Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (30): 6529-6537.doi: 10.12307/2025.902
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anti-inflammatory peptides for oral inflammatory diseases: regulation of inflammatory response to reduce tissue destruction and structural loss
Zhu Menghan, Yang Xuetao, Sun Yimin, Wang Chenglin
- State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Endodontics in West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-25Accepted:2024-11-22Online:2025-10-28Published:2025-03-29 -
Contact:Wang Chenglin, MD, Associate professor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Endodontics in West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China Co-corresponding author: Sun Yimin, MD, Assistant research fellow, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Endodontics in West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhu Menghan, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Department of Endodontics in West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Foundation of Sichuan Province, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Project, No. 2021YFH0185 (to WCL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Menghan, Yang Xuetao, Sun Yimin, Wang Chenglin. Anti-inflammatory peptides for oral inflammatory diseases: regulation of inflammatory response to reduce tissue destruction and structural loss[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6529-6537.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
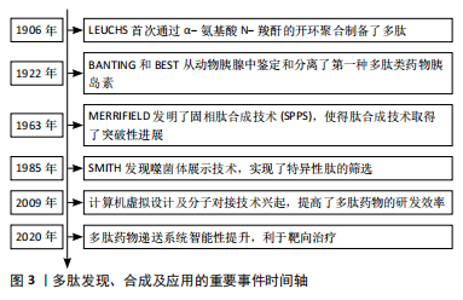
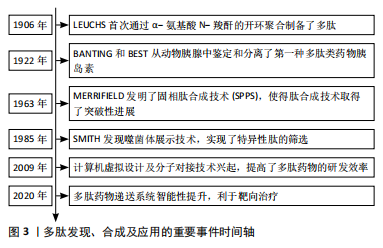
2.1 多肽药物的研究历程 根据纳入的文献结果显示,多肽药物的研究经历了数次研究演变,LEUCHS[13]首次通过α-氨基酸 N-羧酐的开环聚合制备了多肽。研究人员以此为基础通过调整引发剂、反应条件等开发了不同的多肽合成体系。BANTING等[14]从动物胰腺中鉴定和分离了第一种多肽类药物胰岛素,其作为糖尿病的关键性治疗药物沿用至今。MERRIFIELD[15]发明了固相肽合成技术(solid-phase peptide synthesis,SPPS),提高了合成效率,使得肽合成技术取得了突破性进展。SMITH[16]发现的噬菌体展示技术,使外源性编码的多肽或蛋白质基因能够在噬菌体表面表达,实现了特异性肽的筛选。计算机虚拟设计及分子对接技术可以识别及设计针对分子靶点的高亲和力化合物,提高了多肽药物的研发效率[17]。靶向药物递送系统能够将多肽药物输送至目标区域,利于精准治疗[18],见图3。"
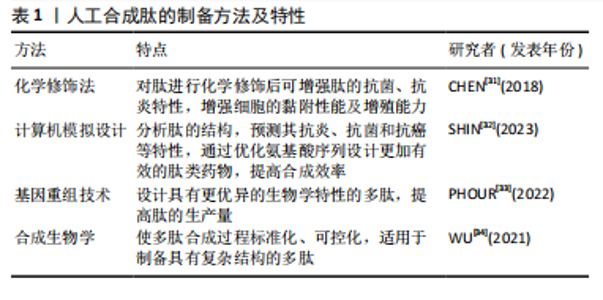
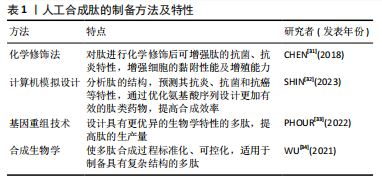
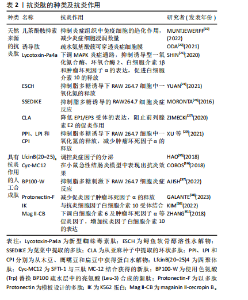
2.2 抗炎肽的分类 具有抗炎作用的活性肽可从动物、植物、微生物等多个物种中提取,除天然存在的多肽、蛋白水解物外,采用化学修饰法、计算机模拟设计及基因重组技术合成的多肽同样可以发挥抗炎功效。 2.2.1 天然来源的抗炎肽 (1)多肽:嗜铬粒蛋白A属于神经内分泌多肽,是由嗜铬细胞、胰岛β细胞或巨噬细胞分泌的一种酸性、亲水性低分子量蛋白,其衍生肽儿茶酚胺抑素(catestatin,CST)具有抗炎活性。MUNTJEWERFF等[19]利用主动脉环血管模型研究儿茶酚胺抑素对炎症组织中免疫细胞的趋化作用,在灌注儿茶酚胺抑素后,炎症组织中巨噬细胞的浸润数量明显减少,表明儿茶酚胺抑素很可能成为慢性炎症性疾病治疗的新靶点。脊椎动物的上皮细胞通过紧密连接维持屏障作用,上皮屏障的破坏会导致各种炎性疾病的发生。ODA等[20]在人体以及小鼠中发现了α1-抗胰蛋白酶(alpha 1-antitrypsin,A1AT)的C端片段具有抗炎性,并将其命名为诱导肽。在右旋糖酐硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎模型中,诱导肽治疗组中小鼠结肠上皮细胞层内中性粒细胞浸润数量显著降低,其抗炎机制可能与诱导肽的N端和C端含有的疏水氨基酸簇有关,这种结构使其可优先穿透具有高通透性的炎症细胞膜并与细胞质中的蛋白质反应,从而发挥抗炎作用。动物毒液由离子、肽和蛋白质组成,含有多种生物活性化合物。SHIN等[21]采用反相高效液相色谱法从星豹蛛毒液中提取了一种多肽Lycotoxin-Pa4a,可减少脂多糖刺激下RAW264.7细胞中一氧化氮的产生,展现出一定的抑炎效果。此外,该多肽还能抑制诱导型一氧化氮合酶、环氧合酶2、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎递质的表达,同时促进抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的释放,其抗炎机制可能与下调丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen actived protein kinase,MAPKs)炎症通路相关。 (2)蛋白水解物:海洋生物种类多样,使用酶水解、微生物发酵、酸性或碱性提取等方法可从贝类、鱼类或海藻中获得具有特殊结构的生物活性肽。其中,酶水解法是最常使用的方法,包括胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶、糜蛋白酶等。研究发现,海洋来源的多肽具有抗炎、抗氧化、抗菌、抗高血压、抗癌等多种生物活性[22]。硫酸软骨素作为鲟鱼软骨的主要成分之一,在免疫调节方面发挥重要作用。YUAN等[23]采用热压法、酶解法及乙醇提取法获得了鲟鱼软骨醇溶性水解物(ESCH),其N端含有的疏水性氨基酸与抗炎性密切相关,研究证明ESCH对脂多糖诱导的RAW264.7细胞具有较好的一氧化氮抑制作用,然而其特异性抗炎机制仍待进一步研究。藻类含有蛋白质、维生素、矿物质、碳水化合物等。许多海藻提取物可通过调节核因子κB激活的炎症信号通路减少炎症递质的释放,从而发挥抗炎特性。研究发现藻类蛋白水解物在小鼠结肠炎模型中的抗炎功效优于临床抗炎药物美沙拉嗪[24]。 通过化学水解、微生物发酵、酶解等方法可以从谷物、水果和其他天然产物中提取生物活性肽。