Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (8): 1705-1713.doi: 10.12307/2025.313
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis
Zhang Zixian1, Xu Youliang2, Wu Shaokui2, 3, Wang Xiangying1
- 1School of Physical Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Physical Education & Health, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China; 3School of Physical Education, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-18Accepted:2024-03-30Online:2025-03-18Published:2024-07-06 -
Contact:Wu Shaokui, PhD candidate, School of Physical Education & Health, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China; School of Physical Education, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China Co-corresponding author: Wang Xiangying, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Physical Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Zixian, Master candidate, School of Physical Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:General Project of National Social Science Foundation, No. 20BTY087 (to WXY [Project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
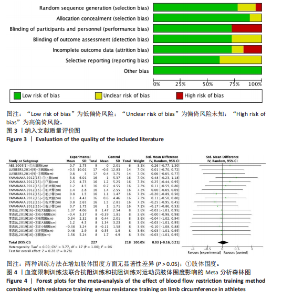
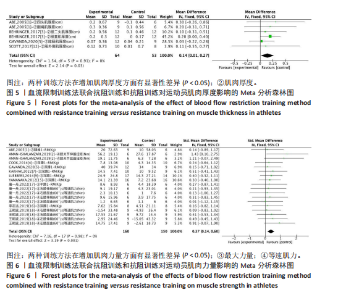
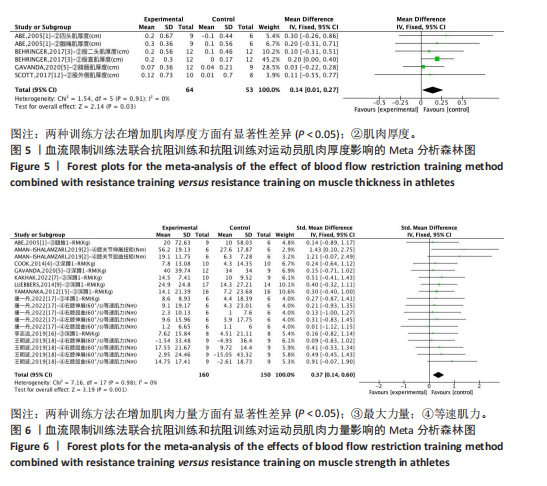
2.1 检索结果及基本特征 对纳入的18篇文献进行Meta分析[22-29]。将血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练和抗阻训练在肢体围度、肌肉厚度、肌肉力量及专项能力方面进行比较。其中,肢体围度、肌肉厚度、肌肉力量属于肌肉相关指标。在18篇文献中,6篇文献考察了相应的专项能力指标,经过分析比对,将30 m冲刺[22]、100 m冲刺定为田径短跑运动者的专项能力[24],将五人制专项能力测试[40]、Hoff测试、MSFT测试、变向能力[28]作为足球项目的专项能力,15 s冲刺峰值和平均值作为自行车项目的专项能力[38]。 2.2 纳入研究的基本特征与质量评价结果 按照Cochrane协作网偏倚风险评估工具标准对纳入文献进行偏倚风险评价[19],见图3。 2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练和抗阻训练对肌肉相关指标的影响肢体围度:纳入的18篇文献中,有4篇文献(18组数据)比较了血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练(试验组)和抗阻训练(对照组)对肢体围度的影响。异质性检验:P=1.00,I2=0%,无异质性存在,采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,两组间无显著性差异(SMD=0.03,95%CI:-0.16-0.21,P=0.78),见图4。 肌肉厚度:纳入的18篇文献中,有4篇(6组数据)比较了血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练(试验组)和抗阻训练(对照组)对肌肉厚度的影响。异质性检验:P=0.91,I2=0%,无异质性存在,采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,两组间有显著性差异(SMD=0.14,95%CI:0.01-0.27,P=0.03),见图5。 肌肉力量:纳入的18篇文献中,有10篇文献(18组数据)比较了血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练(试验组)和抗阻训练(对照组)对肌肉力量的影响。异质性检验:P=0.98,I2=0%,无异质性存在,采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,两组间有显著性差异(SMD=0.37,95%CI:0.14-0.60,P=0.001),见图6。"
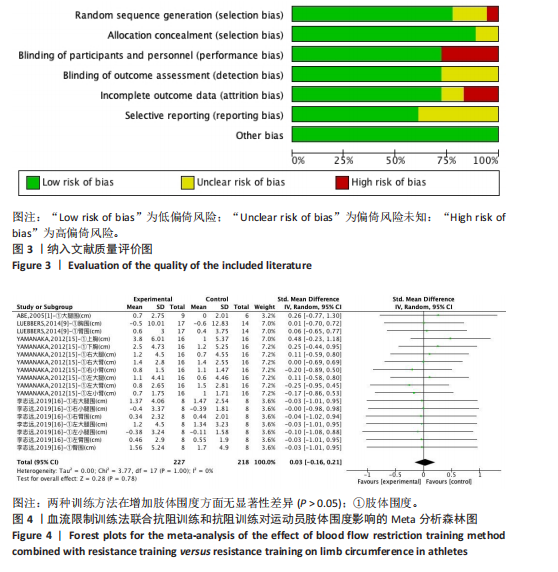
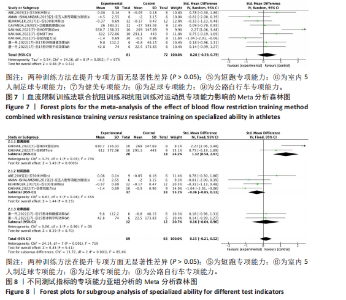
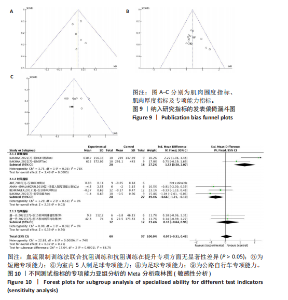
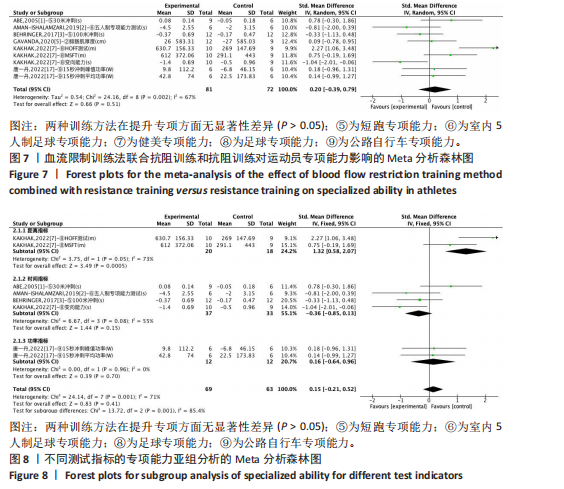
