Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (32): 6939-6946.doi: 10.12307/2025.939
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Agiophyllum Oligo Saccharides on inflammation and apoptosis of mouse synovial cells
Zhao Xuemei1, 2, Wang Rui1, 2, Ao · Wuliji3, Bao Shuyin4, Jiang Xiaohua1, 2
- 1School of Basic Medical Sciences, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China; 2Hebei Key Laboratory for Chronic Diseases, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China; 3The Research Institute of Traditional Mongolian Medicine Engineering Technology, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 4School of Public Health, Inner Mongolia Minzu University, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-10-08Accepted:2024-12-06Online:2025-11-18Published:2025-04-28 -
Contact:Jiang Xiaohua, PhD, Professor, School of Basic Medical Sciences, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China; Hebei Key Laboratory for Chronic Diseases, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China Co-corresponding author: Bao Shuyin, PhD, Associate professor, School of Public Health, Inner Mongolia Minzu University, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhao Xuemei, Master candidate, School of Basic Medical Sciences, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China; Hebei Key Laboratory for Chronic Diseases, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:Open Fund Project of National Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Research and Development of Mongolian Medicines, No. MDK2021023 (to JXH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Xuemei, Wang Rui, Ao · Wuliji, Bao Shuyin, Jiang Xiaohua. Effects of Agiophyllum Oligo Saccharides on inflammation and apoptosis of mouse synovial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6939-6946.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
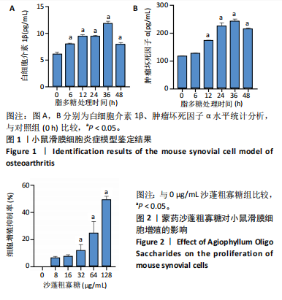
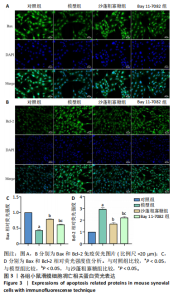
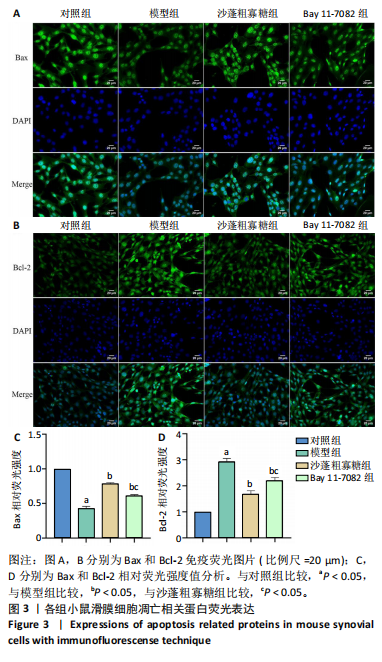
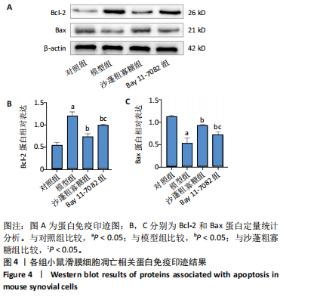
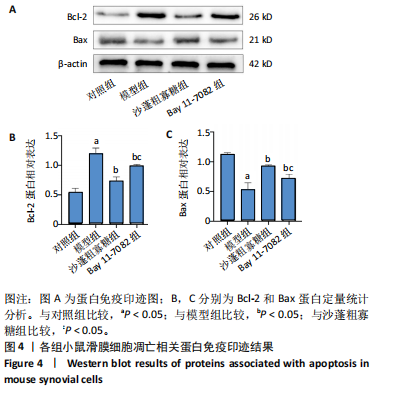
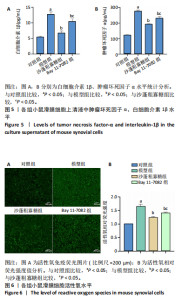
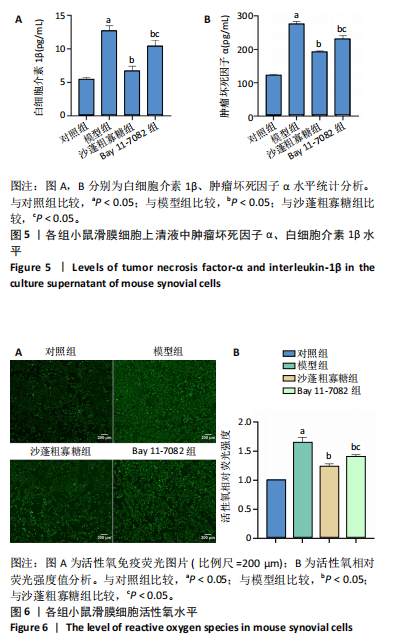
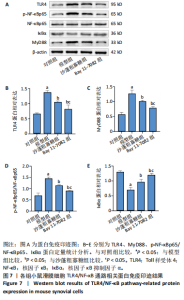
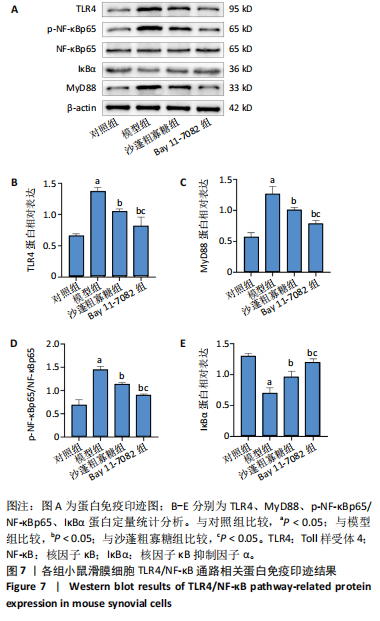
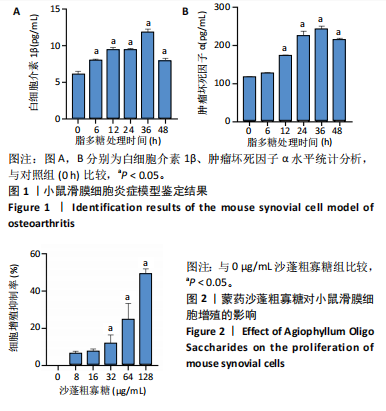
2.1 骨关节炎滑膜细胞模型的鉴定结果 参照文献[8,11],用1.0 μg/mL 脂多糖处理小鼠滑膜细胞6,12,24,36,48 h,与对照组(0 h)比较,脂多糖处理6,12,24,36,48 h细胞上清液中白细胞介素1β水平分别为8.05,9.50,9.49,11.9,7.97 pg/mL,均显著升高(P < 0.05);脂多糖处理12,24,36,48 h细胞上清液中肿瘤坏死因子α水平分别为173.82,213.18,243.61,215.66 pg/mL,均显著升高(P < 0.05)。白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达高峰在脂多糖处理后36 h。根据实验结果,采用1.0 μg/mL 脂多糖作用36 h进行后续实验。结果见图1。 2.2 蒙药沙蓬粗寡糖对小鼠滑膜细胞增殖的影响 为了确定沙蓬粗寡糖的合适质量浓度,采用CCK-8检测小鼠滑膜细胞的增殖抑制率。与0 μg/mL沙蓬粗寡糖组比较,8,16,32,64,128 μg/mL沙蓬粗寡糖组细胞增殖抑制率升高。在32,64,128 μg/mL质量浓度下,细胞增殖抑制率分别为12.03%,25.01%,49.57%,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。选择无显著细胞毒性(细胞抑制率小于15%)的沙蓬粗寡糖质量浓度32 μg/mL进行后续实验。 2.3 蒙药沙蓬粗寡糖对小鼠滑膜细胞凋亡相关蛋白Bax、Bcl-2表达的影响 免疫荧光结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组Bax相对荧光强度显著降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2相对荧光强度显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,沙蓬粗寡糖组Bax相对荧光强度显著升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2相对荧光强度显著降低(P < 0.05);与沙蓬粗寡糖组相比,Bay 11-7082组Bax相对荧光强度显著降低(P < 0.05),但仍高于模型组(P < 0.05),Bcl-2相对荧光强度显著升高(P < 0.05),但仍低于模型组(P < 0.05),见图3。 