其中,来源于植物的多肽由于分子质量低、在人体肠道易于吸收且能靶向发挥抗炎功效,受到人们的广泛关注。大部分植物源性的抗炎生物活性肽都含有亮氨酸、色氨酸和苯丙氨酸等疏水性氨基酸,通常位于肽链的末端。高疏水性可增强肽与细胞膜的结合以及膜的去极化,破坏炎症反应发生的级联通路,从而发挥抗炎作用[25]。从苋菜中提取的多肽SSEDIKE在炎症性肠炎模型中下调核因子κB通路,显示出抗炎活性,另一项研究也表明苋菜蛋白水解物可抑制脂多糖诱导的RAW 264.7细胞炎症反应[26]。从亚麻种子中提取的环状多肽CLA,通过降低EP1/EP3受体的表达,抑制前列腺素E2的促炎作用,在大鼠关节炎模型中有较好治疗效果[27]。豆科植物含有多种生物活性化合物,酚类、异黄酮、肽和蛋白质等都具有抗氧化、抗炎潜能。大豆蛋白酶解后的水解产物可以抑制脂多糖刺激下RAW 264.7细胞中诱导型一氧化氮合酶和环氧合酶2的表达,以及一氧化氮、肿瘤坏死因子α和前列腺素E2的合成[28]。使用酶解法分别从木豆、鹰嘴豆和扁豆中获得蛋白水解物PPI、LPI和CPI,随着水解物浓度的增加,脂多糖诱导下RAW 264.7细胞中一氧化氮的抑制率也增加,证明豆科植物蛋白水解物具有抗炎特性[29]。 2.2.2 具有抗炎作用的人工合成肽 天然多肽在来源、数量上具有优势,但提取工艺复杂、易降解、不稳定、昂贵等问题可能阻碍天然肽进一步开发[30]。而基于已有片段或模拟活性位点设计的人工合成肽具有结构稳定、抗炎活性强等优势,成为了研究热点。文章对于人工合成多肽的方法及特性进行了总结,见表1。 (1)化学修饰:对天然存在的多肽进行化学修饰,例如氨基酸取代,侧链改变、聚合、环化、化学键嵌入、甲基化等不仅能增强多肽原有的抗炎、抗菌、抗氧化功能,还可增加其稳定性。例如四聚体肽LfcinB(20-25)4 相较于其单体形式表现出更强的抗炎特性,可以调控炎症因子的分泌、中和细菌分泌的毒性物质[35]。小型、非结构化的"
多肽在体内降解速度快、缺乏稳定性,将多肽中的活性片段嫁接到肽支架是设计新型药物的可行方法。SFTI-1是从向日葵种子中分离的一种环肽,将其作为支架,与来源于膜联蛋白A1的具有抗炎活性的三肽MC-12结合,获得一种结构稳定的新肽Cyc-MC12;与MC-12相比,Cyc-MC12在小鼠急性结肠炎模型中抗炎效果得到改善,体外稳定性也得到了进一步提升[36]。BP100是一种具有11个氨基酸残基的肽,AJISH等[37]使用色氨酸(Trp)替换BP100疏水层中的亮氨酸(Leu-3)合成了新肽BP100-W,并在脂多糖刺激的RAW 264.7细胞炎症模型中证实了BP100-W的抗炎活性。 (2)计算机模拟设计:通过计算机辅助设计多肽、模拟活性位点的方法提升多肽合成的效率,增强了目标肽的特异性。膜翅目昆虫毒液用于治疗已有数千年的历史,研究数据证明提取自膜翅目昆虫毒液的活性化合物可缓解疼痛,而疼痛与炎症反应的发生有关。黄蜂毒液的主要生物活性成分是肽,GALANTE等[38]以黄蜂毒液中分离鉴定的多肽Protonectin为模板,设计了一种新的多肽Protonectin-F,体内外实验证明在脂多糖刺激前使用该肽可减少促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α的释放,调节炎症反应。K562白血病细胞系中分离出的K562蛋白(IK)是一种新型抗炎药物,IK蛋白第316位蛋氨酸至557位酪氨酸的截断片段称为tIK,具有与抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10相似的抗炎作用。KIM等[39]根据白细胞介素10受体结合位点,合成了3种含有该结合位点的肽tIK-9mer、tIK-14mer和tIK-18mer,其中tIK-9mer具有疏水性,其余两者具有亲水性,后续将通过体内外实验进一步验证其抗炎性。 (3)基因重组技术:从生物体中提取目标肽对于实验设备及溶剂耗材具有较高要求,提取后的纯化过程亦很复杂。基因重组技术通过提取或设计编码目的多肽的基因片段,经载体转染至宿主并在其体内表达,该技术成本低、生产效率高,在多肽药物合成领域应用广泛。JEYARAJAN等[40]以一种具有抗炎、抗菌特性的多肽Epi-1为模板,对其进行改性后克隆至pET32a载体并转载到大肠杆菌中,成功合成了野生型Epi-1。ZHANG等[41]通过基因重组技术成功合成了magainin II-cecropin B(Mag II-CB)肽,在感染性小鼠模型中证实了Mag II-CB可下调白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎因子,并增加抗炎因子白细胞介素10的表达,具有免疫调节特性。 文章总结了抗炎肽的相关研究进展,见表2。 2.3 抗炎肽调控炎症反应的相关通路 2.3.1 核因子κB通路 核因子κB通路包括经典和非经典"

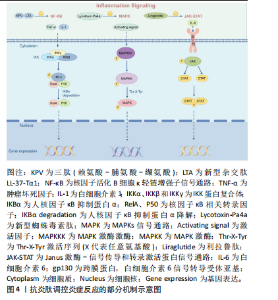
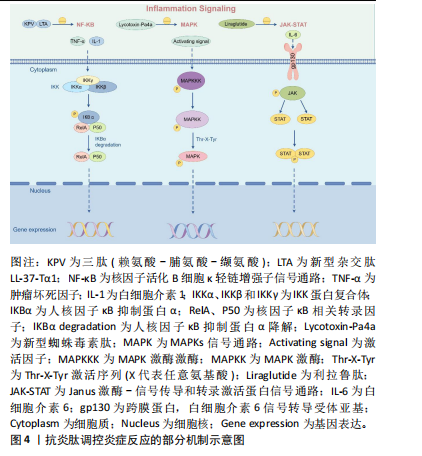
通路,前者作为炎症反应的重要环节,调节各种促炎基因的表达,当其失调时会导致各种炎症相关性疾病发生[42]。核因子κB家族是由p105/p50(Nfkb1)、p100/p52(Nfkb2)、p65(RelA)、c-Rel和RelB五种相关转录因子组成的二聚体[43]。经典通路调控Nfkb1、RelA和c-Rel,而非经典通路调控Nfkb2和RelB[44]。经典通路激活的关键是IKK(IkB蛋白激酶)磷酸化。IkB蛋白作为核因子κB的抑制剂,在静息状态下将核因子κB二聚体隔离在细胞质中。IKK蛋白复合体包括IKKα和IKKβ以及IKKγ三种调节亚基,炎症因子以及各种微生物产物刺激IKKβ后,诱导IKB蛋白磷酸化,核因子κB二聚体脱离抑制,从细胞质中释放进入细胞核并启动靶基因的转录[42]。IKK蛋白激活因子的增加可导致核因子κB活性增加,主要包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β,这些细胞因子是Toll样受体和NOD样受体识别病原体相关分子模式(pathogen associated molecular patterns,PAMP)或损伤相关分子模式(damage associated molecular patterns,DAMP)后诱导巨噬细胞或免疫细胞产生的[45-46]。研究表明核因子κB在口腔扁平苔藓病变组织细胞中高表达,检测发现口腔扁平苔藓患者的血清及唾液中核因子κB相关促炎细胞因子如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和肿瘤坏死因子α水平均升高[47]。牙周组织细胞中的模式识别受体,如Toll样受体能感知PAMP或DAMP,通过核因子κB信号通路调控免疫细胞活化,并将其募集至感染部位介导牙周组织免疫反应[48]。ZHANG等[49]设计开发了一种新型杂交肽LL-37-Tα(LTA),LTA预处理后空肠组织中IκB蛋白磷酸化表达降低,表明LTA通过核因子κB通路实现免疫调控。 2.3.2 MAPK通路 MAPKs主要由丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶组成,包括细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK1/2)和应激活化蛋白激酶家族p38和JNKs三个亚家族成员,三者均参与炎症调控[50]。MAPK通路需要MAPK激酶激酶(MAPKKK,MEKK或MKKK)、MAPK激酶(MAPKK,MEK或MKK)一系列激酶的级联激活启动[51]。MAPKKK激活MAPKK,而MAPKK通过Thr-X-Tyr激活序列(X代表任意氨基酸)的双重磷酸化进一步激活MAPK[52]。MAPK通路在炎症性疾病中发挥着重要作用,例如调控单核细胞、巨噬细胞、血管内皮细胞的活化,以及促炎细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素2、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素7和白细胞介素8等的释放。MAPK通路与哮喘、类风湿性关节炎、炎症性肠炎、阿尔茨海默症等慢性炎症性疾病均相关[53]。以MAPK为抗炎靶点开发的一系列抑制剂霉环氧二烯、AMG-548、SC-79659、槲皮素已进入临床试验[54]。 