Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (25): 5351-5361.doi: 10.12307/2025.508
Previous Articles Next Articles
Histone deacetylase 1 gene inhibits pyroptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and alleviates atherosclerosis and inflammatory response
Zhang Guoan1, Shi Jian1, Song Baoguo1, Huang Xiaoyan2
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, 2Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Infection and lmmune Diseases, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-20Accepted:2024-04-19Online:2025-09-08Published:2024-12-24 -
Contact:Huang Xiaoyan, Master, Associate chief physician, Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Infection and lmmune Diseases, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhang Guoan, Master, Attending physician, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shaanxi Province Key Research & Development Plan Project, No. 2023-YBSF-672 (to SJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Guoan, Shi Jian, Song Baoguo, Huang Xiaoyan. Histone deacetylase 1 gene inhibits pyroptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and alleviates atherosclerosis and inflammatory response[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5351-5361.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
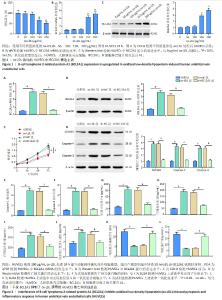
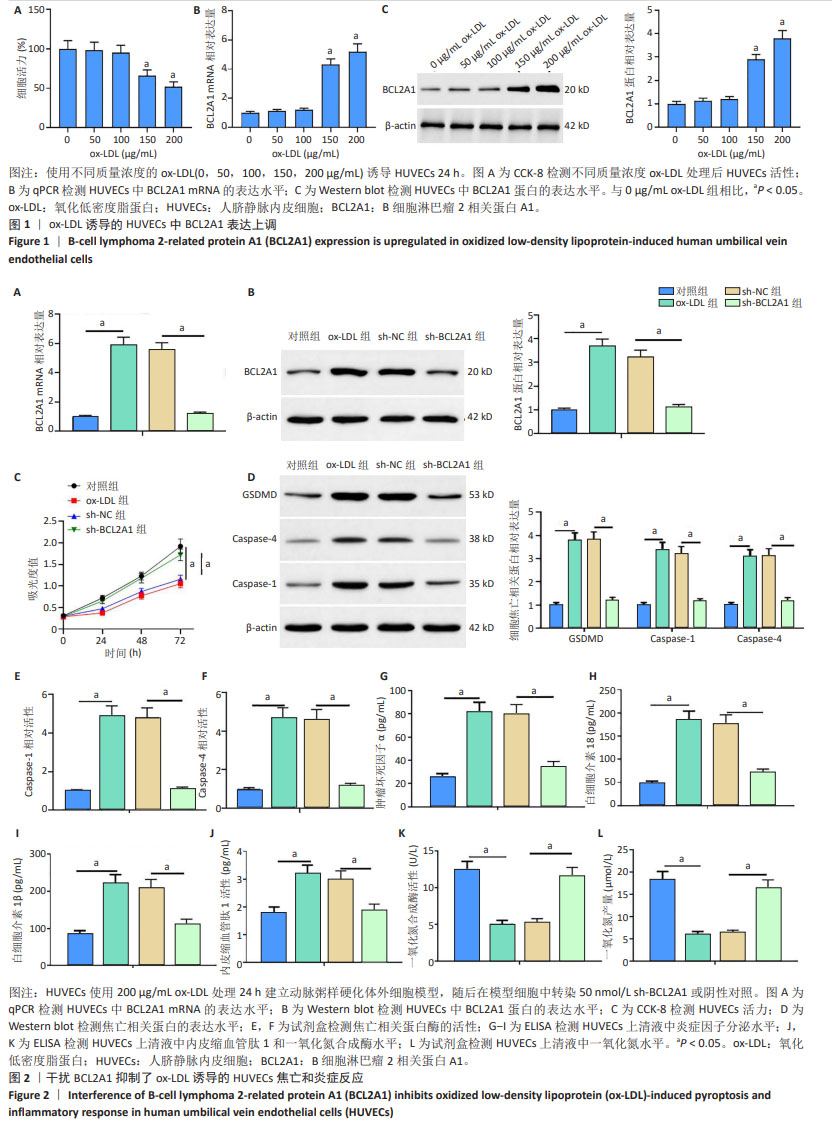
2.1 BCL2A1在氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞中表达上调 氧化低密度脂蛋白以剂量依赖的方式显著降低了人脐静脉内皮细胞活力(图1A)。qPCR和Western blot结果显示,随氧化低密度脂蛋白质量浓度的增加,BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平均增加(图1B,C),且在氧化低密度脂蛋白质量浓度为200 μg/mL时,BCL2A1表达水平最高,因此在后续实验中选择质量浓度为200 μg/mL 的氧化低密度脂蛋白进行实验。 2.2 干扰BCL2A1抑制了氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的人静脉内皮细胞焦亡和炎症反应 qPCR和Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平升高(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,sh-BCL2A1组BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平降低(P < 0.05) (图2A,B)。CCK-8结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组人脐静脉内皮细胞活力下降(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,sh-BCL2A1组人脐静脉内皮细胞活力升高(P < 0.05) (图2C)。Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组细胞焦亡相关蛋白(GSDMD,Caspase-1和Caspase-4)表达水平增加(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,sh-BCL2A1组细胞焦亡相关蛋白表达水平减少(P < 0.05)(图2D)。此外,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组细胞焦亡相关蛋白酶Caspase-1和Caspase-4活性增加(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,sh-BCL2A1组细胞焦亡相关蛋白酶Caspase-1和Caspase-4活性降低(P < 0.05) (图2E,F)。