Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (15): 3215-3226.doi: 10.12307/2025.802
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and validation of a Nomogram prediction model for risk factors of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus
Xu Wenbo1, Wang Lihe2, Li Songwei2, 3, Shi Pengbo2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 3Henan Provincial Hospital of TCM, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-01Accepted:2024-06-17Online:2025-05-28Published:2024-11-05 -
Contact:Wang Lihe, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Xu Wenbo, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Top Talent Training Project, No. Yu Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Education [2018]35 (to WLH); General Program of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2022M721066 (to SPB); Key Research & Development and Promotion Project in Henan Province, No. 232102310474 (to SPB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Wenbo, Wang Lihe, Li Songwei, Shi Pengbo. Establishment and validation of a Nomogram prediction model for risk factors of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3215-3226.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
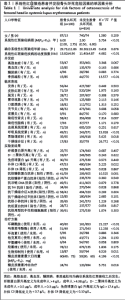
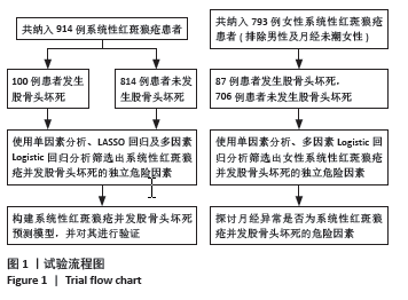
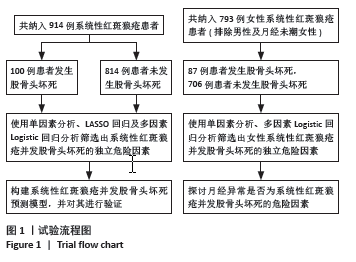
2.3 单因素分析结果 单因素分析显示,股骨头坏死组与未发生股骨头坏死组在系统性红斑狼疮疾病活动度指数、系统性红斑狼疮病程、狼疮性肾炎、呼吸系统受累、胃肠道受累、干燥综合征、骨质疏松、补体C3降低、抗核糖核蛋白阳性、使用环磷酰胺、使用吗替麦考酚酯、使用生物抑制剂、糖皮质激素最大日剂量、糖皮质激素冲击治疗方面差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。见表1。 2.4 LASSO回归结果 考虑到纳入变量之间的相互依赖性和多重共线性,采用LASSO回归分析来进一步优化预测变量。当最优λ为0.025 5时,通过10倍交叉验证确定了10个非零系数的显著预测变量,即系统性红斑狼疮病程、系统性红斑狼疮疾病活动度指数、呼吸系统受累、干燥综合征、骨质疏松、抗核糖核蛋白阳性、使用环磷酰胺、使用吗替麦考酚酯、使用生物抑制剂、糖皮质激素最大日量。详见图2。"
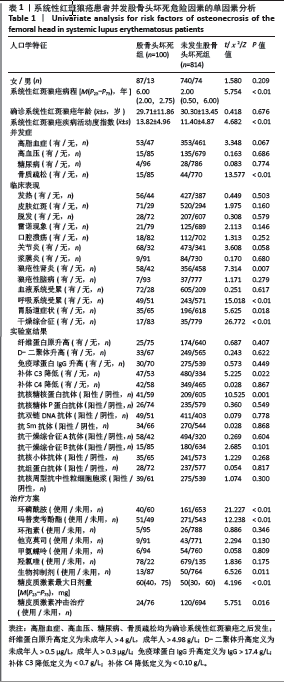
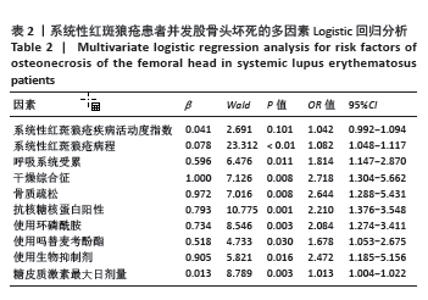
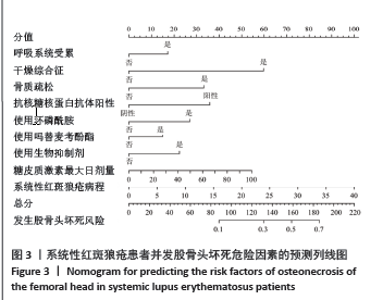
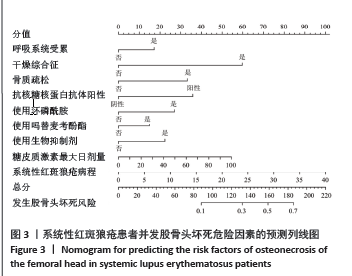
2.5 多因素Logistic回归分析 以系统性红斑狼疮是否发生股骨头坏死为因变量,以LASSO回归筛选出来的10个变量(系统性红斑狼疮病程、系统性红斑狼疮疾病活动度指数、呼吸系统受累、干燥综合征、骨质疏松、抗核糖核蛋白阳性、使用环磷酰胺、使用吗替麦考酚酯、使用生物抑制剂、糖皮质激素最大日量)为自变量进行多因素Logistic回归分析。结果显示,系统性红斑狼疮病程[OR=1.082,95%CI(1.048-1.117),P < 0.01]、呼吸系统受累[OR=1.814,95%CI(1.147-2.870),P=0.011]、继发干燥综合征[OR=2.718,95%CI(1.304-5.662),P=0.008]、骨质疏松[OR=2.644,95%CI(1.288-5.431),P=0.008]、抗核糖核蛋白阳性[OR=2.210,95%CI(1.376-3.548),P=0.001]、使用环磷酰胺[OR=2.084,95%CI(1.274-3.411),P=0.003]、使用吗替麦考酚酯[OR=1.678,95%CI(1.053-2.675),P=0.03]、使用生物抑制剂[OR=2.472,95%CI(1.185-5.156),P=0.016]、糖皮质激素最大日剂量[OR=1.013,95%CI(1.004-1.022),P=0.003]是系统性红斑狼疮患者发生股骨头坏死的独立危险因素。见表2。"
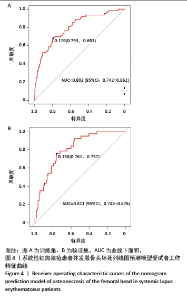
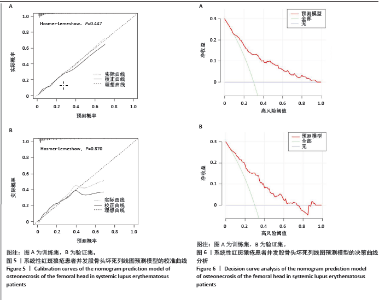
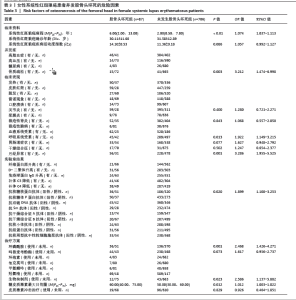
使用受试者工作特征曲线对系统性红斑狼疮患者发生股骨头坏死风险的列线图预测模型进行区分度评估,结果显示,在训练集中,受试者工作特征曲线下面积为0.802(95%CI:0.742-0.862),最佳阈值为0.119,敏感性为0.683,特异性为0.793(图4A);在验证集中,受试者工作特征曲线下面积为0.811 (95%CI:0.745-0.876),最佳阈值为0.158,敏感性为0.757,特异性为0.761(图4B)。训练集和验证集受试者工作特征曲线下面积值均大于0.7,说明该模型具有良好预测系统性红斑狼疮患者并发股骨头坏死的效能。 使用校准曲线和Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验来评估系统性红斑狼疮患者发生股骨头坏死风险的列线图预测模型的校准度。如图5所示,校准图显示列线图的预测值与实际值之间具有良好的一致性(训练集:χ2=7.863,P=0.447;验证集:χ2=3.856,P=0.870)。训练集和验证集均P值> 0.05,表明该模型具有良好的校准能力。 使用决策曲线分析来评估系统性红斑狼疮患者发生股骨头坏死风险的列线图预测模型的临床有效性。结果显示,该模型在训练集和验证集中阈值概率分别为0.10-0.98和0.05-0.75时,列线图预测模型显示出比所有干预和不干预更高的净效益,表明列线图预测模型在临床实践中有一定的应用价值(图6)。"