2.3.3 JAK-STAT通路 JAK是酪氨酸激酶(TYKs)家族,由4个结构域组成,每个结构域含有7个同源区域即JH1-JH7,共包括JAK1、JAK2、JAK3和TYK2四种激酶[55]。JAK-STAT信号通路的启动是细胞因子与其相应受体结合引发的级联反应。JAK激活后募集并使下游主要信号转导分子STAT蛋白发生磷酸化,STAT易位至细胞核中与DNA结合并调控细胞因子和生长因子基因转录,从而调控免疫过程[56-57]。白细胞介素6与糖蛋白130 (gp130)结合后激活JAK/STAT通路可诱导炎症性骨吸收[58]。小鼠模型中过度激活STAT会诱发严重的结肠炎,而抑制STAT可改善结肠炎[57]。JAK-STAT失调与多种自身免疫性疾病相关,使用JAK-STAT通路抑制剂后可抑制炎症反应[59]。 2.3.4 炎症小体 炎症小体是细胞质中的一组大分子复合物,包括传感器蛋白(NLR)或AIM2受体蛋白(ALR)、凋亡相关微粒蛋白(ASC)、Caspase蛋白酶三部分,其中NLR家族蛋白是主要的炎症小体传感器,可识别PAMP和DAMP。NLR或ALR识别配体后,传感器从抑制状态激活,ASC作为支架可募集细胞和介导白蛋白水解以及pro-Caspase-1的激活,激活的pro-Caspase-1进一步控制促炎细胞因子白细胞介素1β的释放从而调控炎症反应[60-61]。 2.3.5 cGAS-STING 环状GMP-AMP合成酶(cGAS)是先天免疫反应的主要DNA传感器,它可与病毒感染或受损的细胞核DNA、受损线粒体的双链细胞质DNA结合促进环状GMP-AMP(cGAMP)合成[62]。在检测到致病性双链脱氧核糖核酸(dsDNA)后,通过cGAS-STING通路可启动核因子κB通路以产生炎性细胞因子,或激活IFN3介导Ⅰ型干扰素的合成[63]。研究表明,细菌感染等各种应激会损伤线粒体DNA(mitochondrial DNA,mtDNA),导致其释放至细胞质中,而mtDNA通过激活cGAS-STING信号通路诱导炎性细胞因子释放,当降低mtDNA水平后,炎性细胞因子白细胞介素6的释放也相应减少[64]。 抗炎肽调控炎症反应的部分机制示意图,见图4。"
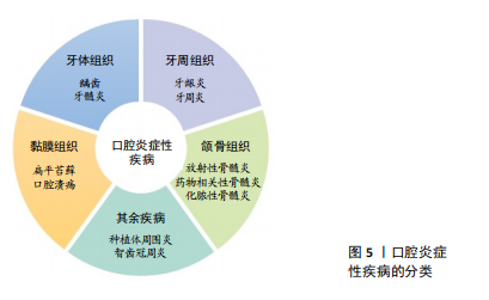
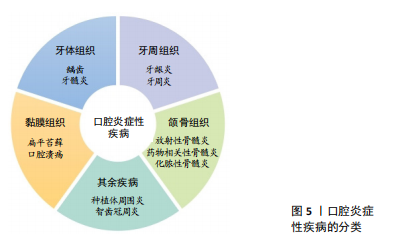
2.4 抗炎肽在口腔疾病中的应用 口腔作为消化道的入口,暴露于外界环境,容易因感染、创伤等发生慢性炎症,如牙龈炎、牙周炎、口腔黏膜炎。在外界刺激下,巨噬细胞发生M1型极化,此型细胞与促炎激活相关。有报道称牙周炎中M1型巨噬细胞数量明显增多,不仅分泌促炎细胞因子,还分泌胶原酶、基质金属蛋白酶等蛋白酶,破坏牙周结缔组织[65-66]。 炎症递质除了影响口腔相关组织外,当其从口腔进入体循环后到达到全身部位可诱发全身炎症反应。例如白细胞介素6可以加速动脉粥样硬化,还能导致心肌细胞凋亡,体循环内白细胞介素6的升高是心房颤动的危险因素之一[67-68]。此外流行病学与实验研究证明牙周炎和心脑血管疾病相关[69],牙周炎患者心血管疾病患病率显著增加[70]。因此,减少口腔炎症性疾病中炎症细胞的数量,抑制促炎相关因子的释放对于口腔疾病的治愈以及全身健康状态至关重要。 文章总结了口腔炎症性疾病的分类[71-75],见图5。"
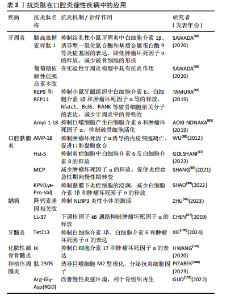
2.4.1 抗炎肽在牙周疾病中的应用 牙周炎是以牙周支持组织破坏为主要特征的口腔炎症性疾病,全球20%-50%人口患有牙周炎[76]。随着病变进展,可导致牙龈退缩、牙根暴露、牙齿松动,最终还可能失牙,严重影响人们的生活质量[77]。此外,牙周炎与全身疾病密切相关,例如脑卒中[78]、心血管疾病[79]、肾炎[80]、慢性阻塞性肺疾病等[81]。目前牙周炎的主要治疗方法是机械性去除细菌,然而并未阻止炎症反应对牙周组织的破坏[82],病变牙周组织细胞除释放促炎因子趋化中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞等迁移至该处参与炎症反应外[77],还激活破骨细胞导致骨吸收[83]。因此牙周炎治疗中控制炎症反应,保存更多的牙周组织是必要的。 葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽(Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide,GIP)和胰高血糖素样肽1均由肠道分泌,葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素多肽已在实验性牙周炎模型中被证明具有抗炎作用,而胰高血糖素样肽1可抑制结扎性小鼠牙周炎中白细胞介素1β、诱导型一氧化氮合酶和基质金属蛋白酶9等炎症基因的表达,降低肿瘤坏死因子α的释放从而减少破骨细胞的形成[66]。口腔菌群失调与牙周炎的发生密切相关,有报道称水稻肽可抑制牙龈卟啉单胞菌,除了抗菌效果外,实验证明来源于水稻的多肽REP9和REP11能抑制小鼠牙龈组织中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α等的释放和Nfatc1、Bcl6、RANK等破骨细胞相关分子的表达,并减少牙周炎中的骨吸收[84]。另一种来源于水稻的多肽Amyl-1-18同样能抑制巨噬细胞产生白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α,从而抑制破骨细胞活化[85]。 2.4.2 抗炎肽在口腔黏膜疾病中的应用 放疗或化疗后活性氧的累积会造成上皮细胞损伤及死亡,造成组织红肿破溃,发生在口腔黏膜时,患者往往出现疼痛、感染、进食困难、体质量减轻等症状。口腔黏膜炎的治疗通常采用单独或者联合应用抗菌、抗炎、镇痛、促进愈合的药物,但抗炎效果仍不理想[86-87]。胃窦上皮细胞分泌的AMP-18肽在放疗诱导的口腔黏膜炎实验模型中,表现出口腔黏膜溃疡形成减少、黏膜愈合速度加快等作用,其机制可能与AMP-18抑制了肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的内皮细胞凋亡有关[88]。Hst-5是含有24个氨基酸的组蛋白多肽,能抑制炎症细胞中白细胞介素6及白细胞介素8的释放。Hst-5治疗组大鼠颊黏膜溃疡周围炎症细胞浸润数量减少,成纤维细胞数量增加,促进了胶原蛋白的沉积和黏膜愈合[87]。在黏膜溃疡处涂布来源于罗非鱼皮肤的海洋生物胶原蛋白水解物MCP后,组织中肿瘤坏死因子α表达显著降低,多形核白细胞浸润减少,并且促使炎症由急性期向慢性期转变[89]。KPV(Lys-Pro-Val)是来源于促黑素细胞激素α(α-MSH)的短肽,其抗炎机制与调节核因子κB信号通路相关。在大鼠牙龈溃疡模型中,含有KPV的水凝胶可以明显抑制黏膜下炎症细胞的浸润,减少白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的释放,并上调抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的表达[90]。口腔扁平苔藓是一种病因尚不明确的口腔慢性炎症疾病,免疫细胞分泌的白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8及肿瘤坏死因子α等炎促炎因子参与了炎症反应过程[91],JAK/STAT通路在其中发挥关键调控作用,研究证明JAK抑制蛋白能有效治疗口腔扁平苔藓,减轻局部炎症[92]。 2.4.3 抗炎肽在牙体疾病中的应用 龋齿是由细菌感染引起的慢性、进行性疾病。牙菌斑生物膜是导致龋坏的重要因素,细菌不断产酸导致牙体组织脱矿、破坏[93],随着病情发展,细菌深入牙本质甚至累及牙髓组织。在深龋患牙的牙髓组织中可观察到淋巴细胞、浆细胞浸润,毛细血管充血征,这表明细菌感染的程度与牙髓炎症状态密切相关[94]。龋病的进展同样受到免疫系统的调控。当进入牙体组织的细菌被Toll样受体识别后会激活核因子kB信号通路及炎症小体,导致白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18等促症因子的产生。在使用革兰阳性菌细胞壁成分脂磷壁酸体外刺激牙髓细胞后,细胞内NLRP3炎性小体的表达明显上调,这表明NLRP3炎性小体很可能是调控龋齿内炎症反应的潜在靶点[95]。