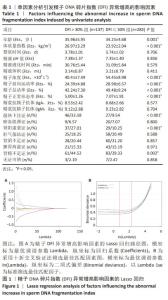
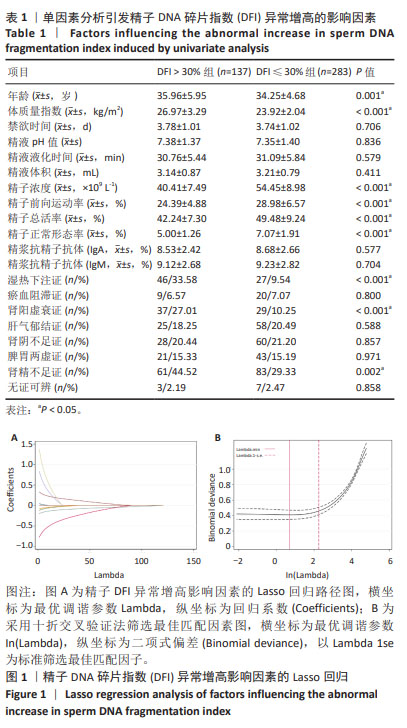
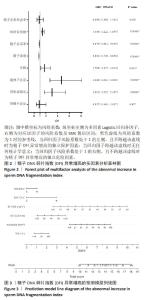
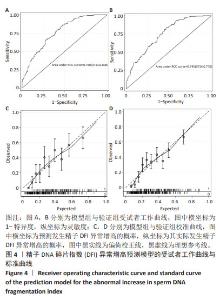
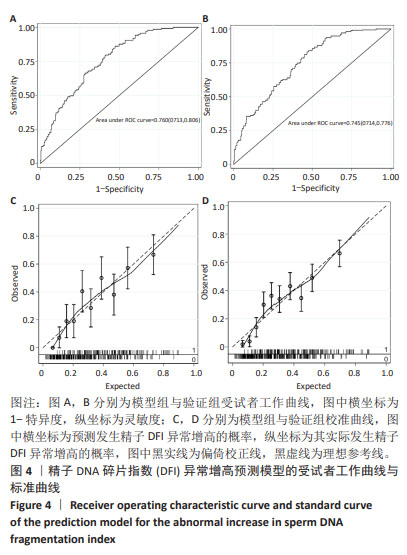
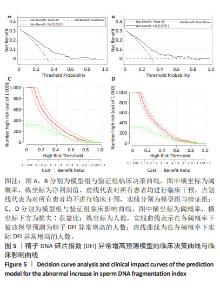
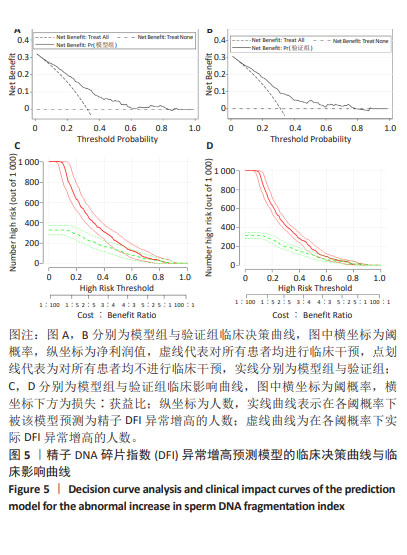
[1] 张孝东,邓成艳,黄学锋,等.中华医学会生殖医学分会:2019年辅助生殖技术数据报告[J].生殖医学杂志,2022,31(8):1015-1021.
[2] BUNGUM M, HUMAIDAN P, AXMON A, et al. Sperm DNA integrity assessment in prediction of assisted reproduction technology outcome. Hum Reprod. 2007;22(1):174-179.
[3] OLESZCZUK K, AUGUSTINSSON L, BAYAT N, et al. Prevalence of high DNA fragmentation index in male partners of unexplained infertile couples. Andrology. 2013;1(3):357-360.
[4] 刘琳,刘学润,李涛,等.精子DNA碎片指数对辅助生殖技术妊娠结局的影响[J].中国性科学,2021,30(12):6-9.
[5] DENG C, LI T, XIE Y, et al. Sperm DNA fragmentation index influences assisted reproductive technology outcome: A systematic review and meta-analysis combined with a retrospective cohort study. Andrologia. 2019;51(6):e13263.
[6] 刘玉林,江峰,陈颖,等.精子DNA碎片对4080例体外受精出生子代的影响研究[J].中华男科学杂志,2020,26(7):669-671.
[7] 武健,李立鹏,曹金凤.精子DNA碎片检测在辅助生殖中的研究进展[J].检验医学与临床,2020,17(21):3216-3220.
[8] 孙健,谭志国.男性精子DNA碎片研究的相关进展[J].现代医学, 2019,47(6):749-754.