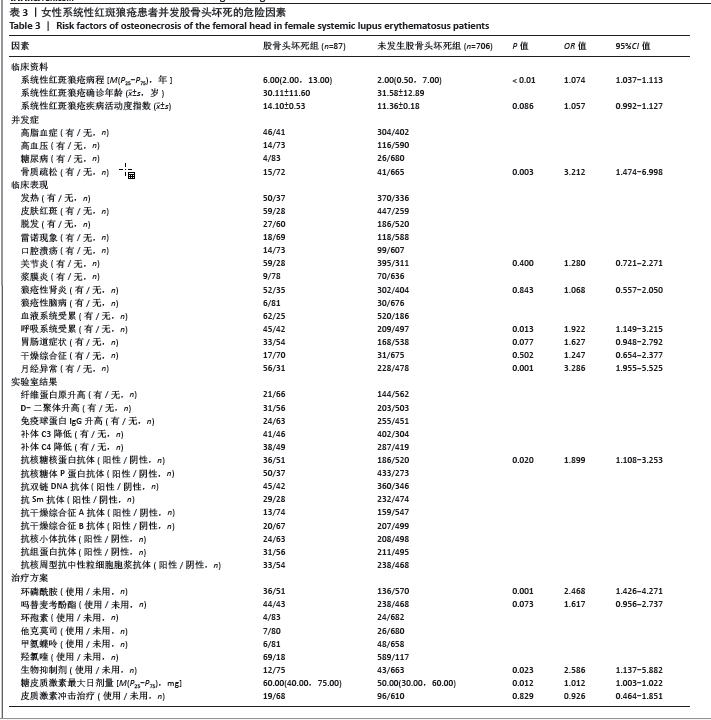
2.7 女性系统性红斑狼疮患者并发股骨头坏死的危险因素 为了探讨月经异常是否为系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头坏死的危险因素,排除了男性及月经未潮的女性患者,最终纳入了793例女性系统性红斑狼疮患者,284例(35.8%)患者存在着月经异常。进一步分析了女性系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头坏死组(87例)与未发生股骨头坏死组(706例)的基本资料、临床表现、实验室结果及治疗方案,单因素分析显示两组在系统性红斑狼疮病程、系统性红斑狼疮疾病活动度指数、骨质疏松、关节炎、狼疮性肾炎、呼吸系统受累、胃肠道症状、干燥综合征、月经异常、抗核糖核蛋白阳性、使用环磷酰胺、使用吗替麦考酚酯、使用生物抑制剂、糖皮质激素最大日剂量、使用糖皮质激素冲击疗法上差异有显著性意义,将这些因素纳入多因素二元Logistic回归分析中,结果显示,月经异常、系统性红斑狼疮病程、骨质疏松、呼吸系统受累、抗核糖核蛋白阳性、使用环磷酰胺、使用生物抑制剂和糖皮质激素最大日剂量是女性系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头坏死的危险因素。见表3。"
| [1] KIRIAKIDOU M, CHING CL. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(11):Itc81-Itc96. [2] KANEKO K, CHEN H, KAUFMAN M, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(10):e526. [3] ERSIN M, DEMIREL M, EKINCI M, et al. Symptomatic osteonecrosis of the hip and knee in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Prevalence, pattern, and comparison of natural course. Lupus. 2021; 30(10):1603-1608. [4] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110. [5] TRENT S, SICAT CS, SLOVER J. Femoral Head Osteonecrosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Total Hip Arthroplasty Outcomes and Considerations. JBJS Rev. 2021;9(4). doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW. 20.00142. [6] CALVO-ALÉN J, MCGWIN G, TOLOZA S, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA): XXIV. Cytotoxic treatment is an additional risk factor for the development of symptomatic osteonecrosis in lupus patients: results of a nested matched case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(6):785-790. [7] OINUMA K, HARADA Y, NAWATA Y, et al. Osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus develops very early after starting high dose corticosteroid treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(12): 1145-1148. [8] 许砚钧, 陈圣宝, 蔡倩莹, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮激素暴露患者发生股骨头坏死情况及临床特征分析:一项基于前瞻性队列的描述性研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(5):605-614. [9] HISADA R, KATO M, OHNISHI N, et al. Antiphospholipid score is a novel risk factor for idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019;58(4):645-649. [10] KURODA T, TANABE N, WAKAMATSU A, et al. High triglyceride is a risk factor for silent osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34(12):2071-2077. [11] HUSSEIN S, SUITNER M, BéLAND-BONENFANT S, et al. Monitoring of Osteonecrosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. J Rheumatol. 2018; 45(10):1462-1476. [12] SUETSUGU H, KIM K, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Novel susceptibility loci for steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet. 2022;31(7):1082-1095. [13] WEBBER D, CAO J, DOMINGUEZ D, et al. Genetics of osteonecrosis in children and adults with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023;62(9):3205-3212. [14] TIAN J, ZHANG D, YAO X, et al. Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comprehensive systematic analysis and modelling study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(3):351-356. [15] HOU Y, JIN J, LUO L, et al. Menstrual irregularity, pregnancy outcomes, and birth outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus of childbearing age in China: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023;136(23):2886-2888. [16] MORALES-MARTíNEZ FA, SALAS-CASTRO C, GARCíA-GARZA MR, et al. Evaluation of the Ovarian Reserve in Women With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Family Reprod Health. 2021;15(1):38-44. [17] GIAMBALVO S, GARAFFONI C, SILVAGNI E, et al. Factors associated with fertility abnormalities in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21(4): 103038. [18] ARINGER M, COSTENBADER K, DAIKH D, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(9):1151-1159. [19] KIM J, LEE SK, KIM JY, et al. CT and MRI findings beyond the subchondral bone in osteonecrosis of the femoral head to distinguish between ARCO stages 2 and 3A. Eur Radiol. 2023;33(7):4789-800. [20] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨循环与骨坏死专业委员会,中华医学会骨科分会骨显微修复学组,国际骨循环学会中国区. 中国成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2020)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020, 40(20):1365-1376. [21] DI MATTEO A, SMERILLI G, CIPOLLETTA E, et al. Imaging of Joint and Soft Tissue Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(9):73. [22] 中华医学会妇产科学分会妇科内分泌学组. 异常子宫出血诊断与治疗指南(2022更新版)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志,2022,57(7):481-490. [23] 沈南,赵毅,段利华,等.系统性红斑狼疮诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志,2023,62(7):775-784. [24] CHEN S, CAI Q, XU Y, et al. Associations between glucocorticoids, antiphospholipid antibodies and femur head necrosis in patients with SLE: a directed acyclic graph-based multicentre study. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021;13:1759720x211002677. [25] 韩俊杰, 武迪, 陈志胜, 等. 2型糖尿病患者并发糖尿病肾病风险的列线图预测模型与验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2024,27(9):1054-1061. [26] HARDY RS, RAZA K, COOPER MS. Therapeutic glucocorticoids: mechanisms of actions in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(3):133-144. [27] HUANG C, WEN Z, NIU J, et al. Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Novel Insight Into the Roles of Bone Endothelial Cells in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:777697. [28] MOTTA F, TIMILSINA S, GERSHWIN ME, et al. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Transl Autoimmun. 2022;5:100168. [29] KALLAS R, LI J, PETRI M. Predictors of Osteonecrosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Prospective Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022;74(7):1122-1132. [30] CHENG C, HUANG C, CHEN Z, et al. Risk factors for avascular necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a multi-center cohort study of Chinese SLE Treatment and Research Group (CSTAR) Registry XXII. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):78. [31] ZHAO D, WANG C, ZHAO Y, et al. Cyclophosphamide causes osteoporosis in C57BL/6 male mice: suppressive effects of cyclophosphamide on osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58): 98163-98183. [32] FAEZI ST, HOSEINIAN AS, PARAGOMI P, et al. Non-corticosteroid risk factors of symptomatic avascular necrosis of bone in systemic lupus erythematosus: A retrospective case-control study. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(4):590-594. [33] LEE J, KWOK SK, JUNG SM, et al. Osteonecrosis of the hip in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: risk factors and clinical outcome. Lupus. 2014;23(1):39-45. [34] FANOURIAKIS A, KOSTOPOULOU M, ALUNNO A, et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(6):736-745. [35] NAWATA K, NAKAMURA J, IKEDA K, et al. Transitional changes in the incidence of osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: focus on immunosuppressant agents and glucocorticoids. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(5):844-849. [36] MA J, GE J, GAO F, et al. The Role of Immune Regulatory Cells in Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Retrospective Clinical Study. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:1302015. [37] 蔡李骏,王秋入,陈长军,等. 免疫细胞调节股骨头坏死发生发展的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(11):1428-1433. [38] ZHANG H, XIAO F, LIU Y, et al. A higher frequency of peripheral blood activated B cells in patients with non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;20(1):95-100. [39] GHOBADINEZHAD F, EBRAHIMI N, MOZAFFARI F, et al. The emerging role of regulatory cell-based therapy in autoimmune disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1075813. [40] FASANO S, MILONE A, NICOLETTI GF, et al. Precision medicine in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(6):331-342. [41] CHENG H, ZHANG XY, YANG HD, et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab/low-dose cyclophosphamide therapy in moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2022;13:911730. [42] 陈明, 林进, 曹恒. 生物靶向治疗药物在狼疮性肾炎中的研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志,2023,32(22):2225-2233. [43] FANOURIAKIS A, KOSTOPOULOU M, ANDERSEN J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(1):15-29. [44] MOGHAZY AA, IBRAHIM AM. Predictors of Avascular Necrosis in a Cohort of Egyptian Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: Retrospective Two Centers Study. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2022;18(2): 144-149. [45] TSELIOS K, GLADMAN DD, TOUMA Z, et al. Disease course patterns in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2019;28(1):114-122. [46] 孔芳,李小霞,赵义. 系统性红斑狼疮并发股骨头坏死或膝关节骨梗死的临床特点分析[J]. 中国医师杂志,2020,22(5):766-770. [47] LONG Y, ZHANG S, ZHAO J, et al. Risk of osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: An 11-year Chinese single-center cohort study. Lupus. 2021;30(9):1459-1468. [48] 张嵩,谢长好,陈琳洁.女性系统性红斑狼疮合并膝关节骨梗死的临床分析[J].中华全科医学,2020,18(7):1103-1106. [49] DE MEDEIROS SF, RODGERS RJ, NORMAN RJ. Adipocyte and steroidogenic cell cross-talk in polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod Update. 2021;27(4):771-796. [50] SHARMA SK, JAIN S, BAHL P, et al. Ovarian dysfunction with moderate-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide (modified NIH regimen) and mycophenolate mofetil in young adults with severe lupus: a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):189. [51] WANG P, WANG C, MENG H, et al. The Role of Structural Deterioration and Biomechanical Changes of the Necrotic Lesion in Collapse Mechanism of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Orthop Surg. 2022; 14(5):831-839. [52] ONO T, HAYASHI M, SASAKI F, et al. RANKL biology: bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm Regen. 