Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 2357-2367.doi: 10.12307/2025.360
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between long non-coding RNA and osteoarthritis
Zheng Shanbin, Xia Tianwei, Sun Jiahao, Chen Zhiyuan, Cao Xun, Zhang Chao, Shen Jirong
- Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, First School of Clinical Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-07Accepted:2024-05-25Online:2025-04-18Published:2024-08-12 -
Contact:Shen Jirong, MD, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, First School of Clinical Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zheng Shanbin, Master candidate, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, First School of Clinical Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82274552 (to SJR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Shanbin, Xia Tianwei, Sun Jiahao, Chen Zhiyuan, Cao Xun, Zhang Chao, Shen Jirong . Relationship between long non-coding RNA and osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2357-2367.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

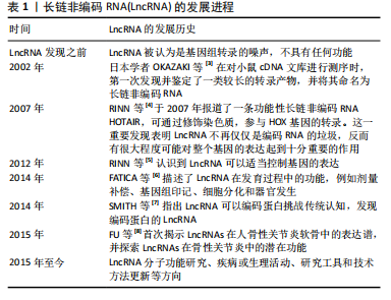
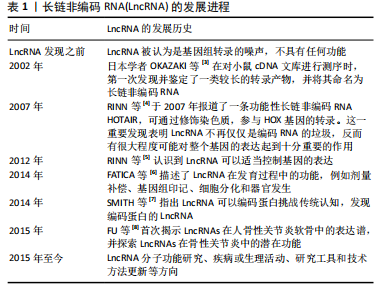
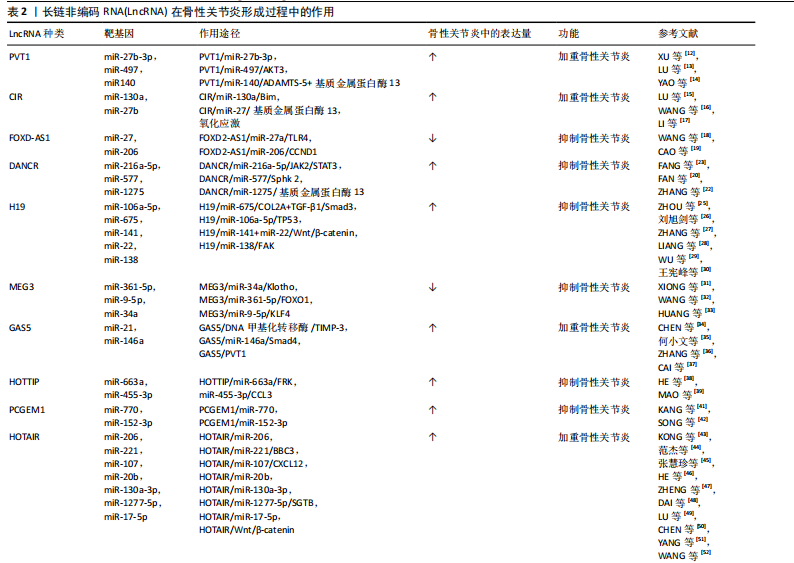
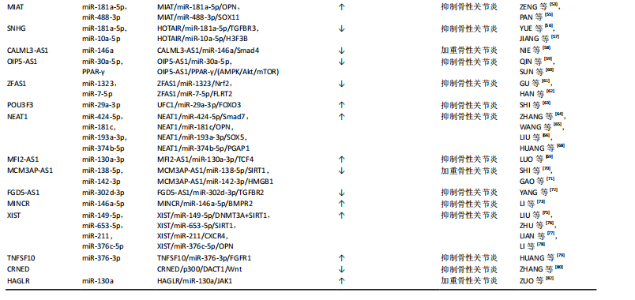
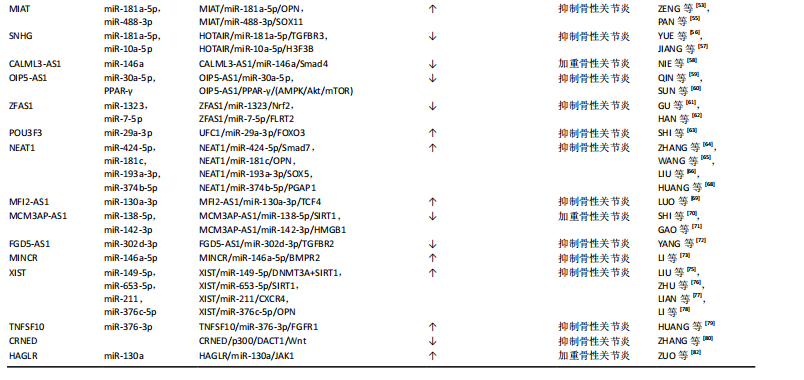
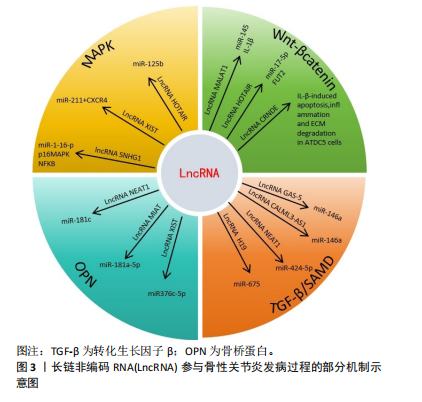
LncRNA和miRNA之间的相互作用在骨性关节炎的发生、发展中起重要作用。细胞来源外泌体中LncRNA PVT1通过与相应miRNA竞争性结合,解除miRNA对其靶基因的抑制作用,升高靶基因的表达水平,以参与疾病进程,该功能称为竞争性内源性RNA机制,被称为分子“海绵”效应[10]。LncRNA和miRNA的结合干扰了miRNA对下游靶基因表达的抑制[11],这也是很多LncRNA发挥作用的机制。 研究表明,白细胞介素1β能够抑制合成代谢基因(如聚集聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原)的合成,并增强分解代谢因子(如基质金属蛋白酶9)的水平,从而加剧软骨细胞的细胞外基质降解,进而致使软骨细胞损伤。白细胞介素1β是诱导骨性关节炎的常用方式。XU等[12]研究表明抑制PVT1表达可通过调控miR-497/AKT3轴抑制白细胞介素1β对软骨细胞外基质的降解,在骨性关节炎患者体内PVT1的表达升高。脂多糖可以诱导软骨细胞的凋亡,也通常用于诱导骨性关节炎进行建模。LIU研究团队[13]发现敲低PVT1可以增加细胞活力,其可以通过上调miR-27b-3p和下调TRAF3抑制白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞凋亡和炎症反应。YAO等[14]研究首次发现PVT1在软骨细胞中作为miR-140的海绵,调控血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶5和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,并参与骨性关节炎的细胞外基质降解,加重骨性关节炎发病进程。 2.2.2 LncRNA CIR LU等[15]研究发现LncRNA CIR在骨性关节炎患者中显著上调,miR‐130a下调,Bim上调,Bim是Bcl-2家族促凋亡蛋白成员,介导内在凋亡通路的发生。生物信息学分析预测miR-130a是LncRNA-CIR和Bim的靶标。LncRNA CIR敲低显著增加Bim的表达,miR‐130a显著抑制Bim的表达,伴随着活性氧水平升高、炎症递质释放、细胞凋亡和相对荧光素酶活性的增加,提示LncRNA CIR/miR‐130a/Bim轴参与骨性关节炎软骨细胞氧化应激相关的凋亡。 LncRNA CIR借助竞争性内源性RNA机制抑制miR-27b的表达,促进细胞外基质的分解[16]。WANG等[16]构建骨性关节炎大鼠模型证实LncRNA CIR的负调控作用,发现si-LncRNA CIR(抑制LncRNA CIR)治疗组比盐水治疗组的关节损伤更轻。LI等[17]研究发现LncRNA CIR在骨性关节炎患者中明显上调,同时miR-27下调,基质金属蛋白酶13上调。LncRNA CIR过表达可显著增加基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,而miR-27可显著抑制基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,LncRNA CIR通过miR-27/基质金属蛋白酶13轴参与骨性关节炎发病过程[17]。 2.2.3 LncRNA FOXD-AS1 FOXD-AS1是一种新发现的致癌 LncRNA分子,在肿瘤学领域研究较为广泛。现代研究发现其与骨性关节炎的发病也密切相关。WANG等[18]研究证实了LncRNA FOXD2-AS1在骨性关节炎患者中低表达,Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptors,TLR4)是炎症相关信号通路,在骨性关节炎进展中发挥着关键作用,进一步实验表明LncRNA FOXD2-AS1通过miR-27a/TLR4轴促进软骨细胞增殖,抑制骨性关节炎的发展。CAO等[19]证实LncRNA FOXD2-AS1通过miR-206/CCND1轴抑制miR-206的表达,LncRNA FOXD2-AS1通过充当miR-206的分子海绵(竞争性内源性RNA机制)上调CCND1的表达,促进骨性关节炎软骨细胞的增殖,抑制骨性关节炎进程。 