ELISA结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组人脐静脉内皮细胞培养上清液中炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素18和白细胞介素1β的分泌量显著增加(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,sh-BCL2A1组细胞炎症因子的产生减少(P < 0.05) (图2G-I)。最后,通过ELISA检测人脐静脉内皮细胞培养基中内皮细胞损伤标志物一氧化氮合成酶、内皮缩血管肽1和一氧化氮水平,结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组人脐静脉内皮细胞培养基中一氧化氮合成酶和一氧化氮水平降低而内皮缩血管肽1水平升高(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,sh-BCL2A1组内皮细胞损伤标志物一氧化氮合成酶和一氧化氮水平增加,而内皮缩血管肽1水平降低(P < 0.05)(图2J-L)。以上数据表明,BCL2A1抑制了人脐静脉内皮细胞活力并通过促进焦亡和炎症反应来加重人脐静脉内皮细胞损伤。"
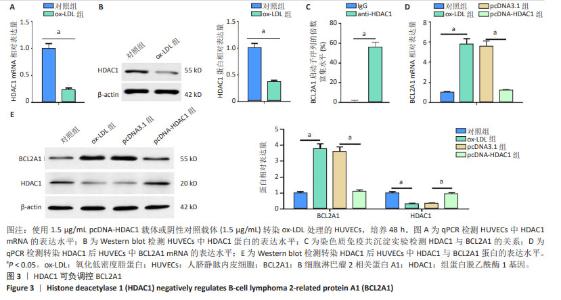
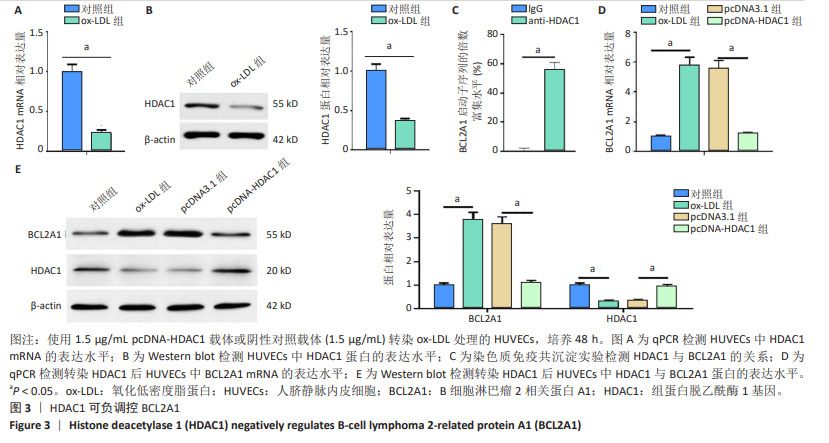
2.3 HDAC1负调控BCL2A1 现有文献提示,HDAC1可作为BCL2A1的转录因子,而其具体作用机制暂未完全证明。qPCR和Western blot结果显示,HDAC1在氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞中表达下调(图3A,B)。染色质免疫共沉淀检测结果显示,与IgG组相比,抗HDAC1组显著富集BCL2A1启动子序列(图3C)。与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平升高(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1组BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平降低(P < 0.05)。过表达HDAC1抑制了氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞中BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平(图3D,E)。可见,HDAC1负调控BCL2A1的表达。"
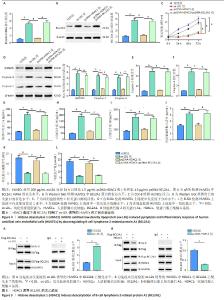
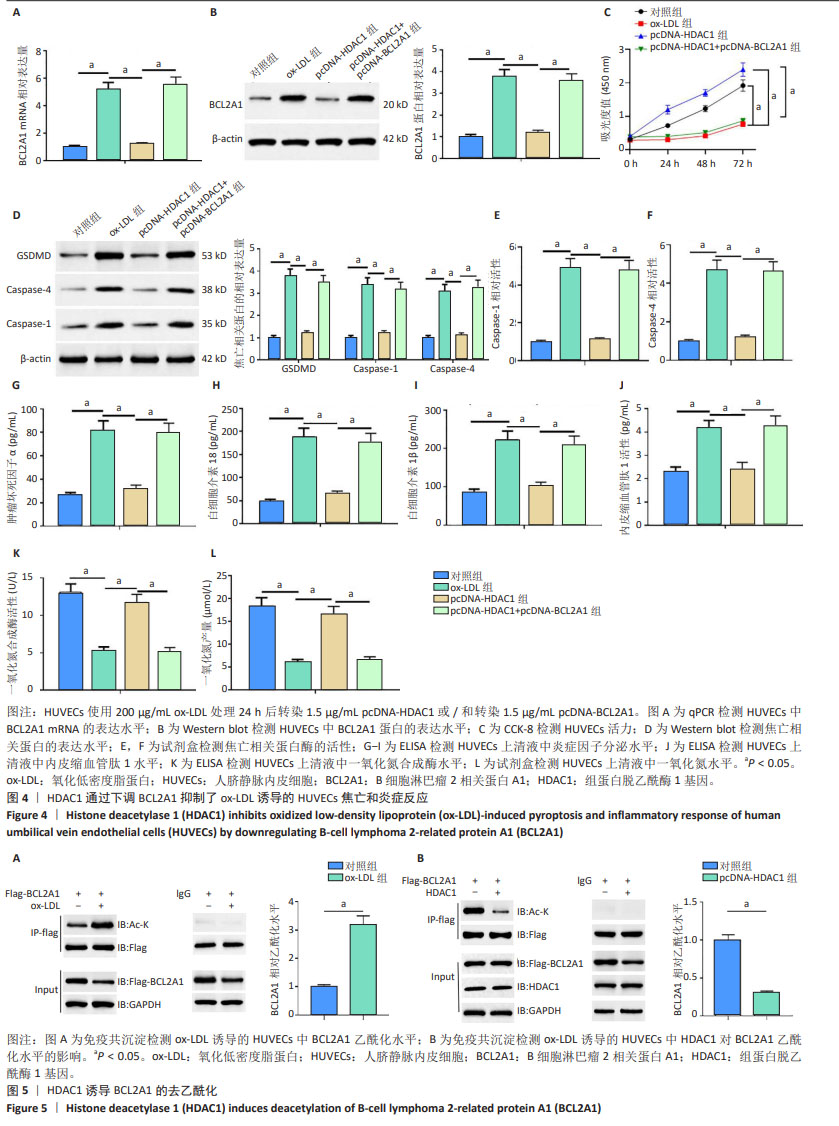
2.4 HDAC1通过下调BCL2A1抑制氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞的焦亡和炎症反应 qPCR和Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平升高(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1组BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平降低(P < 0.05);与pcDNA-HDAC1组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1+ pcDNA-BCL2A1组BCL2A1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平升高(P < 0.05) (图4A,B)。CCK-8结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组人脐静脉内皮细胞活力减弱(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1组细胞活力增加(P < 0.05);与pcDNA-HDAC1组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1+pcDNA-BCL2A1组细胞活力减弱(P < 0.05) (图4C)。Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组细胞焦亡相关蛋白(GSDMD、Caspase-1和Caspase-4)表达水平增加(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1组细胞焦亡相关蛋白表达水平减少(P < 0.05);与pcDNA-HDAC1组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1+pcDNA- BCL2A1组细胞焦亡相关蛋白表达水平增加(P < 0.05)(图4D)。此外,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组细胞焦亡相关蛋白酶(Caspase-1和Caspase-4)活性增加(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1组细胞焦亡相关蛋白酶活性减少(P < 0.05);与pcDNA-HDAC1组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1+pcDNA-BCL2A1组细胞焦亡相关蛋白酶活性增加(P < 0.05) (图4E,F)。