降钙素基因相关肽能够抑制NLRP3炎性小体的激活,利于减轻细菌感染引起的炎症反应,发挥抗炎、抗菌双重作用[96]。CHEN等[97]发现了一种天然肽LL-37,并对其进行改性,抗菌实验结果表明其对变形链球菌具有较强的抑制作用,还可通过下调核因子kB通路抑制肿瘤坏死因子α的释放发挥抗炎作用。 当细菌进一步入侵牙髓组织造成严重感染时,牙髓已发生不可逆性损害。在该阶段患者会表现为自发性疼痛症状,生活质量受到极大影响。研究表明感染牙髓组织中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β等促炎细胞因子的表达高于正常牙髓组织,而这些细胞因子与炎症进展、组织破坏相关[98]。其中肿瘤坏死因子α可激活核因子κB炎症信号通路,增加血管通透性以及募集白细胞至炎症部位。而白细胞介素6在非特异性免疫转变为特异性免疫过程中发挥着重要作用。在机体自身免疫方面,唾液中含有的抗菌肽、分泌型免疫球蛋白A等可在炎症部位参与免疫调控。此外,炎症反应刺激神经系统后,神经末梢释放P物质、降钙素基因相关肽等神经肽,也可以发挥直接抗菌作用以及启动一系列抗炎程序,抵抗细菌及其释放的有害物质。传统的根管治疗以彻底去除感染牙髓,保存患牙为原则,然而对于那些处于可逆性损害阶段的牙髓、能够抑制炎症反应、阻止组织破坏、保存患牙的活髓或许是未来治疗方法的发展方向[99]。XIE等[100]制备了一种含有抗菌、抗炎及促矿化三重特性的Tet213-GelMA水凝胶,其中Tet213肽能够抑制脂多糖处理后人牙髓干细胞中炎症基因的表达,如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等,同时对干酪乳杆菌具有抑制作用。 2.4.4 抗炎肽在骨组织相关疾病中的应用 牙源性感染、外伤、拔牙等因素均可诱发颌骨骨髓炎,临床表现为骨组织及周围软组织肿胀、疼痛,根据炎症反应类型及病程长短可分为急性或慢性骨髓炎。GEORGAKI等[101]报道了1例经抗生素治疗无效,但免疫疗法成功治愈的儿童慢性颌骨骨髓炎,该病例使用泼尼松联合肿瘤坏死因子α抑制剂治疗后患儿颌骨肿胀明显消退。骨质疏松患者长期服用双膦酸盐后,药物相关性骨髓炎或药物相关性颌骨坏死发病率增加[102],然而其发病机制尚不清晰。一项关于药物相关性颌骨坏死组织中破骨细胞形态的研究显示,破骨细胞核体积增大、数量增多倾向于细胞融合形成巨细胞,这表明炎症细胞与破骨细胞形态变化相关,破骨细胞活性增加是由炎症和微生物引起的[103]。另一项基于化脓性颌骨骨髓炎样本的免疫组化结果证明,白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6的表达明显增高,抑制这些炎症因子的表达有望阻止骨髓炎中骨组织的破坏吸收[104]。研究发现,IK蛋白对白细胞介素17和肿瘤坏死因子α具有较强的抑制作用,IK蛋白来源的新型抗炎肽PS4具有良好的生物相容性,可参与组织修复、促进伤口愈合[105]。 2.4.5 抗炎肽在其余口腔炎症疾病中的应用 种植体周围炎表现为植体周围黏膜组织炎症、支持组织丧失,后期种植体逐渐松动甚至脱落。菌斑控制是预防种植体周围炎的主要方法,然而目前仍缺乏有效缓解种植体周围炎症的治疗措施[106]。炎症环境中M1型巨噬细胞释放炎症因子,加快了骨吸收,影响种植体周围的骨整合[107]。有研究发现种植体周围炎对应部位龈沟液内白细胞介素23含量显著增加,白细胞介素23与牙槽骨吸收有关。肽2305能与白细胞介素23受体特异性结合并抑制白细胞介素23的表达,将其作为肽纳米涂层可诱导巨噬细胞M2型极化,分泌抗炎细胞因子,降低种植体周围炎的发生率[108]。此外,GUO等[107]发现在种植体表面涂布短肽Arg-Gly-Asp(RGD)后植入牙槽骨,种植体与骨交界处巨噬细胞会发生M2型极化,改善慢性炎症环境,有利于骨组织再生。智齿冠周炎常见于下颌第三磨牙,表现为萌出不全智齿周围软组织的炎症,急性炎症期间患者自觉肿痛、溢脓,严重时还会导致张口困难影响正常进食。研究表明智齿冠周炎是以厌氧菌为主的混合菌群感染,包括链球菌、放线菌和梭杆菌等,它们参与了冠周炎急性发作过程[109]。对拔除的智齿所黏附的软组织进行病理学检测,可见炎症细胞浸润的牙龈组织,这表明部分萌出智齿的远中盲袋存在持续的炎症反应[110]。临床上通常联合使用非类固醇抗炎药及抗生素减轻局部炎症及缓解疼痛,但是对于妊娠期患者需慎重使用。目前已有多肽药物治疗妊娠期智齿冠周炎的报道,其安全性高,抑菌性强,又可快速控制炎症,为妊娠期智齿冠周炎的临床治疗提供了新思路[111]。 文章总结了抗炎肽在口腔炎症性疾病中的应用相关研究进展,见表3。"

| [1] MEDZHITOV R. The spectrum of inflammatory responses. Science. 2021; 374(6571):1070-1075. [2] DENG Z, LIU S. Inflammation-responsive delivery systems for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021;11(4):1475-1497. [3] LIU C, FAN D, LEI Q, et al. Roles of Resolvins in Chronic Inflammatory Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):14883. [4] WANG J, WU S, LI Z, et al. Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B inducing kinase suppresses inflammatory responses and the symptoms of chronic periodontitis in a mouse model. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021;139:106052. [5] GARG U, AZIM Y. Challenges and opportunities of pharmaceutical cocrystals: a focused review on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. RSC Med Chem. 2021; 12(5):705-721. [6] ROBB CT, GOEPP M, ROSSI AG, et al. Non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and COVID‐19. Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177(21):4899-4920. [7] UNGPRASERT P, CHEUNGPASITPORN W, CROWSON CS, et al. Individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(4): 285-291. [8] CHEDEA VS, MACOVEI ȘO, BOCȘAN IC, et al. Grape Pomace Polyphenols as a Source of Compounds for Management of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation-A Possible Alternative for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs?. Molecules. 