2.2.4 LncRNA DANCR DANCR编码基因位于人类染色体4q12上,在肿瘤领域研究广泛,目前研究发现在骨性关节炎患者体内,LncRNA DANCR的表达增加,LncRNA DANCR通过miR-216a-5p/JAK2轴和miR-577/Sphk2轴促进骨性关节炎软骨细胞的增殖[20]。骨性关节炎的发病机制也受到JAK-STAT信号通路的广泛影响,该通路的激活可以增强基质降解酶和炎性细胞因子的产生,导致软骨细胞外基质降解和滑膜炎症,这是骨性关节炎的关键标志[21]。 ZHANG等[22]发现LncRNA DANCR通过作为miR-216a-5p的竞争性内源性RNA,促进骨性关节炎软骨细胞的存活。JAK2-STAT是miR-216a-5p的直接靶点,即LncRNA DANCR通过调控miR-216a-5p/JAK2/STAT3信号通路,促进骨性关节炎软骨细胞增殖、炎症反应,减少细胞凋亡[23]。 LncRNA DANCR通过miR-1275/基质金属蛋白酶13诱导滑膜间充质干细胞增殖和向软骨分化[24]。采用荧光素酶报告基因测定法和RNA免疫沉淀法检测到了血管内皮细胞中LncRNA DANCR对miR-1275降低的直接作用。研究发现LncRNA DANCR通过miR-1275/基质金属蛋白酶13诱导滑膜间充质干细胞增殖和向软骨分化[24]。 2.2.5 LncRNA H19 研究表明骨性关节炎小鼠注射外源性白细胞介素38可减轻软骨损伤,降低促炎因子水平和软骨细胞凋亡[25]。LncRNA H19通过TP53介导白细胞介素38的上调,因此H19的过表达可以减少炎症因子水平和软骨细胞凋亡[25]。刘旭剑团队[26]收集临床骨性关节炎软骨组织和健康软骨组织,经过一系列实验研究表明,LncRNA H19在骨性关节炎软骨组织中表达上调,LncRNA H19可能通过抑制miR-106a-5p的表达,促进细胞外软骨基质的降解和钙化,从而参与骨性关节炎的发生发展。 ZHANG等[27]研究表明H19通过转化生长因子β/Smad3/组蛋白去乙酰化酶途径促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,源自H19的miR-675在一定程度上促进了这种成骨作用,同时H19和miR-675-5p之间存在负反馈回路,然而H19在脂肪干细胞成骨过程中的直接靶点和详细机制并未明晰。LIANG研究团队[28]通过使用生物信息学和RNA免疫沉淀实验结合荧光素酶报告分析研究显示,LncRNA H19可以通过抑制miR-141和miR-22的表达,最终激活Wnt/β-catenin信号转导通路,从而增强成骨作用,促进人间充质干细胞成骨分化。同时该研究团队发现了miR-675-5p直接靶向H19并抵消成骨细胞分化。 WU团队[29]研究表明,机械张力可以增强人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化并提高H19表达,而H19的缺失抑制了张力诱导的成骨分化。此外,机械张力可以抑制miR-138的表达,促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,荧光素酶报告分析表明H19具有与miR-138的结合位点,并且H19缺失会增加miR-138水平,表明H19可能在人骨髓间充质干细胞中充当miR-138的竞争性内源性RNA,是张力诱导人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨的正调节因子。最新研究表明人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体能够有效促进软骨损伤修复,其中H19高表达,LncRNA H19通过内源竞争RNA机制激活转化生长因子β1/Smad3通路促进软骨再生[30]。 2.2.6 LncRNA MEG3 LncRNA MEG3是位于人染色体14q32.3上的印记基因,其在骨性关节炎中表达下调;Klotho基因与细胞衰老、凋亡相关,Klotho 蛋白可通过抑制胰岛素生长因子来发挥抗氧化应激作用,并最终抑制细胞凋亡,研究表明LncRNA MEG3通过调控miR-34a/Klotho轴调节FGF23、Bcl-2、Bax、转化生长因子β1、Caspase 3和Caspase 8的表达,从而影响骨性关节炎的进展[31]。 另一项研究表明MEG3可能作为骨性关节炎软骨细胞中miR-361-5p的竞争性内源性RNA。MEG3可能通过miR-361-5p/FOXO1轴促进软骨细胞增殖并抑制软骨细胞凋亡[32]。另有研究表明白细胞介素1β可以刺激软骨细胞MEG3表达下调,MEG3抑制miR-9-5p的表达,促进KLF4的表达[33]。MEG3过表达增强了CHON-001和ATDC5细胞的活力,抑制细胞凋亡和局部炎症反应,而抑制MEG3的表达则有相反的作用。抑制miR-9-5p或增强KLF4 的表达可以抵消MEG3基因敲低对软骨细胞的影响。此外,在该研究中MEG3被证明是miR-9-5p的竞争性内源性RNA,KLF4被证实是miR-9-5p的靶点。MEG3通过miR-9-5p/KLF4轴促进软骨细胞增殖和迁移,参与骨性关节炎发展进程。 2.2.7 LncRNA GAS5 Chen团队[34]研究发现LncRNA GAS5在骨性关节炎软骨细胞中表达明显上调,骨性关节炎软骨细胞中基质金属蛋白酶2,3,9,13等多种蛋白酶表达明显较正常软骨细胞增多,说明LncRNA GAS5 参与关节软骨基质代谢调节,故在骨性关节炎的发生发展中也有LncRNA GAS5的参与。何小文团队[35]研究认为,骨性关节炎软骨细胞中组织金属蛋白酶抑制因子3(tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3,TIMP-3)表达相对于正常软骨细胞降低,而LncRNA GAS5表达上调;LncRNA GAS5可富集DNA甲基化转移酶,抑制TIMP-3的表达,促进软骨细胞胶原蛋白降解,进而影响骨性关节炎的发病进程。 ZHANG等[36]研究通过生物信息学分析预测GAS5与miR-146a之间的相互作用,GAS5过表达增加了软骨细胞中Smad4的表达。相反,miR-146a过表达下调软骨细胞中Smad4的表达。此外,GAS5和Smad4过表达抑制了脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞凋亡,而miR-146a过表达起到相反的作用,能够减弱GAS5和Smad4过表达对细胞凋亡的影响。 另一项研究表明LncRNA PVT1和LncRNA GAS5在软骨细胞凋亡中具有相反的功能[37]。PVT1和GAS5在骨性关节炎发病过程中存在相互影响。在骨性关节炎中PVT1表达增强,GAS5表达减少,二者在骨性关节炎发病过程中呈负相关关系。该研究还发现PVT1和GAS5可以直接结合到彼此的启动子区域。脂多糖可以诱导软骨细胞凋亡,在脂多糖处理下,PVT1上调,GAS5下调。GAS5通过上调KLF2抑制细胞凋亡,在脂多糖诱导的炎症损伤中发挥保护作用。PVT1和GAS5都通过脂多糖依赖性途径参与骨性关节炎发病进程,PVT1和GAS5的下游靶点尚不清楚。PVT1和GAS5可能在骨性关节炎发病过程中形成负反馈回路。 2.2.8 LncRNA HOTTIP LncRNA HOTTIP是来源于同源盒蛋白(HOXA)的5′端的一个非编码RNA转录本。