专项能力:纳入的18篇文献中,有6篇文献(9组数据)比较了血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练(试验组)和抗阻训练(对照组)对专项能力的影响。异质性检验:P=0.002,I2=67%,异质性较高,采用随机效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,两组间无显著性差异(SMD=0.20,95%CI:-0.39-0.79,P=0.51),见图7。 2.4 亚组分析结果 全部研究的结局指标不同可能是产生异质性的主要原因,因此对该方面的异质性进行进一步分析。血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练(试验组)和抗阻训练(对照组)对专项能力的亚组分析结果显示:2组数据采用距离指标[41],4组数据采用时间指标[22-24,41],2组数据采用功率指标[38]。结果显示:距离指标的分析结果存在高异质性(I2=73%),时间指标的分析结果存在高异质性(I2=55%),分析可能原因是各研究的测试方法及评估指标意义的不同导致。功率指标的分析结果无异质性(I2=0%)。血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练对距离指标具有显著影响(P < 0.01)。合并效应结果显示:血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练比较抗阻训练对于专项能力的影响(P=0.41),提示不同训练方法对于专项能力不存在显著性影响,见图8。 2.5 发表偏倚分析结果 在纳入的研究中,以肌肉力量为结局指标的文献最多,故以其为例进行漏斗图分析,见图9,漏斗图显示文献分布大致对称,提示研究没有发表偏倚或其他偏倚。 2.6 敏感性分析结果 为检验上述Meta分析结果是否稳定可靠,分别对纳入的18篇文献进行敏感性分析。将纳入的文献逐一剔除后进行合并。结果表明,血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练(试验组)和抗阻训练(对照组)干预肢体围度、肌肉厚度、肌肉力量的结果改变不明显,证明研究结果较为稳健。但是,血流限制训练法联合抗阻训练和抗阻训练对以时间为指标的专项能力的结果出现了变化。当剔除ABE的一组研究数据后,血流限制步行和步行训练对躯体能力影响的结果中P值变化较大(P < 0.05),说明这两项研究数据对总效应量影响较大,见图10。"
| [1] 徐飞,王健.加压力量训练:释义及应用[J].体育科学,2013,33(12):71-80. [2] PATTERSON SD, HUGHES L, WARMINGTON S, et al. Blood flow restriction exercise: considerations of methodology, application, and safety. Front Physiol. 2019;10:533. [3] LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, et al. Blood flow restriction pressure recommendations: a tale of two cuffs. Front Physiol. 2013;4:249. [4] ANICETO RR, DA SILVA LEANDRO L. Practical blood flow restriction training: new methodological directions for practice and research. Sports Med Open. 2022;8(1):87. [5] COLAPIETRO M, PORTNOFF B, MILLER S J, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction training on clinical outcomes for patients with acl reconstruction: a systematic review. Sports Health. 2023;15(2):260-273. [6] CONSTANTINOU A, MAMAIS I, PAPATHANASIOU G, et al. Comparing hip and knee focused exercises versus hip and knee focused exercises with the use of blood flow restriction training in adults with patellofemoral pain. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022;58(2):225-235. [7] 李新通,潘玮敏,覃华生,等.血流限制训练:加速肌肉骨骼康复的新方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(15):2415-2420. [8] ZHANG XZ, XIE WQ, CHEN L, et al. Blood flow restriction training for the intervention of sarcopenia: current stage and future perspective. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9: 894996. [9] NASCIMENTO DDC, ROLNICK N, NETO I V S, et al. A Useful Blood Flow Restriction Training Risk Stratification for Exercise and Rehabilitation. Front Physiol. 