[1] 黄邓华, 吕辉, 郭江, 等. 人工股骨头置换术和人工全髋关节置换术治疗高龄股骨颈骨折的临床疗效分析[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2021,46(4):481-487.
[2] SCOTT CEH, CLEMENT ND, DAVIS ET, et al. Modern total hip arthroplasty: peak of perfection or room for improvement? Bone Joint J. 2022;104-B(2):189-192.
[3] 陈印忠, 刘庆鹏, 郭威, 等. 老年全髋关节置换围手术期三种镇痛方法的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(13):1194-1198.
[4] 孙朝亚, 蔡宁, 马行军, 等. 髋关节置换术老年患者麻醉方案选择及术后认知功能、运动功能及转归的差异[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023,43(7):1581-1584.
[5] 吴文棋, 邓恋, 马武华, 等. 不同麻醉方式对全髋关节置换术老年患者围术期炎症应激及免疫功能的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志,2023, 39(11):1409-1415.
[6] GIRÓN-ARANGO L, PENG PWH, CHIN KJ, et al. Pericapsular nerve group (PENG) block for hip fracture. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018;43(8):859-863.
[7] DEL BUONO R, PADUA E, PASCARELLA G, et al. Pericapsular nerve group block: an overview. Minerva Anestesiol. 2021; 87(4): 458-466.
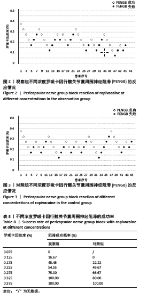
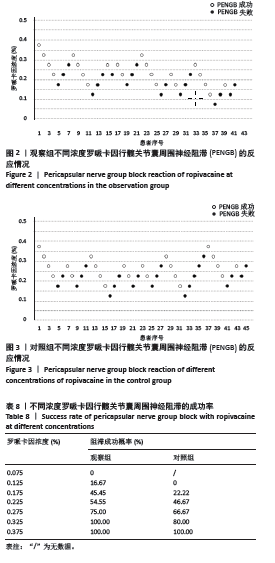
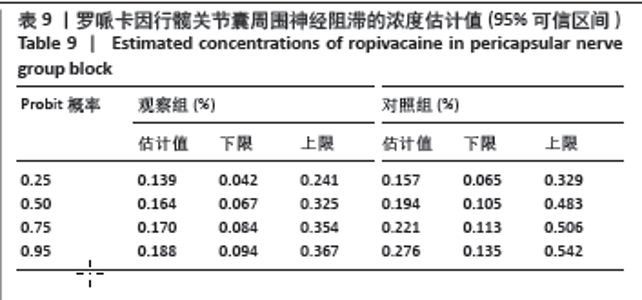
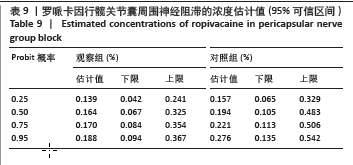
[8] 李欣舫, 郭嘉, 王迎斌. 罗哌卡因在老年患者全髋关节置换术中髋关节囊周围神经阻滞的半数有效浓度[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2023, 39(7):714-718.
[9] 曹雪, 聂永祯. 罗哌卡因复合不同佐剂行竖脊肌平面阻滞的研究进展[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2022,38(3):304-307.
[10] 张森兵, 安池冰, 阎文军. 超声引导下髋关节囊周围神经阻滞的研究进展[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2022,38(8):869-873.
[11] MORRISON C, BROWN B, LIN DY, et al. Analgesia and anesthesia using the pericapsular nerve group block in hip surgery and hip fracture: a scoping review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021;46(2):169-175.
[12] LIN DY, MORRISON C, BROWN B, et al. Pericapsular nerve group (PENG) block provides improved short-term analgesia compared with the femoral nerve block in hip fracture surgery: a single-center double-blinded randomized comparative trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021;46(5):398-403.
[13] 王莹, 傅金英. 分析右美托咪定静脉泵注在全身麻醉中的应用效果[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学,2022,27(2):241.