Hox基因是一个高度保守的基因家族,在分化、增殖和发育等多种生物学功能中发挥着重要作用,对于关节软骨的形成与修复过程也起着重要作用。研究表明,在骨性关节炎发病过程中HOTTIP和FRK的表达上调,而miR-663a的表达下调[38]。 敲低HOTTIP基因降低了骨性关节炎软骨模型细胞的增殖并可以诱导其凋亡,而HOTTIP过表达增加了骨性关节炎软骨模型细胞的增殖并减少了其凋亡。此外,HOTTIP可以作为竞争性内源性RNA与miR-663a结合。抑制miR-663a表达可以减轻HOTTIP基因敲低对骨性关节炎软骨模型细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。此外,FRK被发现是miR-663a的直接靶标,它可以显著下调骨性关节炎软骨细胞中FRK的表达,而HOTTIP可以显著增强FRK的表达。此外,抑制miR-663a可以促进软骨细胞增殖并减少其凋亡,而FRK基因敲低可以逆转miR-663a抑制对软骨细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。同时,miR-663a的过表达降低了骨性关节炎细胞增殖并诱导了细胞凋亡,而FRK过表达则逆转了miR-663a过表达对骨性关节炎细胞增殖和凋亡的影响。LncRNA HOTTIP可以通过miR-663a/FRK轴参与骨性关节炎发病进程。CCL3是趋化细胞因子亚型的一种,CCL3可以诱导促进软骨细胞降解,研究表明miR-455-3p缺失增强了HOTTIP和CCL3的表达,HOTTIP可以竞争性吸附miR-455-3p影响CCL3的表达,HOTTIP可以通过miR-455-3p/CCL3轴影响骨性关节炎进程[39]。 2.2.9 LncRNA PCGEM1 LncRNA PCGEM1最早发现于人前列腺癌LNCaP细胞中,参与前列腺癌、结直肠癌、胃癌等恶性肿瘤的发生发展[40]。有研究发现在骨性关节炎患者滑膜细胞中LncRNA PCGEM1表达明显上调,并且在滑膜炎相对严重的患者体内表达程度更高,PCGEM1表达上调后会通过内源性竞争作用下调miR-770水平,而miR-770下调会使骨性关节炎患者滑膜细胞增殖受到抑制[41],该研究发现miR-770可能通过直接结合PC-GEM1序列中的靶点来调节PCGEM1的表达,但仍需进一步研究。 SONG团队[42]研究表明沉默PCGEM1可通过miR-152-3p促进CHON-001细胞增殖,抑制软骨细胞凋亡,抑制乳酸脱氢酶水平,减轻白细胞介素引起的炎症反应。总之,PCGEM1下调通过调节miR-152-3p的表达来抑制骨性关节炎的进展。 2.2.10 LncRNA HOTAIR 作为一种表观遗传因子,HOTAIR可以与多种因子相互作用,影响细胞增殖、存活、侵袭、迁移、转移和耐药性[43]。有研究发现LncRNA HOTAIR与骨关节炎的进展有关,LncRNA HOTAIR参与膝关节炎形成过程[44]。张慧珍团队[45]研究发现抑制HOTAIR可能通过上调miR-206表达降低类风湿关节炎滑膜细胞增殖,并促进凋亡。 HE等[46]研究表明HOTAIR的异常高表达可以导致软骨细胞凋亡,这可能是通过miR-130a-3p抑制软骨细胞自噬而引起的,可能会促进骨性关节炎的发展。目前HOTAIR在机械刺激处理的软骨细胞中的作用仍不清楚。ZHENG等[47]研究发现机械刺激显著诱导C28/I2细胞凋亡,并且HOTAIR的表达上调,miR-221的表达下调。HOTAIR基因敲低可有效改善机械刺激诱导的细胞凋亡。HOTAIR可以与miR-221相互作用,miR-221能够降低BB3的表达,BBC3过表达可以逆转HOTAIR基因敲低诱导的细胞凋亡率降低。总的来说,HOTAIR通过调节C28/I2细胞中的miR-221/BBC3轴来促进机械刺激诱导的细胞凋亡。 既往研究报道,CXCL12可通过减少软骨细胞增殖和促进细胞外基质降解来促进骨性关节炎的进展[48]。LU等[49]研究表明骨性关节炎患者骨样本中HOTAIR表达增强,HOTAIR基因敲低降低软骨细胞中CXCL12的表达。然而,这种作用通过抑制miR-107的表达而减弱,说明HOTAIR通过调节miR-107来调控CXCL1的表达,因此HOTAIR基因敲低能够促进软骨细胞增殖,但通过调节miR-107/CXCL12轴抑制骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解。既往研究表明HOTAIR可通过调节骨性关节炎中的miR-20b或miR-130a-3p,促进软骨细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解[46,50]。Wnt抑制因子1是Wnt/β-catenin 通路的关键抑制剂,可直接受HOTAIR调控,增加分解代谢基因表达并促进软骨退化[51]。 另有研究表明HOTAIR通过竞争性吸附miR-1277-5p减弱了脂多糖引起的软骨细胞凋亡和炎症[52]。此外,miR-1277-5p 通过靶向SGTB抑制脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞凋亡和炎症。此外,HOTAIR通过吸附miR-1277-5p增强SGTB的表达,HOTAIR通过调节miR-1277-5p/SGTB通路加重骨性关节炎中的软骨细胞凋亡和炎症。 2.2.11 LncRNA MIAT 现有研究提出了通过LncRNA MIAT/miR-181a-5p/骨桥蛋白轴治疗骨性关节炎[53]。骨桥蛋白是一种细胞外基质糖磷蛋白,骨桥蛋白可调节与骨性关节炎发病相关的多个因素的表达水平,如基质金属蛋白酶13、缺氧诱导因子2α、血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶4、金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂,并且可以通过核因子κB信号通路加速软骨细胞增殖,从而诱导大鼠发生骨性关节炎[54]。miR-181a-5p通过直接靶向骨桥蛋白抑制骨性关节炎软骨细胞中的骨桥蛋白表达。miR-181a-5p 过表达抑制骨性关节炎软骨细胞活力,抑制DNA合成,并促进细胞凋亡。骨桥蛋白过表达对骨性关节炎软骨细胞产生相反的作用,并减弱miR-181a-5p过表达在软骨细胞中的作用。MIAT可以抑制miR-181a-5p的表达。MIAT沉默抑制细胞活力,抑制DNA合成,促进细胞凋亡。此外,抑制miR-181a-5p部分逆转了 MIAT 沉默对骨性关节炎软骨细胞的影响。因此LncRNA MIAT可以通过miR-181a-5p/骨桥蛋白轴调节骨性关节炎软骨细胞增殖和凋亡。 有研究表明敲低MIAT基因可以靶向增加miR-488-3p的表达,而过表达的miR-488-3p通过减少SOX11的表达减弱了脂多糖诱导的细胞损伤[55],因此敲低MIAT可以通过抑制miR-488-3p/SOX11轴介导的NF-κB信号通路来减轻脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞损伤,进而影响骨性关节炎的进程。 2.2.12 LncRNA SNHG LncRNA在恶性肿瘤发病机制中研究较为广泛。有研究提出LncRNA SNHG5与骨关节炎发病机制之间存在联系[56]。白细胞介素1β处理的骨关节炎组织和软骨细胞中SNHG5、TGFBR3的表达降低,miR-181a-5p表达增强。