ELISA结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组人脐静脉内皮细胞培养上清液中炎症因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素18和白细胞介素1β)分泌量增加(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比, pcDNA-HDAC1组炎症因子分泌量减少(P < 0.05);与pcDNA-HDAC1组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1+pcDNA-BCL2A1组炎症因子分泌量增加(P < 0.05) (图4G-I)。此外还发现,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白组内皮细胞损伤标志物内皮缩血管肽1水平增加,而一氧化氮合成酶和一氧化氮水平则降低(P < 0.05);与氧化低密度脂蛋白组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1组内皮缩血管肽1水平降低,而一氧化氮合成酶和一氧化氮水平则增加(P < 0.05);与pcDNA-HDAC1组相比,pcDNA-HDAC1+pcDNA-BCL2A1组内皮缩血管肽1水平增加,而一氧化氮合成酶和一氧化氮水平则降低(P < 0.05)(图4J-L)。这些结果表明,HDAC1通过下调BCL2A1抑制了氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞焦亡和炎症反应。 2.5 HDAC1诱导BCL2A1的去乙酰化 HDAC1为组蛋白去乙酰化酶,然而其是否可诱导BCL2A1去乙酰化还暂未被证明。接下来研究了人脐静脉内皮细胞中的BCL2A1乙酰化水平,免疫共沉淀结果显示,与对照组相比,氧化低密度脂蛋白处理后人脐静脉内皮细胞中BCL2A1乙酰化水平显著增加(图5A)。此外,HDAC1显著下调了人脐静脉内皮细胞中BCL2A1的乙酰化水平(图5B)。这些结果表明,HDAC1可诱导BCL2A1的去乙酰化。"
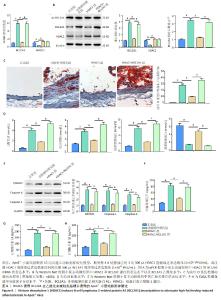
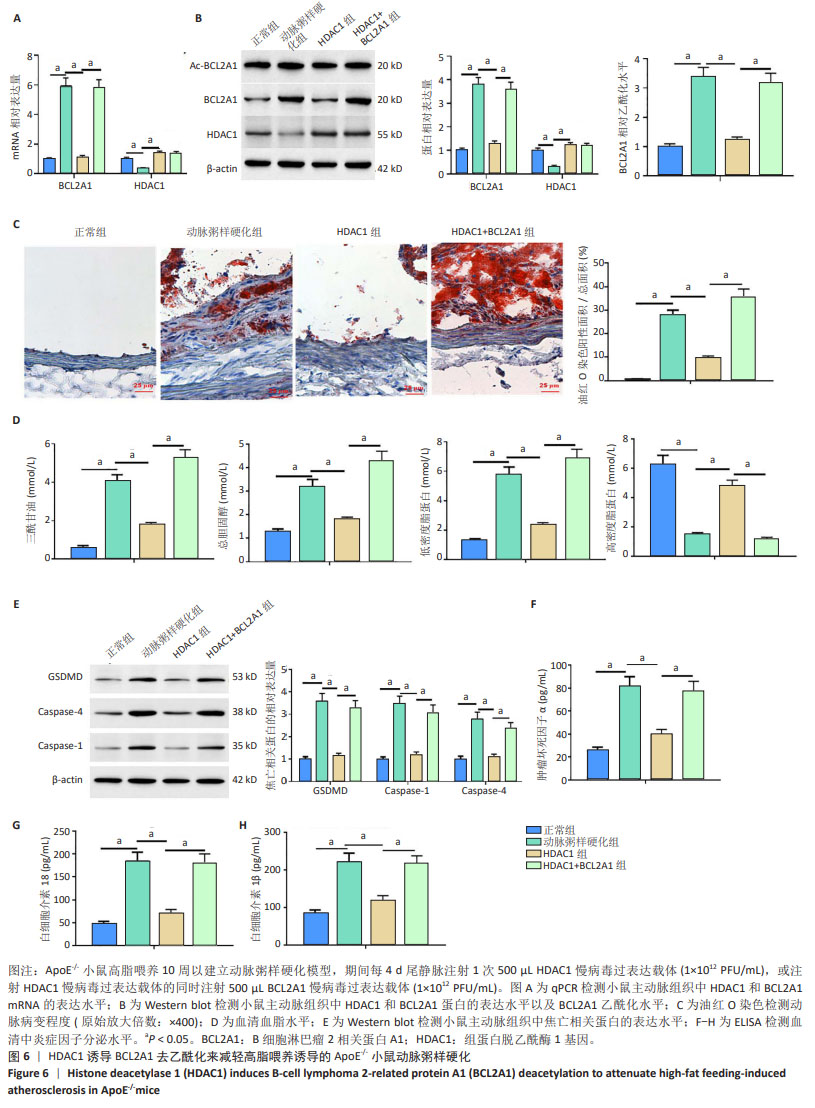
2.6 HDAC1促进BCL2A1的去乙酰化减轻了高脂喂养诱导的ApoE-/-小鼠动脉粥样硬化 qPCR和Western blot结果显示,与正常组相比,动脉粥样硬化组小鼠主动脉组织中BCL2A1高表达,HDAC1低表达(P < 0.05);与动脉粥样硬化组相比,HDAC1组小鼠主动脉组织中BCL2A1低表达,而HDAC1高表达(P < 0.05);与HDAC1组相比,HDAC1+BCL2A1组小鼠主动脉组织中BCL2A1高表达(P < 0.05) (图6A,B)。此外,与正常组相比,动脉粥样硬化组小鼠主动脉组织中BCL2A1乙酰化水平较高(P < 0.05);与动脉粥样硬化组相比,HDAC1组小鼠主动脉组织中BCL2A1乙酰化水平较低(P < 0.05);与HDAC1组相比,HDAC1+BCL2A1组小鼠主动脉组织中BCL2A1乙酰化水平较高(P < 0.05)(图6B),这与体外实验结果一致。主动脉组织油红O染色显示,与正常组相比,动脉粥样硬化组小鼠主动脉病变面积更大(P < 0.05);与动脉粥样硬化组相比,HDAC1组小鼠主动脉病变面积减小(P < 0.05);与HDAC1组相比,HDAC1+BCL2A1组小鼠主动脉病变面积增大(P < 0.05)(图6C)。然后检测HDAC1对血脂水平的影响。与正常组相比,动脉粥样硬化组小鼠眼丛血清总胆固醇、三酰甘油和低密度脂蛋白水平较高,高密度脂蛋白水平较低(P < 0.05);与动脉粥样硬化组相比,HDAC1组小鼠眼丛血清总胆固醇、三酰甘油和低密度脂蛋白水平降低,高密度脂蛋白水平升高(P < 0.05);与HDAC1组相比,HDAC1+BCL2A1组小鼠眼丛血清总胆固醇、三酰甘油和低密度脂蛋白水平升高,高密度脂蛋白水平降低(P < 0.05) (图6D)。Western blot结果显示,与正常组相比,动脉粥样硬化小鼠主动脉组织中焦亡相关蛋白(GSDMD,Caspase-1和Caspase-4)高表达(P < 0.05);与动脉粥样硬化组相比,HDAC1组小鼠主动脉组织中焦亡相关蛋白低表达(P < 0.05);与HDAC1组相比,HDAC1+BCL2A1组小鼠主动脉组织中焦亡相关蛋白表达水平增加(P < 0.05)(图6E)。然后检测动脉粥样硬化小鼠眼丛血清中炎症细胞因子水平,与动脉粥样硬化组相比,HDAC1组小鼠眼丛血清白细胞介素18、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌显著减少(P < 0.05);与HDAC1组相比,HDAC1+BCL2A1组小鼠眼丛血清白细胞介素18、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌显著增多(P < 0.05) (图6F-H)。总的来说,这些结果表明BCL2A1可加重小鼠动脉粥样硬化和炎症反应。"