2022;13: 808622. [10] CENTNER C, WIEGEL P, GOLLHOFER A, et al. Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Training on Muscular Strength and Hypertrophy in Older Individuals: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(1):95-108. [11] LABATA-LEZAUN N, LLURDA-ALMUZARA L, GONZÁLEZ-RUEDA V, et al. Effectiveness of Blood Flow Restriction Training on Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older Adults: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2022; 103(9):1848-1857. [12] 王永超,王保臣,魏祝颖,等.血流限制法对交叉迁移现象的诱导及肌肉功能重建的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(17):2762-2767. [13] WORTMAN RJ, BROWN SM, SAVAGE-ELLIOTT I, et al. Blood flow restriction training for athletes: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(7):1938-1944. [14] ALVES RC, PRESTES J, ENES A, et al. Training programs designed for muscle hypertrophy in bodybuilders: a narrative review. Sports (Basel). 2020;8(11):149. [15] FRY CS, GLYNN EL, DRUMMOND MJ, et al. Blood flow restriction exercise stimulates mTORC1 signaling and muscle protein synthesis in older men. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010;108(5):1199-209. [16] DEPHILLIPO NN, KENNEDY MI, AMAN ZS, et al. The role of blood flow restriction therapy following knee surgery: expert opinion. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(8):2506-2510. [17] PAGE MJ, MCKENZIE JE, BOSSUYT PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Bmj. 2021;372:n71. [18] LIBERATI A, ALTMAN DG, TETZLAFF J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000100. [19] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GØTZSCHE PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj. 2011; 343:d5928. [20] HIGGINS JPT, THOMPSON SG, DEEKS JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557. [21] 王丹,翟俊霞,牟振云,等.Meta分析中的异质性及其处理方法[J].中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(10):1115-1118. [22] ABE T, KAWAMOTO K, YASUDA T, et al. Eight days KAATSU-resistance training improved sprint but not jump performance in collegiate male track and field athletes. Int J Kaatsu Training Res. 2005;1:19-23. [23] AMANI-SHALAMZARI S, FARHANI F, RAJABI H, et al. Blood flow restriction during futsal training increases muscle activation and strength. Front Physiol. 2019;10:614. [24] BEHRINGER M, BEHLAU D, MONTAG JCK, et al. Low-intensity sprint training with blood flow restriction improves 100-m dash. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(9):2462-2472.