SNHG5基因敲低后可抑制软骨细胞的活力,诱导细胞凋亡,并提高解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶5和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达水平。相反,SNHG5过表达可以抵消白细胞介素1β的作用,增加软骨细胞的活力并抑制细胞凋亡。SNHG5可以通过竞争性吸附miR-181a-5p正向调节TGFBR3表达。此外,miR-181a-5p过表达和TGFBR3基因敲低可以抵消SNHG5对软骨细胞的影响。因此SNHG5可能通过调节miR-181a-5p/TGFBR3轴保护软骨细胞免受炎症反应并减少细胞外基质的降解。 另一项研究提示SNHG5的敲低增强了白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞凋亡[57]。SNHG5通过竞争性吸附miR-10a-5p阻碍了白细胞介素1β刺激的软骨细胞凋亡。此外,H3F3B作为miR-10a-5p的靶标,miR-10a-5p通过调节H3F3B促进白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞凋亡。SNHG5还可以在白细胞介素1β处理的软骨细胞中吸附miR-10a-5p来调节H3F3B的表达。SNHG5通过调节miR-10a-5p/H3F3B轴来抑制骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡。 2.2.13 LncRNA CALML3-AS1 NIE等[58]研究表明,LncRNA CALML3-AS1为LncRNA CALML3的反义RNA,miR-146a可以与LncRNA CALML3-AS1相结合。在脂多糖诱导的骨性关节炎软骨细胞中,CALML3-AS1表达下调,而miR-146a表达上调,但未发现它们之间存在显著相关性。此外,CALML3-AS1或miR-146a的过表达不影响彼此的表达。然而,CALML3-AS1的过表达会导致Smad4的上调,Smad4是miR-146a的下游靶标。miR-146a和Smad4的表达呈负相关,CALML3-AS1和Smad4的过表达导致软骨细胞增殖减少。miR-146a起到了相反的作用,降低了CALML3-AS1和Smad4过表达的影响。因此,CALML3-AS1 可能通过竞争性吸附miR-146a上调Smad4来调节软骨细胞凋亡。 2.2.14 LncRNA OIP5-AS1 研究表明骨性关节炎患者软骨组织中的LncRNA OIP5-AS1减少,而miR-30a-5p增加[59]。OIP5-AS1下调引起miR-30a-5p增加miR-30a-5p上调或LncRNA OIP5-AS1下调引起细胞凋亡和炎症反应,抑制细胞增殖,同时上调miR-30a-5p抑制细胞凋亡和炎症反应,加速细胞增殖。LncRNA OIP5-AS1通过负调控miR-30a-5p影响软骨细胞。LncRNA OIP5-AS1通过靶向下调miR-30a-5p抑制软骨细胞凋亡和炎症反应,促进软骨细胞存活,同时上调LncRNA OIP5-AS1和下调miR-30a-5p对骨性关节炎患者有益。最新研究表明OIP5-AS1 促进过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ表达以激活AMPK/Akt/mTOR信号传导,从而增强线粒体自噬并缓解骨性关节炎进展[60]。 2.2.15 LncRNA ZFAS1 GU等[61]研究表明LncRNA ZFAS1在骨性关节炎标本和脂多糖处理的骨性关节炎软骨细胞中表达降低。ZFAS1过表达促进脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞增殖并抑制氧化应激、炎症和细胞凋亡。ZFAS1还激活抗氧化Nrf2-HO-1通路。ZFAS1直接靶向miR-1323,miR-1323能够逆转ZFAS1对软骨细胞促进增殖、抑制炎症和凋亡的影响。此外,Nrf2通路还受到miR-1323的负调控。总的来说,ZFAS1促进软骨细胞增殖并抑制氧化应激,可能通过miR-1323/Nrf2轴来调节脂多糖引发的炎症和细胞凋亡。 另一项研究通过白细胞介素1β刺激软骨细胞建立体外骨性关节炎模型[62],在该模型中ZFAS1和FLRT2的表达下调,而miR-7-5p的表达上调。ZFAS1过表达提高细胞活力并抑制软骨细胞凋亡。此外,ZFAS1过表达抑制基质金属蛋白酶13和解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶5的表达,促进胶原蛋白Ⅱ和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达以抑制细胞外基质降解。ZFAS1吸附miR-7-5p以调节FLRT2 表达。此外,miR-7-5p的过表达可以中和ZFAS1在白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞中的作用。因此ZFAS1可通过调节miR-7-5p/FLRT2轴促进细胞增殖。 2.2.16 LncRNA POU3F3 POU3F3作为癌基因在多种癌症患者组织或血浆中高表达。SHI等[63]研究表明POU3F3在骨性关节炎患者和骨性关节炎模型小鼠以及白细胞介素1β刺激软骨细胞模型中发现LncRNA POU3F3表达增强。POU3F3过表达抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞损伤,抑制细胞凋亡和炎性细胞因子分泌,抑制软骨细胞体外自噬。miR-29a-3p可以直接与POU3F3结合,而FOXO3是miR-29a-3p的靶基因。POU3F3表达增强通过miR-29a-3p/FOXO3轴影响骨性关节炎发病进程。此外,小鼠关节腔内注射POU3F3慢病毒可减轻骨性关节炎小鼠软骨损伤。 2.2.17 LncRNA NEAT1 研究表明在骨性关节炎组织中LncRNA NEAT1的表达高于正常组织,miR-424-5p靶向SMAD7抑制软骨细胞增殖、促进炎性因子表达[64]。NEAT1可以通过吸附miR-424-5p和促进SMAD7的表达来减缓骨关节炎的发展。此外,先前的研究表明NEAT1可以通过miR‐181c抑制骨桥蛋白介导的滑膜细胞增殖,抑制骨性关节炎的发展进程[65]。 另一项研究表明miR-193a-3p的上调和NEAT1的敲低都抑制了炎症和细胞凋亡[66],并降低了基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13和血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶5等水平,同时提高了软骨细胞中ACAN和Col2a1的表达。NEAT1靶向miR-193a-3p,SOX5靶向miR-193a-3p。沉默miR-193a-3p可以逆转NEAT1敲低对炎症、细胞凋亡和细胞外基质产生的影响。SOX5可以消除miR-193a-3p上调对软骨细胞炎症、细胞凋亡和细胞外基质产生的影响。因此,NEAT1/miR-193a-3p/SOX5轴可以调控骨性关节炎中软骨基质降解,进而影响骨性关节炎发病进程。