Western blot蛋白定量结果与免疫荧光检测结果相一致,与对照组相比,模型组Bax蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,沙蓬粗寡糖组Bax蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与沙蓬粗寡糖组相比,Bay 11-7082组Bax蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05),但仍高于模型组(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),但仍低于模型组(P < 0.05),见图4。 2.4 蒙药沙蓬粗寡糖对小鼠滑膜细胞肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β水平的影响 与对照组相比,模型组细胞上清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,沙蓬粗寡糖组细胞上清中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与沙蓬粗寡糖组相比,Bay 11-7082组细胞上清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β水平显著升高(P < 0.05),但仍低于模型组(P < 0.05),见图5。 2.5 蒙药沙蓬粗寡糖对小鼠滑膜细胞活性氧水平的影响 与对照组相比,模型组活性氧水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,沙蓬粗寡糖组活性氧水平显著降低(P < 0.05);与沙蓬粗寡糖组相比,Bay 11-7082组活性氧水平显著升高(P < 0.05),但仍低于模型组(P < 0.05),见图6。 2.6 蒙药沙蓬粗寡糖对小鼠滑膜细胞TLR4、MyD88、NF-κBp65、p-NF-κBp65、IκBα蛋白表达的影响 与对照组相比,模型组TLR4、MyD88蛋白表达和p-NF-κBp65/NF-κBp65比值显著升高(P < 0.05),IκBα蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,沙蓬粗寡糖组TLR4、MyD88蛋白表达和p-NF-κBp65/ NF-κBp65比值显著降低(P < 0.05),IκBα蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型组和沙蓬粗寡糖组相比,Bay 11-7082组TLR4、MyD88蛋白表达和p-NF-κBp65/ NF-κBp65比值显著降低(P < 0.05),IκBα蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),见图7。"
| [1] LOESER RF, COLLINS JA, DIEKMAN BO. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(7):412-420. [2] HÜGLE T, GEURTS J. What drives osteoarthritis?-synovial versus subchondral bone pathology. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56(9): 1461-1471. [3] DAMERAU A, ROSENOW E, ALKHOURY D, et al. Fibrotic pathways and fibroblast-like synoviocyte phenotypes in osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1385006. [4] YI Y, YANG N, YANG Z, et al. LncRNA TM1-3P Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis and Inflammation of Fibroblasts in Osteoarthritis through miR-144-3p/ONECUT2 Axis. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(11):3078-3091. [5] DING Y, WANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNA‑93 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis by targeting the TLR4/NF‑κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2):779-790. [6] LI Z, ZOU Y, FAN D, et al. The mechanism of medial collateral ligament repair in knee osteoarthritis based on the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(3):398-403. [7] 包书茵.蒙药沙蓬粗寡糖调控糖脂代谢紊乱抑制T2DM-NAFLD发生发展的机制研究[D].延边:延边大学,2022. [8] WU S, GUO W, CHEN L, et al. Downregulation of Gadd45β alleviates osteoarthritis by repressing lipopolysaccharide-induced fibroblast-like synoviocyte inflammation, proliferation and migration. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;126:111202. [9] CHELESCHI S, GALLO I, BARBARINO M, et al. MicroRNA Mediate Visfatin and Resistin Induction of Oxidative Stress in Human Osteoarthritic Synovial Fibroblasts Via NF-κB Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5200. [10] ZHU W, JIANG C, XU J, et al. Pristane primed rat T cells enhance TLR3 expression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via TNF-α initiated p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Clin Immunol. 