2020;40:2. [53] ADAMI G, FASSIO A, ROSSINI M, et al. Osteoporosis in Rheumatic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5867. [54] LEE DSW, ROJAS OL, GOMMERMAN JL. B cell depletion therapies in autoimmune disease: advances and mechanistic insights. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(3):179-199. [55] WANG X, YAN S, LIU C, et al. Fracture risk and bone mineral density levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(4):1413-1423. [56] 徐玉德, 李盛华, 周明旺, 等. 基于通络法探讨骨质疏松症与微循环障碍的相关性[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(5):760-762. [57] 李宁宁,陈奕均,冷晓梅,等. 系统性红斑狼疮并发骨坏死118例临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 中华内科杂志,2021,60(8):744-750. [58] 郭娟, 周惠琼, 张清, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮合并骨坏死的临床特点及骨密度结果分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(3):403-406+411. [59] RAMOS-CASALS M, BRITO-ZERÓN P, BOMBARDIERI S, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of Sjögren’s syndrome with topical and systemic therapies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(1):3-18. [60] 姜泉, 周新尧, 唐晓颇, 等. 干燥综合征病证结合诊疗指南[J]. 中医杂志,2024,65(4):434-444. [61] SIEIRO SANTOS C, MORIANO MORALES C, ÁLVAREZ CASTRO C, et al. Polyautoimmunity in systemic lupus erythematosus: secondary Sjogren syndrome. Z Rheumatol. 2023;82(Suppl 1):68-73. [62] NEVSKAYA T, GAMBLE MP, POPE JE. A meta-analysis of avascular necrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and risk factors. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(4):700-710. [63] SAYARLIOGLU M, YUZBASIOGLU N, INANC M, et al. Risk factors for avascular bone necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(1):177-182. [64] 刘岩, 黄婧, 杨路路, 等. 不同疾病活动度系统性红斑狼疮患者血清补体C3、C4、ESR、IL-6及自身抗体的相关性分析[J]. 河北医药, 2023,45(10):1500-1503. [65] CHEBBI PP, GOEL R, RAMYA J, et al. Nailfold capillaroscopy changes associated with anti-RNP antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2022;42(8):1355-1361. [66] LEE BW, KWON EJ, PARK Y, et al. Predictors for future development of systemic lupus erythematosus in Korean Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Lupus. 2023;32(12):1359-1368. [67] LUN X, YANG J, LIU Y, et al. Risk factors of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2023;102(51):e36654. [68] XIONG J, WANG G, XU T, et al. Anti-RNP Antibody: A Potential Novel Predictor for Osteonecrosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:847875. [69] MATSUEDA Y, ARINUMA Y, NAGAI T, et al. Synergistic enhancement of production of proinflammatory cytokines of human peripheral blood monocytes by anti-Sm and anti-RNP antibodies. PloS One. 2018;13(12): e0209282. |
| [1] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [2] | Han Jie, Pan Chengzhen, Shang Yuzhi, Zhang Chi. Identification of immunodiagnostic biomarkers and drug screening for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [3] | Wang Rongqiang, Yang Liu, Wu Xiangkun, Shang Lilin. Analysis of factors associated with prognosis of osteoporosis patients after hip arthroplasty and construction of Nomogram prediction model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7137-7142. |