PGAP1可能与骨性关节炎发病过程相关,PGAP1受LncRNA LEMD1-AS1/miR-944轴的调控[67],最新研究表明表明NEAT1的下调可以与miR-374b-5p/PGAP1轴相互作用,促进软骨细胞凋亡和炎症,从而加速骨性关节炎的发展[68]。 2.2.18 LncRNA MFI2-AS1 研究表明MFI2-AS1的表达在骨性关节炎组织和脂多糖处理的C28/I2细胞中增加[69]。敲除MFI2-AS1可以减弱脂多糖诱导的细胞凋亡、炎症反应和细胞外基质降解。miR-130a-3p过表达通过降低TCF4的表达来抑制脂多糖诱导的C28/I2细胞损伤。MFI2-AS1敲低通过介导miR-130a-3p和TCF4减轻了脂多糖诱导的C28/I2细胞损伤,进而参与骨性关节炎发病过程。 2.2.19 LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 研究表明MCM3AP-AS1在骨性关节炎软骨组织中下调,与SIRT1表达呈正相关,而与 miR-138-5p表达呈负相关[70]。MCM3AP-AS1表达上调增强了CHON-001和ATDC5细胞的活力和迁移,同时抑制了细胞凋亡和炎症反应。此外,miR-138-5p过表达可以抵消MCM3AP-AS1过表达对软骨细胞的影响。MCM3AP-AS1可以作为竞争性内源性RNA竞争性吸附miR-138-5p,SIRT1被证实是miR-138-5p的靶标,SIRT1过表达可以引起MCM3AP-AS1表达增加。因此,MCM3AP-AS1调节软骨细胞miR-138-5p/SIRT1轴参与骨性关节炎发病机制。另一项研究表明MCM3AP-AS1过表达导致 HMGB1的表达上调,HMGB1是miR-142-3p的靶标[71]。脂多糖处理导致软骨细胞中MCM3AP-AS1的表达上调。MCM3AP-AS1和HMGB1过表达导致软骨细胞凋亡率增加。miR-142-3p过表达起到了相反的作用,减弱了MCM3AP-AS1过表达的作用。MCM3AP-AS1调节miR-142-3p/HMGB1以促进脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞凋亡。 2.2.20 LncRNA FGD5-AS1 有研究表明在骨性关节炎患者软骨组织中FGD5-AS1和转化生长因子β受体2表达水平下调,而miR-302d-3p表达增加[72]。敲低FGD5-AS1基因水平能抑制C20/A4细胞的活力,诱导细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解,而FGD5-AS1过表达则产生相反的效果。miR-302d-3p确定为FGD5-AS的靶标,转化生长因子β受体2确定为miR-302d-3p的靶标。FGD5-AS1通过抑制miR-302d-3p的表达可以促进转化生长因子β受体2表达,抑制miR-302d-3p表达可以逆转敲低FGD5-AS1引起的细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解。FGD5-AS1可能通过调节miR-302d-3p/TGFBR2轴来抑制骨性关节炎进展。 2.2.21 LncRNA MINCR MINCR表达上调促进细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡和细胞外基质变性。研究证明MINCR和 miR-146a-5p之间具有结合关系[73]。骨形态发生蛋白及其受体存在于软骨细胞和邻近的软骨膜中,能够诱导软骨细胞生成,在骨骼发育中起着至关重要的作用。骨形态发生蛋白受体2可以作为miR-146a-5p的靶标。MINCR通过靶向miR-146a-5p促进骨形态发生蛋白受体2表达来阻止骨性关节炎进展。 2.2.22 LncRNA XIST XIST编码一个17 kb的LncRNA。XIST在骨性关节炎软骨中上调,并促进人软骨细胞中基质金属蛋白酶13和血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶5的表达,其可以通过作为miR-1277-5p的竞争性内源性RNA在细胞外基质降解中发挥作用[74]。研究发现XIST的敲低可以通过激发miR-149-5p表达来降低DNMT3A水平[75]。既往研究表明DNMT3A异常升高与骨性关节炎相关,XIST可以通过miR-211+CXCR4影响下游靶点丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的表达进而影响骨性关节炎发病[76]。miR-149-5p 为XIST的miRNA靶标,DNMT3A为miR-149-5p的下游靶基因,因此XIST下调对骨性关节炎的抑制通过体内miR-149-5p/DNMT3A轴实现。另一项研究发现XIST的上调增加了CHON-001和ATDC5细胞活力,同时阻碍了白细胞介素1β诱导的细胞凋亡和炎症反应。miR-653-5p表达上调呈现相反的效果,说明miR-653-5p可以被XIST竞争性吸附[77]。此外,SIRT1为miR-653-5p的靶标,并且SIRT1可以被XIST间接抑制。上调XIST可以通过调节miR-653-5p/SIRT1轴保护软骨细胞免受炎症损伤。此外,与正常滑膜相比,骨性关节炎滑膜中XIST表达显著上调。更重要的是,XIST/miR-376c-5p/骨桥蛋白轴已被证明可调节骨性关节炎滑膜巨噬细胞的炎症微环境,从而影响软骨细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解[78]。 2.2.23 LncRNA TNFSF10 研究表明TNFSF10在骨性关节炎软骨中表达上调并刺激软骨细胞增殖、抵抗细胞凋亡和炎症[79]。此外,TNFSF10作为竞争性内源性RNA抑制miR-376-3p的表达,并且TNFSF10对软骨细胞的影响会被miR-376-3p部分逆转。成纤维细胞生长因子受体1作为miR-376-3p的靶标,对miR-376-3p介导的结果具有逆转作用。进一步分析显示,TNFSF10与miR-376-3p、miR-376-3p与成纤维细胞生长因子受体1呈负相关,而成纤维细胞生长因子受体1与TNFSF10呈正相关。此外TNFSF10还具有促进细胞增殖和白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8表达的能力。 2.2.24 LncRNA CRNED 研究发现CRNED过表达可减轻大鼠滑膜炎,抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的ATDC5细胞凋亡、炎症、细胞外基质降解[80]。DACT1在骨性关节炎软骨细胞中表达水平降低,DACT1是Wnt通路的抑制剂,可以调控Wnt下游基因的表达。研究发现过表达DACT1抑制ATDC5细胞中Wnt信号的活性,进而影响骨性关节炎进展[81]。CRNDE通过将p300招募到DACT1启动子并与p300结合形成复合物,调节D3K27ac的富集,最终影响了DACT1的表达。CRNDE在体内缓解膝关节软骨损伤,可能通过p300/DACT1/Wnt轴进行调节。 2.2.25 LncRNA HAGLR 研究发现在白细胞介素1β刺激的CHON-001细胞中HAGLR的表达上调,而miR-130a-3p的表达下调[82]。此外,沉默LncRNA HAGLR能够减轻白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞炎症损伤,表现为细胞活力增加、乳酸脱氢酶释放减少、cleaved-Caspase3表达受到抑制以及炎症因子分泌减少。