2022;27(20):6826. [9] ZHANG Y, HE P, ZHANG P, et al. Polypeptides-Drug Conjugates for Anticancer Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(11):2001974. [10] DADAR M, SHAHALI Y, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. Antiinflammatory peptides: current knowledge and promising prospects. Inflamm Res. 2019;68(2):125-145. [11] KARAMI Z, AKBARI-ADERGANI B. Bioactive food derived peptides: a review on correlation between structure of bioactive peptides and their functional properties. Food Sci Technol. 2019;56(2):535-547. [12] ABRIL AG, PAZOS M, VILLA TG, et al. Proteomics Characterization of Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides with Anti-Allergic and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Nutrients. 2022;14(20):4400. [13] LEUCHS H. Ueber die Glycin-carbonsäure. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges. 1906;39:857-861. [14] BANTING FG, BEST CH, COLLIP JB, et al. Pancreatic Extracts in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Can Med Assoc J. 1922;12(3):141-146. [15] MERRIFIELD RB. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. I. The Synthesis of a Tetrapeptide. J Am Chem Soc. 1963;85(14):2149-2154 [16] SMITH GP. Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science. 1985;228(4705):1315-1317. [17] ZOETE V, GROSDIDIER A, MICHIELIN O. Docking, virtual high throughput screening and in silico fragment‐based drug design. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(2):238-248. [18] LI K, LIU CJ, ZHANG XZ. Multifunctional peptides for tumor therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;160:36-51. [19] MUNTJEWERFF EM, PARV K, MAHATA SK, et al. The anti-inflammatory peptide Catestatin blocks chemotaxis. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;112(2):273-278. [20] ODA Y, TAKAHASHI C, HARADA S, et al. Discovery of anti-inflammatory physiological peptides that promote tissue repair by reinforcing epithelial barrier formation. Sci Adv. 2021;7(47):eabj6895. [21] SHIN MK, HWANG IW, KIM Y, et al. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Novel Peptide Toxin from the Spider Pardosa astrigera. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020; 9(7):422. [22] CUNHA SA, PINTADO ME. Bioactive peptides derived from marine sources: Biological and functional properties. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2022;119:348-370. [23] YUAN L, CHU Q, WU X, et al. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity of Peptides From Ethanol-Soluble Hydrolysates of Sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii) Cartilage. Front Nutr. 2021;8:689648. [24] EILAM Y, KHATTIB H, PINTEL N, et al. Microalgae-Sustainable Source for Alternative Proteins and Functional Ingredients Promoting Gut and Liver Health. Glob Chall. 2023;7(5):2200177. [25] LIU W, CHEN X, LI H, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Function of Plant-Derived Bioactive Peptides: A Review. Foods. 2022;11(15):2361. [26] MORONTA J, SMALDINI PL, DOCENA GH, et al. Peptides of amaranth were targeted as containing sequences with potential anti-inflammatory properties. J Funct Food. 2016;21:463-473. [27] ZIMECKI M, ARTYM J, KAŁAS W, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of a Cyclic Tetrapeptide in Mouse and Human Experimental Models. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(11):1030. [28] JUÁREZ-CHAIREZ MF, MEZA-MÁRQUEZ OG, MÁRQUEZ-FLORES YK, et al. Potential anti-inflammatory effects of legumes: a review. Br J Nutr. 2022;128(11):2158-2169. [29] XU X, QIAO Y, SHI B, et al. Alcalase and bromelain hydrolysis affected physicochemical and functional properties and biological activities of legume proteins. Food Struct. 2021;27:100178. [30] LIU Y, XIA X, XU L, et al. Design of hybrid β-hairpin peptides with enhanced cell specificity and potent anti-inflammatory activity. Biomaterials. 