| [4] | Abuduainijiang·Abulimiti, Alimu·Mamuti, Li Simi. Artificial femoral head replacement for femoral neck fracture in the elderly: validation of a risk prediction model for hip dysfunction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7143-7149. |
| [5] | Yan Jinlian, Xu Zhengquan, Wei Renjie, Wang Yehua. Hip joint function recovery and prediction model construction after proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7189-7195. |
| [6] | Li Jing, Lu Guangqi, Zhuang Minghui, Cui Ying, Yu Zhangjingze, Sun Xinyue, Ma Mingming, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie. Development of a clinical prediction model for cervical instability in young and middle-aged adults based on machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7203-7210. |
| [7] | Wang Yong, Li Hongyu, Liu Yuhang, Wang Fengxing. Knowledge map of surgical treatment for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a bibliometric analysis of data from 2005 to 2024 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7250-7260. |
| [8] | Tang Haoxu, Liang Yingjie, Li Ce, Ding Penglin, Qian Minlong, Yuan Lingli. Deferoxamine alleviates the inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6821-6827. |
| [9] | Xu Zhi, Chen Yundong, Sun Yujie, Gong Xiaonan, Li Yuwan. Data of spinal osteosarcoma patients in United States based on SEER database: construction and validation of a prediction model for treatment outcomes and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6583-6590. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuekun, Liu Heng, Feng Hui, Gao Yunlong, Wen Lei, Cai Xiaosong, Zhao Ben, Zhong Min. Identification of core genes of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 637-644. |
| [11] | Chai Jinlian, Sun Tiefeng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Li Guangzheng, Zhou Zhongqi, Liang Xuezhen, Wang Ping. Therapeutic effect of Cornus Cervi Colla on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rat models: fecal metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6187-6197. |
| [12] | Chen Hao, Wu Pigen, Teng Jiaqi, Zhang Liang, Feng Xinmin. Analysis of risk factors for lumbar fascial edema in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6174-6179. |
| [13] | Tu Zesong, Xu Daxing, Luo Hongbin, Wang Yusheng, Feng Xinglun, Peng Zhonghua, Du Shaolong. Construction of a risk prediction model for failure of proximal femoral nail antirotation fixation in intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5845-5853. |
| [14] | Qiu Boyuan, Liu Fei, Tong Siwen, Ou Zhixue, Wang Weiwei. Bioinformatics identification and validation of aging key genes in hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5608-5620. |
| [15] | Wu Xiuli, Yan Xiaoxia, Ren Zhiqiang, Sun Nan, Li Jinju. Modeling methods and evaluation criteria in animal models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4560-4567. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||