抑制miR-130a-3p可以逆转这些效果。miR-130a-3p可以直接靶向JAK1并负向调节CHON-001细胞中的JAK1表达。此外,JAK1可以逆转miR-130a-3p对白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞炎症损伤的影响。LncRNA HAGLR可以直接靶向miR-130a-3p。沉默LncRNA HAGLR通过miR-130a减轻白细胞介素1β刺激的CHON-001细胞损伤。因此LncRNA HAGLR可以通过miR-130a/JAK1轴调控骨性关节炎发病过程。 长链非编码RNA(LncRNA)在骨性关节炎形成过程中作用,见表2。 2.3 主要机制总结 2.3.1 MAPK信号转导通路 MAPK在真核细胞中普遍存在,失调的MAPK信号通路可以加速炎症反应,进而导致大量酶的释放,这些酶降解软骨基质并加速软骨变性,进而导致骨性关节炎。MAPK亚家族主要包括p38MAPK、ERKs和JNKs等[83]。MAPKs信号通路可以通过多种途径参与骨性关节炎的发病过程,包括促进炎症反应、促进细胞凋亡、促进氧化应激与细胞自噬[84]。 2.3.2 转化生长因子β/Smad信号转导通路 转化生长因子β信号转导通路通过Smad2、转化生长因子β2、基质金属蛋白酶13参与了骨性关节炎的病变过程[85]。基质金属蛋白酶13则是关节软骨受到破坏的关键标志物。转化生长因子β通过Smad1/Smad5/Smad8信号转导通路,促使软骨细胞肥大化,加速分泌基质金属蛋白酶13,使软骨细胞外基质降解,还可以促进滑膜细胞增殖、炎症细胞浸润和纤维化,引起关节滑膜炎。此外转化生长因子β信号转导通路与Wnt信号转导通路可能存在交叉调控作用,其相互影响待进一步研究。 2.3.3 Wnt/β-catenin信号转导通路 Wnt/β-catenin在调节下游靶基因的转录、软骨细胞调亡、关节软骨去分化及软骨基质分解代谢过程中发挥重要的调控作用[86]。它是由细胞外信号段、细胞膜段、细胞质段及细胞核段4个部分组成,细胞外信号段主要由Wnt蛋白介导,细胞膜段主要由Wnt受体卷曲蛋白组成,细胞质段主要包括GSK-3β、CK1,细胞核段主要包括易位到细胞核的β-catenin以及β-catenin的下游靶基因,如基质金属蛋白酶。一旦细胞外Wnt配体与膜受体结合,该通路将被激活,β-catenin也因此被诱导转移至细胞核,使β-catenin得到累积,以促进基质金属蛋白酶的表达以及白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α炎症因子的升高,进而调节软骨细胞增殖与凋亡[87]。 LncRNA参与骨性关节炎发病过程的部分机制示意图,见图3。"
| [1] NG N, PARKINSON L, BROWN WJ, et al. Lifestyle behaviour changes associated with osteoarthritis: a prospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):6242. [2] ZHANG L, ZHANG H, XIE Q, et al. LncRNA-mediated cartilage homeostasis in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1326843. [3] OKAZAKI Y, FURUNO M, KASUKAWA T, et al. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature. 2002;420(6915):563-573. [4] RINN JL, KERTESZ M, WANG JK, et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129(7):1311-1323. [5] RINN JL, CHANG HY. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:145-166. [6] FATICA A, BOZZONI I. Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(1):7-21. [7] SMITH JE, ALVAREZ-DOMINGUEZ JR, KLINE N, et al. Translation of small open reading frames within unannotated RNA transcripts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell Rep. 2014;7(6):1858-1866. [8] FU M, HUANG G, ZHANG Z, et al. Expression profile of long noncoding RNAs in cartilage from knee osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(3):423-432. [9] ZHANG A, WANG G, JIA L, et al. Exosome-mediated microRNA-138 and vascular endothelial growth factor in endometriosis through inflammation and apoptosis via the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(1):358-370. [10] PORCELLI L, DE SUMMA S, FASANO R, et al. miRNA lncRNA network associated with response to cemiplimab in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2024;84(6_Supplement):5172. [11] CHOWDHURY MR, CHATTERJEE C, GHOSH D, et al. Deciphering miRNA-lncRNA-mRNA interaction through experimental validation of miRNAs, lncRNAs, and miRNA targets on mRNAs in Cajanus cajan. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2024;26(4):560-567. [12] XU J, FANG X, QIN L, et al. LncRNA PVT1 regulates biological function of osteoarthritis cells by regulating miR-497/AKT3 axis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(45):e31725.