| [1] WU J, HE S, SONG Z, et al. Macrophage polarization states in atherosclerosis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1185587. [2] ZHANG L, XIA C, YANG Y, et al. DNA methylation and histone post-translational modifications in atherosclerosis and a novel perspective for epigenetic therapy. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):344. [3] MA SR, TONG Q, LIN Y, et al. Berberine treats atherosclerosis via a vitamine-like effect down-regulating Choline-TMA-TMAO production pathway in gut microbiota. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):207. [4] FANG F, NI Y, YU H, et al. Inflammatory endothelium-targeted and cathepsin responsive nanoparticles are effective against atherosclerosis. Theranostics. 2022;12(9):4200-4220. [5] XU YJ, ZHENG L, HU YW, et al. Pyroptosis and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;476:28-37. [6] DUAN H, ZHANG Q, LIU J, et al. Suppression of apoptosis in vascular endothelial cell, the promising way for natural medicines to treat atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;168:105599. [7] ZHANG Q, LIU J, DUAN H, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress. J Adv Res. 2021;34:43-63. [8] ZENG X, LIU D, HUO X, et al. Pyroptosis in NLRP3 inflammasome-related atherosclerosis. Cell Stress. 2022;6(10):79-88. [9] VOGLER M. BCL2A1: the underdog in the BCL2 family. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(1):67-74. [10] LI J, SUN L, XIE F, et al. MiR-3976 regulates HCT-8 cell apoptosis and parasite burden by targeting BCL2A1 in response to Cryptosporidium parvum infection. Parasit Vectors. 2023;16(1):221. [11] LIN P, LI J, YE F, et al. KCNN4 induces multiple chemoresistance in breast cancer by regulating BCL2A1. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(10): 3302-3315. [12] SU W, ZHAO Y, WEI Y, et al. Exploring the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis Complicated With Atherosclerosis via Microarray Data Analysis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:667690. [13] DUMAN M, VAQUIÉ A, NOCERA G, et al. EEF1A1 deacetylation enables transcriptional activation of remyelination. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3420. [14] CHEN J, ZHU Z, XU S, et al. HDAC1 participates in polycystic ovary syndrome through histone modification by regulating H19/miR-29a-3p/NLRP3-mediated granulosa cell pyroptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2023;573:111950. [15] MURTHY SRK, CHENG X, ZHUANG T, et al. BCL2A1 regulates Canady