2013;34(1):237-250. [31] CHEN J, VENKATESAN H, HU J. Chemically Modified Silk Proteins. Adv Eng Mater. 2018;20:1700961. [32] SHIN MK, PARK HR, HWANG IW,et al. In Silico-Based Design of a Hybrid Peptide with Antimicrobial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Using a Spider Toxin Peptide. Toxins (Basel). 2023;15(12):668. [33] PHOUR A, GAUR V, BANERJEE A, et al. Recombinant protein polymers as carriers of chemotherapeutic agents. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;190:114544. [34] WU Z, LI Y, ZHANG L, et al. Microbial production of small peptide: pathway engineering and synthetic biology. Microb Biotechnol. 2021;14(6):2257-2278. [35] HAO Y, YANG N, TENG D, et al. A review of the design and modification of lactoferricins and their derivatives. Biometals. 2018;31(3):331-341. [36] COBOS C, BANSAL PS, JONES L, et al. Engineering of an Anti-Inflammatory Peptide Based on the Disulfide-Rich Linaclotide Scaffold. Biomedicines. 2018;6(4): 97. [37] AJISH C, KUMAR SD, KIM EY, et al. A short novel antimicrobial peptide BP100-W with antimicrobial, antibiofilm and anti-inflammatory activities designed by replacement with tryptophan. J Anal Sci Technol. 2022;13(1):46. [38] GALANTE P, CAMPOS GAA, MOSER JCG, et al. Exploring the therapeutic potential of an antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory peptide from wasp venom. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):12491. [39] KIM M, KIM Y. Structural Studies of Expressed tIK, Anti-Inflammatory Peptide. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):636. [40] JEYARAJAN S, SATHYAN A, PETER AS, et al. Bioproduction and Characterization of Epinecidin-1 and Its Variants Against Multi Drug Resistant Bacteria Through In Silico and In Vitro Studies. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2023;29:66. [41] ZHANG M, SHAN Y, GAO H, et al. Expression of a recombinant hybrid antimicrobial peptide magainin II-cecropin B in the mycelium of the medicinal fungus Cordyceps militaris and its validation in mice. Microb Cell Fact. 2018;17(1):18. [42] YU H, LIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):209. [43] HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. NF-κB in immunobiology. Cell Res. 2011;21(2):223-244. [44] SUN SC. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(9):545-558. [45] CAPECE D, VERZELLA D, FLATI I, et al. NF-κB: blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2022;43(9):757-775. [46] TANIGUCHI K, KARIN M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18(5):309-324. [47] WANG Y, ZHANG H, DU G, et al. Total glucosides of paeony (TGP) inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines in oral lichen planus by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;36:67-72. [48] MOONEY EC, SAHINGUR SE. The Ubiquitin System and A20: Implications in Health and Disease. J Dent Res. 2021;100(1):10-20. [49] ZHANG L, WEI X, ZHANG R, et al. Design and Development of a Novel Peptide for Treating Intestinal Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1841. [50] GAŁGAŃSKA H, JARMUSZKIEWICZ W, GAŁGAŃSKI Ł. Carbon dioxide and MAPK signalling: towards therapy for inflammation. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1): 280. [51] THALHAMER T, MCGRATH MA, HARNETT MM. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(4):409-414. [52] ARTHUR JS, LEY SC. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(9):679-692. [53] YONG HY, KOH MS, MOON A. The p38 MAPK inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;18(12): 1893-1905.