[25] COOK CJ, KILDUFF LP, BEAVEN CM. Improving strength and power in trained athletes with 3 weeks of occlusion training. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2014;9(1):166-172. [26] GAVANDA S, ISENMANN E, SCHLÖDER Y, et al. Low-intensity blood flow restriction calf muscle training leads to similar functional and structural adaptations than conventional low-load strength training: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2020;15(6):e0235377. [27] GEPFERT M, KRZYSZTOFIK M, KOSTRZEWA M, et al. The acute impact of external compression on back squat performance in competitive athletes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(13):4674. [28] HOSSEINI KAKHAK SA, KIANIGUL M, HAGHIGHI AH, et al. Performing soccer-specific training with blood flow restriction enhances physical capacities in youth soccer players. J Strength Cond Res. 2022; 36(7):1972-1977. [29] LAMBERT BS, HEDT C, ANKERSEN JP, et al. Rotator cuff training with upper extremity blood flow restriction produces favorable adaptations in division IA collegiate pitchers: a randomized trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32(6):E279-E292. [30] LUEBBERS PE, FRY AC, KRILEY LM, et al. The effects of a 7-week practical blood flow restriction program on well-trained collegiate athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2014;28(8):2270-2280. [31] MANIMMANAKORN A, HAMLIN MJ, ROSS JJ, et al. Effects of low-load resistance training combined with blood flow restriction or hypoxia on muscle function and performance in netball athletes. J Sci Med Sport. 2013;16(4):337-342. [32] SAKURABA K, ISHIKAWA T. Effect of isokinetic resistance training under a condition of restricted blood flow with pressure. Orthop Sci. 2009;14(5):631-639. [33] SCOTT BR, PEIFFER JJ, GOODS PSR. The effects of supplementary low-load blood flow restriction training on morphological and performance-based adaptations in team sport athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(8):2147-2154. [34] TAKARADA Y, SATO Y, ISHII N. Effects of resistance exercise combined with vascular occlusion on muscle function in athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2002;86(4):308-314. [35] WANG J, MOGENSEN AG, THYBO F, et al. Low-load blood flow-restricted resistance exercise produces fiber type-independent hypertrophy and improves muscle functional capacity in older individuals.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023;134(4): 1047-1062. [36] YAMANAKA T, FARLEY R , Caputo JL. Occlusion training increases muscular strength in division IA football players. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(9):2523-2529. [37] 李志远,赵之光,王明波,等.4周加压训练对男子手球运动员身体成分和最大力量的影响[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(5): 37-43. [38] 唐一丹,屈成刚.4周加压抗阻训练对男子公路自行车运动员下肢肌肉力量和冲刺能力的影响[J].辽宁体育科技,2022, 44(5):63-69. [39] 王明波,李志远,魏文哲,等.高水平男子手球运动员下肢加压力量训练效果实证研究[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(5):30-36. [40] PEARSON SJ, HUSSAIN SR. A review on the mechanisms of blood-flow restriction resistance training-induced muscle hypertrophy. Sports Med. 2015;45(2):187-200. [41] HOSSEINI KAKHAK SA, KIANIGUL M, HAGHIGHI AH, et al. Performing soccer-specific training with blood flow restriction enhances physical capacities in youth soccer players. J Strength Cond Res. 2022; 36(7):1972-1977. [42] ANGELOPOULOS P, TSEKOURA M, MYLONAS K, et al. The effectiveness of blood flow restriction training in cardiovascular disease patients: a scoping review. J Frailty Sarcopenia Falls. 2023;8(2):107-117. [43] MILLER BC, TIRKO AW, SHIPE JM, et al. The systemic effects of blood flow restriction training: a systematic review. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2021;16(4):978-990. [44] PIGNANELLI C, CHRISTIANSEN D, BURR J F. Blood flow restriction training and the high-performance athlete: science to application. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021;130(4): 1163-1170. [45] XIAOLIN W, XIN-MIN Q, SHUYU J, et al. Effects of resistance training with blood flow restriction on explosive power of lower limbs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Kinet. 2023;89:259-268. [46] LOENNEKE JP, THIEBAUD RS, ABE T, et al. Blood flow restriction pressure recommendations: the hormesis hypothesis. Med Hypotheses. 2014;82(5):623-626. [47] SMITH NDW, SCOTT BR, GIRARD O, et al. Aerobic training with blood flow restriction for endurance athletes: potential benefits and considerations of implementation. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(12):3541-3550. [48] GRØNFELDT BM, LINDBERG NIELSEN J, MIERITZ RM, et al. Effect of blood-flow restricted vs heavy-load strength training on muscle strength: systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(5):837-848. [49] TEGTBUR U, HAUFE S, BUSSE MW. Application and effects of blood flow restriction training. Unfallchirurg. 