Helios Cold Plasma-induced cell death in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):4038. [16] ZHENG Q, GAN G, GAO X, et al. Targeting the IDO-BCL2A1-Cytochrome c Pathway Promotes Apoptosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;14:1673-1687. [17] HE M, MAO G, XIANG Y, et al. MicroRNA-664a-3p inhibits the proliferation of ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovary syndrome and promotes apoptosis by targeting BCL2A1. Ann Transl Med. 2021; 9(10):852. [18] HOU X, ZHANG Z, MA Y, et al. Mechanism of hydroxysafflor yellow A on acute liver injury based on transcriptomics. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:966759. [19] MÉTAIS JY, WINKLER T, GEYER JT, et al. BCL2A1a over-expression in murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells decreases apoptosis and results in hematopoietic transformation. PLoS One. 2012;7(10): e48267. [20] NATH P, MODAK S, AKTAR T, et al. Olive leaves extract alleviates inflammation and modifies the intrinsic apoptotic signal in the leukemic bone marrow. Front Immunol. 2023;13:1054186. [21] QIAN Z, ZHAO Y, WAN C, et al. Pyroptosis in the Initiation and Progression of Atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:652963. [22] LIN L, ZHANG MX, ZHANG L, et al. Autophagy, Pyroptosis, and Ferroptosis: New Regulatory Mechanisms for Atherosclerosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:809955. [23] ZHU J, CHEN H, LE Y, et al. Salvianolic acid A regulates pyroptosis of endothelial cells via directly targeting PKM2 and ameliorates diabetic atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1009229. [24] JIANG X, MA C, GAO Y, et al. Tongxinluo attenuates atherosclerosis by inhibiting ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1-mediated endothelial cell pyroptosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;304:116011. [25] YUN WJ, LI J, YIN NC, et al. The facilitating effects of KRT80 on chemoresistance, lipogenesis, and invasion of esophageal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024;25(1):2302162. [26] JIANG T, QIN T, GAO P, et al. SIRT1 attenuates blood-spinal cord barrier disruption after spinal cord injury by deacetylating p66Shc. Redox Biol. 2023;60:102615. [27] GUO Z, YU X, ZHAO S, et al. SIRT6 deficiency in endothelial cells exacerbates oxidative stress by enhancing HIF1α accumulation and H3K9 acetylation at the Ero1α promoter. Clin Transl Med. 2023;13(8): e1377. [28] LUO D, LI W, XIE C, et al. Capsaicin Attenuates Arterial Calcification Through Promoting SIRT6-Mediated Deacetylation and Degradation of Hif1α (Hypoxic-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha). Hypertension. 