[9] 卢文红,谷翊群,贾孟春,等.世界卫生组织《人类精液检查与处理实验室手册(第6版)》简介[J].生殖医学杂志,2021,30(12): 1661-1663.
[10] 周莲,符明昌,蔡添娥,等.精浆同型半胱氨酸与精子形态、DNA碎片指数在男性不育患者中的相关性研究[J].中国性科学,2023, 32(1):23-26.
[11] 檀畅,王喜良,张金艳,等.精子DNA碎片指数对体外受精不同助孕方式妊娠结局的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2022,51(9):817-825.
[12] 李宏军,洪锴,李铮,等.男性不育诊疗指南[J].中华男科学杂志, 2022,28(1):66-76.
[13] 国家中医药管理局.中华人民共和国中医药管理行业标准[S].南京:南京大学出版社,1994:189.
[14] 罗英,徐楗荧,林小民,等.精子DNA碎片率与男性不育及其配偶早期复发性流产的关系[J].实用医学杂志,2021,37(16):2133-2136.
[15] YUAN M, HUANG L, LEUNG WT, et al. Sperm DNA fragmentation valued by SCSA and its correlation with conventional sperm parameters in male partner of recurrent spontaneous abortion couple. Biosci Trends. 2019;13(2):152-159.
[16] COLASANTE A, MINASI MG, SCARSELLI F, et al. The aging male: Relationship between male age, sperm quality and sperm DNA damage in an unselected population of 3124 men attending the fertility centre for the first time. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2019;90(4):254-259.
[17] 辜秀丽,李红钢,熊承良.不育男性精子DNA碎片指数与年龄和精液参数相关性分析[J].中华男科学杂志,2018,24(7):608-612.
[18] NAHER ZU, ALI M, BISWAS SK, et al. Effect of oxidative stress in male infertility. Mymensingh Med J. 2013;22(1):136-142.
[19] 乜照燕,吴海峰,张娜,等.男性年龄对精子氧化应激水平核DNA损伤的影响[J].中国计划生育学杂志,2012,20(1):30-36.
[20] ABAD C, AMENGUAL MJ, GOSÁLVEZ J, et al. Effects of oral antioxidant treatment upon the dynamics of human sperm DNA fragmentation and subpopulations of sperm with highly degraded DNA. Andrologia. 2013; 45(3):211-216.
[21] GONZÁLEZ-MARÍN C, GOSÁLVEZ J, ROY R. Types, causes, detection and repair of DNA fragmentation in animal and human sperm cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(11):14026-14052.
[22] SINGH NP, MULLER CH, BERGER RE. Effects of age on DNA double-strand breaks and apoptosis in human sperm. Fertil Steril. 2003;80(6): 1420-1430.
[23] 彭洋洋.吸烟、体质指数对精子DNA完整性影响的相关性研究[D].大连:大连医科大学,2021.
[24] ERDEMIR F, ATILGAN D, MARKOC F, et al. The effect of diet induced obesity on testicular tissue and serum oxidative stress parameters. Actas Urol Esp. 2012;36(3):153-159.
[25] 帅俊,吴亮,高一博,等.精子DNA碎片指数与精液参数的相关性分析[J].中华男科学杂志,2019,25(2):129-134.
[26] EVENSON D, WIXON R. Meta-analysis of sperm DNA fragmentation using the sperm chromatin structure assay. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;12(4):466-472.
[27] 王丽琼. 精子DNA单双链损伤与精子浓度的关系研究[D].杭州:浙江中医药大学,2017.
[28] SPEIT G, DENNOG C, LAMPL L. Biological significance of DNA damage induced by hyperbaric oxygen. Mutagenesis. 1998;13(1): 85-87.
[29] BOUHALLIER F, ALLIOLI N, LAVIAL F, et al. Role of miR-34c microRNA in the late steps of spermatogenesis. RNA. 2010;16(4):720-731.
[30] 孙自学,陈建设.王琦教授治疗男性不育经验介绍[J].四川中医, 2014,22(1):7-8.
[31] 赵文,王祖龙,王诗琦,等.王祖龙治疗精子DNA损伤性不育辨证规律分析[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2018,24(10):1444-1453.
[32] KORT HI, MASSEY JB, ELSNER CW, et al. Impact of body mass index values on sperm quantity and quality. J Androl. 2006;27(3):450-452.
[33] RAMLAU-HANSEN CH, THULSTRUP AM, NOHR EA, et al. Subfecundity in overweight and obese couples. Hum Reprod. 2007;22(6): 1634-1637.
[34] 陈小超.817例男性不育症患者危险因素及中医证候危险因素分析[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2018.
[35] 刘海娟.精子DFI异常中医证型分布规律及补肾生精方干预的临床研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2021.
[36] 贾域,马静,卢建军,等.基于iTRAQ技术的肾阳虚不育小鼠睾丸差异蛋白表达研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2020,47(5):189-223. |