[14] 杨静, 余卓颖, 李民. 右美托咪定在椎管内麻醉中的研究现状[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2021,21(8):737-740.
[15] 杜远琳, 佘汉, 唐小唪, 等. 右美托咪定对老年患者术后早期认知功能障碍保护机制的代谢组学研究[J]. 陆军军医大学学报,2023, 45(20):2120-2131.
[16] CHEN G, GONG M, LIU Y. Comparison of ropivacaine plus sufentanil and ropivacaine plus dexmedetomidine for labor epidural analgesia: A randomized controlled trial protocol. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99(36):e22113.
[17] MOERENHOUT K, DEROME P, LAFLAMME GY, et al. Direct anterior versus posterior approach for total hip arthroplasty: a multicentre, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Can J Surg. 2020;63(5): E412-E417.
[18] PASCARELLA G, COSTA F, DEL BUONO R, et al. Impact of the pericapsular nerve group (PENG) block on postoperative analgesia and functional recovery following total hip arthroplasty: a randomised, observer-masked, controlled trial. Anaesthesia. 2021;76(11):1492-1498.
[19] 李咸鹏, 郑煜丽, 高晓曼, 等. 连续髋关节囊周围神经阻滞与连续髂筋膜间隙阻滞对老年全髋关节置换术患者围术期镇痛效果影响的比较[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2023,39(3):254-259.
[20] 黄菲菲, 朱建炜, 徐春香, 等. 老年髋关节置换术后髋关节疼痛及生活质量的影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2022,42(16):4089-4092.
[21] 孙朝亚, 蔡宁, 马行军, 等. 髋关节置换术老年患者麻醉方案选择及术后认知功能、运动功能及转归的差异[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023,43(7):1581-1584.
[22] 戴鹏, 王汉兵, 刘洪珍, 等. 超声引导下罗哌卡因复合地塞米松腰方肌阻滞对全髋关节置换术患者术后镇痛的影响[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2021,37(11):1134-1138.
[23] 吴晓彬, 邱灿金, 刘孝国, 等. 罗哌卡因复合右美托咪定或地塞米松竖脊肌平面阻滞用于腰椎后路植骨融合内固定术的效果[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2021,37(9):919-923.
[24] 梁玉柱, 张琳. 不同浓度罗哌卡因在椎间孔镜术中腰麻的应用效果[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(21):1992-1994.
[25] 王东红, 陈丽萍, 薛建军. 不同浓度及容量罗哌卡因髋关节囊周围神经阻滞用于髋部骨折老年患者镇痛效果的比较[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2022,38(5):497-502.
[26] 陈小红, 李萌萌, 黄璜, 等. 右美托咪定对胸外科患者围手术期焦虑的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2022,47(5):464-470.
[27] 丁允莹, 嵇富海, 彭科. 右美托咪定的器官保护作用及其机制概述[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2023,48(11):1267-1275.
[28] 杨静, 余卓颖, 李民. 右美托咪定在椎管内麻醉中的研究现状[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2021,21(8):737-740.
[29] 乔迁, 康芳, 黄祥, 等. 右美托咪定复合罗哌卡因胸椎旁神经阻滞对胸腹腔镜联合食管癌根治术术后恢复质量的影响[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2021,37(5):453-457.
[30] 刘鹏飞, 王劭恒, 胡艳婷, 等. 右美托咪定联合罗哌卡因双侧竖脊肌平面阻滞对老年腰椎间孔镜手术患者镇痛效果及术后恢复的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2021,41(10):2079-2083.
[31] 张佳雷, 张文斌. 右美托咪定对罗哌卡因半数有效浓度的影响[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2021,15(2):239-242.
[32] 徐煌, 王胜斌, 居霞, 等. 静脉泵注右美托咪定联合罗哌卡因切口浸润在小儿腹腔镜手术中的应用[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2021, 31(17):36-40. |