2015;156(2):141-153. [11] YIN S, WANG P, XING R, et al. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) Mediates Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Primary Human Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Inflammation. 2018;41(2):700-709. [12] YAO Q, WU X, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023; 8(1):56. [13] DU X, LIU ZY, TAO XX, et al. Research Progress on the Pathogenesis of Knee Osteoarthritis. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(9):2213-2224. [14] GENG R, LI J, YU C, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: Current status and research progress in treatment (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2023;26(4): 481. [15] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(5):471-478. [16] PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, ABRAMSON SB. Osteoarthritis, an inflammatory disease: potential implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(6):1237-1247. [17] SMITH MD, TRIANTAFILLOU S, PARKER A, et al. Synovial membrane inflammation and cytokine production in patients with early osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1997;24(2):365-371. [18] LUO H, LI L, HAN S, et al. The role of monocyte/macrophage chemokines in pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: A review. Int J Immunogenet. 2024;51(3):130-142. [19] ZHU R, FANG H, WANG J, et al. Inflammation as a therapeutic target for osteoarthritis: A literature review of clinical trials. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(8):2417-2433. [20] CAO P, LI Y, TANG Y, et al. Pharmacotherapy for knee osteoarthritis: current and emerging therapies. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020; 21(7):797-809. [21] XU HY, ZHENG HC, ZHANG HW, et al. Comparison of Antioxidant Constituents of Agriophyllum squarrosum Seed with Conventional Crop Seeds. J Food Sci. 2018;83(7):1823-1831. [22] 冯德培.简明生物学词典[M].上海:上海辞书出版社,1983:673. [23] 国家中医药管理局《中华本草》编写委员会.中华本草.蒙药卷[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2004:236-246. [24] 朱亚民.内蒙古植物药志(第一卷) [M].呼和浩特:内蒙古人民出版社,2000:229. [25] 包书茵,韩淑英,澈力格尔,等.沙蓬粗寡糖对GK大鼠胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2016,32(3):403-409. [26] 包书茵,韩淑英,朝日雅,等.沙蓬粗寡糖对GK大鼠肝、肾保护作用及机制探讨[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(1):147-148. [27] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257. [28] CHEN H, CHEN F, HU F, et al. MicroRNA-224-5p nanoparticles balance homeostasis via inhibiting cartilage degeneration and synovial inflammation for synergistic alleviation of osteoarthritis. Acta Biomater. 2023;167:401-415. [29] 胡善明,王亚楠,许正茂,等.Bcl-2家族分子在细胞凋亡中的作用研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2021,42(10):85-89. [30] LOU C, LIN C, WANG W, et al. Extracts of Oldenlandia diffusa protects chondrocytes via inhibiting apoptosis and associated inflammatory response in osteoarthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;316:116744. [31] 邢丹丹,康文越,王志华,等.右美托咪定通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB信号通路促进佐剂性膝骨关节炎大鼠成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞凋亡[J].中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(8):1479-1486. [32] WERRY F, MAZUR E, THEYSE LFH, et al. Apoptosis Regulation in Osteoarthritis and the Influence of Lipid Interactions. