibitor [J]. J Med Chem, 2020, 63(2): 601-612. [49] SHIN J, LIM J, HAN D, et al. TBK1 inhibitor amlexanox exerts anti-cancer effects against endometrial cancer by regulating AKT/NF-κB signaling [J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2025, 21(1): 143-159. [50] LIN KX, ISTL AC, QUAN D, et al. PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in cold colorectal cancer: challenges and strategies [J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2023, 72(12): 3875-3893. [51] VESELY MD, ZHANG T, CHEN L. Resistance Mechanisms to Anti-PD Cancer Immunotherapy [J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2022, 40: 45-74. |
| [1] | Zhu Xiaolong, Zhang Wei, Yang Yang. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and cutting-edge information in the field of intervertebral disc regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2391-2402. |
| [2] | Wen Fayan, Li Yan, Qiang Tianming, Yang Chen, Shen Linming, Li Yadong, Liu Yongming. Unilateral biportal endoscopic technology for treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: global research status and changing trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2380-2390. |
| [3] | Lai Yu, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Research hotspots and frontier trends of bioactive materials in treating bone infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2132-2144. |
| [4] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [5] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [6] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [7] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [8] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [9] | Yang Jun, Li Bin, Xing Guogang, Cai Jie, Liu Lu, Chen Peng, Zhang Tao, Fu Yuanbo, Liu Huilin. Application of patch-clamp technique in traditional Chinese medicine: a visual analysis of relevant literature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6010-6020. |
| [10] | Li Qian, Li Zhenxing, Qiao Pengyan, Wang Pingzhi. Visual analysis of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6021-6029. |
| [11] | Qu Bolin, Ciren Lunzhu, Guo Jinyang, Meng Hanlu, Ding Guanxiang, Sang Hongpeng. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a visual analysis of current status and emerging trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6040-6050. |
| [12] | Li Yiguang, Guo Haonan, Ding Xiaotao, Yuan Mengyao, Jiang Lijin, Fan Xinfeng, Feng Yan. Visual analysis of research hotspots in the field of gut microbiota in the elderly at home and abroad [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6071-6080. |
| [13] | Deng Qing , Zhang Yeting , Mou Xiangqian , Wang Qingjun. Visualization analysis of dynamic evolution of hot topics in the field of physical activity and neural plasticity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5859-5866. |
| [14] | Zhang Qian, Wang Fuxia, Wang Wen, Zhang Kun. Characteristic analysis of nanogel composite system and its application strategies in visualization of diagnostic imaging and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 480-488. |
| [15] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||