[13] LU X, YU Y, YIN F, et al. Knockdown of PVT1 inhibits IL-1β-induced injury in chondrocytes by regulating miR-27b-3p/TRAF3 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;79:106052. [14] YAO N, PENG S, WU H, et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation by acting as a sponge for miR-140 in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):218. [15] LU Z, LUO M, HUANG Y. lncRNA-CIR regulates cell apoptosis of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(5):7229-7237. [16] WANG CL, PENG JP, CHEN XD. LncRNA-CIR promotes articular cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by regulating autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;505(3):692-698. [17] LI YF, LI SH, LIU Y, et al. Long Noncoding RNA CIR Promotes Chondrocyte Extracellular Matrix Degradation in Osteoarthritis by Acting as a Sponge For Mir-27b. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(2):602-610. [18] WANG Y, CAO L, WANG Q, et al. LncRNA FOXD2-AS1 induces chondrocyte proliferation through sponging miR-27a-3p in osteoarthritis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1241-1247. [19] CAO L, WANG Y, WANG Q, et al. LncRNA FOXD2-AS1 regulates chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis by acting as a sponge of miR-206 to modulate CCND1 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;106:1220-1226. [20] FAN X, YUAN J, XIE J, et al. Long non-protein coding RNA DANCR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate osteoarthritis progression via miR-577/SphK2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(3):658-664. [21] CHEN KT, YEH CT, YADAV VK, et al. Notopterol mitigates IL-1β-triggered pyroptosis by blocking NLRP3 inflammasome via the JAK2/NF-kB/hsa-miR-4282 route in osteoarthritis. Heliyon. 2024;10(6):e28094. [22] ZHANG L, ZHANG P, SUN X, et al. Long non-coding RNA DANCR regulates proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis via miR-216a-5p-JAK2-STAT3 axis. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(6):BSR20181228. [23] FANG P, ZHANG LX, HU Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA DANCR induces chondrogenesis by regulating the miR-1275/MMP-13 axis in synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(23):10459-10469. [24] 房鹏.长链非编码RNA DANCR通过miR-1275/MMP-13诱导滑膜间充质干细胞增殖和向软骨分化的机制研究 [D].南京:南京大学, 2020. [25] ZHOU Y, LI J, XU F, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 alleviates inflammation in osteoarthritis through interactions between TP53, IL-38, and IL-36 receptor. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(8):594-607. [26] 刘旭剑,王东来,李增怀,等.lncRNA-H19通过靶向miR-106a-5p在骨关节炎软骨基质降解和钙化中的调控作用 [J].川北医学院学报, 2021,36(10):1265-1270. [27] ZHANG Z, HUANG G, MAO G, et al. Characterization of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(3):1411-1420. [28] LIANG WC, FU WM, WANG YB, et al. H19 activates Wnt signaling and promotes osteoblast differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20121. [29] WU J, ZHAO J, SUN L, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 mediates mechanical tension-induced osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via FAK by sponging miR-138. Bone. 2018; 108:62-70. [30] 王宪峰,王锟,孙晗,等.脐带间充质干细胞外泌体LncRNA H19修复软骨损伤的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(1):20-25. [31] XIONG G, WANG S, PAN Z, et al. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 regulates the progress of osteoarthritis by regulating the miR-34a/Klotho axis. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(8):454. [32] WANG A, HU N, ZHANG Y, et al. MEG3 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in osteoarthritis chondrocytes by miR-361-5p/FOXO1 axis. BMC Med Genomics. 2019;12(1):201. [33] HUANG Y, CHEN D, YAN Z, et al. LncRNA MEG3 Protects Chondrocytes From IL-1β-Induced Inflammation via Regulating miR-9-5p/KLF4 Axis. Front Physiol. 2021;12:617654. [34] CHEN L, ZHANG T, ZHANG S, et al. Identification of Long Non-Coding RNA-Associated Competing Endogenous RNA Network in the Differentiation of Chicken Preadipocytes. Genes (Basel). 2019; 10(10):795. [35] 何小文,丁徐,张东华,等. LncRNA GAS5通过TIMP-3启动子甲基化促进软骨胶原蛋白降解的实验研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2021, 27(11): 999-1004. [36] ZHANG D, QIU S. LncRNA GAS5 upregulates Smad4 to suppress the apoptosis of chondrocytes induced by lipopolysaccharide. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2021;97:104478. [37] CAI L, HUANG N, ZHANG X, et al. Long non-coding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 and growth arrest specific 5 regulate each other in osteoarthritis to regulate the apoptosis of chondrocytes. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):13680-13688. [38] HE X, GAO K, LU S, et al. LncRNA HOTTIP leads to osteoarthritis progression via regulating miR-663a/ Fyn-related kinase axis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):67. [39] MAO G, KANG Y, LIN R, et al. Long Non-coding RNA HOTTIP Promotes CCL3 Expression and Induces Cartilage Degradation by Sponging miR-455-3p. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:161. [40] 王琦,蒋志阳,张宇,等.结直肠癌组织和血清外泌体lncRNA PCGEM1、miR-152-3p的表达及其临床意义[J].广西医科大学学报, 2023,40(11):1863-1870. [41] KANG Y, SONG J, KIM D, et al. PCGEM1 stimulates proliferation of osteoarthritic synoviocytes by acting as a sponge for miR-770. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(3):412-418. [42] SONG J, CHEN C, ZHANG H. LncRNA Prostate Cancer Gene Expression Marker 1 (PCGEM1) Down-Regulation Inhibits the Development of Osteoarthritis by Modulating miR-152-3p. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2022. [43] KONG W, YIN G, ZHENG S, et al. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR: Pathogenic roles and therapeutic opportunities in gastric cancer. Genes Dis. 2021;9(5):1269-1280. [44] 范杰,金永明,江孝龙,等.lncRNA HOTAIR调控miR-206影响类风湿关节炎滑膜细胞增殖和凋亡的分子机制研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2023,28(7):736-742. [45] 张慧珍,吴伟,罗海涛.中低强度运动干预高脂饲养小鼠膝关节损伤软骨细胞LncRNA HOTAIR的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(11):1684-1689. [46] HE B, JIANG D. HOTAIR-induced apoptosis is mediated by sponging miR-130a-3p to repress chondrocyte autophagy in knee osteoarthritis. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(2):524-535. [47] ZHENG T, HUANG J, LAI J, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIRincreased mechanical stimulation-induced apoptosis by regulating microRNA-221/BBC3 axis in C28/I2 cells. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):10734-10744. [48] DAI Y, LIU S, XIE X, et al. MicroRNA‑31 promotes chondrocyte proliferation by targeting C‑X‑C motif chemokine ligand 12. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(3):2231-2237. [49] LU J, WU Z, XIONG Y. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR inhibits osteoarthritis chondrocyte injury by miR-107/CXCL12 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):410. [50] CHEN Y, ZHANG L, LI E, et al. Long-chain non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes the progression of osteoarthritis via sponging miR-20b/PTEN axis. Life Sci. 2020;253:117685. [51] YANG Y, XING D, WANG Y, et al. A long non-coding RNA, HOTAIR, promotes cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting WIF-1 expression and activating Wnt pathway. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020; 21(1):53. [52] WANG B, SUN Y, LIU N, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR modulates chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-1277-5p/SGTB axis. Wound Repair Regen. 2021;29(3):495-504.
[53] ZENG S, TU M. The lncRNA MIAT/miR-181a-5p axis regulates osteopontin (OPN)-mediated proliferation and apoptosis of human chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. J Mol Histol. 2022;53(2):285-296.