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13028. [33] ERTEN F, OZDEMIR O, TOKMAK M, et al. Novel formulations ameliorate osteoarthritis in rats by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Food Sci Nutr. 2024;12(10):7896-7912. [34] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42. [35] 张梓宁,邓荣辉,付江楠,等.骨关节炎氧化应激及其干预措施的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(15):1401-1405. [36] AN Y, ZHANG H, WANG C, et al. Activation of ROS/MAPKs/NF-κB/NLRP3 and inhibition of efferocytosis in osteoclast-mediated diabetic osteoporosis. FASEB J. 2019;33(11):12515-12527. [37] 陈晨,郑润泉,张贵春.大黄素对骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖、凋亡和氧化应激的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(28):4528-4534. [38] GUO Z, LIN J, SUN K, et al. Deferoxamine Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Chondrocyte Ferroptosis and Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:791376. [39] MARIANO A, BIGIONI I, MISITI F, et al. The Nutraceuticals as Modern Key to Achieve Erythrocyte Oxidative Stress Fighting in Osteoarthritis. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022;44(8):3481-3495. [40] CAI D, YANG Z, ZHONG C, et al. miR-515-5p targeting Toll-like receptor 4 regulates myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88/nuclear factor-kappa B pathway to inhibit apoptosis and inflammatory response of osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024;38(3):315-323. [41] KHOMEIJANI-FARAHANI M, KARAMI J, FARHADI E, et al. TAK-242 (Resatorvid) inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production through the inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in osteoarthritis patients. Adv Rheumatol. 2024;64(1):46. [42] QI X, CHEN X, AN WB, et al. Ligusticum cycloprolactam inhibits IL-1β-induced apoptosis and inflammation of rat chondrocytes via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024;49(4):1007-1016. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [3] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [4] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [6] | Wan Lingling, Wu Mengying, Zhang Yujiao, Luo Qingqing. Inflammatory factor interferon-gamma affects migration and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells through pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1422-1428. |
| [7] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [8] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [9] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [10] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [11] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [12] | Liu Zhezhe, Yu Meiqing, Wang Tingting, Zhang Min, Li Baiyan. Troxerutin modulates nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway to inhibit brain injury and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1137-1143. |
| [13] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [14] | Zhang Debao, Wang Peng, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Li Shuwen, Wu Yimin. Epidural fibrous scar formation in rabbits following autologous ligamentum flavum intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| [15] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||