[54] RAJPOOT S, KUMAR A, ZHANG KYJ, et al. TIRAP-mediated activation of p38 MAPK in inflammatory signaling. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):5601. [55] BANERJEE S, BIEHL A, GADINA M, et al. JAK-STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs. 2017;77(5):521-546. [56] HUANG IH, CHUNG WH, WU PC, et al. JAK-STAT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: An updated review. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 1068260. [57] SALAS A, HERNANDEZ-ROCHA C, DUIJVESTEIN M, et al. JAK–STAT pathway targeting for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17(6):323-337. [58] HU L, LIU R, ZHANG L. Advance in bone destruction participated by JAK/STAT in rheumatoid arthritis and therapeutic effect of JAK/STAT inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109095. [59] PANG W, HU F. C9ORF72 suppresses JAK-STAT mediated inflammation. iScience. 2023;26(5):106579. [60] CHEN Y, FANG ZM, YI X, et al. The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(3):205. [61] KETELUT-CARNEIRO N, FITZGERALD KA. Inflammasomes. Curr Biol.2020;30(12): R689-R694. [62] LI H, HU L, WANG L, et al. Iron Activates cGAS-STING Signaling and Promotes Hepatic Inflammation. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70(7):2211-2220. [63] CHEN K, LIU J, CAO X. cGAS-STING pathway in senescence-related inflammation. Natl Sci Rev. 2018;5(3):308-310. [64] ZHOU L, ZHANG YF, YANG FH, et al. Mitochondrial DNA leakage induces odontoblast inflammation via the cGAS-STING pathway. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):58. [65] YANG J, ZHU Y, DUAN D, et al. Enhanced activity of macrophage M1/M2 phenotypes in periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;96:234-242. [66] SAWADA N, ADACHI K, NAKAMURA N, et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Liraglutide Ameliorates the Development of Periodontitis. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:8843310. [67] AARABI G, SCHNABEL RB, HEYDECKE G, et al. Potential Impact of Oral Inflammations on Cardiac Functions and Atrial Fibrillation. Biomolecules. 2018; 8(3):66. [68] MASI S, D’AIUTO F, DEANFIELD J. Cardiovascular prevention starts from your mouth. Eur Heart J. 2019;40(14):1146-1148. [69] KONKEL J E, O’BOYLE C, KRISHNAN S. Distal Consequences of Oral Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1403. [70] 张程,孙红英.口腔微生物组与全身疾病的相关性[J].生理科学进展,2021, 52(2):128-132. [71] DONG Z, WU L, HONG H. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Oral Inflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20):15483. [72] FERRILLO M, GIUDICE A, MIGLIARIO M, et al. Oral–Gut Microbiota, Periodontal Diseases, and Arthritis: Literature Overview on the Role of Probiotics. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4626. [73] XUE N, WANG Y, CHENG H, et al. Regulatory T cell therapy suppresses inflammation of oral mucosa. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1009742. [74] GROSS C, WEBER M, CREUTZBURG K, et al. Osteoclast profile of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw secondary to bisphosphonate therapy: a comparison with osteoradionecrosis and osteomyelitis. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1): 128. [75] GARCÍA-ARÉVALO F, LEIJA-MONTOYA AG, GONZÁLEZ-RAMÍREZ J, et al. Modulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cell functions by oral inflammatory diseases and important oral pathogens. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1349067. [76] AKIYAMA K, AUNG KT, TALAMINI L, et al. Therapeutic effects of peptide P140 in a mouse periodontitis model. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(10):518. [77] HUANG X, XIE M, XIE Y, et al. The roles of osteocytes in alveolar bone destruction in periodontitis. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):479. [78] ZHENG X, LI X, ZHEN J, et al. Periodontitis is associated with stroke. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):697. [79] PRIYAMVARA A, DEY AK, BANDYOPADHYAY D, et al. Periodontal Inflammation and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Curr Atheroscleros Rep. 2020;22(7):28. [80] BI C, HAN X, LI X, et al. Periodontitis aggravates renal inflammatory response in a mouse model of renal fibrosis. Oral Dis. 2022;28(2):521-528. [81] TAKEUCHI K, MATSUMOTO K, FURUTA M, et al. Periodontitis Is Associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J Dent Res. 2019;98(5):534-540. [82] SAKO H, OMORI K, NAKAYAMA M, et al. The Fungal Metabolite (+)-Terrein Abrogates Inflammatory Bone Resorption via the Suppression of TNF-α Production in a Ligature-Induced Periodontitis Mouse Model. J Fungi. 2023;9(3): 314. [83] HASCOËT E, BLANCHARD F, BLIN-WAKKACH C, et al. New insights into inflammatory osteoclast precursors as therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):26. [84] TAMURA H, MAEKAWA T, DOMON H, et al. Peptides from rice endosperm protein restrain periodontal bone loss in mouse model of periodontitis. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;98:132-139. [85] AOKI-NONAKA Y, TABETA K, MATSUDA Y, et al. A peptide derived from rice inhibits alveolar bone resorption via suppression of inflammatory cytokine production. J Periodontol. 2019;90(10):1160-1169. [86] PULITO C. Oral mucositis: the hidden side of cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):210. [87] GOLSHANI S, VATANARA A, BALALAIE S, et al. Development of a Novel Histatin-5 Mucoadhesive Gel for the Treatment of Oral Mucositis: In Vitro Characterization and In Vivo Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2023;24(7):177. [88] WU X, CHEN P, SONIS ST, et al. A Novel Peptide to Treat Oral Mucositis Blocks Endothelial and Epithelial Cell Apoptosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83(3): e409-e415. [89] SHANG Y, YAO S, QIAO X, et al. Evaluations of Marine Collagen Peptides from tilapia skin on experimental oral ulcer model of mice. Mater Today Commun. 