2022;79(5): 906-917. [29] SUNG JY, KIM SG, KANG YJ, et al. SIRT1-dependent PGC-1α deacetylation by SRT1720 rescues progression of atherosclerosis by enhancing mitochondrial function. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2024;1869(3):159453. [30] LI N, LIU B, HE R, et al. HDAC3 promotes macrophage pyroptosis via regulating histone deacetylation in acute lung injury. iScience. 2023;26(7):107158. [31] WU Z, WANG Y, LU S, et al. SIRT3 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting pyroptosis via regulating the deacetylation of FoxO3a. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2023;82:102244. [32] LIU J, YAN Y, ZHENG D, et al. Inhibiting microRNA-200a-3p attenuates pyroptosis via targeting the SIRT1/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in H2O2-induced HAEC. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(20):11184-11200. [33] YAO F, LV X, JIN Z, et al. Sirt6 inhibits vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis by regulation of the Lin28b/let-7 pathway in atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:109056. [34] DUNAWAY LS, POLLOCK JS. HDAC1: an environmental sensor regulating endothelial function. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118(8):1885-1903. [35] ZHANG X, LU J, ZHANG Q, et al. CircRNA RSF1 regulated ox-LDL induced vascular endothelial cells proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation through modulating miR-135b-5p/HDAC1 axis in atherosclerosis. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):11. [36] WANG H, SUGIMOTO K, LU H, et al. HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of HIF1α prevents atherosclerosis progression by promoting miR-224-3p-mediated inhibition of FOSL2. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;23: 577-591. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [3] | Huang Haina, Yu Yanrong, Bi Jian, Huang Miao, Peng Weijie. Epigenetic characteristics of hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7848-7855. |
| [4] | Hu Shujuan, Liu Dang, Ding Yiting, Liu Xuan, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang. Ameliorative effect of walnut oil and peanut oil on atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6482-6488. |