2020; 123(3):170-175. [50] CENTNER C, LAUBER B. A systematic review and meta-analysis on neural adaptations following blood flow restriction training: what we know and what we don’t know. Front Physiol. 2020;11:887. [51] NUZZO JL, FINN HT, HERBERT RD. Causal mediation analysis could resolve whether training-induced increases in muscle strength are mediated by muscle hypertrophy. Sports Med. 2019;49(9):1309-1315. [52] REGGIANI C, SCHIAFFINO S. Muscle hypertrophy and muscle strength: dependent or independent variables? A provocative review. Eur J Transl Myol. 2020; 30(3):9311. [53] NARICI M, FRANCHI M, Maganaris C. Muscle structural assembly and functional consequences. J Exp Biol. 2016;219(2):276-284. [54] 陈小平.试论“专项能力”的训练──对我国体能类项目训练中存在的主要问题的探析[J].中国体育科技,2002(1):10-13,33. [55] BRANDNER CR, CLARKSON MJ, KIDGELL DJ, et al. Muscular adaptations to whole body blood flow restriction training and detraining. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1099. [56] BENNETT H, SLATTERY F. Effects of blood flow restriction training on aerobic capacity and performance: a systematic review. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(2):572-583. [57] CASTLE JP, TRAMER JS, TURNER E HG, et al. Survey of blood flow restriction therapy for rehabilitation in sports medicine patients. J Orthop. 2023;38:47-52. [58] BOWMAN EN, ELSHAAR R, MILLIGAN H, et al. Proximal, distal, and contralateral effects of blood flow restriction training on the lower extremities: a randomized controlled trial. Sports Health. 2019;11(2):149-156. [59] LOENNEKE JP, WILSON JM, WILSON GJ, et al. Potential safety issues with blood flow restriction training. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011;21(4):510-518. [60] MARTINEZ N, LILLA C, RENTERIA M. Considerations of blood flow restriction (BFR) training-A case for injury prevention and maximizing strength for tactical personnel. NSCA TSAC Rep. 2019;53(2):8-13. [61] CUFFE M, NOVAK J, SAITHNA A, et al. Current trends in blood flow restriction. Front Physiol. 2022;13:882472. |
| [1] | Tao Yunfei, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction in low-intensity resistance training on endothelial function-related inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1184-1195. |
| [2] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [3] | Li Hanyue, Li Yini, Xiang Linmei, Li Sen. Effects of resistance exercise therapy on pain and function in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 987-996. |
| [4] | Sun Jiahe, Shi Jipeng, Zhu Tianrui, Quan Helong, Xu Hongqi. Effect of exercise intervention in elderly individuals with sarcopenia and its comorbidities: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 997-1007. |
| [5] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [6] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [7] | Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619. |
| [8] | Liu Chenchen, Liu Ruize, Bao Mengmeng, Fang Li, Cao Liquan, Wu Jiangbo. Blood flow restriction training intervention in the elderly with sarcopenic obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6963-6970. |
| [9] | Jiang Siqi, Huang Huanhuan, Yu Xinyu, Peng Ying, Zhou Wei, Zhao Qinghua. Meta-analysis of dose-effect of exercise on improving muscle health in community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6295-6304. |
| [10] | Ding Yuan, Gong Jianbao, Zhang Jie, Qiao Yuan, Xu Wenlong. Characteristic analysis of isometric muscle strength of knee joint in patients after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5833-5838. |
| [11] | Wang Xia, Xue Boshi, Yang Chen, Zhou Zhipeng, Zheng Liangliang. Influence of neuromuscular function on the risk of biomechanical injury in landing manoeuvres in patients undergoing anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5556-5562. |
| [12] | Zhu Tianrui, Shi Jipeng, Sun Jiahe, Wang Luyi, Zhang Chen, Xu Hongqi, Quan Helong. Effectiveness of different exercise regimens to reduce fall risks in older adults: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5662-5672. |
| [13] | Hu Tong, Li Xuan, Yuan Jing, Wang Wei. Different electromagnetic stimulation programs improve post-stroke dysphagia: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5224-5236. |
| [14] | Peng Yong, Hu Jiangping, Zhu Huan. Effects of low-load blood flow restriction exercise and high-intensity resistance exercise on the thigh microcirculation function of athletic young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 393-401. |
| [15] | Zhao Yuhan, Li Yamei, Yan Shifang, Jiang Huabei. Immediate effects of different stretching methods on knee joint muscle strength and vertical jump performance of healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3784-3790. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||