2021;26:101893. [90] SHAO W, CHEN R, LIN G, et al. In situ mucoadhesive hydrogel capturing tripeptide KPV: the anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and repairing effect on chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(1):227-242. [91] ČĒMA I, KAKAR J, DZUDZILO M, et al. on behalf of VirA Project Nr 952376. Immunological Aspects of EBV and Oral Mucosa Interactions in Oral Lichen Planus. Appl Sci. 2023;13:6735. [92] WU T, BAI Y, JING Y, et al. What can we learn from treatments of oral lichen planus? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024;14:1279220. [93] LIN B, WANG J, ZHANG Y. Bacterial dynamics in the progression of caries to apical periodontitis in primary teeth of children with severe early childhood caries. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1418261. [94] RICUCCI D, SIQUEIRA JF JR, RÔÇAS IN,et al. Pulp and dentine responses to selective caries excavation: A histological and histobacteriological human study. J Dent. 2020;100:103430. [95] AL NATOUR B, LUNDY FT, ABOUT I, et al. Regulation of caries-induced pulp inflammation by NLRP3 inflammasome: A laboratory-based investigation. Int Endod J. 2023;56(2):193-202. [96] ZHU F, YU D, QIN X, et al. The neuropeptide CGRP enters the macrophage cytosol to suppress the NLRP3 inflammasome during pulmonary infection. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(3):264-276. [97] CHEN Z, YANG G, LU S, et al. Design and antimicrobial activities of LL-37 derivatives inhibiting the formation of Streptococcus mutans biofilm.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019;93(6):1175-1185. [98] LOUZADA LM, ARRUDA-VASCONCELOS R, KEARNEY M, et al. Teeth with vital pulps and stage III periodontitis unresponsive to therapy exhibit a pulpal inflammatory profile similar to symptomatic irreversible pulpitis. Int Endod J. 2024;57(12): 1769-1782. [99] POHL S, AKAMP T, SMEDA M, et al. Understanding dental pulp inflammation: from signaling to structure. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1474466 [100] XIE Z, JIANG W, LIU H, et al. Antimicrobial Peptide- and Dentin Matrix-Functionalized Hydrogel for Vital Pulp Therapy via Synergistic Bacteriostasis, Immunomodulation, and Dentinogenesis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(18):e2303709. [101] GEORGAKI M, DELLI K, PASCHALIDI P, et al. Chronic Osteomyelitis With Proliferative Periostitis of the Mandible in a Child: Report of a Case Managed by Immunosuppressive Treatment. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2022;41(1):e10-e15 [102] HONG SO, LEE CY, JUNG J, et al. A retrospective study of osteomyelitis and osteonecrosis of the jaws and its etiologic implication of bisphosphonate in Asians. Clin Oral Invest. 2017;21(5):1905-1911. [103] NGOC THUY TRAN V, CHAISUPARAT R. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Osteoclast profile in comparison with osteoradionecrosis of the jaw and osteomyelitis of the jaw. J Oral Pathol Med. 2021;50(7):731-740. [104] 王俊英,撒国良,刘志康,等.颌骨骨髓炎中IL-17、IL-6和IL-1β的表达[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(10):1082-1085. [105] HWANG JT, YU JW, NAM HJ, et al. Suppressive Effects of a Truncated Inhibitor K562 Protein-Derived Peptide on Two Proinflammatory Cytokines, IL-17 and TNF-α. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;30(12):1810-1818. [106] ZHUO H, ZHANG X, LI M, et al. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from LL-37. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022;11(6): 754. [107] GUO X, BAI J, GE G, et al. Bioinspired peptide adhesion on Ti implants alleviates wear particle-induced inflammation and improves interfacial osteogenesis. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;605:410-424. [108] PIZAREK JA, FISCHER NG, APARICIO C. Immunomodulatory IL-23 receptor antagonist peptide nanocoatings for implant soft tissue healing. Dent Mater. 2023;39(2):204-216. [109] HUANG X, ZHENG H, AN J, et al. Microbial Profile During Pericoronitis and Microbiota Shift After Treatment. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:1888. [110] MENDITTI D, MARIANI P, RUSSO D, et al. Early pathological changes of peri-coronal tissue in the distal area of erupted or partially impacted lower third molars. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):380. [111] 贾睿,董洪楠,王华,等.半导体激光联合抗菌多肽对妊娠期智齿冠周炎的疗效观察[J].中国现代药物应用,2024,18(13):92-94. |
| [1] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [2] | Gao Hongli, Qin Yufeng, Zhang Yuehan, Shu Jiayu, Chen Helin. Copper metabolism and diagnosis and treatment of oral diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4316-4324. |
| [3] | Ge Ruiyang, Ni Can, Yang Kun, Yan Fuhua. The role of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis and treatment of periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3246-3251. |
| [4] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [5] | Chen Zili, Cao Ning, Xu Meng, Jiang Yan, Ji Meichao, Zheng Yangyang, Yang Lili. Biological characteristics of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3780-3787. |
| [6] | Zhang Yuqing, Wu Jun. Opportunities and challenges of COVID-19 therapy using mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1618-1625. |
| [7] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [8] | Liang Yuan, Jiang Xiaoke, Bai Yangqiu, Luo Xiaoying, Zhang Bingyong. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: possibility and feasibility [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4065-4069. |
| [9] | Zhang Hongqing, Xie Xufang, Wu Xiaomu. Effectiveness and clinical application limitations of stem cells in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and optic neuromyelitis spectrum diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3049-3056. |
| [10] | Wang Jie, Yu Limei. Immunomodulatory characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2108-2113. |
| [11] | Liu Boyu, Pu Lei, Zhang Yingjie, Yang Yingnan, Li Yaxiong. Stem cells in the treatment of skin defects: a focus of future research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 4082-4088. |
| [12] | Xu Ying, Lü Qing, Kang Liang, Zhang Hui-ming. Root canal filling material added with tea polyphenols inhibits the generation of Candida albicans biofilm [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(21): 3983-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||