| [5] | Li Wenjie, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Zeng Xiao, Sun Jinyi, Luo Yuncai, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Dong Qiang . Role of the sirtuins in pyroptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5478-5485. |
| [6] | Yang Jun, Yin Peng, Zheng Zhonghua. Mechanism of stachydrine-induced autophagy in improving atherosclerosis in high-fat-fed mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5140-5147. |
| [7] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5263-5271. |
| [8] | Li Qingyin, Li Linhua, Zhang Chunle, Fu Ping. Endothelial progenitor cell and mesenchymal stem cell therapy for vascular stent-associated diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4091-4101. |
| [9] | Cao Panxia, Peng Zining, Liu Shanshan, Fei Tiantian, Liang Tengyun, Zhang Mengwen, Wu Hong. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates macrophage fatty acid oxidation: an approach to prevent and treat atherosclerosis with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3906-3914. |
| [10] | Song Mingxiao, Chen Junshunzi, Wang Ningwei, Cai Huan, Feng Hong. Role of prohibitin 2 in mitophagy pathway against atherosclerosis in rats undergoing endurance training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2294-2300. |
| [11] | Cao Zheng, Zheng Xiaoxin, Jiang Xuejun. Finite element analysis of safety and efficacy of a novel scored balloon for coronary arteries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2083-2090. |
| [12] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Abnormal modification of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1301-1306. |
| [13] | Zhang Shaoqun, Zheng Chuanjiang, Liu Jiafu, Jiang Shunwan. Effect of positioning and non-positioning cervical rotatory manipulation on tensile mechanical properties of internal carotid artery with different degrees of atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4788-4794. |
| [14] | Li Sijin, Feng Xiaoteng, Wang Yiru, Liu Ping. Macrophage-specific promoter SP146-C1 enhances vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in atherosclerotic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4202-4208. |
| [15] | Zhao Guangjian, Liu Danan, Zhou Bo, Wang Yao. Action mechanism by which fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 inhibits macrophage pyroptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 4005-4012. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||