[54] SUN PF, KONG WK, LIU L, et al. Osteopontin accelerates chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis rats through the NF-κb signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):2836-2842. [55] PAN W, WANG H, RUAN J, et al. lncRNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) knockdown alleviates LPS-induced chondrocytes inflammatory injury via regulating miR-488-3p/sex determining region Y-related HMG-box 11 (SOX11) axis. Open Life Sci. 2021;16(1):511-522. [56] YUE Y, ZHIBO S, FENG L, et al. SNHG5 protects chondrocytes in interleukin-1β-stimulated osteoarthritis via regulating miR-181a-5p/TGFBR3 axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(10):e22866. [57] JIANG H, PANG H, WU P, et al. LncRNA SNHG5 promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in osteoarthritis by regulating miR-10a-5p/H3F3B axis. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(6):605-614. [58] NIE T, ZHANG C, ZHANG G, et al. LncRNA CALML3-AS1 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis by acting as a sponge for miR-146a. Autoimmunity. 2021;54(6):336-342. [59] QIN GH, YANG WC, YAO JN, et al. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 affects the biological behaviors of chondrocytes of patients with osteoarthritis by regulating micro-30a-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(3):1215-1224. [60] SUN Z, TANG J, YOU T, et al. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 promotes mitophagy to alleviate osteoarthritis by up-regulating PPAR-γ to activate AMPK/Akt/mTOR pathway. Mod Rheumatol. 2024. doi: 10.1093/mr/roae015. Epub ahead of print. [61] GU Y, WANG G, XU H. Long non-coding RNA ZNFX1 antisense 1 (ZFAS1) suppresses anti-oxidative stress in chondrocytes during osteoarthritis by sponging microRNA-1323. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):13188-13200. [62] HAN J, LUO Z, WANG Y, et al. LncRNA ZFAS1 protects chondrocytes from IL-1β-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation via regulating miR-7-5p/FLRT2 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):320. [63] SHI M, SUN M, WANG C, et al. Therapeutic Potential of POU3F3, a Novel Long Non-coding RNA, Alleviates the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis by Regulating the miR-29a- 3p/FOXO3 Axis. Curr Gene Ther. 2022;22(5):427-438. [64] ZHANG D, SONG L, WANG X. NEAT1 attenuates osteoarthritis development by sponging miR-424-5p and up-regulating SMAD7 expression. Research Square. 2020[2024-05-17]. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.2.20874/v1. [65] WANG Q, WANG W, ZHANG F, et al. NEAT1/miR-181c Regulates Osteopontin (OPN)-Mediated Synoviocyte Proliferation in Osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(11):3775-3784. [66] LIU F, LIU X, YANG Y, et al. NEAT1/miR-193a-3p/SOX5 axis regulates cartilage matrix degradation in human osteoarthritis. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(4):947-957. [67] LI H, LIAN K, MAO J, et al. LncRNA LEMD1-AS1 relieves chondrocyte inflammation by targeting miR-944/PGAP1 in osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(19):2038-2050. [68] HUANG F, SU Z, YANG J, et al. Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1 interacts with miR-374b-5p/PGAP1 axis to aggravate the development of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):670. [69] LUO X, WANG J, WEI X, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA MFI2-AS1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by miR-130a-3p/TCF4. Life Sci. 2020;240:117019. [70] SHI J, CAO F, CHANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 protects chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1β-induced inflammation via regulating miR-138-5p/SIRT1. Bioengineered. 2021; 12(1):1445-1456. [71] GAO Y, ZHAO H, LI Y. LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 regulates miR-142-3p/HMGB1 to promote LPS-induced chondrocyte apoptosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):605. [72] YANG Y, SUN Z, LIU F, et al. FGD5-AS1 Inhibits Osteoarthritis Development by Modulating miR-302d-3p/TGFBR2 Axis. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):1412S-1420S. [73] LI D, WANG X, YI T, et al. LncRNA MINCR attenuates osteoarthritis progression via sponging miR-146a-5p to promote BMPR2 expression. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(22):2417-2432. [74] WANG T, LIU Y, WANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes extracellular matrix degradation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-1277-5p in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2019;44(2):630-642. [75] LIU Y, LIU K, TANG C, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST contributes to osteoarthritis progression via miR-149-5p/DNMT3A axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;128:110349. [76] ZHU X, CHEN F, LU K, et al. PPARγ preservation via promoter demethylation alleviates osteoarthritis in mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019; 78(10):1420-1429. [77] LIAN LP, XI XY. Long non-coding RNA XIST protects chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1β-induced injury via regulating miR-653-5p/SIRT1 axis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(2):379-391. [78] LI L, LV G, WANG B, et al. XIST/miR-376c-5p/OPN axis modulates the influence of proinflammatory M1 macrophages on osteoarthritis chondrocyte apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(1):281-293. [79] HUANG B, YU H, LI Y, et al. Upregulation of long noncoding TNFSF10 contributes to osteoarthritis progression through the miR-376-3p/FGFR1 axis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(12):19610-19620. [80] ZHANG Z, YANG P, WANG C, et al. LncRNA CRNDE hinders the progression of osteoarthritis by epigenetic regulation of DACT1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(8):405. [81] YIN X, XIANG T, LI L, et al. DACT1, an antagonist to Wnt/β-catenin signaling, suppresses tumor cell growth and is frequently silenced in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(2):R23. [82] ZUO Y, XIONG C, GAN X, et al. LncRNA HAGLR silencing inhibits IL-1β-induced chondrocytes inflammatory injury via miR-130a-3p/JAK1 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):203. [83] LI Z, DAI A, YANG M, et al. p38MAPK Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis: Pathological and Therapeutic Aspects. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:723-734. [84] 白春礼,马钢,苏日力格,等.NF-κB/MAPKs信号调节骨关节炎的研究进展[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2023,55(10):1208-1212. [85] 张晋宁.TGF-β信号转导通路中相关蛋白表达与膝骨性关节炎的研究[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2023. [86] 李鑫.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路研究调膝法治疗膝骨性关节炎的作用机制[D].合肥:安徽中医药大学,2023. [87] LIU J, XIAO Q, XIAO J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):3. [88] WANG YZ, YAO-LI, LIANG SK, et al. LncPVT1 promotes cartilage degradation in diabetic OA mice by downregulating miR-146a and activating TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(4): 534-546. [89] HERRMANN IK, WOOD MJA, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16(7):748-759. [90] YAN L, LIU G, WU X. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e255. [91] ZHANG S, JIN Z. Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Containing Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Relieve Osteoarthritis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:5517648. [92] 樊渝川,殷涵,李钰,等.mRNA疫苗与脂质纳米颗粒递送载体的研究进展[J/OL].科学通报,1-11[2024-05-17].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1784.N.20240315.1710.002.html. [93] KONG YL, WANG HD, GAO M, et al. LncRNA XIST promotes bladder cancer progression by modulating miR-129-5p/TNFSF10 axis. Discov Oncol. 2024;15(1):65. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [3] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [4] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [5] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [6] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [7] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [8] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [9] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [10] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [11] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [12] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [13] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| [14] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [15] | Huang Haina, Yu Yanrong, Bi Jian, Huang Miao, Peng Weijie. Epigenetic characteristics of hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7848-7855. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||